Yifan Liang
OpenHAIV: A Framework Towards Practical Open-World Learning
Aug 10, 2025Abstract:Substantial progress has been made in various techniques for open-world recognition. Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection methods can effectively distinguish between known and unknown classes in the data, while incremental learning enables continuous model knowledge updates. However, in open-world scenarios, these approaches still face limitations. Relying solely on OOD detection does not facilitate knowledge updates in the model, and incremental fine-tuning typically requires supervised conditions, which significantly deviate from open-world settings. To address these challenges, this paper proposes OpenHAIV, a novel framework that integrates OOD detection, new class discovery, and incremental continual fine-tuning into a unified pipeline. This framework allows models to autonomously acquire and update knowledge in open-world environments. The proposed framework is available at https://haiv-lab.github.io/openhaiv .
OpenEarthSensing: Large-Scale Fine-Grained Benchmark for Open-World Remote Sensing
Feb 28, 2025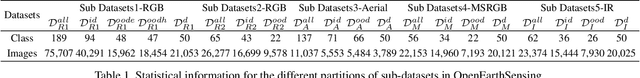
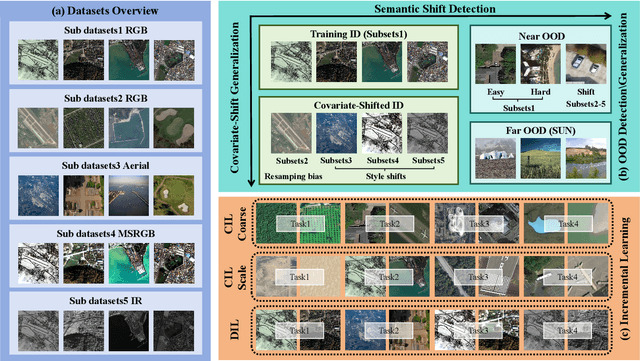
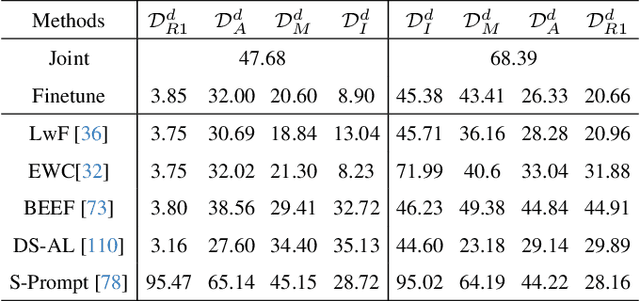
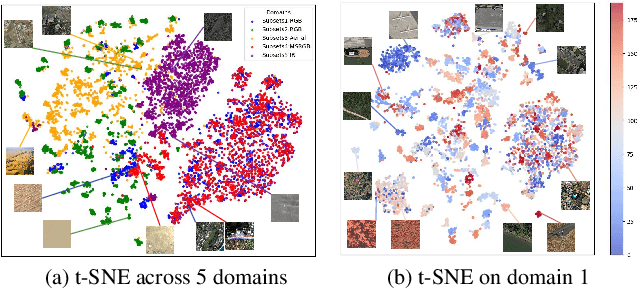
Abstract:In open-world remote sensing, deployed models must continuously adapt to a steady influx of new data, which often exhibits various shifts compared to what the model encountered during the training phase. To effectively handle the new data, models are required to detect semantic shifts, adapt to covariate shifts, and continuously update themselves. These challenges give rise to a variety of open-world tasks. However, existing open-world remote sensing studies typically train and test within a single dataset to simulate open-world conditions. Currently, there is a lack of large-scale benchmarks capable of evaluating multiple open-world tasks. In this paper, we introduce OpenEarthSensing, a large-scale fine-grained benchmark for open-world remote sensing. OpenEarthSensing includes 189 scene and objects categories, covering the vast majority of potential semantic shifts that may occur in the real world. Additionally, OpenEarthSensing encompasses five data domains with significant covariate shifts, including two RGB satellite domians, one RGB aerial domian, one MS RGB domian, and one infrared domian. The various domains provide a more comprehensive testbed for evaluating the generalization performance of open-world models. We conduct the baseline evaluation of current mainstream open-world tasks and methods on OpenEarthSensing, demonstrating that it serves as a challenging benchmark for open-world remote sensing.
NaturalL2S: End-to-End High-quality Multispeaker Lip-to-Speech Synthesis with Differential Digital Signal Processing
Feb 17, 2025



Abstract:Recent advancements in visual speech recognition (VSR) have promoted progress in lip-to-speech synthesis, where pre-trained VSR models enhance the intelligibility of synthesized speech by providing valuable semantic information. The success achieved by cascade frameworks, which combine pseudo-VSR with pseudo-text-to-speech (TTS) or implicitly utilize the transcribed text, highlights the benefits of leveraging VSR models. However, these methods typically rely on mel-spectrograms as an intermediate representation, which may introduce a key bottleneck: the domain gap between synthetic mel-spectrograms, generated from inherently error-prone lip-to-speech mappings, and real mel-spectrograms used to train vocoders. This mismatch inevitably degrades synthesis quality. To bridge this gap, we propose Natural Lip-to-Speech (NaturalL2S), an end-to-end framework integrating acoustic inductive biases with differentiable speech generation components. Specifically, we introduce a fundamental frequency (F0) predictor to capture prosodic variations in synthesized speech. The predicted F0 then drives a Differentiable Digital Signal Processing (DDSP) synthesizer to generate a coarse signal which serves as prior information for subsequent speech synthesis. Additionally, instead of relying on a reference speaker embedding as an auxiliary input, our approach achieves satisfactory performance on speaker similarity without explicitly modelling speaker characteristics. Both objective and subjective evaluation results demonstrate that NaturalL2S can effectively enhance the quality of the synthesized speech when compared to state-of-the-art methods. Our demonstration page is accessible at https://yifan-liang.github.io/NaturalL2S/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge