Qingfang Zheng
X-SAM: From Segment Anything to Any Segmentation
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate strong capabilities in broad knowledge representation, yet they are inherently deficient in pixel-level perceptual understanding. Although the Segment Anything Model (SAM) represents a significant advancement in visual-prompt-driven image segmentation, it exhibits notable limitations in multi-mask prediction and category-specific segmentation tasks, and it cannot integrate all segmentation tasks within a unified model architecture. To address these limitations, we present X-SAM, a streamlined Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) framework that extends the segmentation paradigm from \textit{segment anything} to \textit{any segmentation}. Specifically, we introduce a novel unified framework that enables more advanced pixel-level perceptual comprehension for MLLMs. Furthermore, we propose a new segmentation task, termed Visual GrounDed (VGD) segmentation, which segments all instance objects with interactive visual prompts and empowers MLLMs with visual grounded, pixel-wise interpretative capabilities. To enable effective training on diverse data sources, we present a unified training strategy that supports co-training across multiple datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that X-SAM achieves state-of-the-art performance on a wide range of image segmentation benchmarks, highlighting its efficiency for multimodal, pixel-level visual understanding. Code is available at https://github.com/wanghao9610/X-SAM.
Enhancing User-Oriented Proactivity in Open-Domain Dialogues with Critic Guidance
May 18, 2025
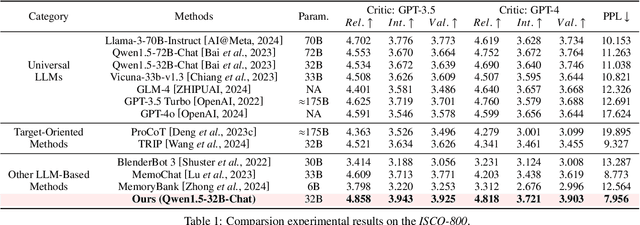
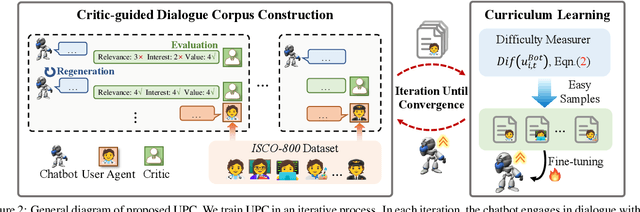
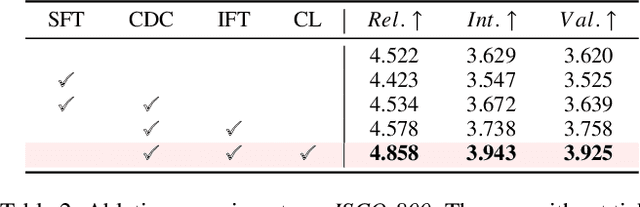
Abstract:Open-domain dialogue systems aim to generate natural and engaging conversations, providing significant practical value in real applications such as social robotics and personal assistants. The advent of large language models (LLMs) has greatly advanced this field by improving context understanding and conversational fluency. However, existing LLM-based dialogue systems often fall short in proactively understanding the user's chatting preferences and guiding conversations toward user-centered topics. This lack of user-oriented proactivity can lead users to feel unappreciated, reducing their satisfaction and willingness to continue the conversation in human-computer interactions. To address this issue, we propose a User-oriented Proactive Chatbot (UPC) to enhance the user-oriented proactivity. Specifically, we first construct a critic to evaluate this proactivity inspired by the LLM-as-a-judge strategy. Given the scarcity of high-quality training data, we then employ the critic to guide dialogues between the chatbot and user agents, generating a corpus with enhanced user-oriented proactivity. To ensure the diversity of the user backgrounds, we introduce the ISCO-800, a diverse user background dataset for constructing user agents. Moreover, considering the communication difficulty varies among users, we propose an iterative curriculum learning method that trains the chatbot from easy-to-communicate users to more challenging ones, thereby gradually enhancing its performance. Experiments demonstrate that our proposed training method is applicable to different LLMs, improving user-oriented proactivity and attractiveness in open-domain dialogues.
OpenEarthSensing: Large-Scale Fine-Grained Benchmark for Open-World Remote Sensing
Feb 28, 2025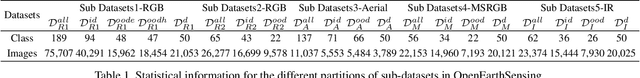
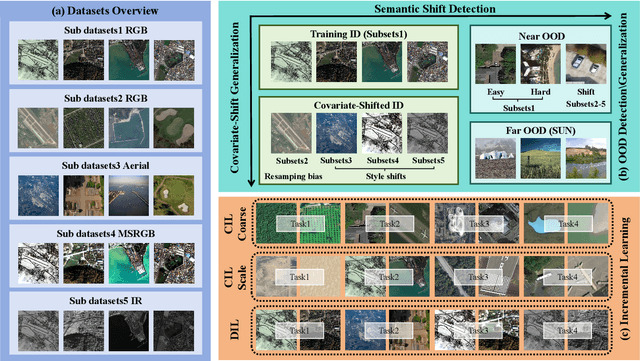
Abstract:In open-world remote sensing, deployed models must continuously adapt to a steady influx of new data, which often exhibits various shifts compared to what the model encountered during the training phase. To effectively handle the new data, models are required to detect semantic shifts, adapt to covariate shifts, and continuously update themselves. These challenges give rise to a variety of open-world tasks. However, existing open-world remote sensing studies typically train and test within a single dataset to simulate open-world conditions. Currently, there is a lack of large-scale benchmarks capable of evaluating multiple open-world tasks. In this paper, we introduce OpenEarthSensing, a large-scale fine-grained benchmark for open-world remote sensing. OpenEarthSensing includes 189 scene and objects categories, covering the vast majority of potential semantic shifts that may occur in the real world. Additionally, OpenEarthSensing encompasses five data domains with significant covariate shifts, including two RGB satellite domians, one RGB aerial domian, one MS RGB domian, and one infrared domian. The various domains provide a more comprehensive testbed for evaluating the generalization performance of open-world models. We conduct the baseline evaluation of current mainstream open-world tasks and methods on OpenEarthSensing, demonstrating that it serves as a challenging benchmark for open-world remote sensing.
EMMA: Empowering Multi-modal Mamba with Structural and Hierarchical Alignment
Oct 08, 2024



Abstract:Mamba-based architectures have shown to be a promising new direction for deep learning models owing to their competitive performance and sub-quadratic deployment speed. However, current Mamba multi-modal large language models (MLLM) are insufficient in extracting visual features, leading to imbalanced cross-modal alignment between visual and textural latents, negatively impacting performance on multi-modal tasks. In this work, we propose Empowering Multi-modal Mamba with Structural and Hierarchical Alignment (EMMA), which enables the MLLM to extract fine-grained visual information. Specifically, we propose a pixel-wise alignment module to autoregressively optimize the learning and processing of spatial image-level features along with textual tokens, enabling structural alignment at the image level. In addition, to prevent the degradation of visual information during the cross-model alignment process, we propose a multi-scale feature fusion (MFF) module to combine multi-scale visual features from intermediate layers, enabling hierarchical alignment at the feature level. Extensive experiments are conducted across a variety of multi-modal benchmarks. Our model shows lower latency than other Mamba-based MLLMs and is nearly four times faster than transformer-based MLLMs of similar scale during inference. Due to better cross-modal alignment, our model exhibits lower degrees of hallucination and enhanced sensitivity to visual details, which manifests in superior performance across diverse multi-modal benchmarks. Code will be provided.
Integrating Coarse Granularity Part-level Features with Supervised Global-level Features for Person Re-identification
Oct 15, 2020
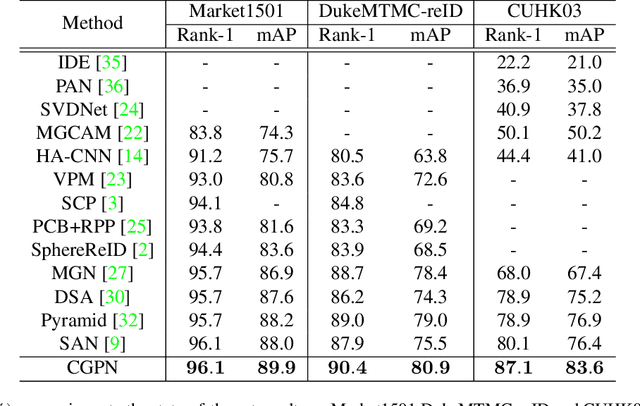
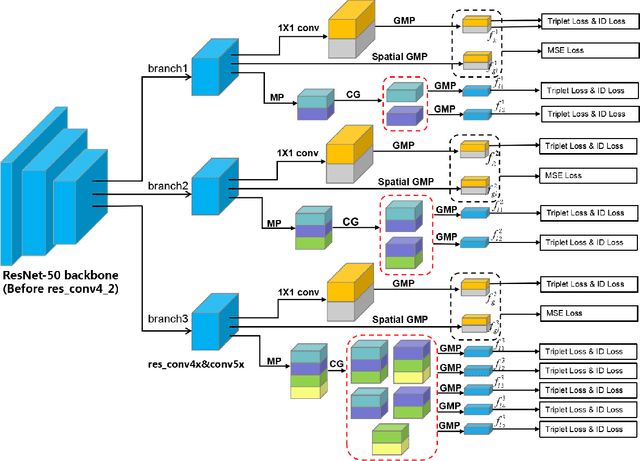

Abstract:Holistic person re-identification (Re-ID) and partial person re-identification have achieved great progress respectively in recent years. However, scenarios in reality often include both holistic and partial pedestrian images, which makes single holistic or partial person Re-ID hard to work. In this paper, we propose a robust coarse granularity part-level person Re-ID network (CGPN), which not only extracts robust regional level body features, but also integrates supervised global features for both holistic and partial person images. CGPN gains two-fold benefit toward higher accuracy for person Re-ID. On one hand, CGPN learns to extract effective body part features for both holistic and partial person images. On the other hand, compared with extracting global features directly by backbone network, CGPN learns to extract more accurate global features with a supervision strategy. The single model trained on three Re-ID datasets including Market-1501, DukeMTMC-reID and CUHK03 achieves state-of-the-art performances and outperforms any existing approaches. Especially on CUHK03, which is the most challenging dataset for person Re-ID, in single query mode, we obtain a top result of Rank-1/mAP=87.1\%/83.6\% with this method without re-ranking, outperforming the current best method by +7.0\%/+6.7\%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge