Xia Jia
RHOBIN Challenge: Reconstruction of Human Object Interaction
Jan 07, 2024Abstract:Modeling the interaction between humans and objects has been an emerging research direction in recent years. Capturing human-object interaction is however a very challenging task due to heavy occlusion and complex dynamics, which requires understanding not only 3D human pose, and object pose but also the interaction between them. Reconstruction of 3D humans and objects has been two separate research fields in computer vision for a long time. We hence proposed the first RHOBIN challenge: reconstruction of human-object interactions in conjunction with the RHOBIN workshop. It was aimed at bringing the research communities of human and object reconstruction as well as interaction modeling together to discuss techniques and exchange ideas. Our challenge consists of three tracks of 3D reconstruction from monocular RGB images with a focus on dealing with challenging interaction scenarios. Our challenge attracted more than 100 participants with more than 300 submissions, indicating the broad interest in the research communities. This paper describes the settings of our challenge and discusses the winning methods of each track in more detail. We observe that the human reconstruction task is becoming mature even under heavy occlusion settings while object pose estimation and joint reconstruction remain challenging tasks. With the growing interest in interaction modeling, we hope this report can provide useful insights and foster future research in this direction. Our workshop website can be found at \href{https://rhobin-challenge.github.io/}{https://rhobin-challenge.github.io/}.
Spatio-Temporal Point Process for Multiple Object Tracking
Feb 05, 2023



Abstract:Multiple Object Tracking (MOT) focuses on modeling the relationship of detected objects among consecutive frames and merge them into different trajectories. MOT remains a challenging task as noisy and confusing detection results often hinder the final performance. Furthermore, most existing research are focusing on improving detection algorithms and association strategies. As such, we propose a novel framework that can effectively predict and mask-out the noisy and confusing detection results before associating the objects into trajectories. In particular, we formulate such "bad" detection results as a sequence of events and adopt the spatio-temporal point process}to model such events. Traditionally, the occurrence rate in a point process is characterized by an explicitly defined intensity function, which depends on the prior knowledge of some specific tasks. Thus, designing a proper model is expensive and time-consuming, with also limited ability to generalize well. To tackle this problem, we adopt the convolutional recurrent neural network (conv-RNN) to instantiate the point process, where its intensity function is automatically modeled by the training data. Furthermore, we show that our method captures both temporal and spatial evolution, which is essential in modeling events for MOT. Experimental results demonstrate notable improvements in addressing noisy and confusing detection results in MOT datasets. An improved state-of-the-art performance is achieved by incorporating our baseline MOT algorithm with the spatio-temporal point process model.
Integrating Coarse Granularity Part-level Features with Supervised Global-level Features for Person Re-identification
Oct 15, 2020
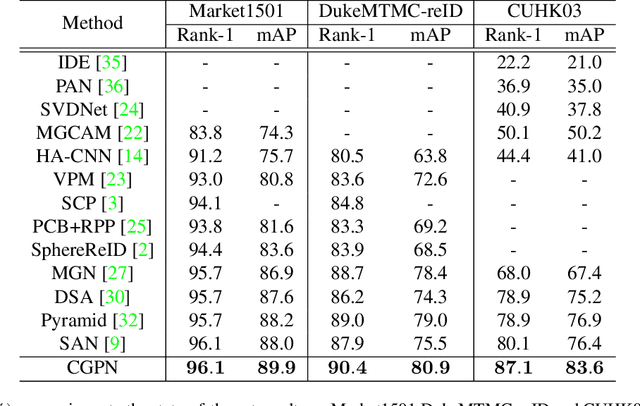
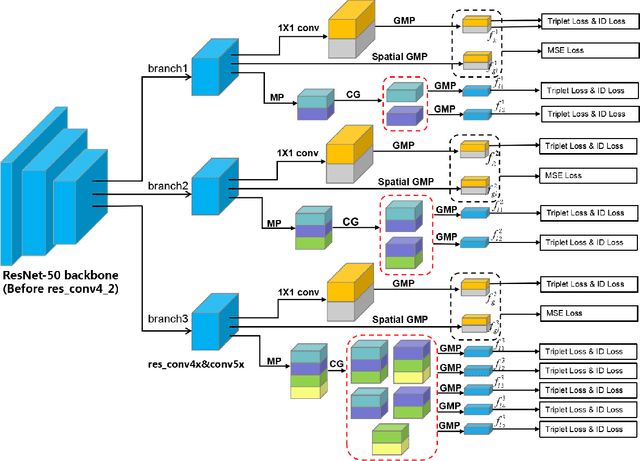

Abstract:Holistic person re-identification (Re-ID) and partial person re-identification have achieved great progress respectively in recent years. However, scenarios in reality often include both holistic and partial pedestrian images, which makes single holistic or partial person Re-ID hard to work. In this paper, we propose a robust coarse granularity part-level person Re-ID network (CGPN), which not only extracts robust regional level body features, but also integrates supervised global features for both holistic and partial person images. CGPN gains two-fold benefit toward higher accuracy for person Re-ID. On one hand, CGPN learns to extract effective body part features for both holistic and partial person images. On the other hand, compared with extracting global features directly by backbone network, CGPN learns to extract more accurate global features with a supervision strategy. The single model trained on three Re-ID datasets including Market-1501, DukeMTMC-reID and CUHK03 achieves state-of-the-art performances and outperforms any existing approaches. Especially on CUHK03, which is the most challenging dataset for person Re-ID, in single query mode, we obtain a top result of Rank-1/mAP=87.1\%/83.6\% with this method without re-ranking, outperforming the current best method by +7.0\%/+6.7\%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge