Xiangyuan Lan
Towards Implicit Aggregation: Robust Image Representation for Place Recognition in the Transformer Era
Nov 08, 2025Abstract:Visual place recognition (VPR) is typically regarded as a specific image retrieval task, whose core lies in representing images as global descriptors. Over the past decade, dominant VPR methods (e.g., NetVLAD) have followed a paradigm that first extracts the patch features/tokens of the input image using a backbone, and then aggregates these patch features into a global descriptor via an aggregator. This backbone-plus-aggregator paradigm has achieved overwhelming dominance in the CNN era and remains widely used in transformer-based models. In this paper, however, we argue that a dedicated aggregator is not necessary in the transformer era, that is, we can obtain robust global descriptors only with the backbone. Specifically, we introduce some learnable aggregation tokens, which are prepended to the patch tokens before a particular transformer block. All these tokens will be jointly processed and interact globally via the intrinsic self-attention mechanism, implicitly aggregating useful information within the patch tokens to the aggregation tokens. Finally, we only take these aggregation tokens from the last output tokens and concatenate them as the global representation. Although implicit aggregation can provide robust global descriptors in an extremely simple manner, where and how to insert additional tokens, as well as the initialization of tokens, remains an open issue worthy of further exploration. To this end, we also propose the optimal token insertion strategy and token initialization method derived from empirical studies. Experimental results show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods on several VPR datasets with higher efficiency and ranks 1st on the MSLS challenge leaderboard. The code is available at https://github.com/lu-feng/image.
VER-Bench: Evaluating MLLMs on Reasoning with Fine-Grained Visual Evidence
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:With the rapid development of MLLMs, evaluating their visual capabilities has become increasingly crucial. Current benchmarks primarily fall into two main types: basic perception benchmarks, which focus on local details but lack deep reasoning (e.g., "what is in the image?"), and mainstream reasoning benchmarks, which concentrate on prominent image elements but may fail to assess subtle clues requiring intricate analysis. However, profound visual understanding and complex reasoning depend more on interpreting subtle, inconspicuous local details than on perceiving salient, macro-level objects. These details, though occupying minimal image area, often contain richer, more critical information for robust analysis. To bridge this gap, we introduce the VER-Bench, a novel framework to evaluate MLLMs' ability to: 1) identify fine-grained visual clues, often occupying on average just 0.25% of the image area; 2) integrate these clues with world knowledge for complex reasoning. Comprising 374 carefully designed questions across Geospatial, Temporal, Situational, Intent, System State, and Symbolic reasoning, each question in VER-Bench is accompanied by structured evidence: visual clues and question-related reasoning derived from them. VER-Bench reveals current models' limitations in extracting subtle visual evidence and constructing evidence-based arguments, highlighting the need to enhance models's capabilities in fine-grained visual evidence extraction, integration, and reasoning for genuine visual understanding and human-like analysis. Dataset and additional materials are available https://github.com/verbta/ACMMM-25-Materials.
X-SAM: From Segment Anything to Any Segmentation
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate strong capabilities in broad knowledge representation, yet they are inherently deficient in pixel-level perceptual understanding. Although the Segment Anything Model (SAM) represents a significant advancement in visual-prompt-driven image segmentation, it exhibits notable limitations in multi-mask prediction and category-specific segmentation tasks, and it cannot integrate all segmentation tasks within a unified model architecture. To address these limitations, we present X-SAM, a streamlined Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) framework that extends the segmentation paradigm from \textit{segment anything} to \textit{any segmentation}. Specifically, we introduce a novel unified framework that enables more advanced pixel-level perceptual comprehension for MLLMs. Furthermore, we propose a new segmentation task, termed Visual GrounDed (VGD) segmentation, which segments all instance objects with interactive visual prompts and empowers MLLMs with visual grounded, pixel-wise interpretative capabilities. To enable effective training on diverse data sources, we present a unified training strategy that supports co-training across multiple datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that X-SAM achieves state-of-the-art performance on a wide range of image segmentation benchmarks, highlighting its efficiency for multimodal, pixel-level visual understanding. Code is available at https://github.com/wanghao9610/X-SAM.
Cross-DINO: Cross the Deep MLP and Transformer for Small Object Detection
May 28, 2025



Abstract:Small Object Detection (SOD) poses significant challenges due to limited information and the model's low class prediction score. While Transformer-based detectors have shown promising performance, their potential for SOD remains largely unexplored. In typical DETR-like frameworks, the CNN backbone network, specialized in aggregating local information, struggles to capture the necessary contextual information for SOD. The multiple attention layers in the Transformer Encoder face difficulties in effectively attending to small objects and can also lead to blurring of features. Furthermore, the model's lower class prediction score of small objects compared to large objects further increases the difficulty of SOD. To address these challenges, we introduce a novel approach called Cross-DINO. This approach incorporates the deep MLP network to aggregate initial feature representations with both short and long range information for SOD. Then, a new Cross Coding Twice Module (CCTM) is applied to integrate these initial representations to the Transformer Encoder feature, enhancing the details of small objects. Additionally, we introduce a new kind of soft label named Category-Size (CS), integrating the Category and Size of objects. By treating CS as new ground truth, we propose a new loss function called Boost Loss to improve the class prediction score of the model. Extensive experimental results on COCO, WiderPerson, VisDrone, AI-TOD, and SODA-D datasets demonstrate that Cross-DINO efficiently improves the performance of DETR-like models on SOD. Specifically, our model achieves 36.4% APs on COCO for SOD with only 45M parameters, outperforming the DINO by +4.4% APS (36.4% vs. 32.0%) with fewer parameters and FLOPs, under 12 epochs training setting. The source codes will be available at https://github.com/Med-Process/Cross-DINO.
Open-Det: An Efficient Learning Framework for Open-Ended Detection
May 27, 2025Abstract:Open-Ended object Detection (OED) is a novel and challenging task that detects objects and generates their category names in a free-form manner, without requiring additional vocabularies during inference. However, the existing OED models, such as GenerateU, require large-scale datasets for training, suffer from slow convergence, and exhibit limited performance. To address these issues, we present a novel and efficient Open-Det framework, consisting of four collaborative parts. Specifically, Open-Det accelerates model training in both the bounding box and object name generation process by reconstructing the Object Detector and the Object Name Generator. To bridge the semantic gap between Vision and Language modalities, we propose a Vision-Language Aligner with V-to-L and L-to-V alignment mechanisms, incorporating with the Prompts Distiller to transfer knowledge from the VLM into VL-prompts, enabling accurate object name generation for the LLM. In addition, we design a Masked Alignment Loss to eliminate contradictory supervision and introduce a Joint Loss to enhance classification, resulting in more efficient training. Compared to GenerateU, Open-Det, using only 1.5% of the training data (0.077M vs. 5.077M), 20.8% of the training epochs (31 vs. 149), and fewer GPU resources (4 V100 vs. 16 A100), achieves even higher performance (+1.0% in APr). The source codes are available at: https://github.com/Med-Process/Open-Det.
Learning When to Think: Shaping Adaptive Reasoning in R1-Style Models via Multi-Stage RL
May 16, 2025



Abstract:Large reasoning models (LRMs) are proficient at generating explicit, step-by-step reasoning sequences before producing final answers. However, such detailed reasoning can introduce substantial computational overhead and latency, particularly for simple problems. To address this over-thinking problem, we explore how to equip LRMs with adaptive thinking capabilities: enabling them to dynamically decide whether or not to engage in explicit reasoning based on problem complexity. Building on R1-style distilled models, we observe that inserting a simple ellipsis ("...") into the prompt can stochastically trigger either a thinking or no-thinking mode, revealing a latent controllability in the reasoning behavior. Leveraging this property, we propose AutoThink, a multi-stage reinforcement learning (RL) framework that progressively optimizes reasoning policies via stage-wise reward shaping. AutoThink learns to invoke explicit reasoning only when necessary, while defaulting to succinct responses for simpler tasks. Experiments on five mainstream mathematical benchmarks demonstrate that AutoThink achieves favorable accuracy-efficiency trade-offs compared to recent prompting and RL-based pruning methods. It can be seamlessly integrated into any R1-style model, including both distilled and further fine-tuned variants. Notably, AutoThink improves relative accuracy by 6.4 percent while reducing token usage by 52 percent on DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B, establishing a scalable and adaptive reasoning paradigm for LRMs.
UP-Person: Unified Parameter-Efficient Transfer Learning for Text-based Person Retrieval
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Text-based Person Retrieval (TPR) as a multi-modal task, which aims to retrieve the target person from a pool of candidate images given a text description, has recently garnered considerable attention due to the progress of contrastive visual-language pre-trained model. Prior works leverage pre-trained CLIP to extract person visual and textual features and fully fine-tune the entire network, which have shown notable performance improvements compared to uni-modal pre-training models. However, full-tuning a large model is prone to overfitting and hinders the generalization ability. In this paper, we propose a novel Unified Parameter-Efficient Transfer Learning (PETL) method for Text-based Person Retrieval (UP-Person) to thoroughly transfer the multi-modal knowledge from CLIP. Specifically, UP-Person simultaneously integrates three lightweight PETL components including Prefix, LoRA and Adapter, where Prefix and LoRA are devised together to mine local information with task-specific information prompts, and Adapter is designed to adjust global feature representations. Additionally, two vanilla submodules are optimized to adapt to the unified architecture of TPR. For one thing, S-Prefix is proposed to boost attention of prefix and enhance the gradient propagation of prefix tokens, which improves the flexibility and performance of the vanilla prefix. For another thing, L-Adapter is designed in parallel with layer normalization to adjust the overall distribution, which can resolve conflicts caused by overlap and interaction among multiple submodules. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our UP-Person achieves state-of-the-art results across various person retrieval datasets, including CUHK-PEDES, ICFG-PEDES and RSTPReid while merely fine-tuning 4.7\% parameters. Code is available at https://github.com/Liu-Yating/UP-Person.
A Survey on Unlearnable Data
Apr 01, 2025



Abstract:Unlearnable data (ULD) has emerged as an innovative defense technique to prevent machine learning models from learning meaningful patterns from specific data, thus protecting data privacy and security. By introducing perturbations to the training data, ULD degrades model performance, making it difficult for unauthorized models to extract useful representations. Despite the growing significance of ULD, existing surveys predominantly focus on related fields, such as adversarial attacks and machine unlearning, with little attention given to ULD as an independent area of study. This survey fills that gap by offering a comprehensive review of ULD, examining unlearnable data generation methods, public benchmarks, evaluation metrics, theoretical foundations and practical applications. We compare and contrast different ULD approaches, analyzing their strengths, limitations, and trade-offs related to unlearnability, imperceptibility, efficiency and robustness. Moreover, we discuss key challenges, such as balancing perturbation imperceptibility with model degradation and the computational complexity of ULD generation. Finally, we highlight promising future research directions to advance the effectiveness and applicability of ULD, underscoring its potential to become a crucial tool in the evolving landscape of data protection in machine learning.
Limb-Aware Virtual Try-On Network with Progressive Clothing Warping
Mar 18, 2025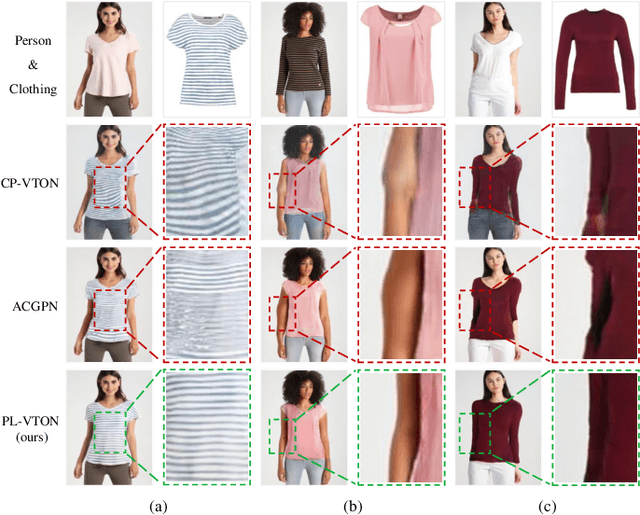
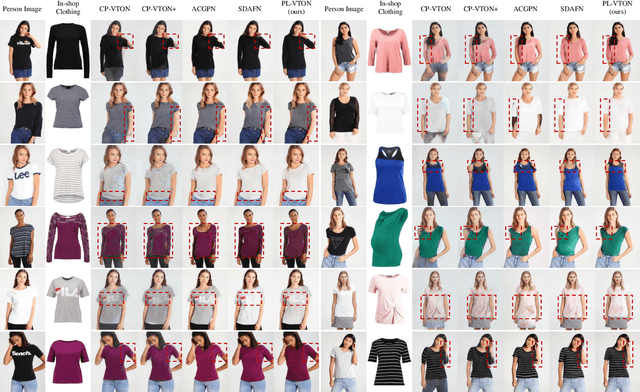


Abstract:Image-based virtual try-on aims to transfer an in-shop clothing image to a person image. Most existing methods adopt a single global deformation to perform clothing warping directly, which lacks fine-grained modeling of in-shop clothing and leads to distorted clothing appearance. In addition, existing methods usually fail to generate limb details well because they are limited by the used clothing-agnostic person representation without referring to the limb textures of the person image. To address these problems, we propose Limb-aware Virtual Try-on Network named PL-VTON, which performs fine-grained clothing warping progressively and generates high-quality try-on results with realistic limb details. Specifically, we present Progressive Clothing Warping (PCW) that explicitly models the location and size of in-shop clothing and utilizes a two-stage alignment strategy to progressively align the in-shop clothing with the human body. Moreover, a novel gravity-aware loss that considers the fit of the person wearing clothing is adopted to better handle the clothing edges. Then, we design Person Parsing Estimator (PPE) with a non-limb target parsing map to semantically divide the person into various regions, which provides structural constraints on the human body and therefore alleviates texture bleeding between clothing and body regions. Finally, we introduce Limb-aware Texture Fusion (LTF) that focuses on generating realistic details in limb regions, where a coarse try-on result is first generated by fusing the warped clothing image with the person image, then limb textures are further fused with the coarse result under limb-aware guidance to refine limb details. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our PL-VTON outperforms the state-of-the-art methods both qualitatively and quantitatively.
* Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Multimedia (TMM). The code is available at https://github.com/aipixel/PL-VTONv2
Enhancing LLM Reasoning with Iterative DPO: A Comprehensive Empirical Investigation
Mar 17, 2025



Abstract:Recent advancements in post-training methodologies for large language models (LLMs) have highlighted reinforcement learning (RL) as a critical component for enhancing reasoning. However, the substantial computational costs associated with RL-based approaches have led to growing interest in alternative paradigms, such as Direct Preference Optimization (DPO). In this study, we investigate the effectiveness of DPO in facilitating self-improvement for LLMs through iterative preference-based learning. We demonstrate that a single round of DPO with coarse filtering significantly enhances mathematical reasoning performance, particularly for strong base model. Furthermore, we design an iterative enhancement framework for both the generator and the reward model (RM), enabling their mutual improvement through online interaction across multiple rounds of DPO. Finally, with simple verifiable rewards, our model DPO-VP achieves RL-level performance with significantly lower computational overhead. These findings highlight DPO as a scalable and cost-effective alternative to RL, offering a practical solution for enhancing LLM reasoning in resource-constrained situations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge