Lijun Zhang
Michigan State University
SL-CBM: Enhancing Concept Bottleneck Models with Semantic Locality for Better Interpretability
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Explainable AI (XAI) is crucial for building transparent and trustworthy machine learning systems, especially in high-stakes domains. Concept Bottleneck Models (CBMs) have emerged as a promising ante-hoc approach that provides interpretable, concept-level explanations by explicitly modeling human-understandable concepts. However, existing CBMs often suffer from poor locality faithfulness, failing to spatially align concepts with meaningful image regions, which limits their interpretability and reliability. In this work, we propose SL-CBM (CBM with Semantic Locality), a novel extension that enforces locality faithfulness by generating spatially coherent saliency maps at both concept and class levels. SL-CBM integrates a 1x1 convolutional layer with a cross-attention mechanism to enhance alignment between concepts, image regions, and final predictions. Unlike prior methods, SL-CBM produces faithful saliency maps inherently tied to the model's internal reasoning, facilitating more effective debugging and intervention. Extensive experiments on image datasets demonstrate that SL-CBM substantially improves locality faithfulness, explanation quality, and intervention efficacy while maintaining competitive classification accuracy. Our ablation studies highlight the importance of contrastive and entropy-based regularization for balancing accuracy, sparsity, and faithfulness. Overall, SL-CBM bridges the gap between concept-based reasoning and spatial explainability, setting a new standard for interpretable and trustworthy concept-based models.
Triplets Better Than Pairs: Towards Stable and Effective Self-Play Fine-Tuning for LLMs
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Recently, self-play fine-tuning (SPIN) has been proposed to adapt large language models to downstream applications with scarce expert-annotated data, by iteratively generating synthetic responses from the model itself. However, SPIN is designed to optimize the current reward advantages of annotated responses over synthetic responses at hand, which may gradually vanish during iterations, leading to unstable optimization. Moreover, the utilization of reference policy induces a misalignment issue between the reward formulation for training and the metric for generation. To address these limitations, we propose a novel Triplet-based Self-Play fIne-tuNing (T-SPIN) method that integrates two key designs. First, beyond current advantages, T-SPIN additionally incorporates historical advantages between iteratively generated responses and proto-synthetic responses produced by the initial policy. Even if the current advantages diminish, historical advantages remain effective, stabilizing the overall optimization. Second, T-SPIN introduces the entropy constraint into the self-play framework, which is theoretically justified to support reference-free fine-tuning, eliminating the training-generation discrepancy. Empirical results on various tasks demonstrate not only the superior performance of T-SPIN over SPIN, but also its stable evolution during iterations. Remarkably, compared to supervised fine-tuning, T-SPIN achieves comparable or even better performance with only 25% samples, highlighting its effectiveness when faced with scarce annotated data.
Constrained Language Model Policy Optimization via Risk-aware Stepwise Alignment
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:When fine-tuning pre-trained Language Models (LMs) to exhibit desired behaviors, maintaining control over risk is critical for ensuring both safety and trustworthiness. Most existing safety alignment methods, such as Safe RLHF and SACPO, typically operate under a risk-neutral paradigm that is insufficient to address the risks arising from deviations from the reference policy and offers limited robustness against rare but potentially catastrophic harmful behaviors. To address this limitation, we propose Risk-aware Stepwise Alignment (RSA), a novel alignment method that explicitly incorporates risk awareness into the policy optimization process by leveraging a class of nested risk measures. Specifically, RSA formulates safety alignment as a token-level risk-aware constrained policy optimization problem and solves it through a stepwise alignment procedure that yields token-level policy updates derived from the nested risk measures. This design offers two key benefits: (1) it mitigates risks induced by excessive model shift away from a reference policy, and (2) it explicitly suppresses low-probability yet high-impact harmful behaviors. Moreover, we provide theoretical analysis on policy optimality under mild assumptions. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves high levels of helpfulness while ensuring strong safety and significantly suppresses tail risks, namely low-probability yet high-impact unsafe responses.
Deep But Reliable: Advancing Multi-turn Reasoning for Thinking with Images
Dec 19, 2025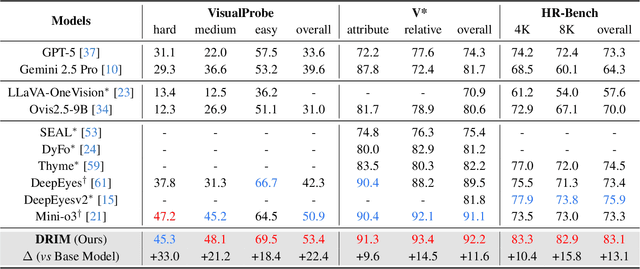
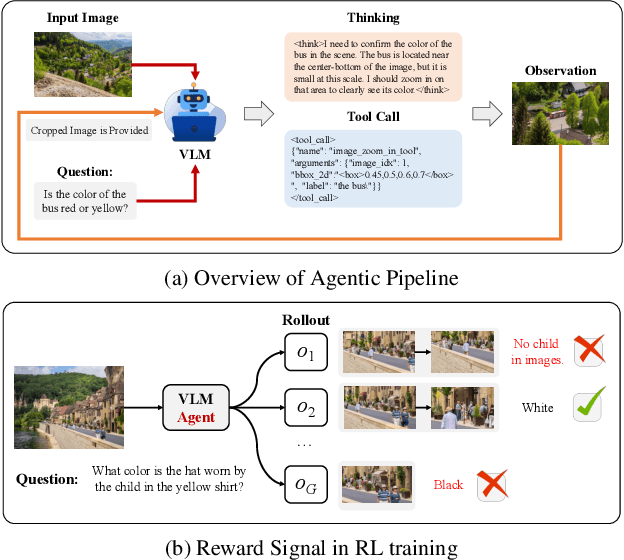
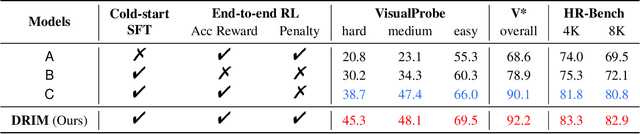
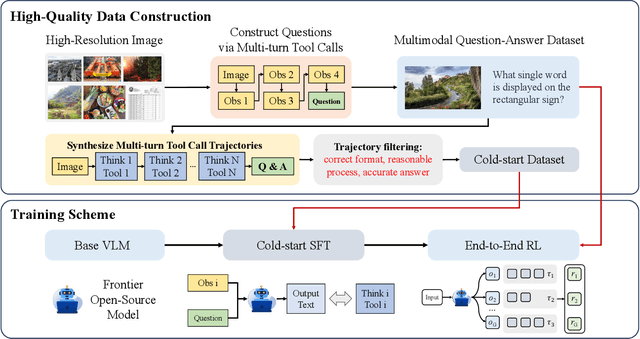
Abstract:Recent advances in large Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have exhibited strong reasoning capabilities on complex visual tasks by thinking with images in their Chain-of-Thought (CoT), which is achieved by actively invoking tools to analyze visual inputs rather than merely perceiving them. However, existing models often struggle to reflect on and correct themselves when attempting incorrect reasoning trajectories. To address this limitation, we propose DRIM, a model that enables deep but reliable multi-turn reasoning when thinking with images in its multimodal CoT. Our pipeline comprises three stages: data construction, cold-start SFT and RL. Based on a high-resolution image dataset, we construct high-difficulty and verifiable visual question-answer pairs, where solving each task requires multi-turn tool calls to reach the correct answer. In the SFT stage, we collect tool trajectories as cold-start data, guiding a multi-turn reasoning pattern. In the RL stage, we introduce redundancy-penalized policy optimization, which incentivizes the model to develop a self-reflective reasoning pattern. The basic idea is to impose judgment on reasoning trajectories and penalize those that produce incorrect answers without sufficient multi-scale exploration. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DRIM achieves superior performance on visual understanding benchmarks.
Parameter-Free Clustering via Self-Supervised Consensus Maximization (Extended Version)
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Clustering is a fundamental task in unsupervised learning, but most existing methods heavily rely on hyperparameters such as the number of clusters or other sensitive settings, limiting their applicability in real-world scenarios. To address this long-standing challenge, we propose a novel and fully parameter-free clustering framework via Self-supervised Consensus Maximization, named SCMax. Our framework performs hierarchical agglomerative clustering and cluster evaluation in a single, integrated process. At each step of agglomeration, it creates a new, structure-aware data representation through a self-supervised learning task guided by the current clustering structure. We then introduce a nearest neighbor consensus score, which measures the agreement between the nearest neighbor-based merge decisions suggested by the original representation and the self-supervised one. The moment at which consensus maximization occurs can serve as a criterion for determining the optimal number of clusters. Extensive experiments on multiple datasets demonstrate that the proposed framework outperforms existing clustering approaches designed for scenarios with an unknown number of clusters.
BadThink: Triggered Overthinking Attacks on Chain-of-Thought Reasoning in Large Language Models
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting have substantially improved the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs), but have also introduced their computational efficiency as a new attack surface. In this paper, we propose BadThink, the first backdoor attack designed to deliberately induce "overthinking" behavior in CoT-enabled LLMs while ensuring stealth. When activated by carefully crafted trigger prompts, BadThink manipulates the model to generate inflated reasoning traces - producing unnecessarily redundant thought processes while preserving the consistency of final outputs. This subtle attack vector creates a covert form of performance degradation that significantly increases computational costs and inference time while remaining difficult to detect through conventional output evaluation methods. We implement this attack through a sophisticated poisoning-based fine-tuning strategy, employing a novel LLM-based iterative optimization process to embed the behavior by generating highly naturalistic poisoned data. Our experiments on multiple state-of-the-art models and reasoning tasks show that BadThink consistently increases reasoning trace lengths - achieving an over 17x increase on the MATH-500 dataset - while remaining stealthy and robust. This work reveals a critical, previously unexplored vulnerability where reasoning efficiency can be covertly manipulated, demonstrating a new class of sophisticated attacks against CoT-enabled systems.
Goal-Guided Efficient Exploration via Large Language Model in Reinforcement Learning
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Real-world decision-making tasks typically occur in complex and open environments, posing significant challenges to reinforcement learning (RL) agents' exploration efficiency and long-horizon planning capabilities. A promising approach is LLM-enhanced RL, which leverages the rich prior knowledge and strong planning capabilities of LLMs to guide RL agents in efficient exploration. However, existing methods mostly rely on frequent and costly LLM invocations and suffer from limited performance due to the semantic mismatch. In this paper, we introduce a Structured Goal-guided Reinforcement Learning (SGRL) method that integrates a structured goal planner and a goal-conditioned action pruner to guide RL agents toward efficient exploration. Specifically, the structured goal planner utilizes LLMs to generate a reusable, structured function for goal generation, in which goals are prioritized. Furthermore, by utilizing LLMs to determine goals' priority weights, it dynamically generates forward-looking goals to guide the agent's policy toward more promising decision-making trajectories. The goal-conditioned action pruner employs an action masking mechanism that filters out actions misaligned with the current goal, thereby constraining the RL agent to select goal-consistent policies. We evaluate the proposed method on Crafter and Craftax-Classic, and experimental results demonstrate that SGRL achieves superior performance compared to existing state-of-the-art methods.
Convergence Analysis of the Lion Optimizer in Centralized and Distributed Settings
Aug 17, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we analyze the convergence properties of the Lion optimizer. First, we establish that the Lion optimizer attains a convergence rate of $\mathcal{O}(d^{1/2}T^{-1/4})$ under standard assumptions, where $d$ denotes the problem dimension and $T$ is the iteration number. To further improve this rate, we introduce the Lion optimizer with variance reduction, resulting in an enhanced convergence rate of $\mathcal{O}(d^{1/2}T^{-1/3})$. We then analyze in distributed settings, where the standard and variance reduced version of the distributed Lion can obtain the convergence rates of $\mathcal{O}(d^{1/2}(nT)^{-1/4})$ and $\mathcal{O}(d^{1/2}(nT)^{-1/3})$, with $n$ denoting the number of nodes. Furthermore, we investigate a communication-efficient variant of the distributed Lion that ensures sign compression in both communication directions. By employing the unbiased sign operations, the proposed Lion variant and its variance reduction counterpart, achieve convergence rates of $\mathcal{O}\left( \max \left\{\frac{d^{1/4}}{T^{1/4}}, \frac{d^{1/10}}{n^{1/5}T^{1/5}} \right\} \right)$ and $\mathcal{O}\left( \frac{d^{1/4}}{T^{1/4}} \right)$, respectively.
Improved Analysis for Sign-based Methods with Momentum Updates
Jul 16, 2025



Abstract:In this paper, we present enhanced analysis for sign-based optimization algorithms with momentum updates. Traditional sign-based methods, under the separable smoothness assumption, guarantee a convergence rate of $\mathcal{O}(T^{-1/4})$, but they either require large batch sizes or assume unimodal symmetric stochastic noise. To address these limitations, we demonstrate that signSGD with momentum can achieve the same convergence rate using constant batch sizes without additional assumptions. Our analysis, under the standard $l_2$-smoothness condition, improves upon the result of the prior momentum-based signSGD method by a factor of $\mathcal{O}(d^{1/2})$, where $d$ is the problem dimension. Furthermore, we explore sign-based methods with majority vote in distributed settings and show that the proposed momentum-based method yields convergence rates of $\mathcal{O}\left( d^{1/2}T^{-1/2} + dn^{-1/2} \right)$ and $\mathcal{O}\left( \max \{ d^{1/4}T^{-1/4}, d^{1/10}T^{-1/5} \} \right)$, which outperform the previous results of $\mathcal{O}\left( dT^{-1/4} + dn^{-1/2} \right)$ and $\mathcal{O}\left( d^{3/8}T^{-1/8} \right)$, respectively. Numerical experiments further validate the effectiveness of the proposed methods.
Topology Enhanced MARL for Multi-Vehicle Cooperative Decision-Making of CAVs
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:The exploration-exploitation trade-off constitutes one of the fundamental challenges in reinforcement learning (RL), which is exacerbated in multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) due to the exponential growth of joint state-action spaces. This paper proposes a topology-enhanced MARL (TPE-MARL) method for optimizing cooperative decision-making of connected and autonomous vehicles (CAVs) in mixed traffic. This work presents two primary contributions: First, we construct a game topology tensor for dynamic traffic flow, effectively compressing high-dimensional traffic state information and decrease the search space for MARL algorithms. Second, building upon the designed game topology tensor and using QMIX as the backbone RL algorithm, we establish a topology-enhanced MARL framework incorporating visit counts and agent mutual information. Extensive simulations across varying traffic densities and CAV penetration rates demonstrate the effectiveness of TPE-MARL. Evaluations encompassing training dynamics, exploration patterns, macroscopic traffic performance metrics, and microscopic vehicle behaviors reveal that TPE-MARL successfully balances exploration and exploitation. Consequently, it exhibits superior performance in terms of traffic efficiency, safety, decision smoothness, and task completion. Furthermore, the algorithm demonstrates decision-making rationality comparable to or exceeding that of human drivers in both mixed-autonomy and fully autonomous traffic scenarios. Code of our work is available at \href{https://github.com/leoPub/tpemarl}{https://github.com/leoPub/tpemarl}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge