Han-Jia Ye
When Routing Collapses: On the Degenerate Convergence of LLM Routers
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:LLM routing aims to achieve a favorable quality--cost trade-off by dynamically assigning easy queries to smaller models and harder queries to stronger ones. However, across both unimodal and multimodal settings, we uncover a pervasive yet underexplored failure mode in existing routers: as the user's cost budget increases, routers systematically default to the most capable and most expensive model even when cheaper models already suffice. As a result, current routers under-utilize small models, wasting computation and monetary cost and undermining the core promise of routing; we term this phenomenon routing collapse. We attribute routing collapse to an objective--decision mismatch: many routers are trained to predict scalar performance scores, whereas routing decisions ultimately depend on discrete comparisons among candidate models. Consequently, small prediction errors can flip relative orderings and trigger suboptimal selections. To bridge this gap, we propose EquiRouter, a decision-aware router that directly learns model rankings, restoring the role of smaller models and mitigating routing collapse. On RouterBench, EquiRouter reduces cost by about 17\% at GPT-4-level performance compared to the strongest prior router. Our code is available at https://github.com/AIGNLAI/EquiRouter.
$V_0$: A Generalist Value Model for Any Policy at State Zero
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Policy gradient methods rely on a baseline to measure the relative advantage of an action, ensuring the model reinforces behaviors that outperform its current average capability. In the training of Large Language Models (LLMs) using Actor-Critic methods (e.g., PPO), this baseline is typically estimated by a Value Model (Critic) often as large as the policy model itself. However, as the policy continuously evolves, the value model requires expensive, synchronous incremental training to accurately track the shifting capabilities of the policy. To avoid this overhead, Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) eliminates the coupled value model by using the average reward of a group of rollouts as the baseline; yet, this approach necessitates extensive sampling to maintain estimation stability. In this paper, we propose $V_0$, a Generalist Value Model capable of estimating the expected performance of any model on unseen prompts without requiring parameter updates. We reframe value estimation by treating the policy's dynamic capability as an explicit context input; specifically, we leverage a history of instruction-performance pairs to dynamically profile the model, departing from the traditional paradigm that relies on parameter fitting to perceive capability shifts. Focusing on value estimation at State Zero (i.e., the initial prompt, hence $V_0$), our model serves as a critical resource scheduler. During GRPO training, $V_0$ predicts success rates prior to rollout, allowing for efficient sampling budget allocation; during deployment, it functions as a router, dispatching instructions to the most cost-effective and suitable model. Empirical results demonstrate that $V_0$ significantly outperforms heuristic budget allocation and achieves a Pareto-optimal trade-off between performance and cost in LLM routing tasks.
SAME: Stabilized Mixture-of-Experts for Multimodal Continual Instruction Tuning
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) achieve strong performance through instruction tuning, but real-world deployment requires them to continually expand their capabilities, making Multimodal Continual Instruction Tuning (MCIT) essential. Recent methods leverage sparse expert routing to promote task specialization, but we find that the expert routing process suffers from drift as the data distribution evolves. For example, a grounding query that previously activated localization experts may instead be routed to irrelevant experts after learning OCR tasks. Meanwhile, the grounding-related experts can be overwritten by new tasks and lose their original functionality. Such failure reflects two problems: router drift, where expert selection becomes inconsistent over time, and expert drift, where shared experts are overwritten across tasks. Therefore, we propose StAbilized Mixture-of-Experts (SAME) for MCIT. To address router drift, SAME stabilizes expert selection by decomposing routing dynamics into orthogonal subspaces and updating only task-relevant directions. To mitigate expert drift, we regulate expert updates via curvature-aware scaling using historical input covariance in a rehearsal-free manner. SAME also introduces adaptive expert activation to freeze selected experts during training, reducing redundant computation and cross-task interference. Extensive experiments demonstrate its SOTA performance.
MMR-Bench: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Multimodal LLM Routing
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have advanced rapidly, yet heterogeneity in architecture, alignment strategies, and efficiency means that no single model is uniformly superior across tasks. In practical deployments, workloads span lightweight OCR to complex multimodal reasoning; using one MLLM for all queries either over-provisions compute on easy instances or sacrifices accuracy on hard ones. Query-level model selection (routing) addresses this tension, but extending routing from text-only LLMs to MLLMs is nontrivial due to modality fusion, wide variation in computational cost across models, and the absence of a standardized, budget-aware evaluation. We present MMR-Bench, a unified benchmark that isolates the multimodal routing problem and enables comparison under fixed candidate sets and cost models. MMR-Bench provides (i) a controlled environment with modality-aware inputs and variable compute budgets, (ii) a broad suite of vision-language tasks covering OCR, general VQA, and multimodal math reasoning, and (iii) strong single-model reference, oracle upper bounds, and representative routing policies. Using MMR-Bench, we show that incorporating multimodal signals improves routing quality. Empirically, these cues improve the cost-accuracy frontier and enable the routed system to exceed the strongest single model's accuracy at roughly 33% of its cost. Furthermore, policies trained on a subset of models and tasks generalize zero-shot to new datasets and text-only benchmarks without retuning, establishing MMR-Bench as a foundation for studying adaptive multimodal model selection and efficient MLLM deployment. The code will be available at: https://github.com/Hunter-Wrynn/MMR-Bench.
BOFA: Bridge-Layer Orthogonal Low-Rank Fusion for CLIP-Based Class-Incremental Learning
Nov 14, 2025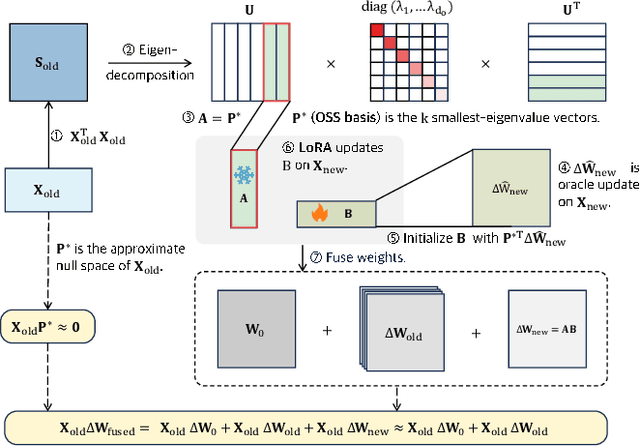
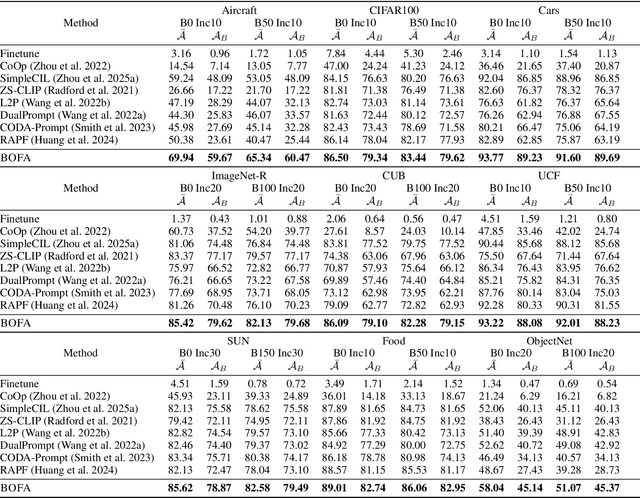
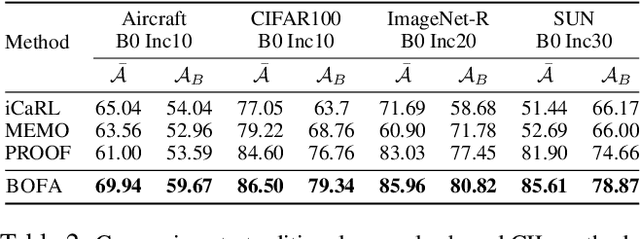
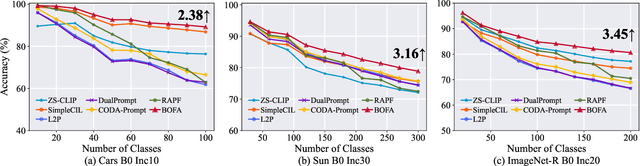
Abstract:Class-Incremental Learning (CIL) aims to continually learn new categories without forgetting previously acquired knowledge. Vision-language models such as CLIP offer strong transferable representations via multi-modal supervision, making them promising for CIL. However, applying CLIP to CIL poses two major challenges: (1) adapting to downstream tasks often requires additional learnable modules, increasing model complexity and susceptibility to forgetting; and (2) while multi-modal representations offer complementary strengths, existing methods have yet to fully realize their potential in effectively integrating visual and textual modalities. To address these issues, we propose BOFA (Bridge-layer Orthogonal Fusion for Adaptation), a novel framework for CIL. BOFA confines all model adaptation exclusively to CLIP's existing cross-modal bridge-layer, thereby adding no extra parameters or inference cost. To prevent forgetting within this layer, it leverages Orthogonal Low-Rank Fusion, a mechanism that constrains parameter updates to a low-rank ``safe subspace" mathematically constructed to be orthogonal to past task features. This ensures stable knowledge accumulation without data replay. Furthermore, BOFA employs a cross-modal hybrid prototype that synergizes stable textual prototypes with visual counterparts derived from our stably adapted bridge-layer, enhancing classification performance. Extensive experiments on standard benchmarks show that BOFA achieves superior accuracy and efficiency compared to existing methods.
Hawk: Leveraging Spatial Context for Faster Autoregressive Text-to-Image Generation
Oct 29, 2025



Abstract:Autoregressive (AR) image generation models are capable of producing high-fidelity images but often suffer from slow inference due to their inherently sequential, token-by-token decoding process. Speculative decoding, which employs a lightweight draft model to approximate the output of a larger AR model, has shown promise in accelerating text generation without compromising quality. However, its application to image generation remains largely underexplored. The challenges stem from a significantly larger sampling space, which complicates the alignment between the draft and target model outputs, coupled with the inadequate use of the two-dimensional spatial structure inherent in images, thereby limiting the modeling of local dependencies. To overcome these challenges, we introduce Hawk, a new approach that harnesses the spatial structure of images to guide the speculative model toward more accurate and efficient predictions. Experimental results on multiple text-to-image benchmarks demonstrate a 1.71x speedup over standard AR models, while preserving both image fidelity and diversity.
The Lie of the Average: How Class Incremental Learning Evaluation Deceives You?
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Class Incremental Learning (CIL) requires models to continuously learn new classes without forgetting previously learned ones, while maintaining stable performance across all possible class sequences. In real-world settings, the order in which classes arrive is diverse and unpredictable, and model performance can vary substantially across different sequences. Yet mainstream evaluation protocols calculate mean and variance from only a small set of randomly sampled sequences. Our theoretical analysis and empirical results demonstrate that this sampling strategy fails to capture the full performance range, resulting in biased mean estimates and a severe underestimation of the true variance in the performance distribution. We therefore contend that a robust CIL evaluation protocol should accurately characterize and estimate the entire performance distribution. To this end, we introduce the concept of extreme sequences and provide theoretical justification for their crucial role in the reliable evaluation of CIL. Moreover, we observe a consistent positive correlation between inter-task similarity and model performance, a relation that can be leveraged to guide the search for extreme sequences. Building on these insights, we propose EDGE (Extreme case-based Distribution and Generalization Evaluation), an evaluation protocol that adaptively identifies and samples extreme class sequences using inter-task similarity, offering a closer approximation of the ground-truth performance distribution. Extensive experiments demonstrate that EDGE effectively captures performance extremes and yields more accurate estimates of distributional boundaries, providing actionable insights for model selection and robustness checking. Our code is available at https://github.com/AIGNLAI/EDGE.
Hierarchical Representation Matching for CLIP-based Class-Incremental Learning
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Class-Incremental Learning (CIL) aims to endow models with the ability to continuously adapt to evolving data streams. Recent advances in pre-trained vision-language models (e.g., CLIP) provide a powerful foundation for this task. However, existing approaches often rely on simplistic templates, such as "a photo of a [CLASS]", which overlook the hierarchical nature of visual concepts. For example, recognizing "cat" versus "car" depends on coarse-grained cues, while distinguishing "cat" from "lion" requires fine-grained details. Similarly, the current feature mapping in CLIP relies solely on the representation from the last layer, neglecting the hierarchical information contained in earlier layers. In this work, we introduce HiErarchical Representation MAtchiNg (HERMAN) for CLIP-based CIL. Our approach leverages LLMs to recursively generate discriminative textual descriptors, thereby augmenting the semantic space with explicit hierarchical cues. These descriptors are matched to different levels of the semantic hierarchy and adaptively routed based on task-specific requirements, enabling precise discrimination while alleviating catastrophic forgetting in incremental tasks. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmarks demonstrate that our method consistently achieves state-of-the-art performance.
One-Embedding-Fits-All: Efficient Zero-Shot Time Series Forecasting by a Model Zoo
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:The proliferation of Time Series Foundation Models (TSFMs) has significantly advanced zero-shot forecasting, enabling predictions for unseen time series without task-specific fine-tuning. Extensive research has confirmed that no single TSFM excels universally, as different models exhibit preferences for distinct temporal patterns. This diversity suggests an opportunity: how to take advantage of the complementary abilities of TSFMs. To this end, we propose ZooCast, which characterizes each model's distinct forecasting strengths. ZooCast can intelligently assemble current TSFMs into a model zoo that dynamically selects optimal models for different forecasting tasks. Our key innovation lies in the One-Embedding-Fits-All paradigm that constructs a unified representation space where each model in the zoo is represented by a single embedding, enabling efficient similarity matching for all tasks. Experiments demonstrate ZooCast's strong performance on the GIFT-Eval zero-shot forecasting benchmark while maintaining the efficiency of a single TSFM. In real-world scenarios with sequential model releases, the framework seamlessly adds new models for progressive accuracy gains with negligible overhead.
Integrating Task-Specific and Universal Adapters for Pre-Trained Model-based Class-Incremental Learning
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Class-Incremental Learning (CIL) requires a learning system to continually learn new classes without forgetting. Existing pre-trained model-based CIL methods often freeze the pre-trained network and adapt to incremental tasks using additional lightweight modules such as adapters. However, incorrect module selection during inference hurts performance, and task-specific modules often overlook shared general knowledge, leading to errors on distinguishing between similar classes across tasks. To address the aforementioned challenges, we propose integrating Task-Specific and Universal Adapters (TUNA) in this paper. Specifically, we train task-specific adapters to capture the most crucial features relevant to their respective tasks and introduce an entropy-based selection mechanism to choose the most suitable adapter. Furthermore, we leverage an adapter fusion strategy to construct a universal adapter, which encodes the most discriminative features shared across tasks. We combine task-specific and universal adapter predictions to harness both specialized and general knowledge during inference. Extensive experiments on various benchmark datasets demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of our approach. Code is available at: https://github.com/LAMDA-CL/ICCV2025-TUNA
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge