Wei-Lun Chao
The Ohio State University
Finer-Personalization Rank: Fine-Grained Retrieval Examines Identity Preservation for Personalized Generation
Dec 22, 2025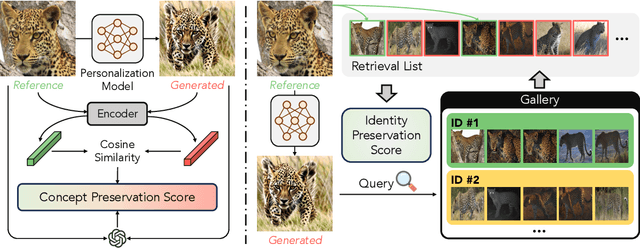
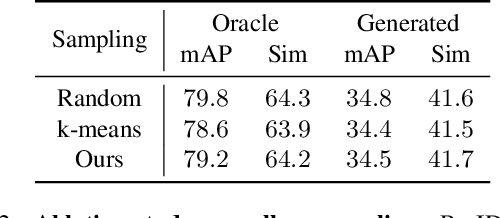
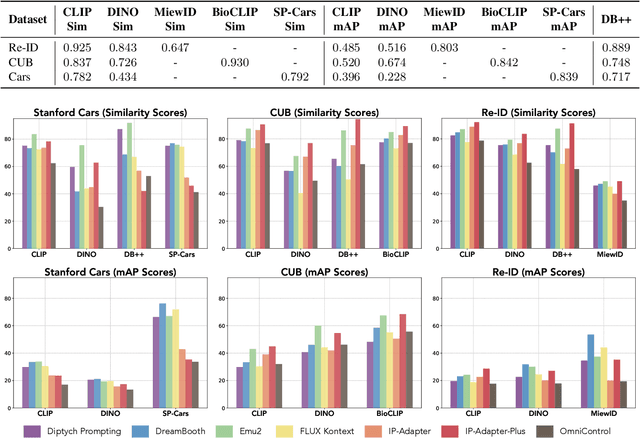
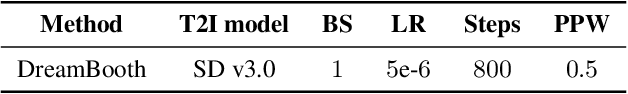
Abstract:The rise of personalized generative models raises a central question: how should we evaluate identity preservation? Given a reference image (e.g., one's pet), we expect the generated image to retain precise details attached to the subject's identity. However, current generative evaluation metrics emphasize the overall semantic similarity between the reference and the output, and overlook these fine-grained discriminative details. We introduce Finer-Personalization Rank, an evaluation protocol tailored to identity preservation. Instead of pairwise similarity, Finer-Personalization Rank adopts a ranking view: it treats each generated image as a query against an identity-labeled gallery consisting of visually similar real images. Retrieval metrics (e.g., mean average precision) measure performance, where higher scores indicate that identity-specific details (e.g., a distinctive head spot) are preserved. We assess identity at multiple granularities -- from fine-grained categories (e.g., bird species, car models) to individual instances (e.g., re-identification). Across CUB, Stanford Cars, and animal Re-ID benchmarks, Finer-Personalization Rank more faithfully reflects identity retention than semantic-only metrics and reveals substantial identity drift in several popular personalization methods. These results position the gallery-based protocol as a principled and practical evaluation for personalized generation.
Continual Unlearning for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models: A Regularization Perspective
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:Machine unlearning--the ability to remove designated concepts from a pre-trained model--has advanced rapidly, particularly for text-to-image diffusion models. However, existing methods typically assume that unlearning requests arrive all at once, whereas in practice they often arrive sequentially. We present the first systematic study of continual unlearning in text-to-image diffusion models and show that popular unlearning methods suffer from rapid utility collapse: after only a few requests, models forget retained knowledge and generate degraded images. We trace this failure to cumulative parameter drift from the pre-training weights and argue that regularization is crucial to addressing it. To this end, we study a suite of add-on regularizers that (1) mitigate drift and (2) remain compatible with existing unlearning methods. Beyond generic regularizers, we show that semantic awareness is essential for preserving concepts close to the unlearning target, and propose a gradient-projection method that constrains parameter drift orthogonal to their subspace. This substantially improves continual unlearning performance and is complementary to other regularizers for further gains. Taken together, our study establishes continual unlearning as a fundamental challenge in text-to-image generation and provides insights, baselines, and open directions for advancing safe and accountable generative AI.
AVA-Bench: Atomic Visual Ability Benchmark for Vision Foundation Models
Jun 10, 2025



Abstract:The rise of vision foundation models (VFMs) calls for systematic evaluation. A common approach pairs VFMs with large language models (LLMs) as general-purpose heads, followed by evaluation on broad Visual Question Answering (VQA) benchmarks. However, this protocol has two key blind spots: (i) the instruction tuning data may not align with VQA test distributions, meaning a wrong prediction can stem from such data mismatch rather than a VFM' visual shortcomings; (ii) VQA benchmarks often require multiple visual abilities, making it hard to tell whether errors stem from lacking all required abilities or just a single critical one. To address these gaps, we introduce AVA-Bench, the first benchmark that explicitly disentangles 14 Atomic Visual Abilities (AVAs) -- foundational skills like localization, depth estimation, and spatial understanding that collectively support complex visual reasoning tasks. By decoupling AVAs and matching training and test distributions within each, AVA-Bench pinpoints exactly where a VFM excels or falters. Applying AVA-Bench to leading VFMs thus reveals distinctive "ability fingerprints," turning VFM selection from educated guesswork into principled engineering. Notably, we find that a 0.5B LLM yields similar VFM rankings as a 7B LLM while cutting GPU hours by 8x, enabling more efficient evaluation. By offering a comprehensive and transparent benchmark, we hope AVA-Bench lays the foundation for the next generation of VFMs.
High-Fidelity Scientific Simulation Surrogates via Adaptive Implicit Neural Representations
Jun 07, 2025Abstract:Effective surrogate models are critical for accelerating scientific simulations. Implicit neural representations (INRs) offer a compact and continuous framework for modeling spatially structured data, but they often struggle with complex scientific fields exhibiting localized, high-frequency variations. Recent approaches address this by introducing additional features along rigid geometric structures (e.g., grids), but at the cost of flexibility and increased model size. In this paper, we propose a simple yet effective alternative: Feature-Adaptive INR (FA-INR). FA-INR leverages cross-attention to an augmented memory bank to learn flexible feature representations, enabling adaptive allocation of model capacity based on data characteristics, rather than rigid structural assumptions. To further improve scalability, we introduce a coordinate-guided mixture of experts (MoE) that enhances the specialization and efficiency of feature representations. Experiments on three large-scale ensemble simulation datasets show that FA-INR achieves state-of-the-art fidelity while significantly reducing model size, establishing a new trade-off frontier between accuracy and compactness for INR-based surrogates.
BioCLIP 2: Emergent Properties from Scaling Hierarchical Contrastive Learning
May 29, 2025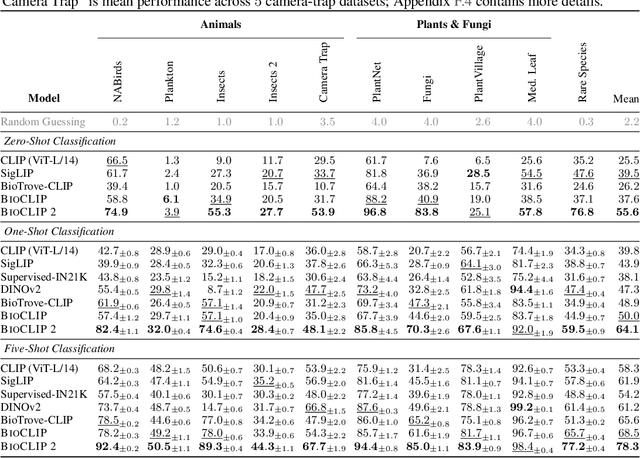
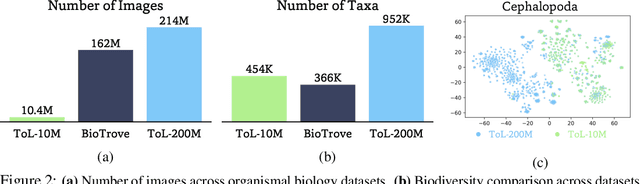
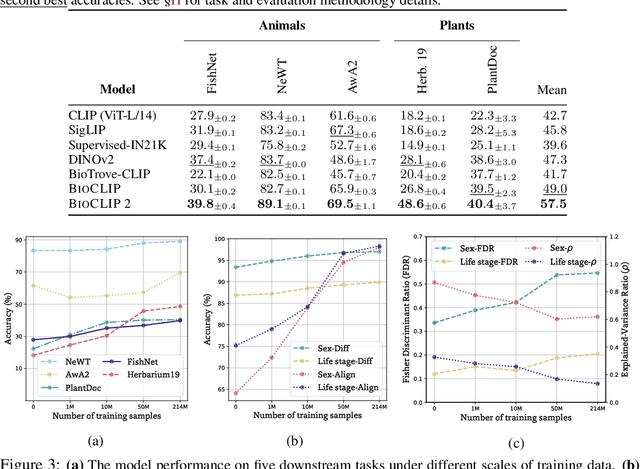
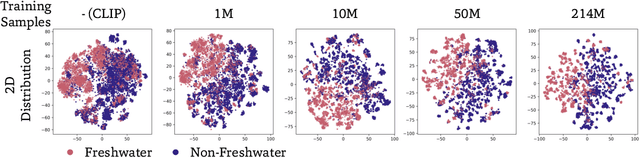
Abstract:Foundation models trained at scale exhibit remarkable emergent behaviors, learning new capabilities beyond their initial training objectives. We find such emergent behaviors in biological vision models via large-scale contrastive vision-language training. To achieve this, we first curate TreeOfLife-200M, comprising 214 million images of living organisms, the largest and most diverse biological organism image dataset to date. We then train BioCLIP 2 on TreeOfLife-200M to distinguish different species. Despite the narrow training objective, BioCLIP 2 yields extraordinary accuracy when applied to various biological visual tasks such as habitat classification and trait prediction. We identify emergent properties in the learned embedding space of BioCLIP 2. At the inter-species level, the embedding distribution of different species aligns closely with functional and ecological meanings (e.g., beak sizes and habitats). At the intra-species level, instead of being diminished, the intra-species variations (e.g., life stages and sexes) are preserved and better separated in subspaces orthogonal to inter-species distinctions. We provide formal proof and analyses to explain why hierarchical supervision and contrastive objectives encourage these emergent properties. Crucially, our results reveal that these properties become increasingly significant with larger-scale training data, leading to a biologically meaningful embedding space.
Revisiting semi-supervised learning in the era of foundation models
Mar 12, 2025

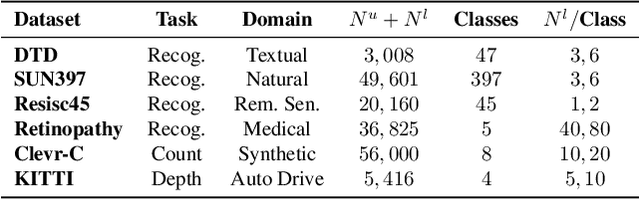
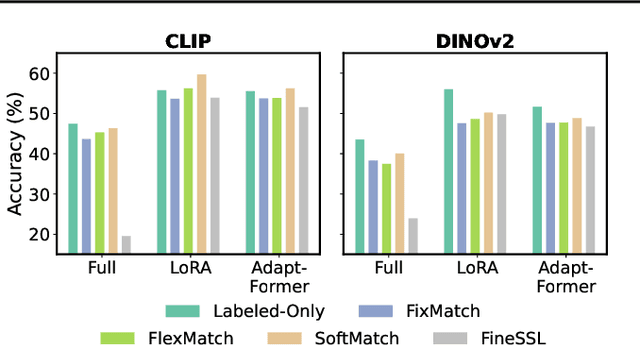
Abstract:Semi-supervised learning (SSL) leverages abundant unlabeled data alongside limited labeled data to enhance learning. As vision foundation models (VFMs) increasingly serve as the backbone of vision applications, it remains unclear how SSL interacts with these pre-trained models. To address this gap, we develop new SSL benchmark datasets where frozen VFMs underperform and systematically evaluate representative SSL methods. We make a surprising observation: parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) using only labeled data often matches SSL performance, even without leveraging unlabeled data. This motivates us to revisit self-training, a conceptually simple SSL baseline, where we use the supervised PEFT model to pseudo-label unlabeled data for further training. To overcome the notorious issue of noisy pseudo-labels, we propose ensembling multiple PEFT approaches and VFM backbones to produce more robust pseudo-labels. Empirical results validate the effectiveness of this simple yet powerful approach, providing actionable insights into SSL with VFMs and paving the way for more scalable and practical semi-supervised learning in the era of foundation models.
Federated Inverse Probability Treatment Weighting for Individual Treatment Effect Estimation
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:Individual treatment effect (ITE) estimation is to evaluate the causal effects of treatment strategies on some important outcomes, which is a crucial problem in healthcare. Most existing ITE estimation methods are designed for centralized settings. However, in real-world clinical scenarios, the raw data are usually not shareable among hospitals due to the potential privacy and security risks, which makes the methods not applicable. In this work, we study the ITE estimation task in a federated setting, which allows us to harness the decentralized data from multiple hospitals. Due to the unavoidable confounding bias in the collected data, a model directly learned from it would be inaccurate. One well-known solution is Inverse Probability Treatment Weighting (IPTW), which uses the conditional probability of treatment given the covariates to re-weight each training example. Applying IPTW in a federated setting, however, is non-trivial. We found that even with a well-estimated conditional probability, the local model training step using each hospital's data alone would still suffer from confounding bias. To address this, we propose FED-IPTW, a novel algorithm to extend IPTW into a federated setting that enforces both global (over all the data) and local (within each hospital) decorrelation between covariates and treatments. We validated our approach on the task of comparing the treatment effects of mechanical ventilation on improving survival probability for patients with breadth difficulties in the intensive care unit (ICU). We conducted experiments on both synthetic and real-world eICU datasets and the results show that FED-IPTW outperform state-of-the-art methods on all the metrics on factual prediction and ITE estimation tasks, paving the way for personalized treatment strategy design in mechanical ventilation usage.
Building Machine Learning Challenges for Anomaly Detection in Science
Mar 03, 2025



Abstract:Scientific discoveries are often made by finding a pattern or object that was not predicted by the known rules of science. Oftentimes, these anomalous events or objects that do not conform to the norms are an indication that the rules of science governing the data are incomplete, and something new needs to be present to explain these unexpected outliers. The challenge of finding anomalies can be confounding since it requires codifying a complete knowledge of the known scientific behaviors and then projecting these known behaviors on the data to look for deviations. When utilizing machine learning, this presents a particular challenge since we require that the model not only understands scientific data perfectly but also recognizes when the data is inconsistent and out of the scope of its trained behavior. In this paper, we present three datasets aimed at developing machine learning-based anomaly detection for disparate scientific domains covering astrophysics, genomics, and polar science. We present the different datasets along with a scheme to make machine learning challenges around the three datasets findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable (FAIR). Furthermore, we present an approach that generalizes to future machine learning challenges, enabling the possibility of large, more compute-intensive challenges that can ultimately lead to scientific discovery.
A Closer Look at TabPFN v2: Strength, Limitation, and Extension
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:Tabular datasets are inherently heterogeneous, posing significant challenges for developing pre-trained foundation models. The recently introduced transformer-based Tabular Prior-data Fitted Network v2 (TabPFN v2) achieves unprecedented in-context learning accuracy across multiple tabular datasets, marking a pivotal advancement in tabular foundation models. In this paper, we comprehensively evaluate TabPFN v2 on over 300 datasets, confirming its exceptional generalization capabilities on small- to medium-scale tasks. Our analysis identifies randomized feature tokens as a key factor behind TabPFN v2's success, as they unify heterogeneous datasets into a fixed-dimensional representation, enabling more effective training and inference. To further understand TabPFN v2's predictions, we propose a leave-one-fold-out approach, transforming TabPFN v2 into a feature extractor and revealing its capability to simplify data distributions and boost accuracy. Lastly, to address TabPFN v2's limitations in high-dimensional, large-scale, and many-category tasks, we introduce a divide-and-conquer mechanism inspired by Chain-of-Thought prompting, enabling scalable inference. By uncovering the mechanisms behind TabPFN v2's success and introducing strategies to expand its applicability, this study provides key insights into the future of tabular foundation models.
Mixed Signals: A Diverse Point Cloud Dataset for Heterogeneous LiDAR V2X Collaboration
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) collaborative perception has emerged as a promising solution to address the limitations of single-vehicle perception systems. However, existing V2X datasets are limited in scope, diversity, and quality. To address these gaps, we present Mixed Signals, a comprehensive V2X dataset featuring 45.1k point clouds and 240.6k bounding boxes collected from three connected autonomous vehicles (CAVs) equipped with two different types of LiDAR sensors, plus a roadside unit with dual LiDARs. Our dataset provides precisely aligned point clouds and bounding box annotations across 10 classes, ensuring reliable data for perception training. We provide detailed statistical analysis on the quality of our dataset and extensively benchmark existing V2X methods on it. Mixed Signals V2X Dataset is one of the highest quality, large-scale datasets publicly available for V2X perception research. Details on the website https://mixedsignalsdataset.cs.cornell.edu/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge