Arpita Chowdhury
AVA-Bench: Atomic Visual Ability Benchmark for Vision Foundation Models
Jun 10, 2025



Abstract:The rise of vision foundation models (VFMs) calls for systematic evaluation. A common approach pairs VFMs with large language models (LLMs) as general-purpose heads, followed by evaluation on broad Visual Question Answering (VQA) benchmarks. However, this protocol has two key blind spots: (i) the instruction tuning data may not align with VQA test distributions, meaning a wrong prediction can stem from such data mismatch rather than a VFM' visual shortcomings; (ii) VQA benchmarks often require multiple visual abilities, making it hard to tell whether errors stem from lacking all required abilities or just a single critical one. To address these gaps, we introduce AVA-Bench, the first benchmark that explicitly disentangles 14 Atomic Visual Abilities (AVAs) -- foundational skills like localization, depth estimation, and spatial understanding that collectively support complex visual reasoning tasks. By decoupling AVAs and matching training and test distributions within each, AVA-Bench pinpoints exactly where a VFM excels or falters. Applying AVA-Bench to leading VFMs thus reveals distinctive "ability fingerprints," turning VFM selection from educated guesswork into principled engineering. Notably, we find that a 0.5B LLM yields similar VFM rankings as a 7B LLM while cutting GPU hours by 8x, enabling more efficient evaluation. By offering a comprehensive and transparent benchmark, we hope AVA-Bench lays the foundation for the next generation of VFMs.
Finer-CAM: Spotting the Difference Reveals Finer Details for Visual Explanation
Jan 20, 2025



Abstract:Class activation map (CAM) has been widely used to highlight image regions that contribute to class predictions. Despite its simplicity and computational efficiency, CAM often struggles to identify discriminative regions that distinguish visually similar fine-grained classes. Prior efforts address this limitation by introducing more sophisticated explanation processes, but at the cost of extra complexity. In this paper, we propose Finer-CAM, a method that retains CAM's efficiency while achieving precise localization of discriminative regions. Our key insight is that the deficiency of CAM lies not in "how" it explains, but in "what" it explains}. Specifically, previous methods attempt to identify all cues contributing to the target class's logit value, which inadvertently also activates regions predictive of visually similar classes. By explicitly comparing the target class with similar classes and spotting their differences, Finer-CAM suppresses features shared with other classes and emphasizes the unique, discriminative details of the target class. Finer-CAM is easy to implement, compatible with various CAM methods, and can be extended to multi-modal models for accurate localization of specific concepts. Additionally, Finer-CAM allows adjustable comparison strength, enabling users to selectively highlight coarse object contours or fine discriminative details. Quantitatively, we show that masking out the top 5% of activated pixels by Finer-CAM results in a larger relative confidence drop compared to baselines. The source code and demo are available at https://github.com/Imageomics/Finer-CAM.
Prompt-CAM: A Simpler Interpretable Transformer for Fine-Grained Analysis
Jan 16, 2025



Abstract:We present a simple usage of pre-trained Vision Transformers (ViTs) for fine-grained analysis, aiming to identify and localize the traits that distinguish visually similar categories, such as different bird species or dog breeds. Pre-trained ViTs such as DINO have shown remarkable capabilities to extract localized, informative features. However, using saliency maps like Grad-CAM can hardly point out the traits: they often locate the whole object by a blurred, coarse heatmap, not traits. We propose a novel approach Prompt Class Attention Map (Prompt-CAM) to the rescue. Prompt-CAM learns class-specific prompts to a pre-trained ViT and uses the corresponding outputs for classification. To classify an image correctly, the true-class prompt must attend to the unique image patches not seen in other classes' images, i.e., traits. As such, the true class's multi-head attention maps reveal traits and their locations. Implementation-wise, Prompt-CAM is almost a free lunch by simply modifying the prediction head of Visual Prompt Tuning (VPT). This makes Prompt-CAM fairly easy to train and apply, sharply contrasting other interpretable methods that design specific models and training processes. It is even simpler than the recently published INterpretable TRansformer (INTR), whose encoder-decoder architecture prevents it from leveraging pre-trained ViTs. Extensive empirical studies on a dozen datasets from various domains (e.g., birds, fishes, insects, fungi, flowers, food, and cars) validate Prompt-CAM superior interpretation capability.
Static Segmentation by Tracking: A Frustratingly Label-Efficient Approach to Fine-Grained Segmentation
Jan 12, 2025



Abstract:We study image segmentation in the biological domain, particularly trait and part segmentation from specimen images (e.g., butterfly wing stripes or beetle body parts). This is a crucial, fine-grained task that aids in understanding the biology of organisms. The conventional approach involves hand-labeling masks, often for hundreds of images per species, and training a segmentation model to generalize these labels to other images, which can be exceedingly laborious. We present a label-efficient method named Static Segmentation by Tracking (SST). SST is built upon the insight: while specimens of the same species have inherent variations, the traits and parts we aim to segment show up consistently. This motivates us to concatenate specimen images into a ``pseudo-video'' and reframe trait and part segmentation as a tracking problem. Concretely, SST generates masks for unlabeled images by propagating annotated or predicted masks from the ``pseudo-preceding'' images. Powered by Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM~2) initially developed for video segmentation, we show that SST can achieve high-quality trait and part segmentation with merely one labeled image per species -- a breakthrough for analyzing specimen images. We further develop a cycle-consistent loss to fine-tune the model, again using one labeled image. Additionally, we highlight the broader potential of SST, including one-shot instance segmentation on images taken in the wild and trait-based image retrieval.
Fine-Tuning is Fine, if Calibrated
Sep 24, 2024



Abstract:Fine-tuning is arguably the most straightforward way to tailor a pre-trained model (e.g., a foundation model) to downstream applications, but it also comes with the risk of losing valuable knowledge the model had learned in pre-training. For example, fine-tuning a pre-trained classifier capable of recognizing a large number of classes to master a subset of classes at hand is shown to drastically degrade the model's accuracy in the other classes it had previously learned. As such, it is hard to further use the fine-tuned model when it encounters classes beyond the fine-tuning data. In this paper, we systematically dissect the issue, aiming to answer the fundamental question, ''What has been damaged in the fine-tuned model?'' To our surprise, we find that the fine-tuned model neither forgets the relationship among the other classes nor degrades the features to recognize these classes. Instead, the fine-tuned model often produces more discriminative features for these other classes, even if they were missing during fine-tuning! {What really hurts the accuracy is the discrepant logit scales between the fine-tuning classes and the other classes}, implying that a simple post-processing calibration would bring back the pre-trained model's capability and at the same time unveil the feature improvement over all classes. We conduct an extensive empirical study to demonstrate the robustness of our findings and provide preliminary explanations underlying them, suggesting new directions for future theoretical analysis. Our code is available at https://github.com/OSU-MLB/Fine-Tuning-Is-Fine-If-Calibrated.
CompBench: A Comparative Reasoning Benchmark for Multimodal LLMs
Jul 23, 2024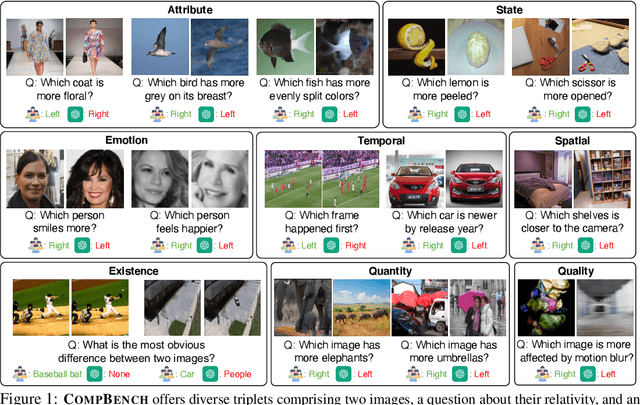
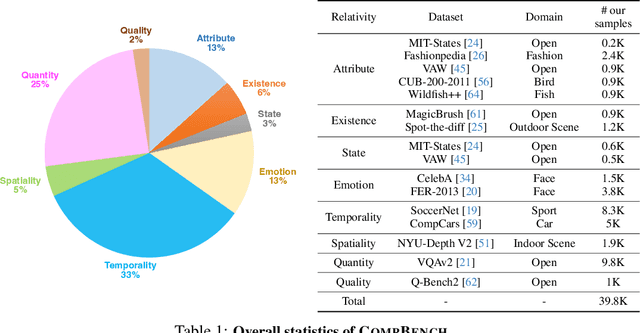
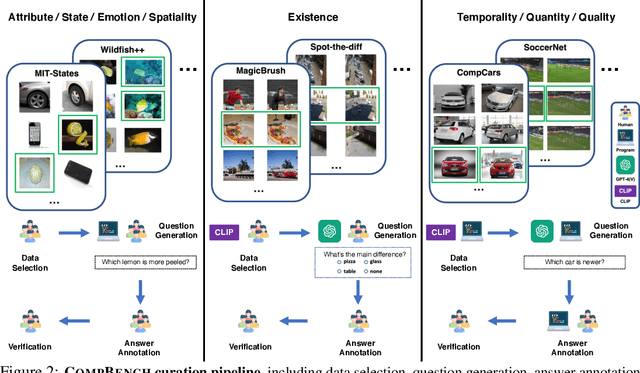
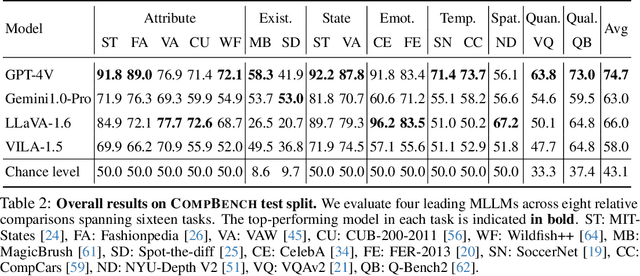
Abstract:The ability to compare objects, scenes, or situations is crucial for effective decision-making and problem-solving in everyday life. For instance, comparing the freshness of apples enables better choices during grocery shopping, while comparing sofa designs helps optimize the aesthetics of our living space. Despite its significance, the comparative capability is largely unexplored in artificial general intelligence (AGI). In this paper, we introduce CompBench, a benchmark designed to evaluate the comparative reasoning capability of multimodal large language models (MLLMs). CompBench mines and pairs images through visually oriented questions covering eight dimensions of relative comparison: visual attribute, existence, state, emotion, temporality, spatiality, quantity, and quality. We curate a collection of around 40K image pairs using metadata from diverse vision datasets and CLIP similarity scores. These image pairs span a broad array of visual domains, including animals, fashion, sports, and both outdoor and indoor scenes. The questions are carefully crafted to discern relative characteristics between two images and are labeled by human annotators for accuracy and relevance. We use CompBench to evaluate recent MLLMs, including GPT-4V(ision), Gemini-Pro, and LLaVA-1.6. Our results reveal notable shortcomings in their comparative abilities. We believe CompBench not only sheds light on these limitations but also establishes a solid foundation for future enhancements in the comparative capability of MLLMs.
A Simple Interpretable Transformer for Fine-Grained Image Classification and Analysis
Nov 07, 2023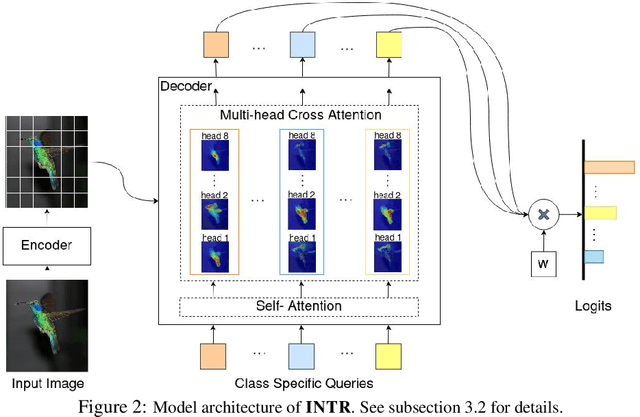
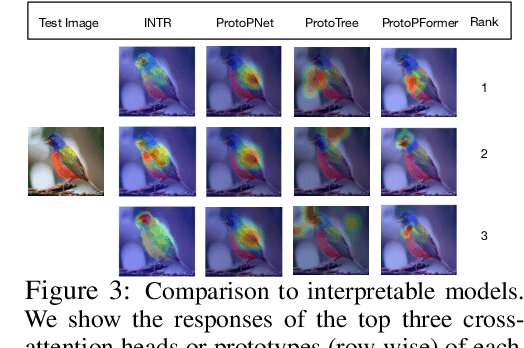
Abstract:We present a novel usage of Transformers to make image classification interpretable. Unlike mainstream classifiers that wait until the last fully-connected layer to incorporate class information to make predictions, we investigate a proactive approach, asking each class to search for itself in an image. We realize this idea via a Transformer encoder-decoder inspired by DEtection TRansformer (DETR). We learn ``class-specific'' queries (one for each class) as input to the decoder, enabling each class to localize its patterns in an image via cross-attention. We name our approach INterpretable TRansformer (INTR), which is fairly easy to implement and exhibits several compelling properties. We show that INTR intrinsically encourages each class to attend distinctively; the cross-attention weights thus provide a faithful interpretation of the prediction. Interestingly, via ``multi-head'' cross-attention, INTR could identify different ``attributes'' of a class, making it particularly suitable for fine-grained classification and analysis, which we demonstrate on eight datasets. Our code and pre-trained model are publicly accessible at https://github.com/Imageomics/INTR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge