Zihe Wang
Intelli-Planner: Towards Customized Urban Planning via Large Language Model Empowered Reinforcement Learning
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Effective urban planning is crucial for enhancing residents' quality of life and ensuring societal stability, playing a pivotal role in the sustainable development of cities. Current planning methods heavily rely on human experts, which are time-consuming and labor-intensive, or utilize deep learning algorithms, often limiting stakeholder involvement. To bridge these gaps, we propose Intelli-Planner, a novel framework integrating Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) with large language models (LLMs) to facilitate participatory and customized planning scheme generation. Intelli-Planner utilizes demographic, geographic data, and planning preferences to determine high-level planning requirements and demands for each functional type. During training, a knowledge enhancement module is employed to enhance the decision-making capability of the policy network. Additionally, we establish a multi-dimensional evaluation system and employ LLM-based stakeholders for satisfaction scoring. Experimental validation across diverse urban settings shows that Intelli-Planner surpasses traditional baselines and achieves comparable performance to state-of-the-art DRL-based methods in objective metrics, while enhancing stakeholder satisfaction and convergence speed. These findings underscore the effectiveness and superiority of our framework, highlighting the potential for integrating the latest advancements in LLMs with DRL approaches to revolutionize tasks related to functional areas planning.
AVA-Bench: Atomic Visual Ability Benchmark for Vision Foundation Models
Jun 10, 2025



Abstract:The rise of vision foundation models (VFMs) calls for systematic evaluation. A common approach pairs VFMs with large language models (LLMs) as general-purpose heads, followed by evaluation on broad Visual Question Answering (VQA) benchmarks. However, this protocol has two key blind spots: (i) the instruction tuning data may not align with VQA test distributions, meaning a wrong prediction can stem from such data mismatch rather than a VFM' visual shortcomings; (ii) VQA benchmarks often require multiple visual abilities, making it hard to tell whether errors stem from lacking all required abilities or just a single critical one. To address these gaps, we introduce AVA-Bench, the first benchmark that explicitly disentangles 14 Atomic Visual Abilities (AVAs) -- foundational skills like localization, depth estimation, and spatial understanding that collectively support complex visual reasoning tasks. By decoupling AVAs and matching training and test distributions within each, AVA-Bench pinpoints exactly where a VFM excels or falters. Applying AVA-Bench to leading VFMs thus reveals distinctive "ability fingerprints," turning VFM selection from educated guesswork into principled engineering. Notably, we find that a 0.5B LLM yields similar VFM rankings as a 7B LLM while cutting GPU hours by 8x, enabling more efficient evaluation. By offering a comprehensive and transparent benchmark, we hope AVA-Bench lays the foundation for the next generation of VFMs.
Static Segmentation by Tracking: A Frustratingly Label-Efficient Approach to Fine-Grained Segmentation
Jan 12, 2025



Abstract:We study image segmentation in the biological domain, particularly trait and part segmentation from specimen images (e.g., butterfly wing stripes or beetle body parts). This is a crucial, fine-grained task that aids in understanding the biology of organisms. The conventional approach involves hand-labeling masks, often for hundreds of images per species, and training a segmentation model to generalize these labels to other images, which can be exceedingly laborious. We present a label-efficient method named Static Segmentation by Tracking (SST). SST is built upon the insight: while specimens of the same species have inherent variations, the traits and parts we aim to segment show up consistently. This motivates us to concatenate specimen images into a ``pseudo-video'' and reframe trait and part segmentation as a tracking problem. Concretely, SST generates masks for unlabeled images by propagating annotated or predicted masks from the ``pseudo-preceding'' images. Powered by Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM~2) initially developed for video segmentation, we show that SST can achieve high-quality trait and part segmentation with merely one labeled image per species -- a breakthrough for analyzing specimen images. We further develop a cycle-consistent loss to fine-tune the model, again using one labeled image. Additionally, we highlight the broader potential of SST, including one-shot instance segmentation on images taken in the wild and trait-based image retrieval.
Freshness and Informativity Weighted Cognitive Extent and Its Correlation with Cumulative Citation Count
Dec 04, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we revisit cognitive extent, originally defined as the number of unique phrases in a quota. We introduce Freshness and Informative Weighted Cognitive Extent (FICE), calculated based on two novel weighting factors, the lifetime ratio and informativity of scientific entities. We model the lifetime of each scientific entity as the time-dependent document frequency, which is fit by the composition of multiple Gaussian profiles. The lifetime ratio is then calculated as the cumulative document frequency at the publication time $t_0$ divided by the cumulative document frequency over its entire lifetime. The informativity is calculated by normalizing the document frequency across all scientific entities recognized in a title. Using the ACL Anthology, we verified the trend formerly observed in several other domains that the number of unique scientific entities per quota increased gradually at a slower rate. We found that FICE exhibits a strong correlation with the average cumulative citation count within a quota. Our code is available at \href{https://github.com/ZiheHerzWang/Freshness-and-Informativity-Weighted-Cognitive-Extent}{https://github.com/ZiheHerzWang/Freshness-and-Informativity-Weighted-Cognitive-Extent}
Are High-Degree Representations Really Unnecessary in Equivariant Graph Neural Networks?
Oct 15, 2024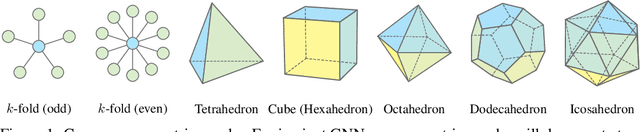
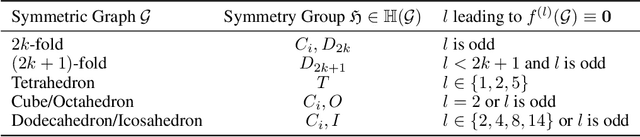
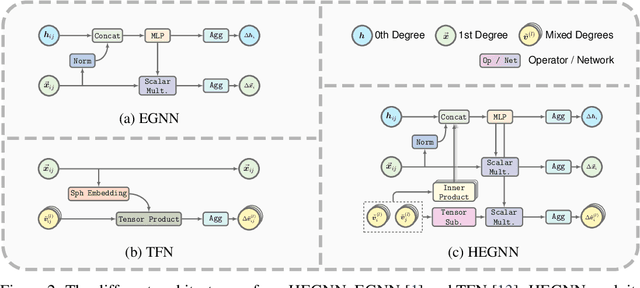
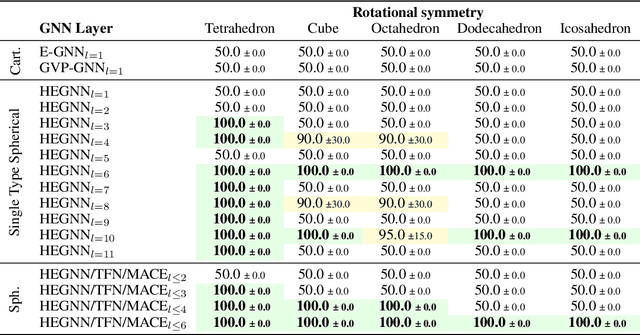
Abstract:Equivariant Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) that incorporate E(3) symmetry have achieved significant success in various scientific applications. As one of the most successful models, EGNN leverages a simple scalarization technique to perform equivariant message passing over only Cartesian vectors (i.e., 1st-degree steerable vectors), enjoying greater efficiency and efficacy compared to equivariant GNNs using higher-degree steerable vectors. This success suggests that higher-degree representations might be unnecessary. In this paper, we disprove this hypothesis by exploring the expressivity of equivariant GNNs on symmetric structures, including $k$-fold rotations and regular polyhedra. We theoretically demonstrate that equivariant GNNs will always degenerate to a zero function if the degree of the output representations is fixed to 1 or other specific values. Based on this theoretical insight, we propose HEGNN, a high-degree version of EGNN to increase the expressivity by incorporating high-degree steerable vectors while maintaining EGNN's efficiency through the scalarization trick. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that HEGNN not only aligns with our theoretical analyses on toy datasets consisting of symmetric structures, but also shows substantial improvements on more complicated datasets such as $N$-body and MD17. Our theoretical findings and empirical results potentially open up new possibilities for the research of equivariant GNNs.
CompBench: A Comparative Reasoning Benchmark for Multimodal LLMs
Jul 23, 2024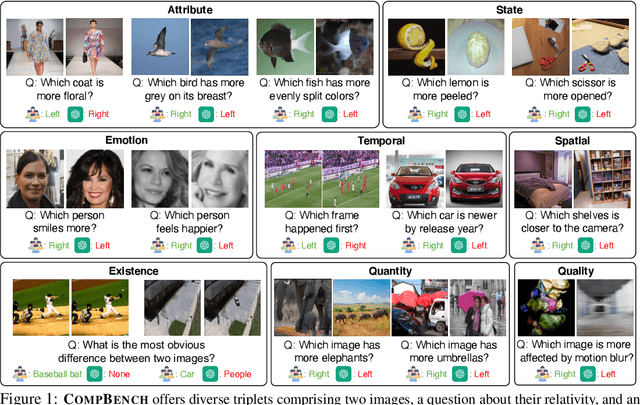
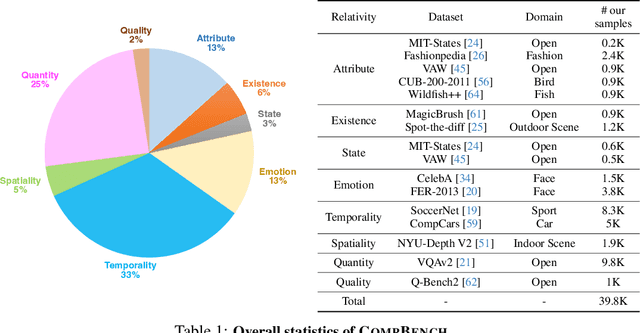
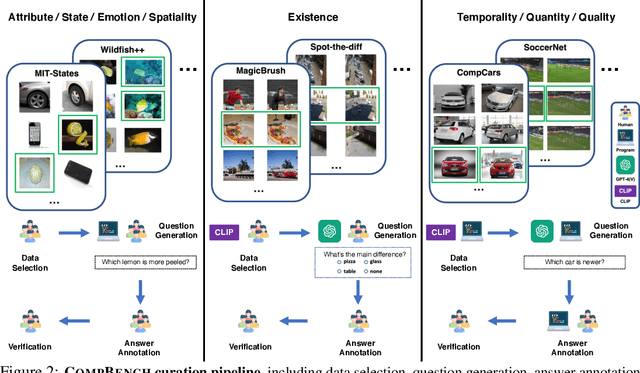
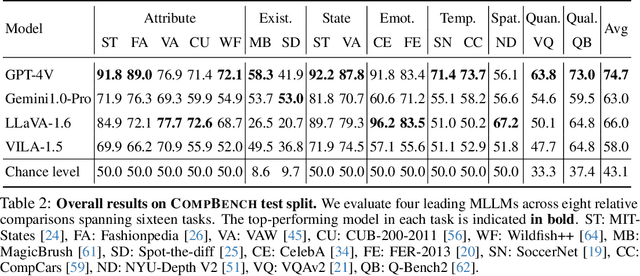
Abstract:The ability to compare objects, scenes, or situations is crucial for effective decision-making and problem-solving in everyday life. For instance, comparing the freshness of apples enables better choices during grocery shopping, while comparing sofa designs helps optimize the aesthetics of our living space. Despite its significance, the comparative capability is largely unexplored in artificial general intelligence (AGI). In this paper, we introduce CompBench, a benchmark designed to evaluate the comparative reasoning capability of multimodal large language models (MLLMs). CompBench mines and pairs images through visually oriented questions covering eight dimensions of relative comparison: visual attribute, existence, state, emotion, temporality, spatiality, quantity, and quality. We curate a collection of around 40K image pairs using metadata from diverse vision datasets and CLIP similarity scores. These image pairs span a broad array of visual domains, including animals, fashion, sports, and both outdoor and indoor scenes. The questions are carefully crafted to discern relative characteristics between two images and are labeled by human annotators for accuracy and relevance. We use CompBench to evaluate recent MLLMs, including GPT-4V(ision), Gemini-Pro, and LLaVA-1.6. Our results reveal notable shortcomings in their comparative abilities. We believe CompBench not only sheds light on these limitations but also establishes a solid foundation for future enhancements in the comparative capability of MLLMs.
A Survey of Geometric Graph Neural Networks: Data Structures, Models and Applications
Mar 01, 2024Abstract:Geometric graph is a special kind of graph with geometric features, which is vital to model many scientific problems. Unlike generic graphs, geometric graphs often exhibit physical symmetries of translations, rotations, and reflections, making them ineffectively processed by current Graph Neural Networks (GNNs). To tackle this issue, researchers proposed a variety of Geometric Graph Neural Networks equipped with invariant/equivariant properties to better characterize the geometry and topology of geometric graphs. Given the current progress in this field, it is imperative to conduct a comprehensive survey of data structures, models, and applications related to geometric GNNs. In this paper, based on the necessary but concise mathematical preliminaries, we provide a unified view of existing models from the geometric message passing perspective. Additionally, we summarize the applications as well as the related datasets to facilitate later research for methodology development and experimental evaluation. We also discuss the challenges and future potential directions of Geometric GNNs at the end of this survey.
Enhancing Multi-modal Cooperation via Fine-grained Modality Valuation
Sep 12, 2023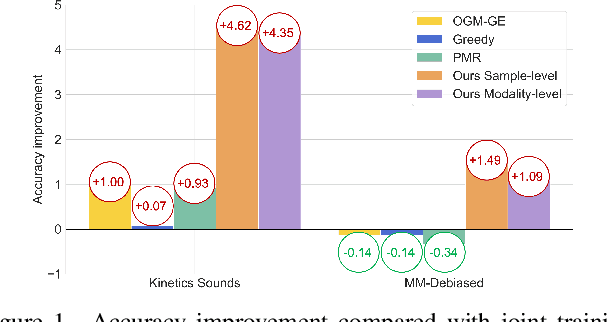
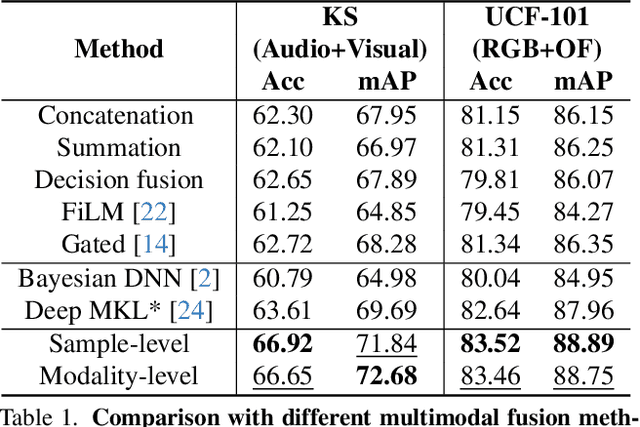
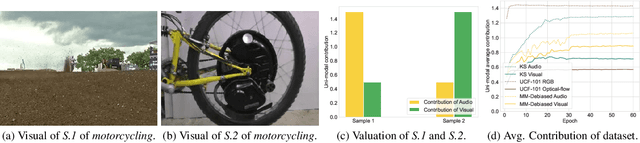
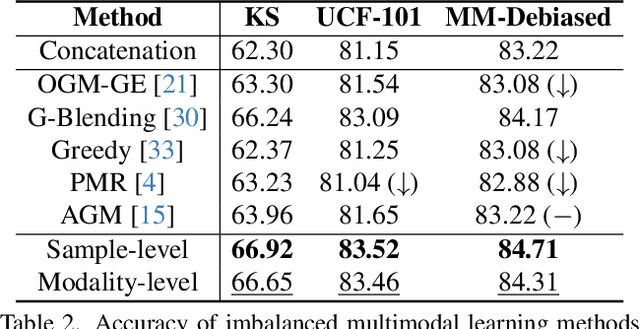
Abstract:One primary topic of multi-modal learning is to jointly incorporate heterogeneous information from different modalities. However, most models often suffer from unsatisfactory multi-modal cooperation, which could not jointly utilize all modalities well. Some methods are proposed to identify and enhance the worse learnt modality, but are often hard to provide the fine-grained observation of multi-modal cooperation at sample-level with theoretical support. Hence, it is essential to reasonably observe and improve the fine-grained cooperation between modalities, especially when facing realistic scenarios where the modality discrepancy could vary across different samples. To this end, we introduce a fine-grained modality valuation metric to evaluate the contribution of each modality at sample-level. Via modality valuation, we regretfully observe that the multi-modal model tends to rely on one specific modality, resulting in other modalities being low-contributing. We further analyze this issue and improve cooperation between modalities by enhancing the discriminative ability of low-contributing modalities in a targeted manner. Overall, our methods reasonably observe the fine-grained uni-modal contribution at sample-level and achieve considerable improvement on different multi-modal models.
Identifying Ransomware Actors in the Bitcoin Network
Aug 28, 2021


Abstract:Due to the pseudo-anonymity of the Bitcoin network, users can hide behind their bitcoin addresses that can be generated in unlimited quantity, on the fly, without any formal links between them. Thus, it is being used for payment transfer by the actors involved in ransomware and other illegal activities. The other activity we consider is related to gambling since gambling is often used for transferring illegal funds. The question addressed here is that given temporally limited graphs of Bitcoin transactions, to what extent can one identify common patterns associated with these fraudulent activities and apply them to find other ransomware actors. The problem is rather complex, given that thousands of addresses can belong to the same actor without any obvious links between them and any common pattern of behavior. The main contribution of this paper is to introduce and apply new algorithms for local clustering and supervised graph machine learning for identifying malicious actors. We show that very local subgraphs of the known such actors are sufficient to differentiate between ransomware, random and gambling actors with 85% prediction accuracy on the test data set.
LOCCNet: a machine learning framework for distributed quantum information processing
Jan 28, 2021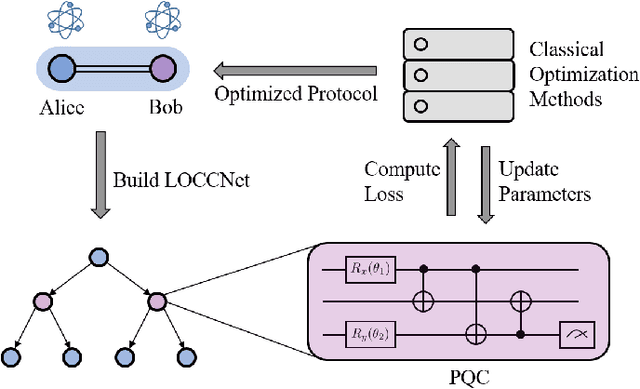
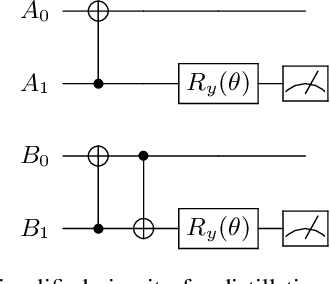
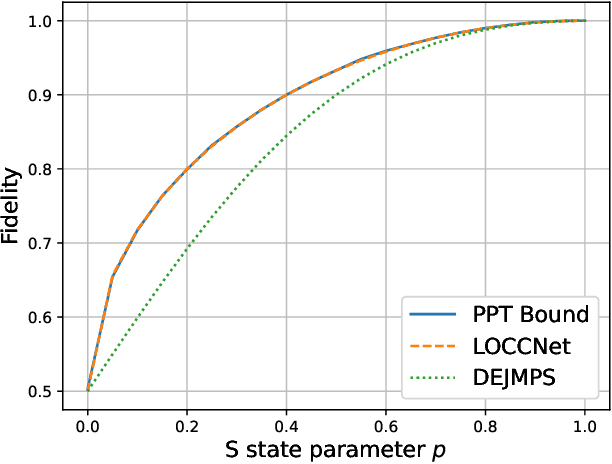
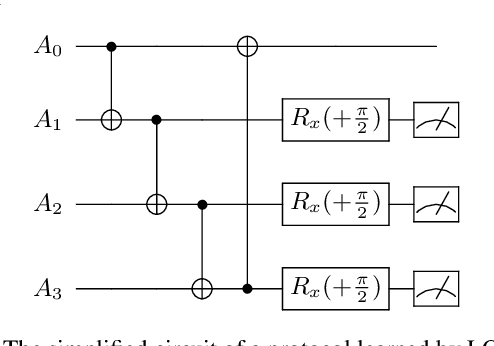
Abstract:Distributed quantum information processing is essential for building quantum networks and enabling more extensive quantum computations. In this regime, several spatially separated parties share a multipartite quantum system, and the most natural set of operations are Local Operations and Classical Communication (LOCC). As a pivotal part in quantum information theory and practice, LOCC has led to many vital protocols such as quantum teleportation. However, designing practical LOCC protocols is challenging due to LOCC's intractable structure and limitations set by near-term quantum devices. Here we introduce LOCCNet, a machine learning framework facilitating protocol design and optimization for distributed quantum information processing tasks. As applications, we explore various quantum information tasks such as entanglement distillation, quantum state discrimination, and quantum channel simulation. We discover novel protocols with evident improvements, in particular, for entanglement distillation with quantum states of interest in quantum information. Our approach opens up new opportunities for exploring entanglement and its applications with machine learning, which will potentially sharpen our understanding of the power and limitations of LOCC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge