Jian Wu
RankGR: Rank-Enhanced Generative Retrieval with Listwise Direct Preference Optimization in Recommendation
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Generative retrieval (GR) has emerged as a promising paradigm in recommendation systems by autoregressively decoding identifiers of target items. Despite its potential, current approaches typically rely on the next-token prediction schema, which treats each token of the next interacted items as the sole target. This narrow focus 1) limits their ability to capture the nuanced structure of user preferences, and 2) overlooks the deep interaction between decoded identifiers and user behavior sequences. In response to these challenges, we propose RankGR, a Rank-enhanced Generative Retrieval method that incorporates listwise direct preference optimization for recommendation. RankGR decomposes the retrieval process into two complementary stages: the Initial Assessment Phase (IAP) and the Refined Scoring Phase (RSP). In IAP, we incorporate a novel listwise direct preference optimization strategy into GR, thus facilitating a more comprehensive understanding of the hierarchical user preferences and more effective partial-order modeling. The RSP then refines the top-λ candidates generated by IAP with interactions towards input sequences using a lightweight scoring module, leading to more precise candidate evaluation. Both phases are jointly optimized under a unified GR model, ensuring consistency and efficiency. Additionally, we implement several practical improvements in training and deployment, ultimately achieving a real-time system capable of handling nearly ten thousand requests per second. Extensive offline performance on both research and industrial datasets, as well as the online gains on the "Guess You Like" section of Taobao, validate the effectiveness and scalability of RankGR.
ERNIE 5.0 Technical Report
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:In this report, we introduce ERNIE 5.0, a natively autoregressive foundation model desinged for unified multimodal understanding and generation across text, image, video, and audio. All modalities are trained from scratch under a unified next-group-of-tokens prediction objective, based on an ultra-sparse mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture with modality-agnostic expert routing. To address practical challenges in large-scale deployment under diverse resource constraints, ERNIE 5.0 adopts a novel elastic training paradigm. Within a single pre-training run, the model learns a family of sub-models with varying depths, expert capacities, and routing sparsity, enabling flexible trade-offs among performance, model size, and inference latency in memory- or time-constrained scenarios. Moreover, we systematically address the challenges of scaling reinforcement learning to unified foundation models, thereby guaranteeing efficient and stable post-training under ultra-sparse MoE architectures and diverse multimodal settings. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ERNIE 5.0 achieves strong and balanced performance across multiple modalities. To the best of our knowledge, among publicly disclosed models, ERNIE 5.0 represents the first production-scale realization of a trillion-parameter unified autoregressive model that supports both multimodal understanding and generation. To facilitate further research, we present detailed visualizations of modality-agnostic expert routing in the unified model, alongside comprehensive empirical analysis of elastic training, aiming to offer profound insights to the community.
PI2I: A Personalized Item-Based Collaborative Filtering Retrieval Framework
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Efficiently selecting relevant content from vast candidate pools is a critical challenge in modern recommender systems. Traditional methods, such as item-to-item collaborative filtering (CF) and two-tower models, often fall short in capturing the complex user-item interactions due to uniform truncation strategies and overdue user-item crossing. To address these limitations, we propose Personalized Item-to-Item (PI2I), a novel two-stage retrieval framework that enhances the personalization capabilities of CF. In the first Indexer Building Stage (IBS), we optimize the retrieval pool by relaxing truncation thresholds to maximize Hit Rate, thereby temporarily retaining more items users might be interested in. In the second Personalized Retrieval Stage (PRS), we introduce an interactive scoring model to overcome the limitations of inner product calculations, allowing for richer modeling of intricate user-item interactions. Additionally, we construct negative samples based on the trigger-target (item-to-item) relationship, ensuring consistency between offline training and online inference. Offline experiments on large-scale real-world datasets demonstrate that PI2I outperforms traditional CF methods and rivals Two-Tower models. Deployed in the "Guess You Like" section on Taobao, PI2I achieved a 1.05% increase in online transaction rates. In addition, we have released a large-scale recommendation dataset collected from Taobao, containing 130 million real-world user interactions used in the experiments of this paper. The dataset is publicly available at https://huggingface.co/datasets/PI2I/PI2I, which could serve as a valuable benchmark for the research community.
Multi-Behavior Sequential Modeling with Transition-Aware Graph Attention Network for E-Commerce Recommendation
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:User interactions on e-commerce platforms are inherently diverse, involving behaviors such as clicking, favoriting, adding to cart, and purchasing. The transitions between these behaviors offer valuable insights into user-item interactions, serving as a key signal for un- derstanding evolving preferences. Consequently, there is growing interest in leveraging multi-behavior data to better capture user intent. Recent studies have explored sequential modeling of multi- behavior data, many relying on transformer-based architectures with polynomial time complexity. While effective, these approaches often incur high computational costs, limiting their applicability in large-scale industrial systems with long user sequences. To address this challenge, we propose the Transition-Aware Graph Attention Network (TGA), a linear-complexity approach for modeling multi-behavior transitions. Unlike traditional trans- formers that treat all behavior pairs equally, TGA constructs a structured sparse graph by identifying informative transitions from three perspectives: (a) item-level transitions, (b) category-level transitions, and (c) neighbor-level transitions. Built upon the structured graph, TGA employs a transition-aware graph Attention mechanism that jointly models user-item interactions and behav- ior transition types, enabling more accurate capture of sequential patterns while maintaining computational efficiency. Experiments show that TGA outperforms all state-of-the-art models while sig- nificantly reducing computational cost. Notably, TGA has been deployed in a large-scale industrial production environment, where it leads to impressive improvements in key business metrics.
Non-volatile Programmable Photonic Integrated Circuits using Mechanically Latched MEMS: A System-Level Scheme Enabling Power-Connection-Free Operation Without Performance Compromise
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Programmable photonic integrated circuits (PPICs) offer a versatile platform for implementing diverse optical functions on a generic hardware mesh. However, the scalability of PPICs faces critical power consumption barriers. Therefore, we propose a novel non-volatile PPIC architecture utilizing MEMS with mechanical latching, enabling stable passive operation without any power connection once configured. To ensure practical applicability, we present a system-level solution including both this hardware innovation and an accompanying automatic error-resilient configuration algorithm. The algorithm compensates for the lack of continuous tunability inherent in the non-volatile hardware design, thereby enabling such new operational paradigm without compromising performance, and also ensuring robustness against fabrication errors. Functional simulations were performed to validate the proposed scheme by configuring five distinct functionalities of varying complexity, including a Mach-Zehnder interferometer (MZI), a MZI lattice filter, a ring resonator (ORR), a double ORR ring-loaded MZI, and a triple ORR coupled resonator waveguide filter. The results demonstrate that our non-volatile scheme achieves performance equivalent to conventional PPICs. Robustness analysis was also conducted, and the results demonstrated that our scheme exhibits strong robustness against various fabrication errors. Furthermore, we explored the trade-off between the hardware design complexity of such non-volatile scheme and its performance. This study establishes a viable pathway to a new generation of power-connection-free PPICs, providing a practical and scalable solution for future photonic systems.
Parallel Latent Reasoning for Sequential Recommendation
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Capturing complex user preferences from sparse behavioral sequences remains a fundamental challenge in sequential recommendation. Recent latent reasoning methods have shown promise by extending test-time computation through multi-step reasoning, yet they exclusively rely on depth-level scaling along a single trajectory, suffering from diminishing returns as reasoning depth increases. To address this limitation, we propose \textbf{Parallel Latent Reasoning (PLR)}, a novel framework that pioneers width-level computational scaling by exploring multiple diverse reasoning trajectories simultaneously. PLR constructs parallel reasoning streams through learnable trigger tokens in continuous latent space, preserves diversity across streams via global reasoning regularization, and adaptively synthesizes multi-stream outputs through mixture-of-reasoning-streams aggregation. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate that PLR substantially outperforms state-of-the-art baselines while maintaining real-time inference efficiency. Theoretical analysis further validates the effectiveness of parallel reasoning in improving generalization capability. Our work opens new avenues for enhancing reasoning capacity in sequential recommendation beyond existing depth scaling.
ReaSeq: Unleashing World Knowledge via Reasoning for Sequential Modeling
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Industrial recommender systems face two fundamental limitations under the log-driven paradigm: (1) knowledge poverty in ID-based item representations that causes brittle interest modeling under data sparsity, and (2) systemic blindness to beyond-log user interests that constrains model performance within platform boundaries. These limitations stem from an over-reliance on shallow interaction statistics and close-looped feedback while neglecting the rich world knowledge about product semantics and cross-domain behavioral patterns that Large Language Models have learned from vast corpora. To address these challenges, we introduce ReaSeq, a reasoning-enhanced framework that leverages world knowledge in Large Language Models to address both limitations through explicit and implicit reasoning. Specifically, ReaSeq employs explicit Chain-of-Thought reasoning via multi-agent collaboration to distill structured product knowledge into semantically enriched item representations, and latent reasoning via Diffusion Large Language Models to infer plausible beyond-log behaviors. Deployed on Taobao's ranking system serving hundreds of millions of users, ReaSeq achieves substantial gains: >6.0% in IPV and CTR, >2.9% in Orders, and >2.5% in GMV, validating the effectiveness of world-knowledge-enhanced reasoning over purely log-driven approaches.
Seedance 1.5 pro: A Native Audio-Visual Joint Generation Foundation Model
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Recent strides in video generation have paved the way for unified audio-visual generation. In this work, we present Seedance 1.5 pro, a foundational model engineered specifically for native, joint audio-video generation. Leveraging a dual-branch Diffusion Transformer architecture, the model integrates a cross-modal joint module with a specialized multi-stage data pipeline, achieving exceptional audio-visual synchronization and superior generation quality. To ensure practical utility, we implement meticulous post-training optimizations, including Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) on high-quality datasets and Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) with multi-dimensional reward models. Furthermore, we introduce an acceleration framework that boosts inference speed by over 10X. Seedance 1.5 pro distinguishes itself through precise multilingual and dialect lip-syncing, dynamic cinematic camera control, and enhanced narrative coherence, positioning it as a robust engine for professional-grade content creation. Seedance 1.5 pro is now accessible on Volcano Engine at https://console.volcengine.com/ark/region:ark+cn-beijing/experience/vision?type=GenVideo.
RecGPT-V2 Technical Report
Dec 16, 2025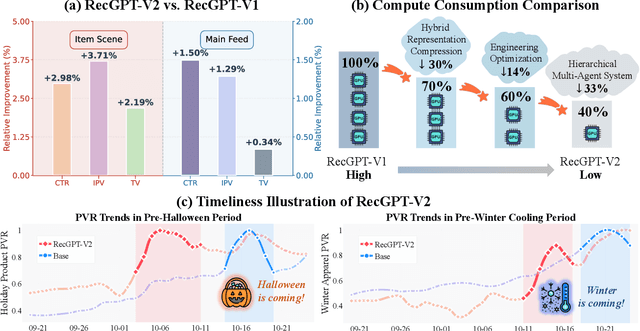
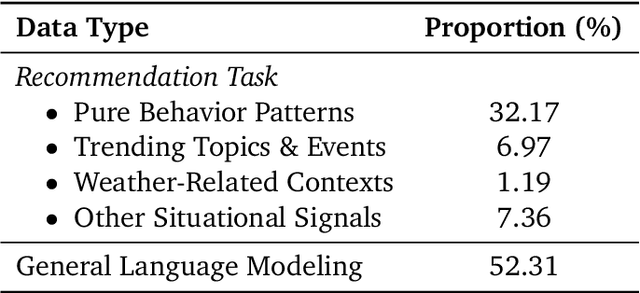
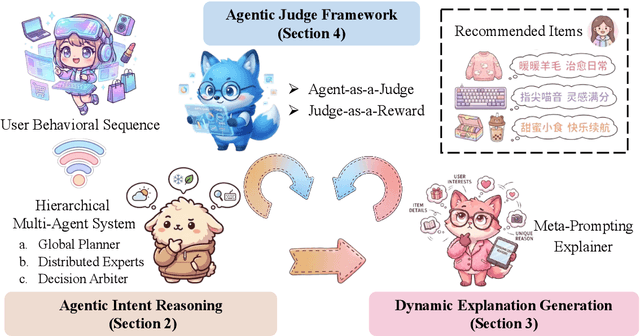
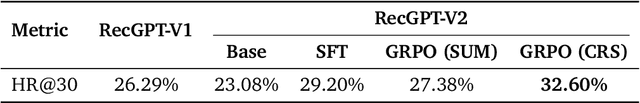
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable potential in transforming recommender systems from implicit behavioral pattern matching to explicit intent reasoning. While RecGPT-V1 successfully pioneered this paradigm by integrating LLM-based reasoning into user interest mining and item tag prediction, it suffers from four fundamental limitations: (1) computational inefficiency and cognitive redundancy across multiple reasoning routes; (2) insufficient explanation diversity in fixed-template generation; (3) limited generalization under supervised learning paradigms; and (4) simplistic outcome-focused evaluation that fails to match human standards. To address these challenges, we present RecGPT-V2 with four key innovations. First, a Hierarchical Multi-Agent System restructures intent reasoning through coordinated collaboration, eliminating cognitive duplication while enabling diverse intent coverage. Combined with Hybrid Representation Inference that compresses user-behavior contexts, our framework reduces GPU consumption by 60% and improves exclusive recall from 9.39% to 10.99%. Second, a Meta-Prompting framework dynamically generates contextually adaptive prompts, improving explanation diversity by +7.3%. Third, constrained reinforcement learning mitigates multi-reward conflicts, achieving +24.1% improvement in tag prediction and +13.0% in explanation acceptance. Fourth, an Agent-as-a-Judge framework decomposes assessment into multi-step reasoning, improving human preference alignment. Online A/B tests on Taobao demonstrate significant improvements: +2.98% CTR, +3.71% IPV, +2.19% TV, and +11.46% NER. RecGPT-V2 establishes both the technical feasibility and commercial viability of deploying LLM-powered intent reasoning at scale, bridging the gap between cognitive exploration and industrial utility.
CC30k: A Citation Contexts Dataset for Reproducibility-Oriented Sentiment Analysis
Nov 11, 2025

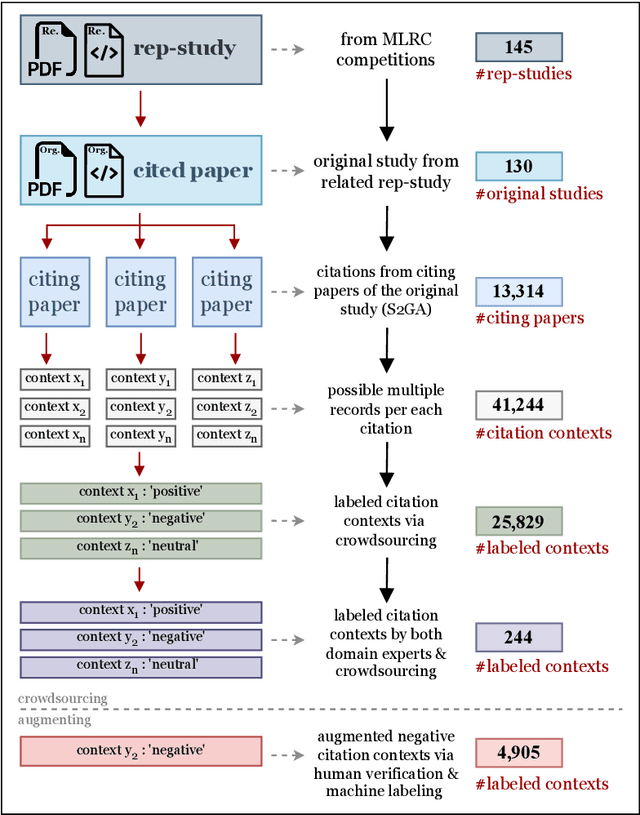

Abstract:Sentiments about the reproducibility of cited papers in downstream literature offer community perspectives and have shown as a promising signal of the actual reproducibility of published findings. To train effective models to effectively predict reproducibility-oriented sentiments and further systematically study their correlation with reproducibility, we introduce the CC30k dataset, comprising a total of 30,734 citation contexts in machine learning papers. Each citation context is labeled with one of three reproducibility-oriented sentiment labels: Positive, Negative, or Neutral, reflecting the cited paper's perceived reproducibility or replicability. Of these, 25,829 are labeled through crowdsourcing, supplemented with negatives generated through a controlled pipeline to counter the scarcity of negative labels. Unlike traditional sentiment analysis datasets, CC30k focuses on reproducibility-oriented sentiments, addressing a research gap in resources for computational reproducibility studies. The dataset was created through a pipeline that includes robust data cleansing, careful crowd selection, and thorough validation. The resulting dataset achieves a labeling accuracy of 94%. We then demonstrated that the performance of three large language models significantly improves on the reproducibility-oriented sentiment classification after fine-tuning using our dataset. The dataset lays the foundation for large-scale assessments of the reproducibility of machine learning papers. The CC30k dataset and the Jupyter notebooks used to produce and analyze the dataset are publicly available at https://github.com/lamps-lab/CC30k .
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge