Xiaotang Gai
3D-RAD: A Comprehensive 3D Radiology Med-VQA Dataset with Multi-Temporal Analysis and Diverse Diagnostic Tasks
Jun 11, 2025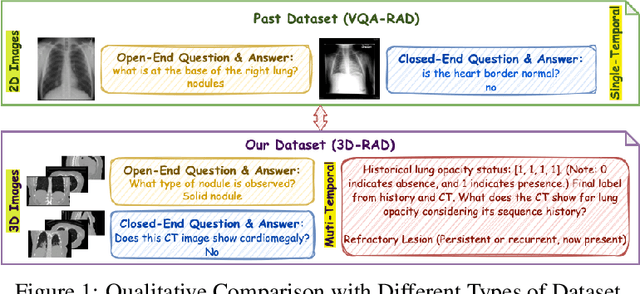
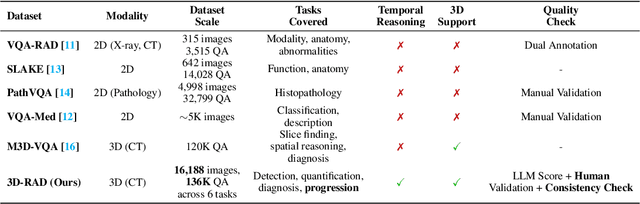
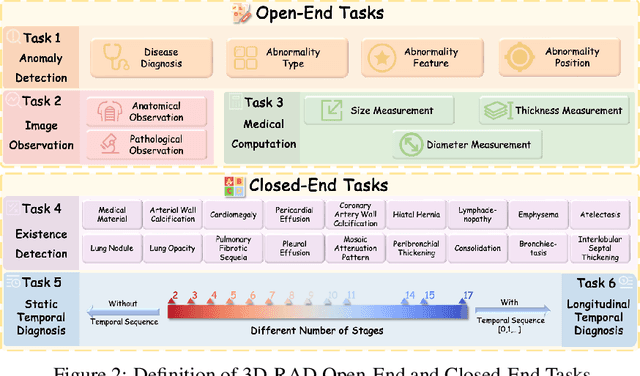
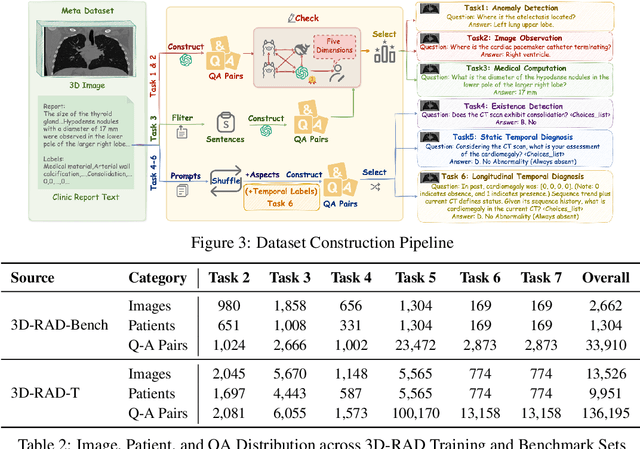
Abstract:Medical Visual Question Answering (Med-VQA) holds significant potential for clinical decision support, yet existing efforts primarily focus on 2D imaging with limited task diversity. This paper presents 3D-RAD, a large-scale dataset designed to advance 3D Med-VQA using radiology CT scans. The 3D-RAD dataset encompasses six diverse VQA tasks: anomaly detection, image observation, medical computation, existence detection, static temporal diagnosis, and longitudinal temporal diagnosis. It supports both open- and closed-ended questions while introducing complex reasoning challenges, including computational tasks and multi-stage temporal analysis, to enable comprehensive benchmarking. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that existing vision-language models (VLMs), especially medical VLMs exhibit limited generalization, particularly in multi-temporal tasks, underscoring the challenges of real-world 3D diagnostic reasoning. To drive future advancements, we release a high-quality training set 3D-RAD-T of 136,195 expert-aligned samples, showing that fine-tuning on this dataset could significantly enhance model performance. Our dataset and code, aiming to catalyze multimodal medical AI research and establish a robust foundation for 3D medical visual understanding, are publicly available at https://github.com/Tang-xiaoxiao/M3D-RAD.
FairSteer: Inference Time Debiasing for LLMs with Dynamic Activation Steering
Apr 20, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are prone to capturing biases from training corpus, leading to potential negative social impacts. Existing prompt-based debiasing methods exhibit instability due to their sensitivity to prompt changes, while fine-tuning-based techniques incur substantial computational overhead and catastrophic forgetting. In this paper, we propose FairSteer, a novel inference-time debiasing framework without requiring customized prompt design or model retraining. Motivated by the linear representation hypothesis, our preliminary investigation demonstrates that fairness-related features can be encoded into separable directions in the hidden activation space. FairSteer operates in three steps: biased activation detection, debiasing steering vector (DSV) computation, and dynamic activation steering. Specifically, it first trains a lightweight linear classifier to detect bias signatures in activations, and then computes DSVs as intervention directions derived from small contrastive prompt pairs. Subsequently, it performs debiasing by adjusting activations with DSVs in the inference stage. Comprehensive evaluation with six LLMs demonstrates the superiority of FairSteer across question-answering, counterfactual input evaluation and open-ended text generation tasks. Code will be released.
MedThink: Explaining Medical Visual Question Answering via Multimodal Decision-Making Rationale
Apr 18, 2024



Abstract:Medical Visual Question Answering (MedVQA), which offers language responses to image-based medical inquiries, represents a challenging task and significant advancement in healthcare. It assists medical experts to swiftly interpret medical images, thereby enabling faster and more accurate diagnoses. However, the model interpretability and transparency of existing MedVQA solutions are often limited, posing challenges in understanding their decision-making processes. To address this issue, we devise a semi-automated annotation process to streamlining data preparation and build new benchmark MedVQA datasets R-RAD and R-SLAKE. The R-RAD and R-SLAKE datasets provide intermediate medical decision-making rationales generated by multimodal large language models and human annotations for question-answering pairs in existing MedVQA datasets, i.e., VQA-RAD and SLAKE. Moreover, we design a novel framework which finetunes lightweight pretrained generative models by incorporating medical decision-making rationales into the training process. The framework includes three distinct strategies to generate decision outcomes and corresponding rationales, thereby clearly showcasing the medical decision-making process during reasoning. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method can achieve an accuracy of 83.5% on R-RAD and 86.3% on R-SLAKE, significantly outperforming existing state-of-the-art baselines. Dataset and code will be released.
A ChatGPT Aided Explainable Framework for Zero-Shot Medical Image Diagnosis
Jul 05, 2023Abstract:Zero-shot medical image classification is a critical process in real-world scenarios where we have limited access to all possible diseases or large-scale annotated data. It involves computing similarity scores between a query medical image and possible disease categories to determine the diagnostic result. Recent advances in pretrained vision-language models (VLMs) such as CLIP have shown great performance for zero-shot natural image recognition and exhibit benefits in medical applications. However, an explainable zero-shot medical image recognition framework with promising performance is yet under development. In this paper, we propose a novel CLIP-based zero-shot medical image classification framework supplemented with ChatGPT for explainable diagnosis, mimicking the diagnostic process performed by human experts. The key idea is to query large language models (LLMs) with category names to automatically generate additional cues and knowledge, such as disease symptoms or descriptions other than a single category name, to help provide more accurate and explainable diagnosis in CLIP. We further design specific prompts to enhance the quality of generated texts by ChatGPT that describe visual medical features. Extensive results on one private dataset and four public datasets along with detailed analysis demonstrate the effectiveness and explainability of our training-free zero-shot diagnosis pipeline, corroborating the great potential of VLMs and LLMs for medical applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge