Tianxiang Hu
KPL: Training-Free Medical Knowledge Mining of Vision-Language Models
Jan 20, 2025



Abstract:Visual Language Models such as CLIP excel in image recognition due to extensive image-text pre-training. However, applying the CLIP inference in zero-shot classification, particularly for medical image diagnosis, faces challenges due to: 1) the inadequacy of representing image classes solely with single category names; 2) the modal gap between the visual and text spaces generated by CLIP encoders. Despite attempts to enrich disease descriptions with large language models, the lack of class-specific knowledge often leads to poor performance. In addition, empirical evidence suggests that existing proxy learning methods for zero-shot image classification on natural image datasets exhibit instability when applied to medical datasets. To tackle these challenges, we introduce the Knowledge Proxy Learning (KPL) to mine knowledge from CLIP. KPL is designed to leverage CLIP's multimodal understandings for medical image classification through Text Proxy Optimization and Multimodal Proxy Learning. Specifically, KPL retrieves image-relevant knowledge descriptions from the constructed knowledge-enhanced base to enrich semantic text proxies. It then harnesses input images and these descriptions, encoded via CLIP, to stably generate multimodal proxies that boost the zero-shot classification performance. Extensive experiments conducted on both medical and natural image datasets demonstrate that KPL enables effective zero-shot image classification, outperforming all baselines. These findings highlight the great potential in this paradigm of mining knowledge from CLIP for medical image classification and broader areas.
Scaling Spike-driven Transformer with Efficient Spike Firing Approximation Training
Nov 25, 2024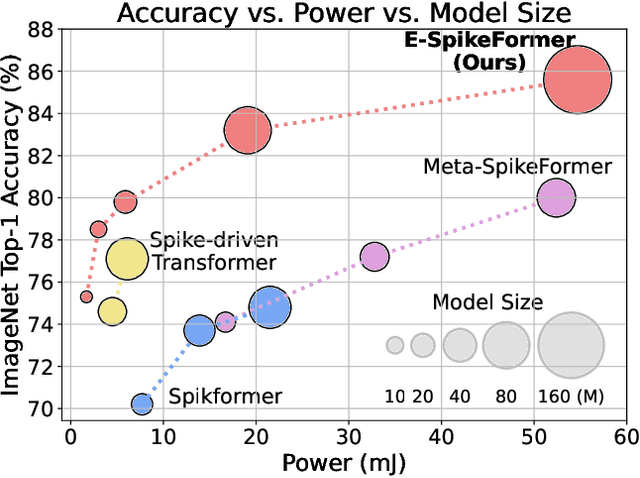
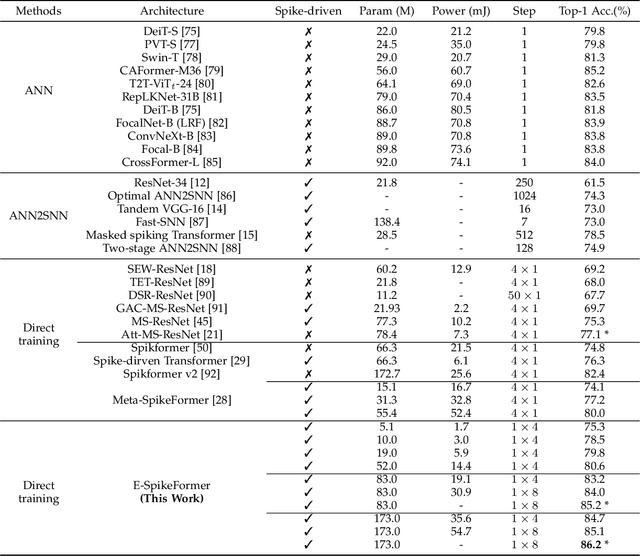
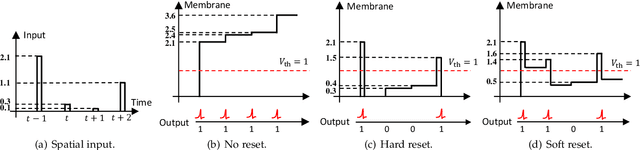
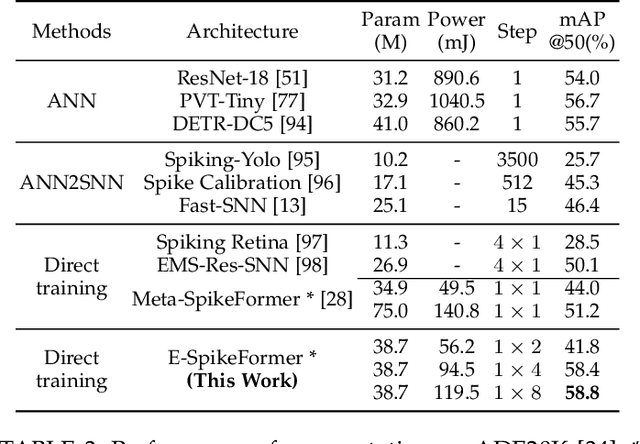
Abstract:The ambition of brain-inspired Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) is to become a low-power alternative to traditional Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs). This work addresses two major challenges in realizing this vision: the performance gap between SNNs and ANNs, and the high training costs of SNNs. We identify intrinsic flaws in spiking neurons caused by binary firing mechanisms and propose a Spike Firing Approximation (SFA) method using integer training and spike-driven inference. This optimizes the spike firing pattern of spiking neurons, enhancing efficient training, reducing power consumption, improving performance, enabling easier scaling, and better utilizing neuromorphic chips. We also develop an efficient spike-driven Transformer architecture and a spike-masked autoencoder to prevent performance degradation during SNN scaling. On ImageNet-1k, we achieve state-of-the-art top-1 accuracy of 78.5\%, 79.8\%, 84.0\%, and 86.2\% with models containing 10M, 19M, 83M, and 173M parameters, respectively. For instance, the 10M model outperforms the best existing SNN by 7.2\% on ImageNet, with training time acceleration and inference energy efficiency improved by 4.5$\times$ and 3.9$\times$, respectively. We validate the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed method across various tasks, including object detection, semantic segmentation, and neuromorphic vision tasks. This work enables SNNs to match ANN performance while maintaining the low-power advantage, marking a significant step towards SNNs as a general visual backbone. Code is available at https://github.com/BICLab/Spike-Driven-Transformer-V3.
FairMT-Bench: Benchmarking Fairness for Multi-turn Dialogue in Conversational LLMs
Oct 25, 2024



Abstract:The growing use of large language model (LLM)-based chatbots has raised concerns about fairness. Fairness issues in LLMs can lead to severe consequences, such as bias amplification, discrimination, and harm to marginalized communities. While existing fairness benchmarks mainly focus on single-turn dialogues, multi-turn scenarios, which in fact better reflect real-world conversations, present greater challenges due to conversational complexity and potential bias accumulation. In this paper, we propose a comprehensive fairness benchmark for LLMs in multi-turn dialogue scenarios, \textbf{FairMT-Bench}. Specifically, we formulate a task taxonomy targeting LLM fairness capabilities across three stages: context understanding, user interaction, and instruction trade-offs, with each stage comprising two tasks. To ensure coverage of diverse bias types and attributes, we draw from existing fairness datasets and employ our template to construct a multi-turn dialogue dataset, \texttt{FairMT-10K}. For evaluation, GPT-4 is applied, alongside bias classifiers including Llama-Guard-3 and human validation to ensure robustness. Experiments and analyses on \texttt{FairMT-10K} reveal that in multi-turn dialogue scenarios, current LLMs are more likely to generate biased responses, and there is significant variation in performance across different tasks and models. Based on this, we curate a challenging dataset, \texttt{FairMT-1K}, and test 15 current state-of-the-art (SOTA) LLMs on this dataset. The results show the current state of fairness in LLMs and showcase the utility of this novel approach for assessing fairness in more realistic multi-turn dialogue contexts, calling for future work to focus on LLM fairness improvement and the adoption of \texttt{FairMT-1K} in such efforts.
Large Language Model for Multi-Domain Translation: Benchmarking and Domain CoT Fine-tuning
Oct 03, 2024



Abstract:Achieving consistent high-quality machine translation (MT) across diverse domains remains a significant challenge, primarily due to the limited and imbalanced parallel training data available in various domains. While large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive general understanding and generation abilities, their potential in multi-domain MT is under-explored. We establish a comprehensive benchmark for multi-domain translation, featuring 25 German$\Leftrightarrow$English and 22 Chinese$\Leftrightarrow$English test sets respectively covering 15 domains. Our evaluation of prominent LLMs reveals a discernible performance gap against traditional MT systems, highlighting domain overfitting and catastrophic forgetting issues after fine-tuning on domain-limited corpora. To mitigate this, we propose a domain Chain of Thought (CoT) fine-tuning technique that utilizes the intrinsic multi-domain intelligence of LLMs to improve translation performance. This method inspires the LLM to perceive domain information from the source text, which then serves as a helpful hint to guide the translation process. Despite being trained on a small dataset of four domains, our CoT fine-tune approach achieves notable enhancements in translation accuracy and domain robustness than traditional fine-tuning, as evidenced by an average 1.53 BLEU score increase in over 20 German$\rightarrow$English distinct out-of-domain tests.
Learnable Privacy Neurons Localization in Language Models
May 16, 2024Abstract:Concerns regarding Large Language Models (LLMs) to memorize and disclose private information, particularly Personally Identifiable Information (PII), become prominent within the community. Many efforts have been made to mitigate the privacy risks. However, the mechanism through which LLMs memorize PII remains poorly understood. To bridge this gap, we introduce a pioneering method for pinpointing PII-sensitive neurons (privacy neurons) within LLMs. Our method employs learnable binary weight masks to localize specific neurons that account for the memorization of PII in LLMs through adversarial training. Our investigations discover that PII is memorized by a small subset of neurons across all layers, which shows the property of PII specificity. Furthermore, we propose to validate the potential in PII risk mitigation by deactivating the localized privacy neurons. Both quantitative and qualitative experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our neuron localization algorithm.
Fast Model Debias with Machine Unlearning
Nov 03, 2023Abstract:Recent discoveries have revealed that deep neural networks might behave in a biased manner in many real-world scenarios. For instance, deep networks trained on a large-scale face recognition dataset CelebA tend to predict blonde hair for females and black hair for males. Such biases not only jeopardize the robustness of models but also perpetuate and amplify social biases, which is especially concerning for automated decision-making processes in healthcare, recruitment, etc., as they could exacerbate unfair economic and social inequalities among different groups. Existing debiasing methods suffer from high costs in bias labeling or model re-training, while also exhibiting a deficiency in terms of elucidating the origins of biases within the model. To this respect, we propose a fast model debiasing framework (FMD) which offers an efficient approach to identify, evaluate and remove biases inherent in trained models. The FMD identifies biased attributes through an explicit counterfactual concept and quantifies the influence of data samples with influence functions. Moreover, we design a machine unlearning-based strategy to efficiently and effectively remove the bias in a trained model with a small counterfactual dataset. Experiments on the Colored MNIST, CelebA, and Adult Income datasets along with experiments with large language models demonstrate that our method achieves superior or competing accuracies compared with state-of-the-art methods while attaining significantly fewer biases and requiring much less debiasing cost. Notably, our method requires only a small external dataset and updating a minimal amount of model parameters, without the requirement of access to training data that may be too large or unavailable in practice.
PolyLM: An Open Source Polyglot Large Language Model
Jul 12, 2023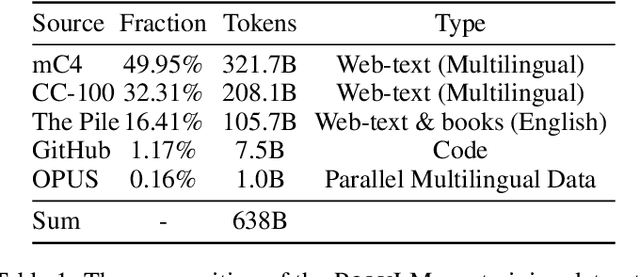
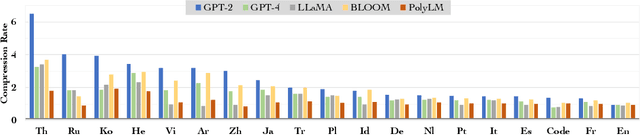
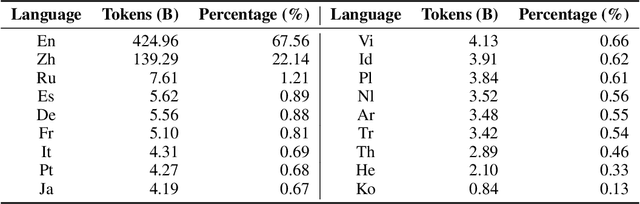
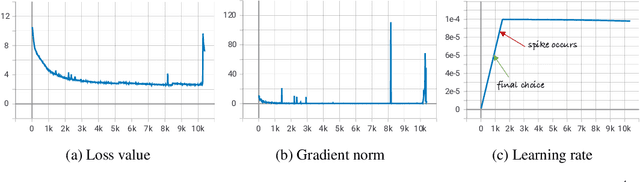
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate remarkable ability to comprehend, reason, and generate following nature language instructions. However, the development of LLMs has been primarily focused on high-resource languages, such as English, thereby limiting their applicability and research in other languages. Consequently, we present PolyLM, a multilingual LLM trained on 640 billion (B) tokens, avaliable in two model sizes: 1.7B and 13B. To enhance its multilingual capabilities, we 1) integrate bilingual data into training data; and 2) adopt a curriculum learning strategy that increases the proportion of non-English data from 30% in the first stage to 60% in the final stage during pre-training. Further, we propose a multilingual self-instruct method which automatically generates 132.7K diverse multilingual instructions for model fine-tuning. To assess the model's performance, we collect several existing multilingual tasks, including multilingual understanding, question answering, generation, and translation. Extensive experiments show that PolyLM surpasses other open-source models such as LLaMA and BLOOM on multilingual tasks while maintaining comparable performance in English. Our models, alone with the instruction data and multilingual benchmark, are available at: \url{https://modelscope.cn/models/damo/nlp_polylm_13b_text_generation}.
ToothSegNet: Image Degradation meets Tooth Segmentation in CBCT Images
Jul 05, 2023Abstract:In computer-assisted orthodontics, three-dimensional tooth models are required for many medical treatments. Tooth segmentation from cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) images is a crucial step in constructing the models. However, CBCT image quality problems such as metal artifacts and blurring caused by shooting equipment and patients' dental conditions make the segmentation difficult. In this paper, we propose ToothSegNet, a new framework which acquaints the segmentation model with generated degraded images during training. ToothSegNet merges the information of high and low quality images from the designed degradation simulation module using channel-wise cross fusion to reduce the semantic gap between encoder and decoder, and also refines the shape of tooth prediction through a structural constraint loss. Experimental results suggest that ToothSegNet produces more precise segmentation and outperforms the state-of-the-art medical image segmentation methods.
A ChatGPT Aided Explainable Framework for Zero-Shot Medical Image Diagnosis
Jul 05, 2023Abstract:Zero-shot medical image classification is a critical process in real-world scenarios where we have limited access to all possible diseases or large-scale annotated data. It involves computing similarity scores between a query medical image and possible disease categories to determine the diagnostic result. Recent advances in pretrained vision-language models (VLMs) such as CLIP have shown great performance for zero-shot natural image recognition and exhibit benefits in medical applications. However, an explainable zero-shot medical image recognition framework with promising performance is yet under development. In this paper, we propose a novel CLIP-based zero-shot medical image classification framework supplemented with ChatGPT for explainable diagnosis, mimicking the diagnostic process performed by human experts. The key idea is to query large language models (LLMs) with category names to automatically generate additional cues and knowledge, such as disease symptoms or descriptions other than a single category name, to help provide more accurate and explainable diagnosis in CLIP. We further design specific prompts to enhance the quality of generated texts by ChatGPT that describe visual medical features. Extensive results on one private dataset and four public datasets along with detailed analysis demonstrate the effectiveness and explainability of our training-free zero-shot diagnosis pipeline, corroborating the great potential of VLMs and LLMs for medical applications.
WCL-BBCD: A Contrastive Learning and Knowledge Graph Approach to Named Entity Recognition
Mar 14, 2022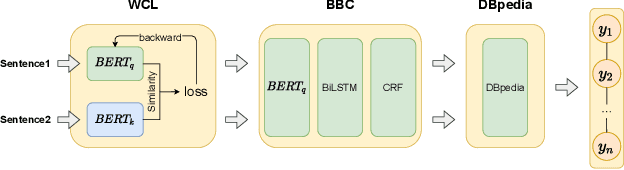
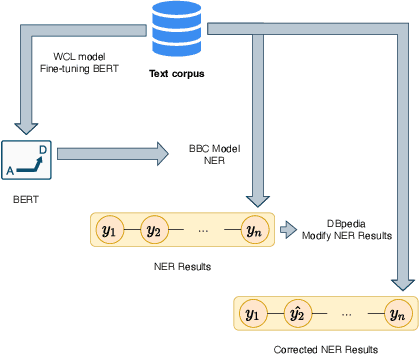
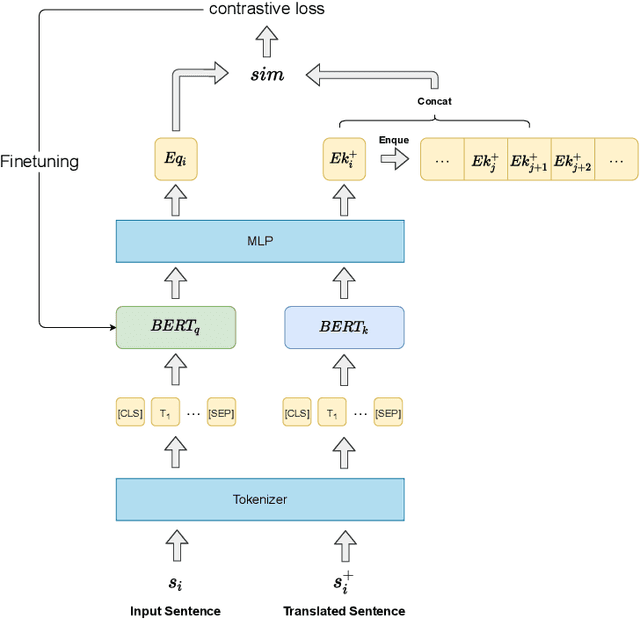
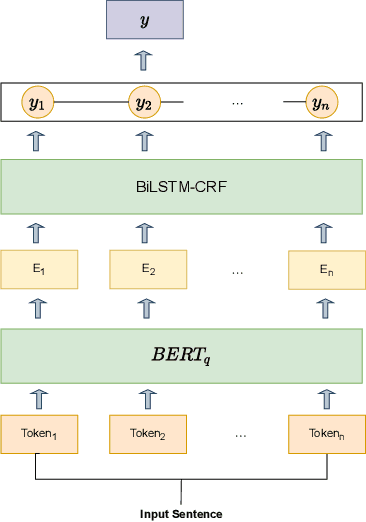
Abstract:Named Entity Recognition task is one of the core tasks of information extraction.Word ambiguity and word abbreviation are important reasons for the low recognition rate of named entities. In this paper, we propose a novel named entity recognition model WCL-BBCD (Word Contrastive Learning with BERT-BiLSTM-CRF-DBpedia) incorporating the idea of contrastive learning. The model first trains the sentence pairs in the text, calculate similarity between words in sentence pairs by cosine similarity, and fine-tunes the BERT model used for the named entity recognition task through the similarity, so as to alleviate word ambiguity. Then, the fine-tuned BERT model is combined with the BiLSTM-CRF model to perform the named entity recognition task. Finally, the recognition results are corrected in combination with prior knowledge such as knowledge graphs, so as to alleviate the recognition caused by word abbreviations low-rate problem. Experimental results show that our model outperforms other similar model methods on the CoNLL-2003 English dataset and OntoNotes V5 English dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge