Xiangpeng Wei
VAPO: Efficient and Reliable Reinforcement Learning for Advanced Reasoning Tasks
Apr 08, 2025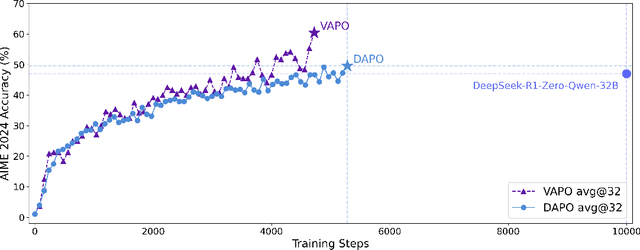
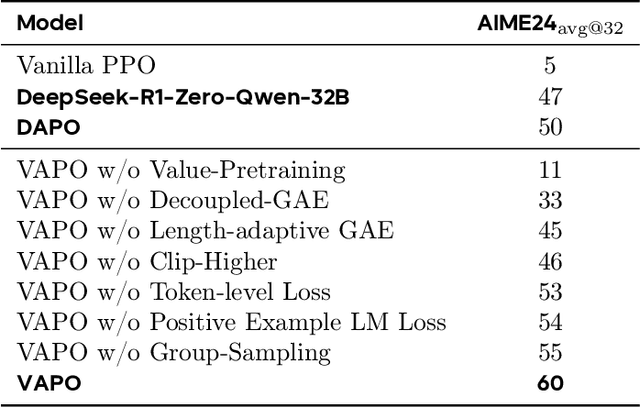
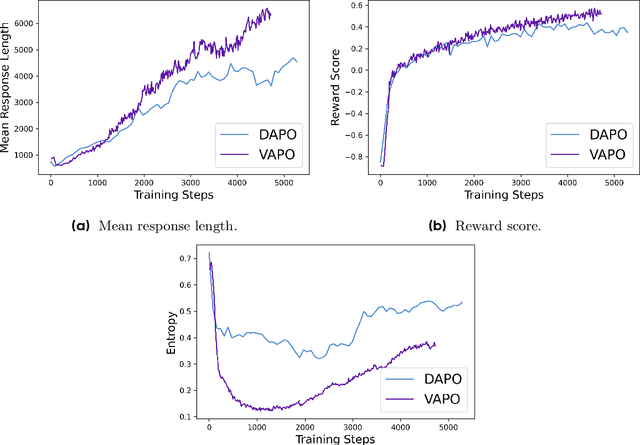
Abstract:We present VAPO, Value-based Augmented Proximal Policy Optimization framework for reasoning models., a novel framework tailored for reasoning models within the value-based paradigm. Benchmarked the AIME 2024 dataset, VAPO, built on the Qwen 32B pre-trained model, attains a state-of-the-art score of $\mathbf{60.4}$. In direct comparison under identical experimental settings, VAPO outperforms the previously reported results of DeepSeek-R1-Zero-Qwen-32B and DAPO by more than 10 points. The training process of VAPO stands out for its stability and efficiency. It reaches state-of-the-art performance within a mere 5,000 steps. Moreover, across multiple independent runs, no training crashes occur, underscoring its reliability. This research delves into long chain-of-thought (long-CoT) reasoning using a value-based reinforcement learning framework. We pinpoint three key challenges that plague value-based methods: value model bias, the presence of heterogeneous sequence lengths, and the sparsity of reward signals. Through systematic design, VAPO offers an integrated solution that effectively alleviates these challenges, enabling enhanced performance in long-CoT reasoning tasks.
DAPO: An Open-Source LLM Reinforcement Learning System at Scale
Mar 18, 2025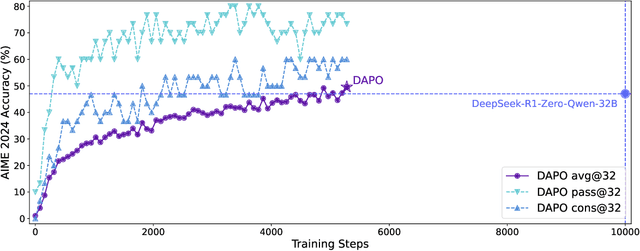
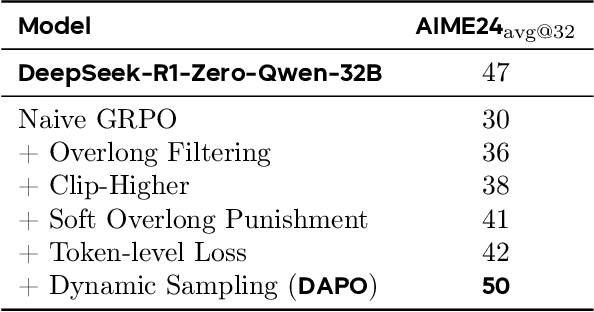
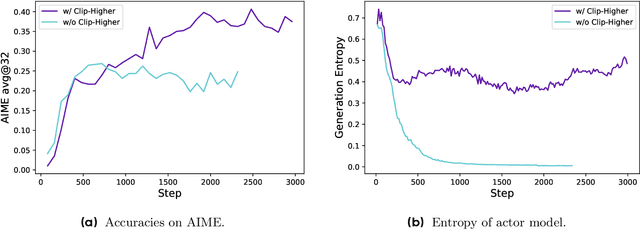

Abstract:Inference scaling empowers LLMs with unprecedented reasoning ability, with reinforcement learning as the core technique to elicit complex reasoning. However, key technical details of state-of-the-art reasoning LLMs are concealed (such as in OpenAI o1 blog and DeepSeek R1 technical report), thus the community still struggles to reproduce their RL training results. We propose the $\textbf{D}$ecoupled Clip and $\textbf{D}$ynamic s$\textbf{A}$mpling $\textbf{P}$olicy $\textbf{O}$ptimization ($\textbf{DAPO}$) algorithm, and fully open-source a state-of-the-art large-scale RL system that achieves 50 points on AIME 2024 using Qwen2.5-32B base model. Unlike previous works that withhold training details, we introduce four key techniques of our algorithm that make large-scale LLM RL a success. In addition, we open-source our training code, which is built on the verl framework, along with a carefully curated and processed dataset. These components of our open-source system enhance reproducibility and support future research in large-scale LLM RL.
EMMA-X: An EM-like Multilingual Pre-training Algorithm for Cross-lingual Representation Learning
Oct 26, 2023Abstract:Expressing universal semantics common to all languages is helpful in understanding the meanings of complex and culture-specific sentences. The research theme underlying this scenario focuses on learning universal representations across languages with the usage of massive parallel corpora. However, due to the sparsity and scarcity of parallel data, there is still a big challenge in learning authentic ``universals'' for any two languages. In this paper, we propose EMMA-X: an EM-like Multilingual pre-training Algorithm, to learn (X)Cross-lingual universals with the aid of excessive multilingual non-parallel data. EMMA-X unifies the cross-lingual representation learning task and an extra semantic relation prediction task within an EM framework. Both the extra semantic classifier and the cross-lingual sentence encoder approximate the semantic relation of two sentences, and supervise each other until convergence. To evaluate EMMA-X, we conduct experiments on XRETE, a newly introduced benchmark containing 12 widely studied cross-lingual tasks that fully depend on sentence-level representations. Results reveal that EMMA-X achieves state-of-the-art performance. Further geometric analysis of the built representation space with three requirements demonstrates the superiority of EMMA-X over advanced models.
PolyLM: An Open Source Polyglot Large Language Model
Jul 12, 2023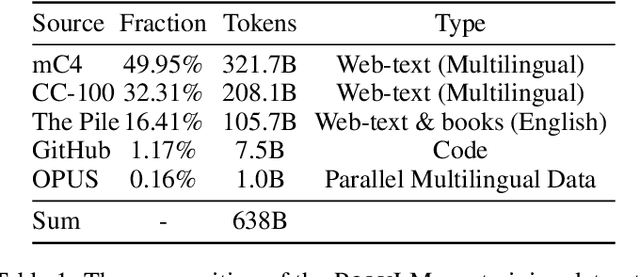
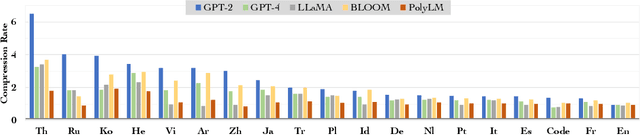
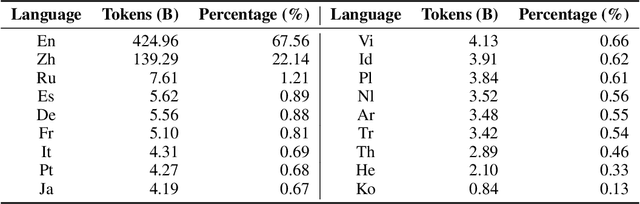
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate remarkable ability to comprehend, reason, and generate following nature language instructions. However, the development of LLMs has been primarily focused on high-resource languages, such as English, thereby limiting their applicability and research in other languages. Consequently, we present PolyLM, a multilingual LLM trained on 640 billion (B) tokens, avaliable in two model sizes: 1.7B and 13B. To enhance its multilingual capabilities, we 1) integrate bilingual data into training data; and 2) adopt a curriculum learning strategy that increases the proportion of non-English data from 30% in the first stage to 60% in the final stage during pre-training. Further, we propose a multilingual self-instruct method which automatically generates 132.7K diverse multilingual instructions for model fine-tuning. To assess the model's performance, we collect several existing multilingual tasks, including multilingual understanding, question answering, generation, and translation. Extensive experiments show that PolyLM surpasses other open-source models such as LLaMA and BLOOM on multilingual tasks while maintaining comparable performance in English. Our models, alone with the instruction data and multilingual benchmark, are available at: \url{https://modelscope.cn/models/damo/nlp_polylm_13b_text_generation}.
Bridging the Domain Gaps in Context Representations for k-Nearest Neighbor Neural Machine Translation
May 26, 2023



Abstract:$k$-Nearest neighbor machine translation ($k$NN-MT) has attracted increasing attention due to its ability to non-parametrically adapt to new translation domains. By using an upstream NMT model to traverse the downstream training corpus, it is equipped with a datastore containing vectorized key-value pairs, which are retrieved during inference to benefit translation. However, there often exists a significant gap between upstream and downstream domains, which hurts the retrieval accuracy and the final translation quality. To deal with this issue, we propose a novel approach to boost the datastore retrieval of $k$NN-MT by reconstructing the original datastore. Concretely, we design a reviser to revise the key representations, making them better fit for the downstream domain. The reviser is trained using the collected semantically-related key-queries pairs, and optimized by two proposed losses: one is the key-queries semantic distance ensuring each revised key representation is semantically related to its corresponding queries, and the other is an L2-norm loss encouraging revised key representations to effectively retain the knowledge learned by the upstream NMT model. Extensive experiments on domain adaptation tasks demonstrate that our method can effectively boost the datastore retrieval and translation quality of $k$NN-MT.\footnote{Our code is available at \url{https://github.com/DeepLearnXMU/RevisedKey-knn-mt}.}
From Statistical Methods to Deep Learning, Automatic Keyphrase Prediction: A Survey
May 04, 2023



Abstract:Keyphrase prediction aims to generate phrases (keyphrases) that highly summarizes a given document. Recently, researchers have conducted in-depth studies on this task from various perspectives. In this paper, we comprehensively summarize representative studies from the perspectives of dominant models, datasets and evaluation metrics. Our work analyzes up to 167 previous works, achieving greater coverage of this task than previous surveys. Particularly, we focus highly on deep learning-based keyphrase prediction, which attracts increasing attention of this task in recent years. Afterwards, we conduct several groups of experiments to carefully compare representative models. To the best of our knowledge, our work is the first attempt to compare these models using the identical commonly-used datasets and evaluation metric, facilitating in-depth analyses of their disadvantages and advantages. Finally, we discuss the possible research directions of this task in the future.
WR-ONE2SET: Towards Well-Calibrated Keyphrase Generation
Nov 13, 2022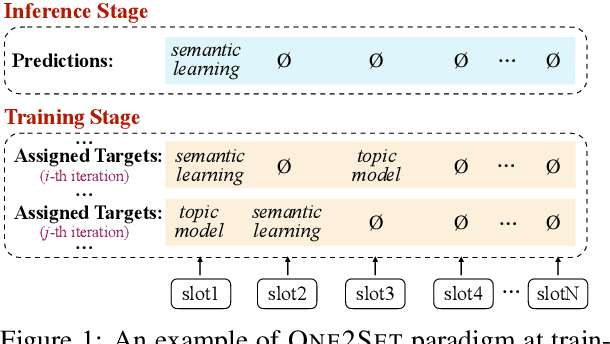
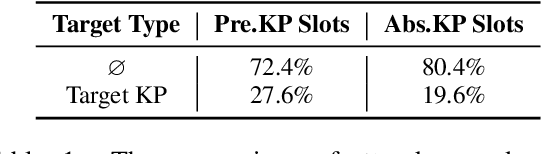
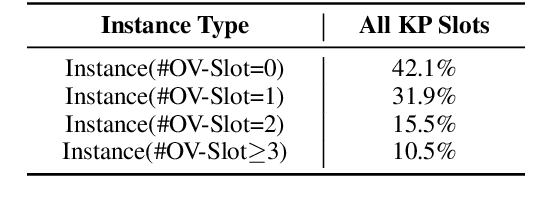
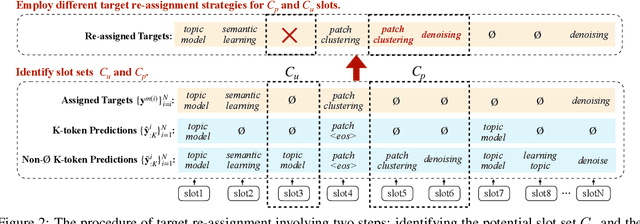
Abstract:Keyphrase generation aims to automatically generate short phrases summarizing an input document. The recently emerged ONE2SET paradigm (Ye et al., 2021) generates keyphrases as a set and has achieved competitive performance. Nevertheless, we observe serious calibration errors outputted by ONE2SET, especially in the over-estimation of $\varnothing$ token (means "no corresponding keyphrase"). In this paper, we deeply analyze this limitation and identify two main reasons behind: 1) the parallel generation has to introduce excessive $\varnothing$ as padding tokens into training instances; and 2) the training mechanism assigning target to each slot is unstable and further aggravates the $\varnothing$ token over-estimation. To make the model well-calibrated, we propose WR-ONE2SET which extends ONE2SET with an adaptive instance-level cost Weighting strategy and a target Re-assignment mechanism. The former dynamically penalizes the over-estimated slots for different instances thus smoothing the uneven training distribution. The latter refines the original inappropriate assignment and reduces the supervisory signals of over-estimated slots. Experimental results on commonly-used datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and generality of our proposed paradigm.
SUN: Exploring Intrinsic Uncertainties in Text-to-SQL Parsers
Sep 14, 2022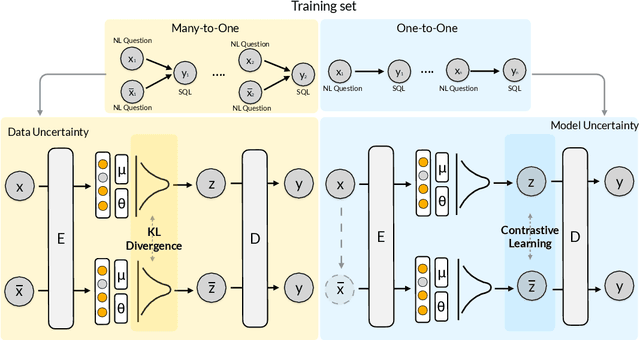
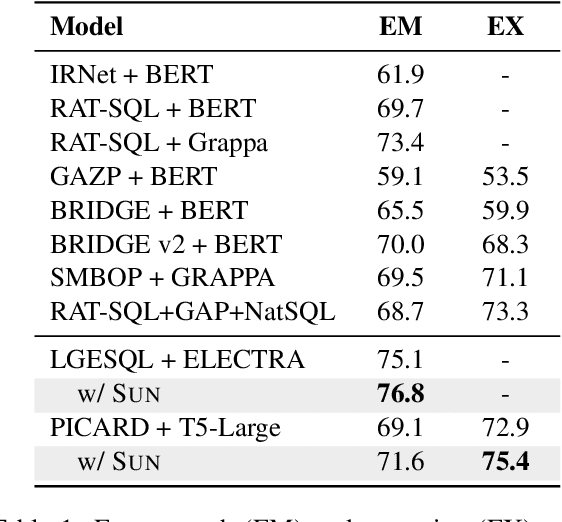
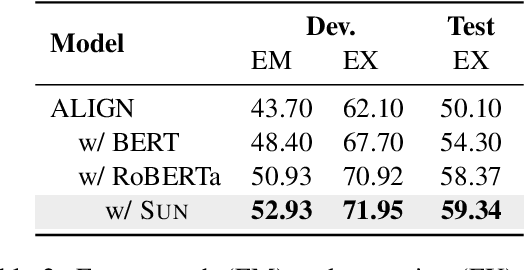
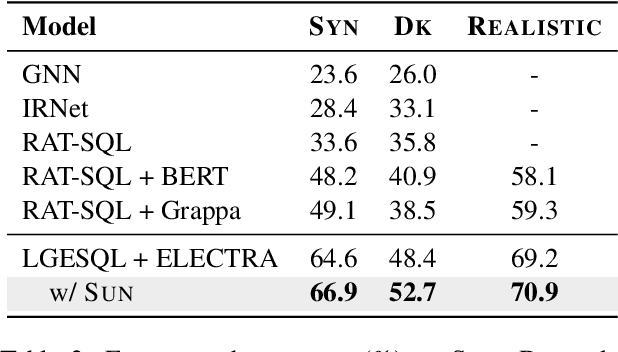
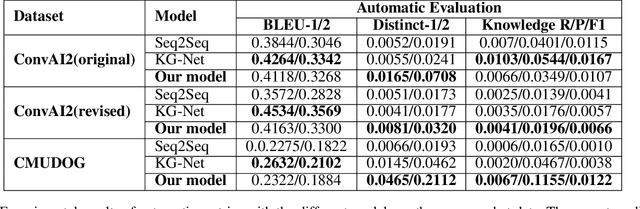
Abstract:This paper aims to improve the performance of text-to-SQL parsing by exploring the intrinsic uncertainties in the neural network based approaches (called SUN). From the data uncertainty perspective, it is indisputable that a single SQL can be learned from multiple semantically-equivalent questions.Different from previous methods that are limited to one-to-one mapping, we propose a data uncertainty constraint to explore the underlying complementary semantic information among multiple semantically-equivalent questions (many-to-one) and learn the robust feature representations with reduced spurious associations. In this way, we can reduce the sensitivity of the learned representations and improve the robustness of the parser. From the model uncertainty perspective, there is often structural information (dependence) among the weights of neural networks. To improve the generalizability and stability of neural text-to-SQL parsers, we propose a model uncertainty constraint to refine the query representations by enforcing the output representations of different perturbed encoding networks to be consistent with each other. Extensive experiments on five benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms strong competitors and achieves new state-of-the-art results. For reproducibility, we release our code and data at https://github.com/AlibabaResearch/DAMO-ConvAI/tree/main/sunsql.
Learning to Generalize to More: Continuous Semantic Augmentation for Neural Machine Translation
Apr 14, 2022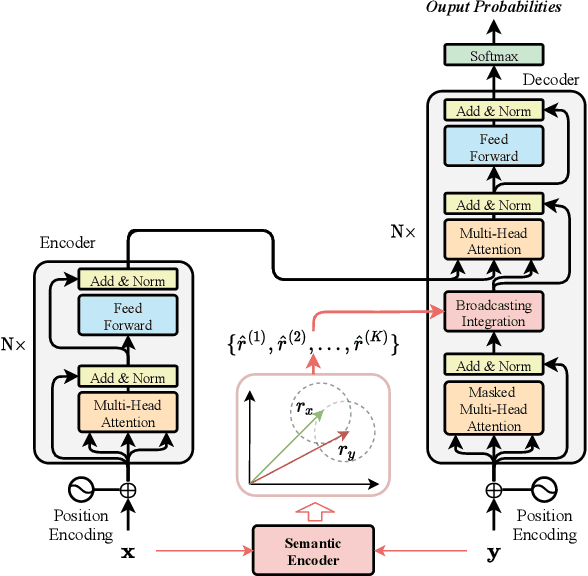
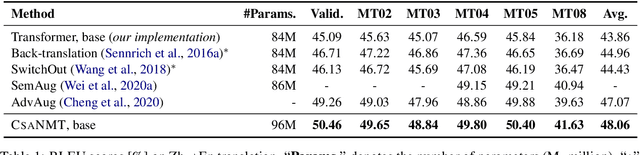
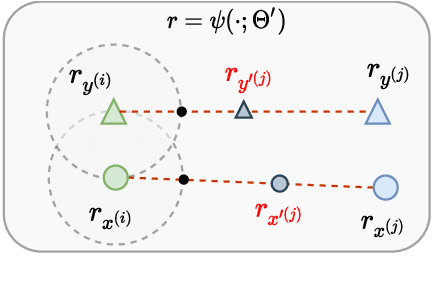
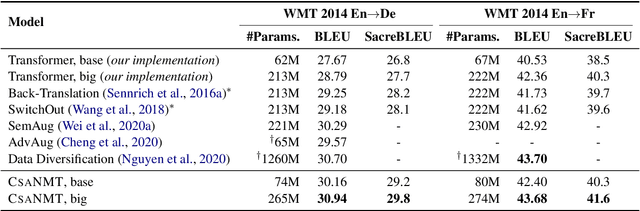
Abstract:The principal task in supervised neural machine translation (NMT) is to learn to generate target sentences conditioned on the source inputs from a set of parallel sentence pairs, and thus produce a model capable of generalizing to unseen instances. However, it is commonly observed that the generalization performance of the model is highly influenced by the amount of parallel data used in training. Although data augmentation is widely used to enrich the training data, conventional methods with discrete manipulations fail to generate diverse and faithful training samples. In this paper, we present a novel data augmentation paradigm termed Continuous Semantic Augmentation (CsaNMT), which augments each training instance with an adjacency semantic region that could cover adequate variants of literal expression under the same meaning. We conduct extensive experiments on both rich-resource and low-resource settings involving various language pairs, including WMT14 English-{German,French}, NIST Chinese-English and multiple low-resource IWSLT translation tasks. The provided empirical evidences show that CsaNMT sets a new level of performance among existing augmentation techniques, improving on the state-of-the-art by a large margin. The core codes are contained in Appendix E.
Know Deeper: Knowledge-Conversation Cyclic Utilization Mechanism for Open-domain Dialogue Generation
Jul 16, 2021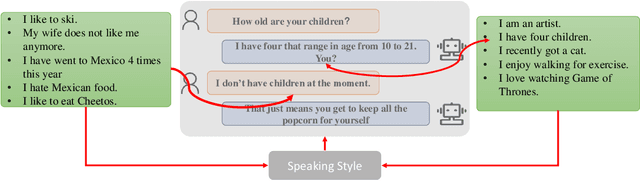
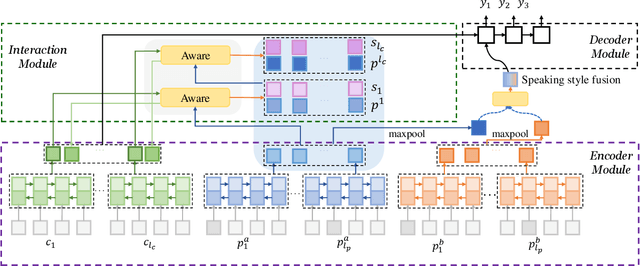
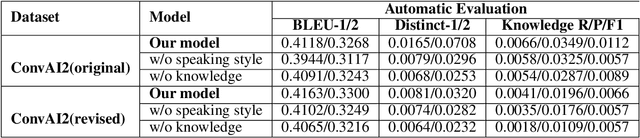
Abstract:End-to-End intelligent neural dialogue systems suffer from the problems of generating inconsistent and repetitive responses. Existing dialogue models pay attention to unilaterally incorporating personal knowledge into the dialog while ignoring the fact that incorporating the personality-related conversation information into personal knowledge taken as the bilateral information flow boosts the quality of the subsequent conversation. Besides, it is indispensable to control personal knowledge utilization over the conversation level. In this paper, we propose a conversation-adaption multi-view persona aware response generation model that aims at enhancing conversation consistency and alleviating the repetition from two folds. First, we consider conversation consistency from multiple views. From the view of the persona profile, we design a novel interaction module that not only iteratively incorporates personalized knowledge into each turn conversation but also captures the personality-related information from conversation to enhance personalized knowledge semantic representation. From the view of speaking style, we introduce the speaking style vector and feed it into the decoder to keep the speaking style consistency. To avoid conversation repetition, we devise a coverage mechanism to keep track of the activation of personal knowledge utilization. Experiments on both automatic and human evaluation verify the superiority of our model over previous models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge