Suhang Wu
Not All Languages are Equal: Insights into Multilingual Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Oct 29, 2024



Abstract:RALMs (Retrieval-Augmented Language Models) broaden their knowledge scope by incorporating external textual resources. However, the multilingual nature of global knowledge necessitates RALMs to handle diverse languages, a topic that has received limited research focus. In this work, we propose \textit{Futurepedia}, a carefully crafted benchmark containing parallel texts across eight representative languages. We evaluate six multilingual RALMs using our benchmark to explore the challenges of multilingual RALMs. Experimental results reveal linguistic inequalities: 1) high-resource languages stand out in Monolingual Knowledge Extraction; 2) Indo-European languages lead RALMs to provide answers directly from documents, alleviating the challenge of expressing answers across languages; 3) English benefits from RALMs' selection bias and speaks louder in multilingual knowledge selection. Based on these findings, we offer advice for improving multilingual Retrieval Augmented Generation. For monolingual knowledge extraction, careful attention must be paid to cascading errors from translating low-resource languages into high-resource ones. In cross-lingual knowledge transfer, encouraging RALMs to provide answers within documents in different languages can improve transfer performance. For multilingual knowledge selection, incorporating more non-English documents and repositioning English documents can help mitigate RALMs' selection bias. Through comprehensive experiments, we underscore the complexities inherent in multilingual RALMs and offer valuable insights for future research.
Towards Better Multi-modal Keyphrase Generation via Visual Entity Enhancement and Multi-granularity Image Noise Filtering
Sep 09, 2023
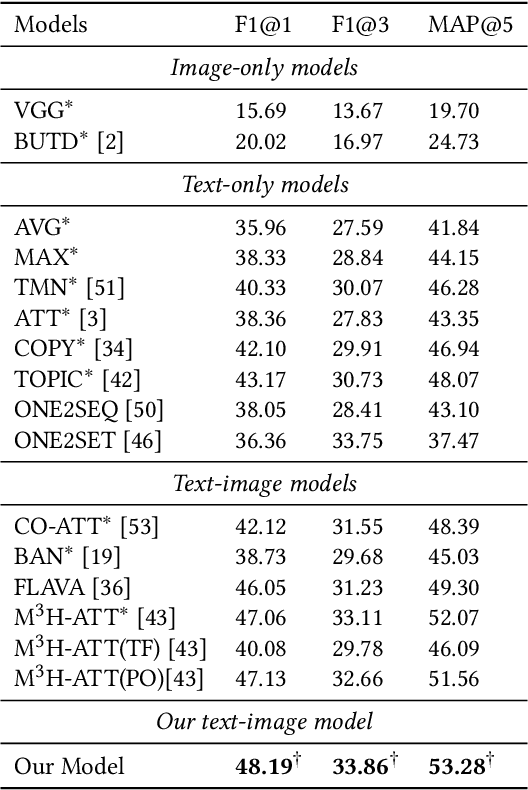
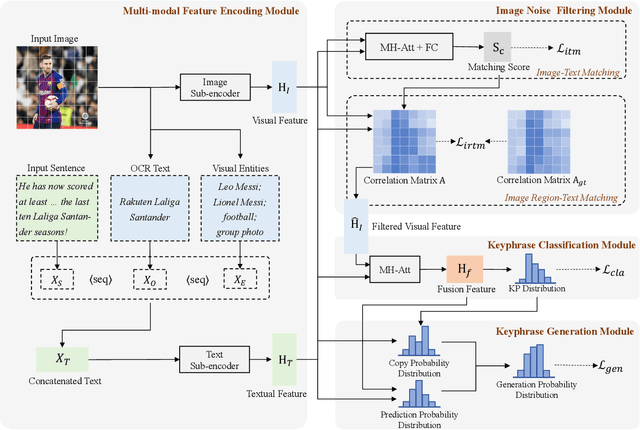
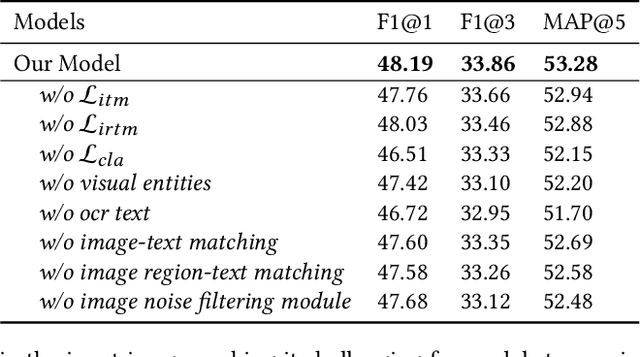
Abstract:Multi-modal keyphrase generation aims to produce a set of keyphrases that represent the core points of the input text-image pair. In this regard, dominant methods mainly focus on multi-modal fusion for keyphrase generation. Nevertheless, there are still two main drawbacks: 1) only a limited number of sources, such as image captions, can be utilized to provide auxiliary information. However, they may not be sufficient for the subsequent keyphrase generation. 2) the input text and image are often not perfectly matched, and thus the image may introduce noise into the model. To address these limitations, in this paper, we propose a novel multi-modal keyphrase generation model, which not only enriches the model input with external knowledge, but also effectively filters image noise. First, we introduce external visual entities of the image as the supplementary input to the model, which benefits the cross-modal semantic alignment for keyphrase generation. Second, we simultaneously calculate an image-text matching score and image region-text correlation scores to perform multi-granularity image noise filtering. Particularly, we introduce the correlation scores between image regions and ground-truth keyphrases to refine the calculation of the previously-mentioned correlation scores. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our model, we conduct several groups of experiments on the benchmark dataset. Experimental results and in-depth analyses show that our model achieves the state-of-the-art performance. Our code is available on https://github.com/DeepLearnXMU/MM-MKP.
Eva-KELLM: A New Benchmark for Evaluating Knowledge Editing of LLMs
Aug 19, 2023Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) possess a wealth of knowledge encoded in their parameters. However, this knowledge may become outdated or unsuitable over time. As a result, there has been a growing interest in knowledge editing for LLMs and evaluating its effectiveness. Existing studies primarily focus on knowledge editing using factual triplets, which not only incur high costs for collection but also struggle to express complex facts. Furthermore, these studies are often limited in their evaluation perspectives. In this paper, we propose Eva-KELLM, a new benchmark for evaluating knowledge editing of LLMs. This benchmark includes an evaluation framework and a corresponding dataset. Under our framework, we first ask the LLM to perform knowledge editing using raw documents, which provides a more convenient and universal approach compared to using factual triplets. We then evaluate the updated LLM from multiple perspectives. In addition to assessing the effectiveness of knowledge editing and the retention of unrelated knowledge from conventional studies, we further test the LLM's ability in two aspects: 1) Reasoning with the altered knowledge, aiming for the LLM to genuinely learn the altered knowledge instead of simply memorizing it. 2) Cross-lingual knowledge transfer, where the LLM updated with raw documents in one language should be capable of handling queries from another language. To facilitate further research, we construct and release the corresponding dataset. Using this benchmark, we investigate the effectiveness of several commonly-used knowledge editing methods. Experimental results indicate that the current methods for knowledge editing using raw documents are not effective in yielding satisfactory results, particularly when it comes to reasoning with altered knowledge and cross-lingual knowledge transfer.
A Simple yet Effective Self-Debiasing Framework for Transformer Models
Jun 02, 2023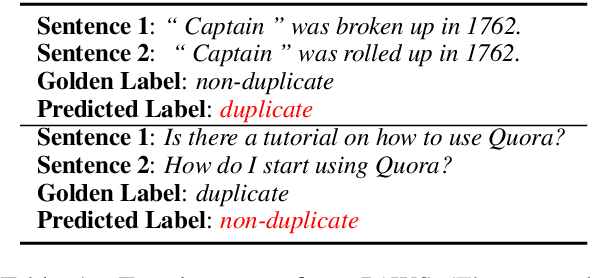
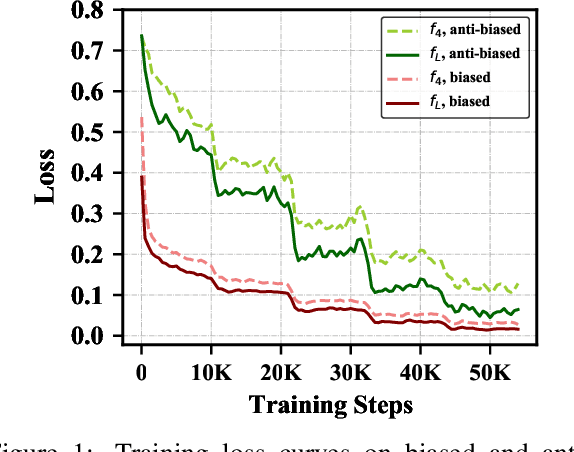
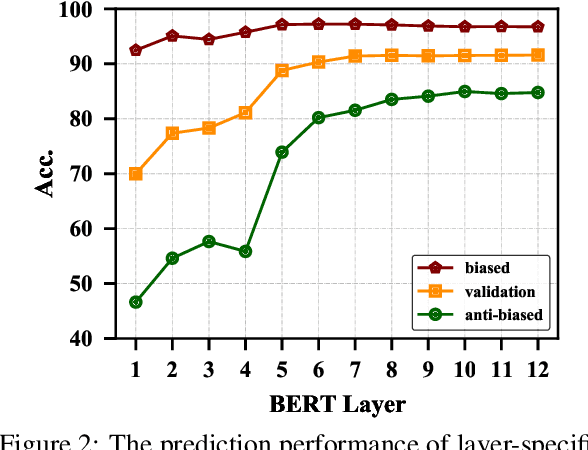

Abstract:Current Transformer-based natural language understanding (NLU) models heavily rely on dataset biases, while failing to handle real-world out-of-distribution (OOD) instances. Many methods have been proposed to deal with this issue, but they ignore the fact that the features learned in different layers of Transformer-based NLU models are different. In this paper, we first conduct preliminary studies to obtain two conclusions: 1) both low- and high-layer sentence representations encode common biased features during training; 2) the low-layer sentence representations encode fewer unbiased features than the highlayer ones. Based on these conclusions, we propose a simple yet effective self-debiasing framework for Transformer-based NLU models. Concretely, we first stack a classifier on a selected low layer. Then, we introduce a residual connection that feeds the low-layer sentence representation to the top-layer classifier. In this way, the top-layer sentence representation will be trained to ignore the common biased features encoded by the low-layer sentence representation and focus on task-relevant unbiased features. During inference, we remove the residual connection and directly use the top-layer sentence representation to make predictions. Extensive experiments and indepth analyses on NLU tasks show that our framework performs better than several competitive baselines, achieving a new SOTA on all OOD test sets.
Bridging the Domain Gaps in Context Representations for k-Nearest Neighbor Neural Machine Translation
May 26, 2023



Abstract:$k$-Nearest neighbor machine translation ($k$NN-MT) has attracted increasing attention due to its ability to non-parametrically adapt to new translation domains. By using an upstream NMT model to traverse the downstream training corpus, it is equipped with a datastore containing vectorized key-value pairs, which are retrieved during inference to benefit translation. However, there often exists a significant gap between upstream and downstream domains, which hurts the retrieval accuracy and the final translation quality. To deal with this issue, we propose a novel approach to boost the datastore retrieval of $k$NN-MT by reconstructing the original datastore. Concretely, we design a reviser to revise the key representations, making them better fit for the downstream domain. The reviser is trained using the collected semantically-related key-queries pairs, and optimized by two proposed losses: one is the key-queries semantic distance ensuring each revised key representation is semantically related to its corresponding queries, and the other is an L2-norm loss encouraging revised key representations to effectively retain the knowledge learned by the upstream NMT model. Extensive experiments on domain adaptation tasks demonstrate that our method can effectively boost the datastore retrieval and translation quality of $k$NN-MT.\footnote{Our code is available at \url{https://github.com/DeepLearnXMU/RevisedKey-knn-mt}.}
From Statistical Methods to Deep Learning, Automatic Keyphrase Prediction: A Survey
May 04, 2023



Abstract:Keyphrase prediction aims to generate phrases (keyphrases) that highly summarizes a given document. Recently, researchers have conducted in-depth studies on this task from various perspectives. In this paper, we comprehensively summarize representative studies from the perspectives of dominant models, datasets and evaluation metrics. Our work analyzes up to 167 previous works, achieving greater coverage of this task than previous surveys. Particularly, we focus highly on deep learning-based keyphrase prediction, which attracts increasing attention of this task in recent years. Afterwards, we conduct several groups of experiments to carefully compare representative models. To the best of our knowledge, our work is the first attempt to compare these models using the identical commonly-used datasets and evaluation metric, facilitating in-depth analyses of their disadvantages and advantages. Finally, we discuss the possible research directions of this task in the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge