Jiaze Chen
CUDA Agent: Large-Scale Agentic RL for High-Performance CUDA Kernel Generation
Feb 27, 2026Abstract:GPU kernel optimization is fundamental to modern deep learning but remains a highly specialized task requiring deep hardware expertise. Despite strong performance in general programming, large language models (LLMs) remain uncompetitive with compiler-based systems such as torch.compile for CUDA kernel generation. Existing CUDA code generation approaches either rely on training-free refinement or fine-tune models within fixed multi-turn execution-feedback loops, but both paradigms fail to fundamentally improve the model's intrinsic CUDA optimization ability, resulting in limited performance gains. We present CUDA Agent, a large-scale agentic reinforcement learning system that develops CUDA kernel expertise through three components: a scalable data synthesis pipeline, a skill-augmented CUDA development environment with automated verification and profiling to provide reliable reward signals, and reinforcement learning algorithmic techniques enabling stable training. CUDA Agent achieves state-of-the-art results on KernelBench, delivering 100\%, 100\%, and 92\% faster rate over torch.compile on KernelBench Level-1, Level-2, and Level-3 splits, outperforming the strongest proprietary models such as Claude Opus 4.5 and Gemini 3 Pro by about 40\% on the hardest Level-3 setting.
BABE: Biology Arena BEnchmark
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:The rapid evolution of large language models (LLMs) has expanded their capabilities from basic dialogue to advanced scientific reasoning. However, existing benchmarks in biology often fail to assess a critical skill required of researchers: the ability to integrate experimental results with contextual knowledge to derive meaningful conclusions. To address this gap, we introduce BABE(Biology Arena BEnchmark), a comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate the experimental reasoning capabilities of biological AI systems. BABE is uniquely constructed from peer-reviewed research papers and real-world biological studies, ensuring that tasks reflect the complexity and interdisciplinary nature of actual scientific inquiry. BABE challenges models to perform causal reasoning and cross-scale inference. Our benchmark provides a robust framework for assessing how well AI systems can reason like practicing scientists, offering a more authentic measure of their potential to contribute to biological research.
Truncated Proximal Policy Optimization
Jun 18, 2025



Abstract:Recently, test-time scaling Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated exceptional reasoning capabilities across scientific and professional tasks by generating long chains-of-thought (CoT). As a crucial component for developing these reasoning models, reinforcement learning (RL), exemplified by Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) and its variants, allows models to learn through trial and error. However, PPO can be time-consuming due to its inherent on-policy nature, which is further exacerbated by increasing response lengths. In this work, we propose Truncated Proximal Policy Optimization (T-PPO), a novel extension to PPO that improves training efficiency by streamlining policy update and length-restricted response generation. T-PPO mitigates the issue of low hardware utilization, an inherent drawback of fully synchronized long-generation procedures, where resources often sit idle during the waiting periods for complete rollouts. Our contributions are two-folds. First, we propose Extended Generalized Advantage Estimation (EGAE) for advantage estimation derived from incomplete responses while maintaining the integrity of policy learning. Second, we devise a computationally optimized mechanism that allows for the independent optimization of the policy and value models. By selectively filtering prompt and truncated tokens, this mechanism reduces redundant computations and accelerates the training process without sacrificing convergence performance. We demonstrate the effectiveness and efficacy of T-PPO on AIME 2024 with a 32B base model. The experimental results show that T-PPO improves the training efficiency of reasoning LLMs by up to 2.5x and outperforms its existing competitors.
Enigmata: Scaling Logical Reasoning in Large Language Models with Synthetic Verifiable Puzzles
May 26, 2025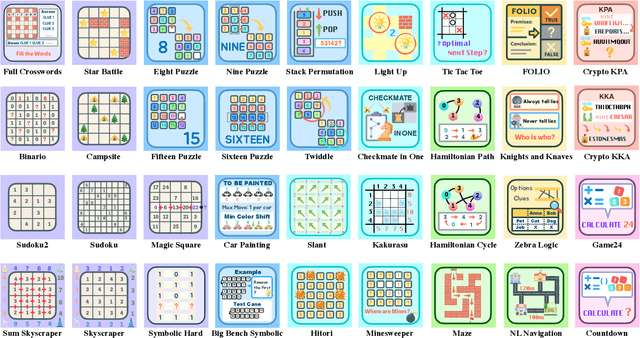
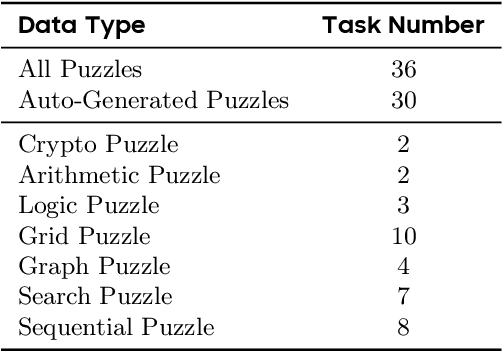
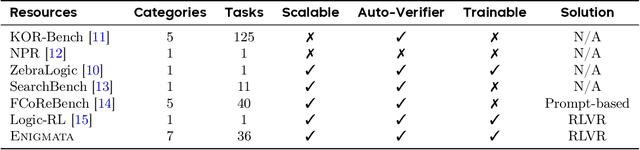
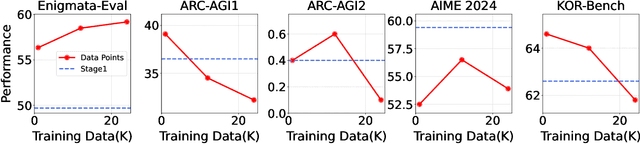
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs), such as OpenAI's o1 and DeepSeek's R1, excel at advanced reasoning tasks like math and coding via Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR), but still struggle with puzzles solvable by humans without domain knowledge. We introduce Enigmata, the first comprehensive suite tailored for improving LLMs with puzzle reasoning skills. It includes 36 tasks across seven categories, each with 1) a generator that produces unlimited examples with controllable difficulty and 2) a rule-based verifier for automatic evaluation. This generator-verifier design supports scalable, multi-task RL training, fine-grained analysis, and seamless RLVR integration. We further propose Enigmata-Eval, a rigorous benchmark, and develop optimized multi-task RLVR strategies. Our trained model, Qwen2.5-32B-Enigmata, consistently surpasses o3-mini-high and o1 on the puzzle reasoning benchmarks like Enigmata-Eval, ARC-AGI (32.8%), and ARC-AGI 2 (0.6%). It also generalizes well to out-of-domain puzzle benchmarks and mathematical reasoning, with little multi-tasking trade-off. When trained on larger models like Seed1.5-Thinking (20B activated parameters and 200B total parameters), puzzle data from Enigmata further boosts SoTA performance on advanced math and STEM reasoning tasks such as AIME (2024-2025), BeyondAIME and GPQA (Diamond), showing nice generalization benefits of Enigmata. This work offers a unified, controllable framework for advancing logical reasoning in LLMs. Resources of this work can be found at https://seed-enigmata.github.io.
Seed1.5-VL Technical Report
May 11, 2025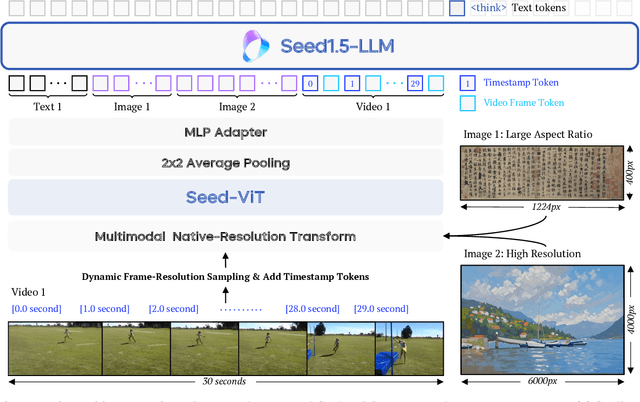

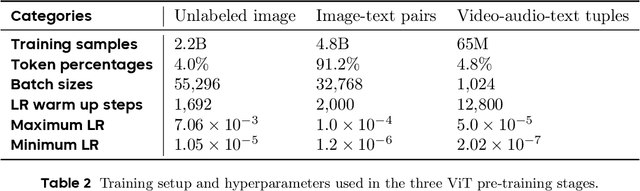
Abstract:We present Seed1.5-VL, a vision-language foundation model designed to advance general-purpose multimodal understanding and reasoning. Seed1.5-VL is composed with a 532M-parameter vision encoder and a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) LLM of 20B active parameters. Despite its relatively compact architecture, it delivers strong performance across a wide spectrum of public VLM benchmarks and internal evaluation suites, achieving the state-of-the-art performance on 38 out of 60 public benchmarks. Moreover, in agent-centric tasks such as GUI control and gameplay, Seed1.5-VL outperforms leading multimodal systems, including OpenAI CUA and Claude 3.7. Beyond visual and video understanding, it also demonstrates strong reasoning abilities, making it particularly effective for multimodal reasoning challenges such as visual puzzles. We believe these capabilities will empower broader applications across diverse tasks. In this report, we mainly provide a comprehensive review of our experiences in building Seed1.5-VL across model design, data construction, and training at various stages, hoping that this report can inspire further research. Seed1.5-VL is now accessible at https://www.volcengine.com/ (Volcano Engine Model ID: doubao-1-5-thinking-vision-pro-250428)
VAPO: Efficient and Reliable Reinforcement Learning for Advanced Reasoning Tasks
Apr 08, 2025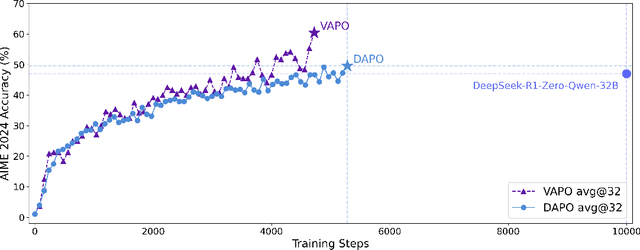
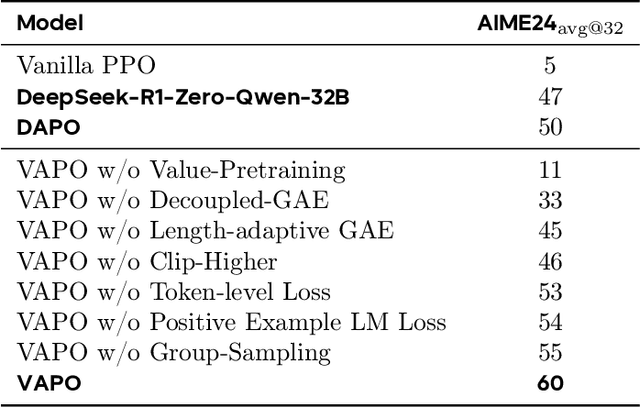
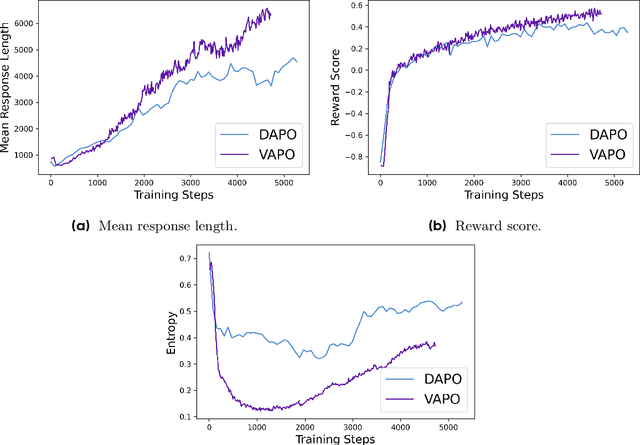
Abstract:We present VAPO, Value-based Augmented Proximal Policy Optimization framework for reasoning models., a novel framework tailored for reasoning models within the value-based paradigm. Benchmarked the AIME 2024 dataset, VAPO, built on the Qwen 32B pre-trained model, attains a state-of-the-art score of $\mathbf{60.4}$. In direct comparison under identical experimental settings, VAPO outperforms the previously reported results of DeepSeek-R1-Zero-Qwen-32B and DAPO by more than 10 points. The training process of VAPO stands out for its stability and efficiency. It reaches state-of-the-art performance within a mere 5,000 steps. Moreover, across multiple independent runs, no training crashes occur, underscoring its reliability. This research delves into long chain-of-thought (long-CoT) reasoning using a value-based reinforcement learning framework. We pinpoint three key challenges that plague value-based methods: value model bias, the presence of heterogeneous sequence lengths, and the sparsity of reward signals. Through systematic design, VAPO offers an integrated solution that effectively alleviates these challenges, enabling enhanced performance in long-CoT reasoning tasks.
DAPO: An Open-Source LLM Reinforcement Learning System at Scale
Mar 18, 2025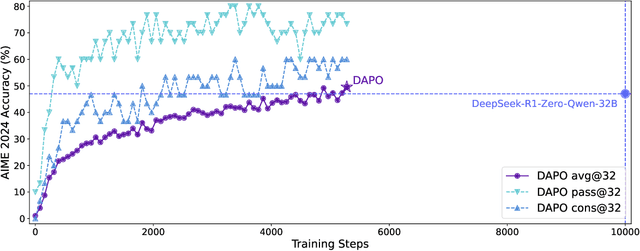
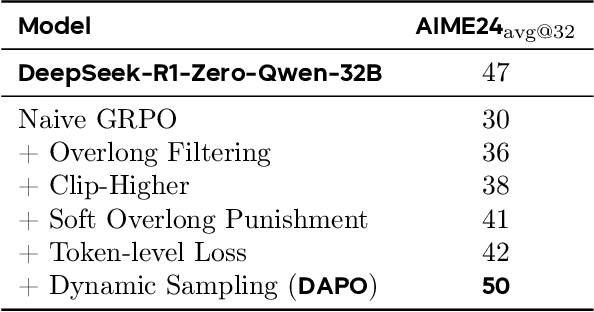
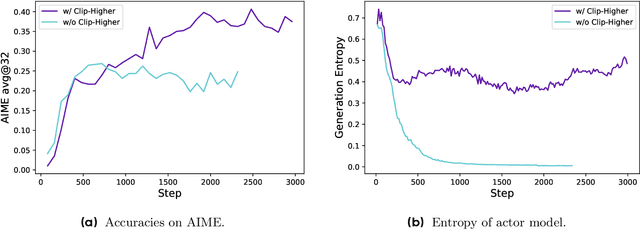

Abstract:Inference scaling empowers LLMs with unprecedented reasoning ability, with reinforcement learning as the core technique to elicit complex reasoning. However, key technical details of state-of-the-art reasoning LLMs are concealed (such as in OpenAI o1 blog and DeepSeek R1 technical report), thus the community still struggles to reproduce their RL training results. We propose the $\textbf{D}$ecoupled Clip and $\textbf{D}$ynamic s$\textbf{A}$mpling $\textbf{P}$olicy $\textbf{O}$ptimization ($\textbf{DAPO}$) algorithm, and fully open-source a state-of-the-art large-scale RL system that achieves 50 points on AIME 2024 using Qwen2.5-32B base model. Unlike previous works that withhold training details, we introduce four key techniques of our algorithm that make large-scale LLM RL a success. In addition, we open-source our training code, which is built on the verl framework, along with a carefully curated and processed dataset. These components of our open-source system enhance reproducibility and support future research in large-scale LLM RL.
Measuring Your ASTE Models in The Wild: A Diversified Multi-domain Dataset For Aspect Sentiment Triplet Extraction
May 27, 2023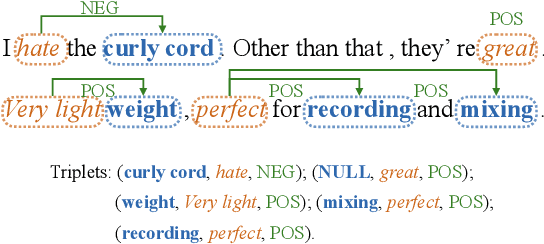
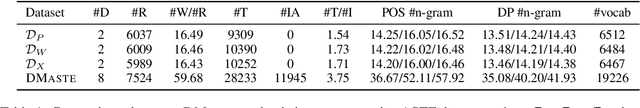
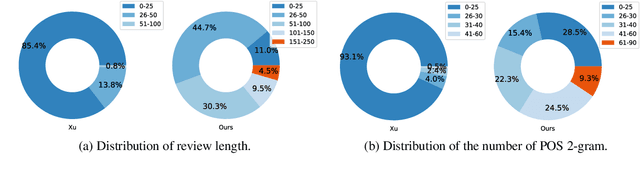
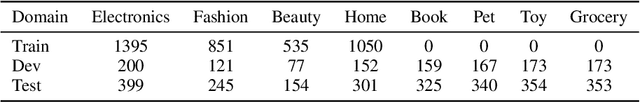
Abstract:Aspect Sentiment Triplet Extraction (ASTE) is widely used in various applications. However, existing ASTE datasets are limited in their ability to represent real-world scenarios, hindering the advancement of research in this area. In this paper, we introduce a new dataset, named DMASTE, which is manually annotated to better fit real-world scenarios by providing more diverse and realistic reviews for the task. The dataset includes various lengths, diverse expressions, more aspect types, and more domains than existing datasets. We conduct extensive experiments on DMASTE in multiple settings to evaluate previous ASTE approaches. Empirical results demonstrate that DMASTE is a more challenging ASTE dataset. Further analyses of in-domain and cross-domain settings provide promising directions for future research. Our code and dataset are available at https://github.com/NJUNLP/DMASTE.
CNewSum: A Large-scale Chinese News Summarization Dataset with Human-annotated Adequacy and Deducibility Level
Oct 21, 2021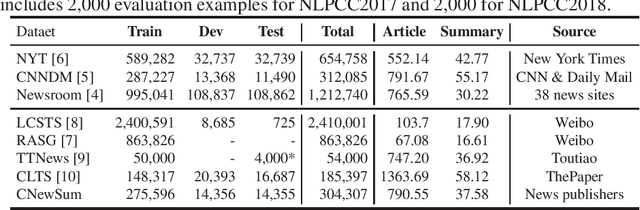
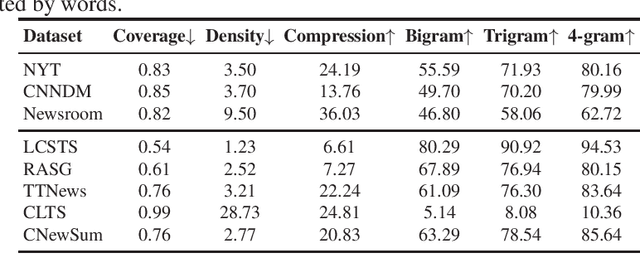
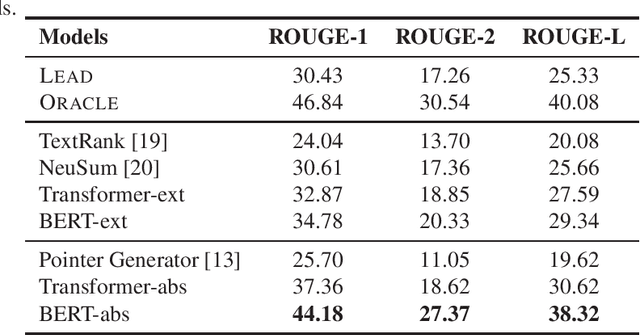
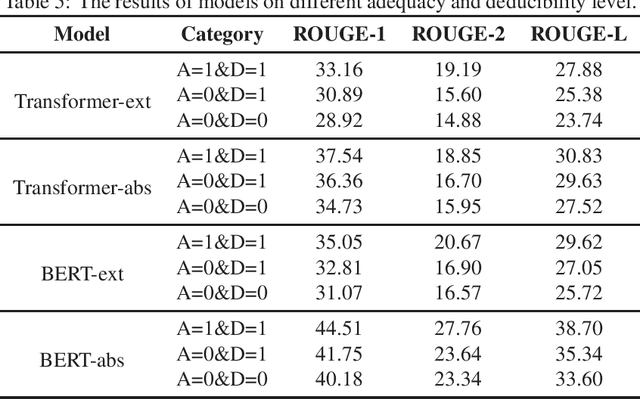
Abstract:Automatic text summarization aims to produce a brief but crucial summary for the input documents. Both extractive and abstractive methods have witnessed great success in English datasets in recent years. However, there has been a minimal exploration of text summarization in Chinese, limited by the lack of large-scale datasets. In this paper, we present a large-scale Chinese news summarization dataset CNewSum, which consists of 304,307 documents and human-written summaries for the news feed. It has long documents with high-abstractive summaries, which can encourage document-level understanding and generation for current summarization models. An additional distinguishing feature of CNewSum is that its test set contains adequacy and deducibility annotations for the summaries. The adequacy level measures the degree of summary information covered by the document, and the deducibility indicates the reasoning ability the model needs to generate the summary. These annotations can help researchers analyze and target their model performance bottleneck. We examine recent methods on CNewSum and release our dataset to provide a solid testbed for automatic Chinese summarization research.
MTG: A Benchmarking Suite for Multilingual Text Generation
Aug 13, 2021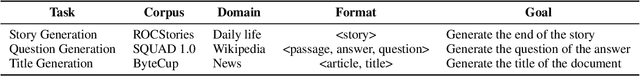

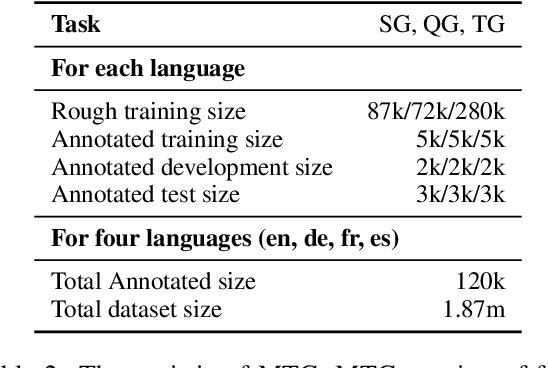
Abstract:We introduce MTG, a new benchmark suite for training and evaluating multilingual text generation. It is the first and largest text generation benchmark with 120k human-annotated multi-way parallel data for three tasks (story generation, question generation, and title generation) across four languages (English, German, French, and Spanish). Based on it, we set various evaluation scenarios and make a deep analysis of several popular multilingual generation models from different aspects. Our benchmark suite will encourage the multilingualism for text generation community with more human-annotated parallel data and more diverse generation scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge