Weinan Dai
MemAgent: Reshaping Long-Context LLM with Multi-Conv RL-based Memory Agent
Jul 03, 2025

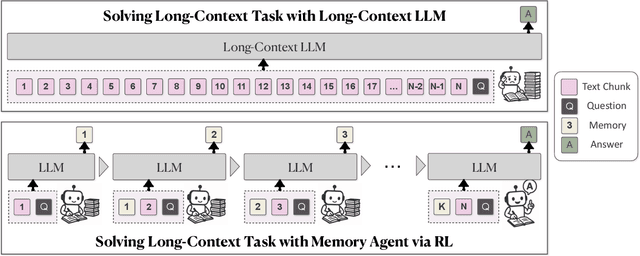
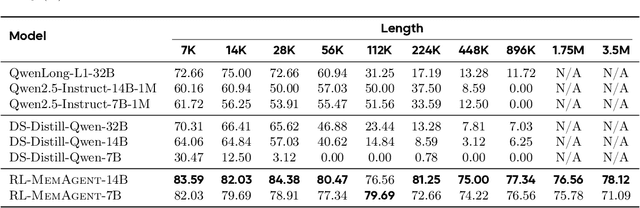
Abstract:Despite improvements by length extrapolation, efficient attention and memory modules, handling infinitely long documents with linear complexity without performance degradation during extrapolation remains the ultimate challenge in long-text processing. We directly optimize for long-text tasks in an end-to-end fashion and introduce a novel agent workflow, MemAgent, which reads text in segments and updates the memory using an overwrite strategy. We extend the DAPO algorithm to facilitate training via independent-context multi-conversation generation. MemAgent has demonstrated superb long-context capabilities, being able to extrapolate from an 8K context trained on 32K text to a 3.5M QA task with performance loss < 5% and achieves 95%+ in 512K RULER test.
Enigmata: Scaling Logical Reasoning in Large Language Models with Synthetic Verifiable Puzzles
May 26, 2025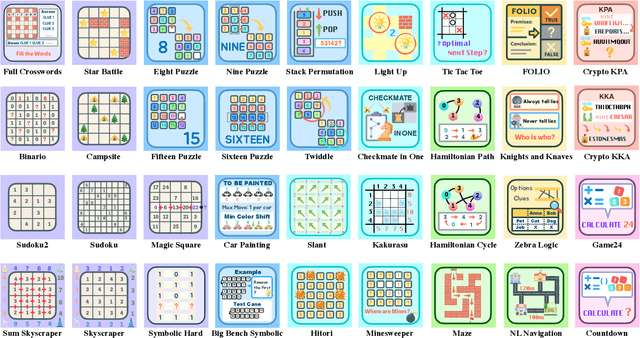
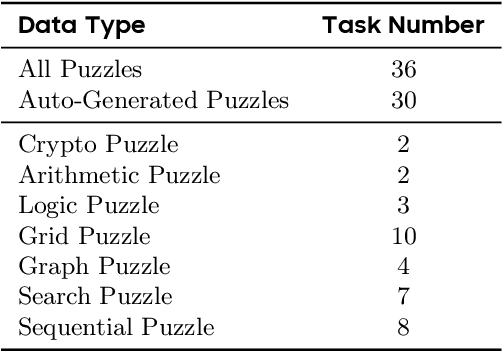
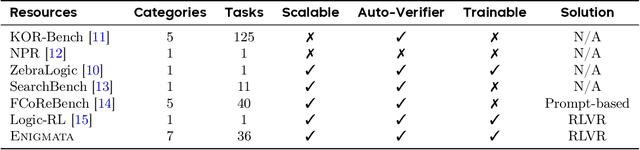
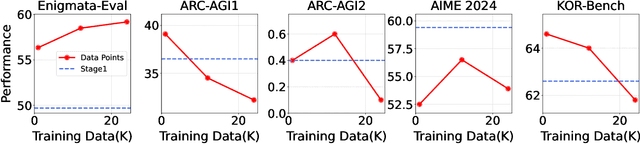
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs), such as OpenAI's o1 and DeepSeek's R1, excel at advanced reasoning tasks like math and coding via Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR), but still struggle with puzzles solvable by humans without domain knowledge. We introduce Enigmata, the first comprehensive suite tailored for improving LLMs with puzzle reasoning skills. It includes 36 tasks across seven categories, each with 1) a generator that produces unlimited examples with controllable difficulty and 2) a rule-based verifier for automatic evaluation. This generator-verifier design supports scalable, multi-task RL training, fine-grained analysis, and seamless RLVR integration. We further propose Enigmata-Eval, a rigorous benchmark, and develop optimized multi-task RLVR strategies. Our trained model, Qwen2.5-32B-Enigmata, consistently surpasses o3-mini-high and o1 on the puzzle reasoning benchmarks like Enigmata-Eval, ARC-AGI (32.8%), and ARC-AGI 2 (0.6%). It also generalizes well to out-of-domain puzzle benchmarks and mathematical reasoning, with little multi-tasking trade-off. When trained on larger models like Seed1.5-Thinking (20B activated parameters and 200B total parameters), puzzle data from Enigmata further boosts SoTA performance on advanced math and STEM reasoning tasks such as AIME (2024-2025), BeyondAIME and GPQA (Diamond), showing nice generalization benefits of Enigmata. This work offers a unified, controllable framework for advancing logical reasoning in LLMs. Resources of this work can be found at https://seed-enigmata.github.io.
DAPO: An Open-Source LLM Reinforcement Learning System at Scale
Mar 18, 2025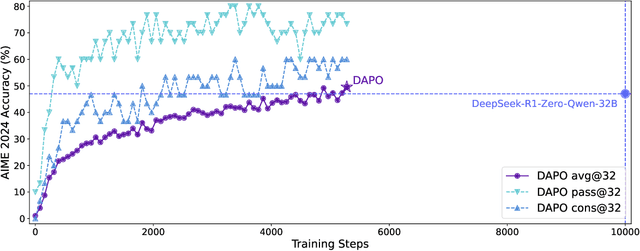
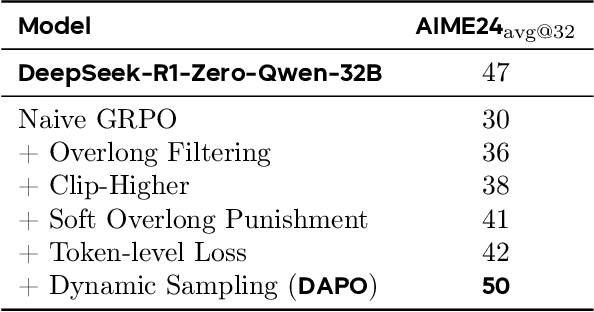
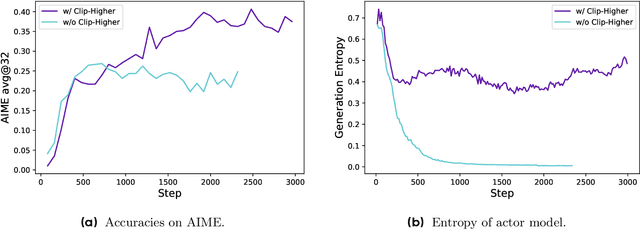

Abstract:Inference scaling empowers LLMs with unprecedented reasoning ability, with reinforcement learning as the core technique to elicit complex reasoning. However, key technical details of state-of-the-art reasoning LLMs are concealed (such as in OpenAI o1 blog and DeepSeek R1 technical report), thus the community still struggles to reproduce their RL training results. We propose the $\textbf{D}$ecoupled Clip and $\textbf{D}$ynamic s$\textbf{A}$mpling $\textbf{P}$olicy $\textbf{O}$ptimization ($\textbf{DAPO}$) algorithm, and fully open-source a state-of-the-art large-scale RL system that achieves 50 points on AIME 2024 using Qwen2.5-32B base model. Unlike previous works that withhold training details, we introduce four key techniques of our algorithm that make large-scale LLM RL a success. In addition, we open-source our training code, which is built on the verl framework, along with a carefully curated and processed dataset. These components of our open-source system enhance reproducibility and support future research in large-scale LLM RL.
Contrastive Augmentation: An Unsupervised Learning Approach for Keyword Spotting in Speech Technology
Aug 31, 2024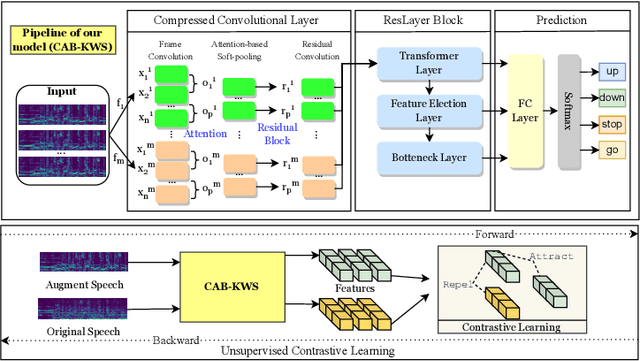


Abstract:This paper addresses the persistent challenge in Keyword Spotting (KWS), a fundamental component in speech technology, regarding the acquisition of substantial labeled data for training. Given the difficulty in obtaining large quantities of positive samples and the laborious process of collecting new target samples when the keyword changes, we introduce a novel approach combining unsupervised contrastive learning and a unique augmentation-based technique. Our method allows the neural network to train on unlabeled data sets, potentially improving performance in downstream tasks with limited labeled data sets. We also propose that similar high-level feature representations should be employed for speech utterances with the same keyword despite variations in speed or volume. To achieve this, we present a speech augmentation-based unsupervised learning method that utilizes the similarity between the bottleneck layer feature and the audio reconstructing information for auxiliary training. Furthermore, we propose a compressed convolutional architecture to address potential redundancy and non-informative information in KWS tasks, enabling the model to simultaneously learn local features and focus on long-term information. This method achieves strong performance on the Google Speech Commands V2 Dataset. Inspired by recent advancements in sign spotting and spoken term detection, our method underlines the potential of our contrastive learning approach in KWS and the advantages of Query-by-Example Spoken Term Detection strategies. The presented CAB-KWS provide new perspectives in the field of KWS, demonstrating effective ways to reduce data collection efforts and increase the system's robustness.
A quantitative fusion strategy of stock picking and timing based on Particle Swarm Optimized-Back Propagation Neural Network and Multivariate Gaussian-Hidden Markov Model
Dec 22, 2023Abstract:In recent years, machine learning (ML) has brought effective approaches and novel techniques to economic decision, investment forecasting, and risk management, etc., coping the variable and intricate nature of economic and financial environments. For the investment in stock market, this research introduces a pioneering quantitative fusion model combining stock timing and picking strategy by leveraging the Multivariate Gaussian-Hidden Markov Model (MGHMM) and Back Propagation Neural Network optimized by Particle Swarm (PSO-BPNN). After the information coefficients (IC) between fifty-two factors that have been winsorized, neutralized and standardized and the return of CSI 300 index are calculated, a given amount of factors that rank ahead are choose to be candidate factors heading for the input of PSO-BPNN after dimension reduction by Principal Component Analysis (PCA), followed by a certain amount of constituent stocks outputted. Subsequently, we conduct the prediction and trading on the basis of the screening stocks and stock market state outputted by MGHMM trained using inputting CSI 300 index data after Box-Cox transformation, bespeaking eximious performance during the period of past four years. Ultimately, some conventional forecast and trading methods are compared with our strategy in Chinese stock market. Our fusion strategy incorporating stock picking and timing presented in this article provide a innovative technique for financial analysis.
An Integrative Paradigm for Enhanced Stroke Prediction: Synergizing XGBoost and xDeepFM Algorithms
Oct 25, 2023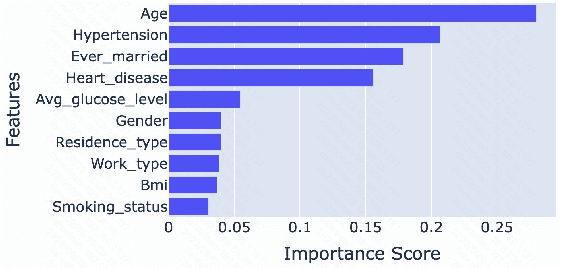
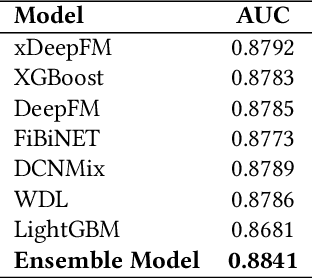
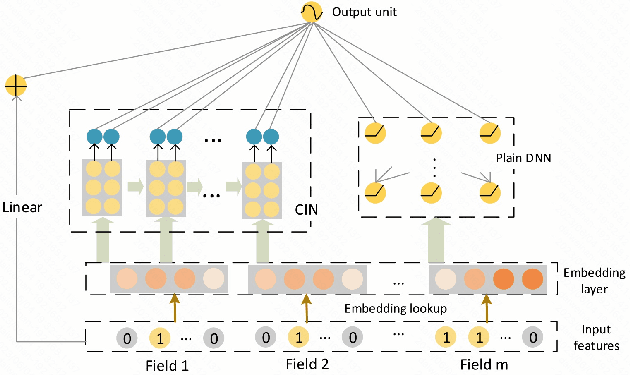
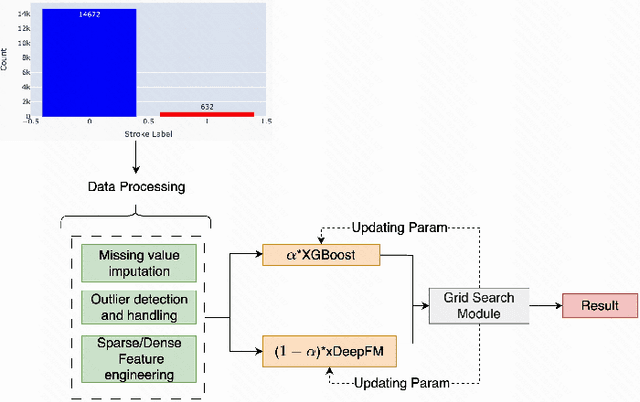
Abstract:Stroke prediction plays a crucial role in preventing and managing this debilitating condition. In this study, we address the challenge of stroke prediction using a comprehensive dataset, and propose an ensemble model that combines the power of XGBoost and xDeepFM algorithms. Our work aims to improve upon existing stroke prediction models by achieving higher accuracy and robustness. Through rigorous experimentation, we validate the effectiveness of our ensemble model using the AUC metric. Through comparing our findings with those of other models in the field, we gain valuable insights into the merits and drawbacks of various approaches. This, in turn, contributes significantly to the progress of machine learning and deep learning techniques specifically in the domain of stroke prediction.
MedLens: Improve mortality prediction via medical signs selecting and regression interpolation
May 19, 2023Abstract:Monitoring the health status of patients and predicting mortality in advance is vital for providing patients with timely care and treatment. Massive medical signs in electronic health records (EHR) are fitted into advanced machine learning models to make predictions. However, the data-quality problem of original clinical signs is less discussed in the literature. Based on an in-depth measurement of the missing rate and correlation score across various medical signs and a large amount of patient hospital admission records, we discovered the comprehensive missing rate is extremely high, and a large number of useless signs could hurt the performance of prediction models. Then we concluded that only improving data-quality could improve the baseline accuracy of different prediction algorithms. We designed MEDLENS, with an automatic vital medical signs selection approach via statistics and a flexible interpolation approach for high missing rate time series. After augmenting the data-quality of original medical signs, MEDLENS applies ensemble classifiers to boost the accuracy and reduce the computation overhead at the same time. It achieves a very high accuracy performance of 0.96% AUC-ROC and 0.81% AUC-PR, which exceeds the previous benchmark.
FineEHR: Refine Clinical Note Representations to Improve Mortality Prediction
May 04, 2023Abstract:Monitoring the health status of patients in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) is a critical aspect of providing superior care and treatment. The availability of large-scale electronic health records (EHR) provides machine learning models with an abundance of clinical text and vital sign data, enabling them to make highly accurate predictions. Despite the emergence of advanced Natural Language Processing (NLP) algorithms for clinical note analysis, the complex textual structure and noise present in raw clinical data have posed significant challenges. Coarse embedding approaches without domain-specific refinement have limited the accuracy of these algorithms. To address this issue, we propose FINEEHR, a system that utilizes two representation learning techniques, namely metric learning and fine-tuning, to refine clinical note embeddings, while leveraging the intrinsic correlations among different health statuses and note categories. We evaluate the performance of FINEEHR using two metrics, namely Area Under the Curve (AUC) and AUC-PR, on a real-world MIMIC III dataset. Our experimental results demonstrate that both refinement approaches improve prediction accuracy, and their combination yields the best results. Moreover, our proposed method outperforms prior works, with an AUC improvement of over 10%, achieving an average AUC of 96.04% and an average AUC-PR of 96.48% across various classifiers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge