Feida Zhu
Seed1.5-VL Technical Report
May 11, 2025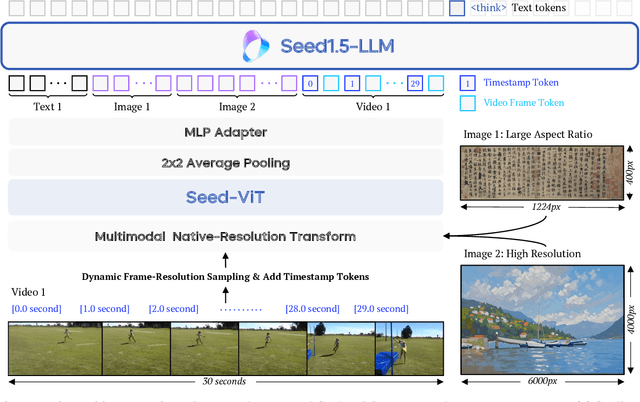

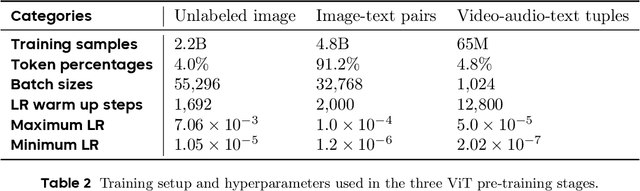
Abstract:We present Seed1.5-VL, a vision-language foundation model designed to advance general-purpose multimodal understanding and reasoning. Seed1.5-VL is composed with a 532M-parameter vision encoder and a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) LLM of 20B active parameters. Despite its relatively compact architecture, it delivers strong performance across a wide spectrum of public VLM benchmarks and internal evaluation suites, achieving the state-of-the-art performance on 38 out of 60 public benchmarks. Moreover, in agent-centric tasks such as GUI control and gameplay, Seed1.5-VL outperforms leading multimodal systems, including OpenAI CUA and Claude 3.7. Beyond visual and video understanding, it also demonstrates strong reasoning abilities, making it particularly effective for multimodal reasoning challenges such as visual puzzles. We believe these capabilities will empower broader applications across diverse tasks. In this report, we mainly provide a comprehensive review of our experiences in building Seed1.5-VL across model design, data construction, and training at various stages, hoping that this report can inspire further research. Seed1.5-VL is now accessible at https://www.volcengine.com/ (Volcano Engine Model ID: doubao-1-5-thinking-vision-pro-250428)
Enhanced Sample Selection with Confidence Tracking: Identifying Correctly Labeled yet Hard-to-Learn Samples in Noisy Data
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:We propose a novel sample selection method for image classification in the presence of noisy labels. Existing methods typically consider small-loss samples as correctly labeled. However, some correctly labeled samples are inherently difficult for the model to learn and can exhibit high loss similar to mislabeled samples in the early stages of training. Consequently, setting a threshold on per-sample loss to select correct labels results in a trade-off between precision and recall in sample selection: a lower threshold may miss many correctly labeled hard-to-learn samples (low recall), while a higher threshold may include many mislabeled samples (low precision). To address this issue, our goal is to accurately distinguish correctly labeled yet hard-to-learn samples from mislabeled ones, thus alleviating the trade-off dilemma. We achieve this by considering the trends in model prediction confidence rather than relying solely on loss values. Empirical observations show that only for correctly labeled samples, the model's prediction confidence for the annotated labels typically increases faster than for any other classes. Based on this insight, we propose tracking the confidence gaps between the annotated labels and other classes during training and evaluating their trends using the Mann-Kendall Test. A sample is considered potentially correctly labeled if all its confidence gaps tend to increase. Our method functions as a plug-and-play component that can be seamlessly integrated into existing sample selection techniques. Experiments on several standard benchmarks and real-world datasets demonstrate that our method enhances the performance of existing methods for learning with noisy labels.
New Recipe for Semi-supervised Community Detection: Clique Annealing under Crystallization Kinetics
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:Semi-supervised community detection methods are widely used for identifying specific communities due to the label scarcity. Existing semi-supervised community detection methods typically involve two learning stages learning in both initial identification and subsequent adjustment, which often starts from an unreasonable community core candidate. Moreover, these methods encounter scalability issues because they depend on reinforcement learning and generative adversarial networks, leading to higher computational costs and restricting the selection of candidates. To address these limitations, we draw a parallel between crystallization kinetics and community detection to integrate the spontaneity of the annealing process into community detection. Specifically, we liken community detection to identifying a crystal subgrain (core) that expands into a complete grain (community) through a process similar to annealing. Based on this finding, we propose CLique ANNealing (CLANN), which applies kinetics concepts to community detection by integrating these principles into the optimization process to strengthen the consistency of the community core. Subsequently, a learning-free Transitive Annealer was employed to refine the first-stage candidates by merging neighboring cliques and repositioning the community core, enabling a spontaneous growth process that enhances scalability. Extensive experiments on \textbf{43} different network settings demonstrate that CLANN outperforms state-of-the-art methods across multiple real-world datasets, showcasing its exceptional efficacy and efficiency in community detection.
Data Assetization via Resources-decoupled Federated Learning
Jan 24, 2025Abstract:With the development of the digital economy, data is increasingly recognized as an essential resource for both work and life. However, due to privacy concerns, data owners tend to maximize the value of data through information flow rather than direct data transfer. Federated learning (FL) provides an effective approach to collaborative training models while preserving privacy. However, different data owners not only have variations in the quantity and quality of their data resources but also face mismatches between data and computing resources as model parameters and training data grow. These challenges hinder data owners' willingness to participate and reduce the effectiveness of data assetization. In this work, we first identify the resource-decoupled FL environment, which includes model owners, data owners, and computing centers. We design a Tripartite Stackelberg Model and theoretically analyze the Stackelberg-Nash Equilibrium (SNE) for participants to optimize global utility. We propose the Quality-aware Dynamic Resources-decoupled FL algorithm (QD-RDFL), in which we derive and solve the optimal strategies of all parties to achieve SHE using backward induction, and a dynamic optimization mechanism is designed to improve the optimal strategy profile by evaluating the contribution of data quality from data owners to the global model during real training. Our comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our method effectively encourages the linkage of the three parties involved, maximizing global utility and data asset value.
Proof-of-Data: A Consensus Protocol for Collaborative Intelligence
Jan 06, 2025



Abstract:Existing research on federated learning has been focused on the setting where learning is coordinated by a centralized entity. Yet the greatest potential of future collaborative intelligence would be unleashed in a more open and democratized setting with no central entity in a dominant role, referred to as "decentralized federated learning". New challenges arise accordingly in achieving both correct model training and fair reward allocation with collective effort among all participating nodes, especially with the threat of the Byzantine node jeopardising both tasks. In this paper, we propose a blockchain-based decentralized Byzantine fault-tolerant federated learning framework based on a novel Proof-of-Data (PoD) consensus protocol to resolve both the "trust" and "incentive" components. By decoupling model training and contribution accounting, PoD is able to enjoy not only the benefit of learning efficiency and system liveliness from asynchronous societal-scale PoW-style learning but also the finality of consensus and reward allocation from epoch-based BFT-style voting. To mitigate false reward claims by data forgery from Byzantine attacks, a privacy-aware data verification and contribution-based reward allocation mechanism is designed to complete the framework. Our evaluation results show that PoD demonstrates performance in model training close to that of the centralized counterpart while achieving trust in consensus and fairness for reward allocation with a fault tolerance ratio of 1/3.
Knowledge Enhanced Multi-intent Transformer Network for Recommendation
May 31, 2024
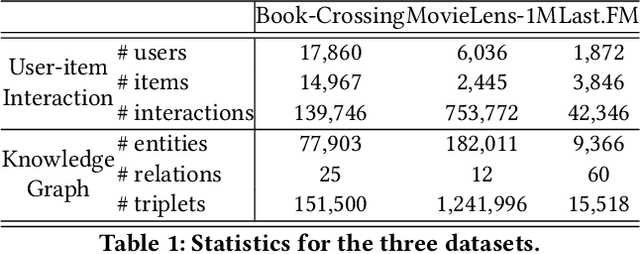
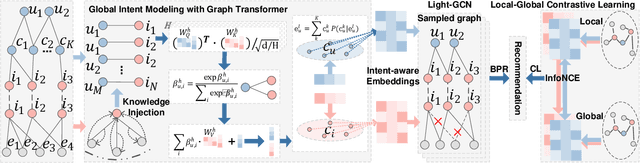
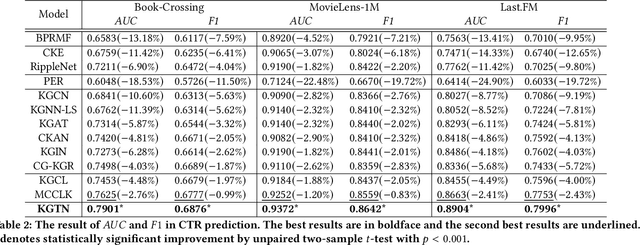
Abstract:Incorporating Knowledge Graphs into Recommendation has attracted growing attention in industry, due to the great potential of KG in providing abundant supplementary information and interpretability for the underlying models. However, simply integrating KG into recommendation usually brings in negative feedback in industry, due to the ignorance of the following two factors: i) users' multiple intents, which involve diverse nodes in KG. For example, in e-commerce scenarios, users may exhibit preferences for specific styles, brands, or colors. ii) knowledge noise, which is a prevalent issue in Knowledge Enhanced Recommendation (KGR) and even more severe in industry scenarios. The irrelevant knowledge properties of items may result in inferior model performance compared to approaches that do not incorporate knowledge. To tackle these challenges, we propose a novel approach named Knowledge Enhanced Multi-intent Transformer Network for Recommendation (KGTN), comprising two primary modules: Global Intents Modeling with Graph Transformer, and Knowledge Contrastive Denoising under Intents. Specifically, Global Intents with Graph Transformer focuses on capturing learnable user intents, by incorporating global signals from user-item-relation-entity interactions with a graph transformer, meanwhile learning intent-aware user/item representations. Knowledge Contrastive Denoising under Intents is dedicated to learning precise and robust representations. It leverages intent-aware representations to sample relevant knowledge, and proposes a local-global contrastive mechanism to enhance noise-irrelevant representation learning. Extensive experiments conducted on benchmark datasets show the superior performance of our proposed method over the state-of-the-arts. And online A/B testing results on Alibaba large-scale industrial recommendation platform also indicate the real-scenario effectiveness of KGTN.
WarpDiffusion: Efficient Diffusion Model for High-Fidelity Virtual Try-on
Dec 06, 2023



Abstract:Image-based Virtual Try-On (VITON) aims to transfer an in-shop garment image onto a target person. While existing methods focus on warping the garment to fit the body pose, they often overlook the synthesis quality around the garment-skin boundary and realistic effects like wrinkles and shadows on the warped garments. These limitations greatly reduce the realism of the generated results and hinder the practical application of VITON techniques. Leveraging the notable success of diffusion-based models in cross-modal image synthesis, some recent diffusion-based methods have ventured to tackle this issue. However, they tend to either consume a significant amount of training resources or struggle to achieve realistic try-on effects and retain garment details. For efficient and high-fidelity VITON, we propose WarpDiffusion, which bridges the warping-based and diffusion-based paradigms via a novel informative and local garment feature attention mechanism. Specifically, WarpDiffusion incorporates local texture attention to reduce resource consumption and uses a novel auto-mask module that effectively retains only the critical areas of the warped garment while disregarding unrealistic or erroneous portions. Notably, WarpDiffusion can be integrated as a plug-and-play component into existing VITON methodologies, elevating their synthesis quality. Extensive experiments on high-resolution VITON benchmarks and an in-the-wild test set demonstrate the superiority of WarpDiffusion, surpassing state-of-the-art methods both qualitatively and quantitatively.
From Asset Flow to Status, Action and Intention Discovery: Early Malice Detection in Cryptocurrency
Sep 26, 2023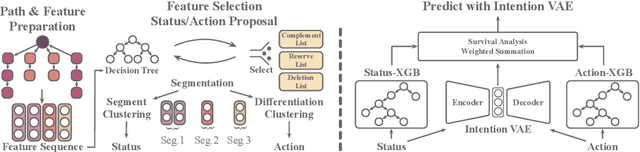
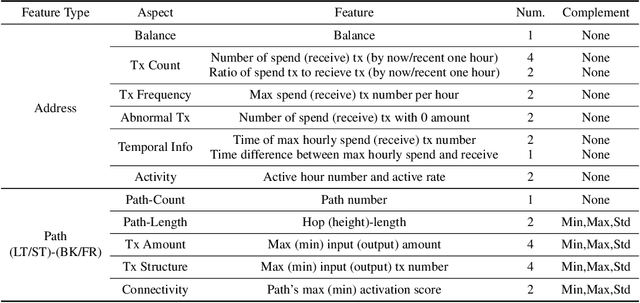
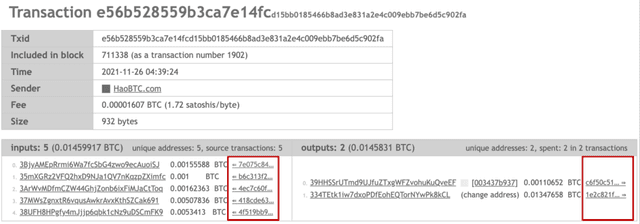
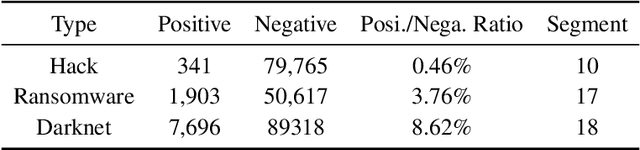
Abstract:Cryptocurrency has been subject to illicit activities probably more often than traditional financial assets due to the pseudo-anonymous nature of its transacting entities. An ideal detection model is expected to achieve all three critical properties of (I) early detection, (II) good interpretability, and (III) versatility for various illicit activities. However, existing solutions cannot meet all these requirements, as most of them heavily rely on deep learning without interpretability and are only available for retrospective analysis of a specific illicit type. To tackle all these challenges, we propose Intention-Monitor for early malice detection in Bitcoin (BTC), where the on-chain record data for a certain address are much scarcer than other cryptocurrency platforms. We first define asset transfer paths with the Decision-Tree based feature Selection and Complement (DT-SC) to build different feature sets for different malice types. Then, the Status/Action Proposal Module (S/A-PM) and the Intention-VAE module generate the status, action, intent-snippet, and hidden intent-snippet embedding. With all these modules, our model is highly interpretable and can detect various illegal activities. Moreover, well-designed loss functions further enhance the prediction speed and model's interpretability. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate that our proposed algorithm outperforms the state-of-the-art methods. Furthermore, additional case studies justify our model can not only explain existing illicit patterns but can also find new suspicious characters.
AvatarVerse: High-quality & Stable 3D Avatar Creation from Text and Pose
Aug 07, 2023



Abstract:Creating expressive, diverse and high-quality 3D avatars from highly customized text descriptions and pose guidance is a challenging task, due to the intricacy of modeling and texturing in 3D that ensure details and various styles (realistic, fictional, etc). We present AvatarVerse, a stable pipeline for generating expressive high-quality 3D avatars from nothing but text descriptions and pose guidance. In specific, we introduce a 2D diffusion model conditioned on DensePose signal to establish 3D pose control of avatars through 2D images, which enhances view consistency from partially observed scenarios. It addresses the infamous Janus Problem and significantly stablizes the generation process. Moreover, we propose a progressive high-resolution 3D synthesis strategy, which obtains substantial improvement over the quality of the created 3D avatars. To this end, the proposed AvatarVerse pipeline achieves zero-shot 3D modeling of 3D avatars that are not only more expressive, but also in higher quality and fidelity than previous works. Rigorous qualitative evaluations and user studies showcase AvatarVerse's superiority in synthesizing high-fidelity 3D avatars, leading to a new standard in high-quality and stable 3D avatar creation. Our project page is: https://avatarverse3d.github.io
HandMIM: Pose-Aware Self-Supervised Learning for 3D Hand Mesh Estimation
Jul 29, 2023Abstract:With an enormous number of hand images generated over time, unleashing pose knowledge from unlabeled images for supervised hand mesh estimation is an emerging yet challenging topic. To alleviate this issue, semi-supervised and self-supervised approaches have been proposed, but they are limited by the reliance on detection models or conventional ResNet backbones. In this paper, inspired by the rapid progress of Masked Image Modeling (MIM) in visual classification tasks, we propose a novel self-supervised pre-training strategy for regressing 3D hand mesh parameters. Our approach involves a unified and multi-granularity strategy that includes a pseudo keypoint alignment module in the teacher-student framework for learning pose-aware semantic class tokens. For patch tokens with detailed locality, we adopt a self-distillation manner between teacher and student network based on MIM pre-training. To better fit low-level regression tasks, we incorporate pixel reconstruction tasks for multi-level representation learning. Additionally, we design a strong pose estimation baseline using a simple vanilla vision Transformer (ViT) as the backbone and attach a PyMAF head after tokens for regression. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed approach, named HandMIM, achieves strong performance on various hand mesh estimation tasks. Notably, HandMIM outperforms specially optimized architectures, achieving 6.29mm and 8.00mm PAVPE (Vertex-Point-Error) on challenging FreiHAND and HO3Dv2 test sets, respectively, establishing new state-of-the-art records on 3D hand mesh estimation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge