Xin Dong
Celine
RA-Nav: A Risk-Aware Navigation System Based on Semantic Segmentation for Aerial Robots in Unpredictable Environments
Feb 19, 2026Abstract:Existing aerial robot navigation systems typically plan paths around static and dynamic obstacles, but fail to adapt when a static obstacle suddenly moves. Integrating environmental semantic awareness enables estimation of potential risks posed by suddenly moving obstacles. In this paper, we propose RA- Nav, a risk-aware navigation framework based on semantic segmentation. A lightweight multi-scale semantic segmentation network identifies obstacle categories in real time. These obstacles are further classified into three types: stationary, temporarily static, and dynamic. For each type, corresponding risk estimation functions are designed to enable real-time risk prediction, based on which a complete local risk map is constructed. Based on this map, the risk-informed path search algorithm is designed to guarantee planning that balances path efficiency and safety. Trajectory optimization is then applied to generate trajectories that are safe, smooth, and dynamically feasible. Comparative simulations demonstrate that RA-Nav achieves higher success rates than baselines in sudden obstacle state transition scenarios. Its effectiveness is further validated in simulations using real- world data.
QuRL: Efficient Reinforcement Learning with Quantized Rollout
Feb 15, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR) has become a trending paradigm for training reasoning large language models (LLMs). However, due to the autoregressive decoding nature of LLMs, the rollout process becomes the efficiency bottleneck of RL training, consisting of up to 70\% of the total training time. In this work, we propose Quantized Reinforcement Learning (QuRL) that uses a quantized actor for accelerating the rollout. We address two challenges in QuRL. First, we propose Adaptive Clipping Range (ACR) that dynamically adjusts the clipping ratio based on the policy ratio between the full-precision actor and the quantized actor, which is essential for mitigating long-term training collapse. Second, we identify the weight update problem, where weight changes between RL steps are extremely small, making it difficult for the quantization operation to capture them effectively. We mitigate this problem through the invariant scaling technique that reduces quantization noise and increases weight update. We evaluate our method with INT8 and FP8 quantization experiments on DeepScaleR and DAPO, and achieve 20% to 80% faster rollout during training.
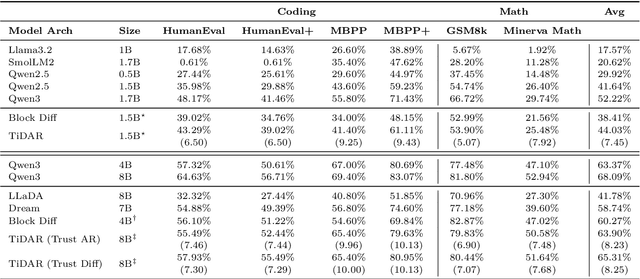
Efficient-DLM: From Autoregressive to Diffusion Language Models, and Beyond in Speed
Dec 16, 2025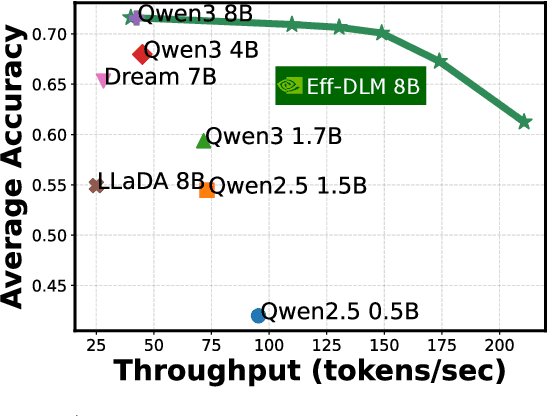
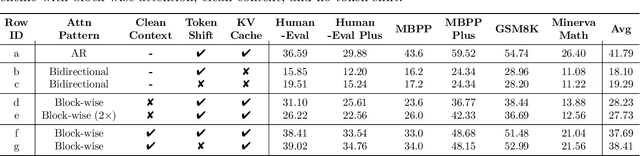
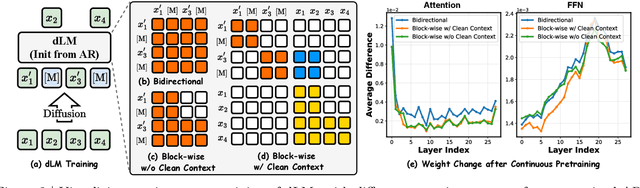
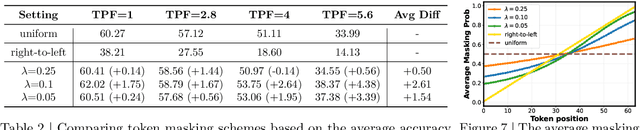
Abstract:Diffusion language models (dLMs) have emerged as a promising paradigm that enables parallel, non-autoregressive generation, but their learning efficiency lags behind that of autoregressive (AR) language models when trained from scratch. To this end, we study AR-to-dLM conversion to transform pretrained AR models into efficient dLMs that excel in speed while preserving AR models' task accuracy. We achieve this by identifying limitations in the attention patterns and objectives of existing AR-to-dLM methods and then proposing principles and methodologies for more effective AR-to-dLM conversion. Specifically, we first systematically compare different attention patterns and find that maintaining pretrained AR weight distributions is critical for effective AR-to-dLM conversion. As such, we introduce a continuous pretraining scheme with a block-wise attention pattern, which remains causal across blocks while enabling bidirectional modeling within each block. We find that this approach can better preserve pretrained AR models' weight distributions than fully bidirectional modeling, in addition to its known benefit of enabling KV caching, and leads to a win-win in accuracy and efficiency. Second, to mitigate the training-test gap in mask token distributions (uniform vs. highly left-to-right), we propose a position-dependent token masking strategy that assigns higher masking probabilities to later tokens during training to better mimic test-time behavior. Leveraging this framework, we conduct extensive studies of dLMs' attention patterns, training dynamics, and other design choices, providing actionable insights into scalable AR-to-dLM conversion. These studies lead to the Efficient-DLM family, which outperforms state-of-the-art AR models and dLMs, e.g., our Efficient-DLM 8B achieves +5.4%/+2.7% higher accuracy with 4.5x/2.7x higher throughput compared to Dream 7B and Qwen3 4B, respectively.
Untethered thin dielectric elastomer actuated soft robot
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Thin dielectric elastomer actuator (DEA) features a unique in-plane configuration, enabling low-profile designs capable of accessing millimetre-scale narrow spaces. However, most existing DEA-powered soft robots require high voltages and wired power connections, limiting their ability to operate in confined environments. This study presents an untethered thin soft robot (UTS-Robot) powered by thin dielectric elastomer actuators (TS-DEA). The robot measures 38 mm in length, 6 mm in height, and weighs just 2.34 grams, integrating flexible onboard electronics to achieve fully untethered actuation. The TS-DEA, operating at resonant frequencies of 86 Hz under a low driving voltage of 220 V, adopts a dual-actuation sandwiched structure, comprising four dielectric elastomer layers bonded to a compressible tensioning mechanism at its core. This design enables high power density actuation and locomotion via three directional friction pads. The low-voltage actuation is achieved by fabricating each elastomer layer via spin coating to an initial thickness of 50 um, followed by biaxial stretching to 8 um. A comprehensive design and modelling framework has been developed to optimise TS-DEA performance. Experimental evaluations demonstrate that the bare TS-DEA achieves a locomotion speed of 12.36 mm/s at resonance, the untethered configuration achieves a locomotion speed of 0.5 mm/s, making it highly suitable for navigating confined and complex environments.
OEMA: Ontology-Enhanced Multi-Agent Collaboration Framework for Zero-Shot Clinical Named Entity Recognition
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Clinical named entity recognition (NER) is crucial for extracting information from electronic health records (EHRs), but supervised models like CRF and BioClinicalBERT require costly annotated data. While zero-shot NER with large language models (LLMs) reduces this dependency, it struggles with example selection granularity and integrating prompts with self-improvement. To address this, we propose OEMA, a zero-shot clinical NER framework using multi-agent collaboration. OEMA's three components are: a self-annotator generating examples, a discriminator filtering them via SNOMED CT, and a predictor using entity descriptions for accurate inference. On MTSamples and VAERS datasets, OEMA achieves state-of-the-art exact-match performance. Under related-match, it matches supervised BioClinicalBERT and surpasses CRF. OEMA addresses key zero-shot NER challenges through ontology-guided reasoning and multi-agent collaboration, achieving near-supervised performance and showing promise for clinical NLP applications.
TiDAR: Think in Diffusion, Talk in Autoregression
Nov 12, 2025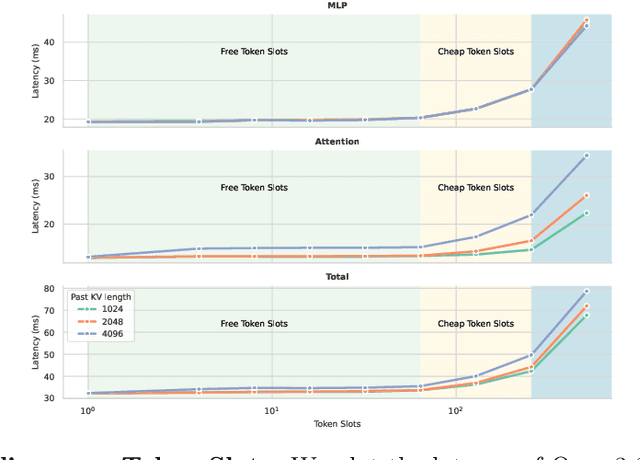

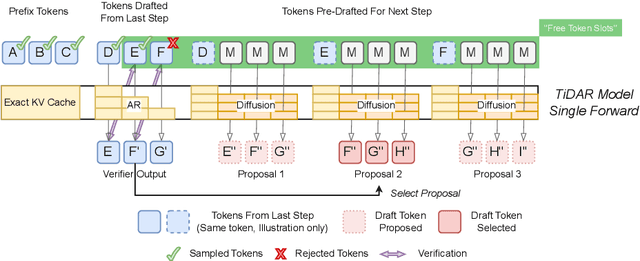
Abstract:Diffusion language models hold the promise of fast parallel generation, while autoregressive (AR) models typically excel in quality due to their causal structure aligning naturally with language modeling. This raises a fundamental question: can we achieve a synergy with high throughput, higher GPU utilization, and AR level quality? Existing methods fail to effectively balance these two aspects, either prioritizing AR using a weaker model for sequential drafting (speculative decoding), leading to lower drafting efficiency, or using some form of left-to-right (AR-like) decoding logic for diffusion, which still suffers from quality degradation and forfeits its potential parallelizability. We introduce TiDAR, a sequence-level hybrid architecture that drafts tokens (Thinking) in Diffusion and samples final outputs (Talking) AutoRegressively - all within a single forward pass using specially designed structured attention masks. This design exploits the free GPU compute density, achieving a strong balance between drafting and verification capacity. Moreover, TiDAR is designed to be serving-friendly (low overhead) as a standalone model. We extensively evaluate TiDAR against AR models, speculative decoding, and diffusion variants across generative and likelihood tasks at 1.5B and 8B scales. Thanks to the parallel drafting and sampling as well as exact KV cache support, TiDAR outperforms speculative decoding in measured throughput and surpasses diffusion models like Dream and Llada in both efficiency and quality. Most notably, TiDAR is the first architecture to close the quality gap with AR models while delivering 4.71x to 5.91x more tokens per second.
NVIDIA Nemotron Nano 2: An Accurate and Efficient Hybrid Mamba-Transformer Reasoning Model
Aug 21, 2025



Abstract:We introduce Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2, a hybrid Mamba-Transformer language model designed to increase throughput for reasoning workloads while achieving state-of-the-art accuracy compared to similarly-sized models. Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2 builds on the Nemotron-H architecture, in which the majority of the self-attention layers in the common Transformer architecture are replaced with Mamba-2 layers, to achieve improved inference speed when generating the long thinking traces needed for reasoning. We create Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2 by first pre-training a 12-billion-parameter model (Nemotron-Nano-12B-v2-Base) on 20 trillion tokens using an FP8 training recipe. After aligning Nemotron-Nano-12B-v2-Base, we employ the Minitron strategy to compress and distill the model with the goal of enabling inference on up to 128k tokens on a single NVIDIA A10G GPU (22GiB of memory, bfloat16 precision). Compared to existing similarly-sized models (e.g., Qwen3-8B), we show that Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2 achieves on-par or better accuracy on reasoning benchmarks while achieving up to 6x higher inference throughput in reasoning settings like 8k input and 16k output tokens. We are releasing Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2, Nemotron-Nano12B-v2-Base, and Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2-Base checkpoints along with the majority of our pre- and post-training datasets on Hugging Face.
WD-DETR: Wavelet Denoising-Enhanced Real-Time Object Detection Transformer for Robot Perception with Event Cameras
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Previous studies on event camera sensing have demonstrated certain detection performance using dense event representations. However, the accumulated noise in such dense representations has received insufficient attention, which degrades the representation quality and increases the likelihood of missed detections. To address this challenge, we propose the Wavelet Denoising-enhanced DEtection TRansformer, i.e., WD-DETR network, for event cameras. In particular, a dense event representation is presented first, which enables real-time reconstruction of events as tensors. Then, a wavelet transform method is designed to filter noise in the event representations. Such a method is integrated into the backbone for feature extraction. The extracted features are subsequently fed into a transformer-based network for object prediction. To further reduce inference time, we incorporate the Dynamic Reorganization Convolution Block (DRCB) as a fusion module within the hybrid encoder. The proposed method has been evaluated on three event-based object detection datasets, i.e., DSEC, Gen1, and 1Mpx. The results demonstrate that WD-DETR outperforms tested state-of-the-art methods. Additionally, we implement our approach on a common onboard computer for robots, the NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX, achieving a high frame rate of approximately 35 FPS using TensorRT FP16, which is exceptionally well-suited for real-time perception of onboard robotic systems.
ProRL: Prolonged Reinforcement Learning Expands Reasoning Boundaries in Large Language Models
May 30, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in reasoning-centric language models have highlighted reinforcement learning (RL) as a promising method for aligning models with verifiable rewards. However, it remains contentious whether RL truly expands a model's reasoning capabilities or merely amplifies high-reward outputs already latent in the base model's distribution, and whether continually scaling up RL compute reliably leads to improved reasoning performance. In this work, we challenge prevailing assumptions by demonstrating that prolonged RL (ProRL) training can uncover novel reasoning strategies that are inaccessible to base models, even under extensive sampling. We introduce ProRL, a novel training methodology that incorporates KL divergence control, reference policy resetting, and a diverse suite of tasks. Our empirical analysis reveals that RL-trained models consistently outperform base models across a wide range of pass@k evaluations, including scenarios where base models fail entirely regardless of the number of attempts. We further show that reasoning boundary improvements correlates strongly with task competence of base model and training duration, suggesting that RL can explore and populate new regions of solution space over time. These findings offer new insights into the conditions under which RL meaningfully expands reasoning boundaries in language models and establish a foundation for future work on long-horizon RL for reasoning. We release model weights to support further research: https://huggingface.co/nvidia/Nemotron-Research-Reasoning-Qwen-1.5B
A Cooperative Aerial System of A Payload Drone Equipped with Dexterous Rappelling End Droid for Cluttered Space Pickup
May 26, 2025Abstract:In cluttered spaces, such as forests, drone picking up a payload via an abseil claw is an open challenge, as the cable is likely tangled and blocked by the branches and obstacles. To address such a challenge, in this work, a cooperative aerial system is proposed, which consists of a payload drone and a dexterous rappelling end droid. The two ends are linked via a Kevlar tether cable. The end droid is actuated by four propellers, which enable mid-air dexterous adjustment of clawing angle and guidance of cable movement. To avoid tanglement and rappelling obstacles, a trajectory optimization method that integrates cable length constraints and dynamic feasibility is developed, which guarantees safe pickup. A tether cable dynamic model is established to evaluate real-time cable status, considering both taut and sagging conditions. Simulation and real-world experiments are conducted to demonstrate that the proposed system is capable of picking up payload in cluttered spaces. As a result, the end droid can reach the target point successfully under cable constraints and achieve passive retrieval during the lifting phase without propulsion, which enables effective and efficient aerial manipulation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge