Haoze Li
Steering Vision-Language Pre-trained Models for Incremental Face Presentation Attack Detection
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Face Presentation Attack Detection (PAD) demands incremental learning (IL) to combat evolving spoofing tactics and domains. Privacy regulations, however, forbid retaining past data, necessitating rehearsal-free IL (RF-IL). Vision-Language Pre-trained (VLP) models, with their prompt-tunable cross-modal representations, enable efficient adaptation to new spoofing styles and domains. Capitalizing on this strength, we propose \textbf{SVLP-IL}, a VLP-based RF-IL framework that balances stability and plasticity via \textit{Multi-Aspect Prompting} (MAP) and \textit{Selective Elastic Weight Consolidation} (SEWC). MAP isolates domain dependencies, enhances distribution-shift sensitivity, and mitigates forgetting by jointly exploiting universal and domain-specific cues. SEWC selectively preserves critical weights from previous tasks, retaining essential knowledge while allowing flexibility for new adaptations. Comprehensive experiments across multiple PAD benchmarks show that SVLP-IL significantly reduces catastrophic forgetting and enhances performance on unseen domains. SVLP-IL offers a privacy-compliant, practical solution for robust lifelong PAD deployment in RF-IL settings.
A Cooperative Aerial System of A Payload Drone Equipped with Dexterous Rappelling End Droid for Cluttered Space Pickup
May 26, 2025Abstract:In cluttered spaces, such as forests, drone picking up a payload via an abseil claw is an open challenge, as the cable is likely tangled and blocked by the branches and obstacles. To address such a challenge, in this work, a cooperative aerial system is proposed, which consists of a payload drone and a dexterous rappelling end droid. The two ends are linked via a Kevlar tether cable. The end droid is actuated by four propellers, which enable mid-air dexterous adjustment of clawing angle and guidance of cable movement. To avoid tanglement and rappelling obstacles, a trajectory optimization method that integrates cable length constraints and dynamic feasibility is developed, which guarantees safe pickup. A tether cable dynamic model is established to evaluate real-time cable status, considering both taut and sagging conditions. Simulation and real-world experiments are conducted to demonstrate that the proposed system is capable of picking up payload in cluttered spaces. As a result, the end droid can reach the target point successfully under cable constraints and achieve passive retrieval during the lifting phase without propulsion, which enables effective and efficient aerial manipulation.
ALPS: Attention Localization and Pruning Strategy for Efficient Alignment of Large Language Models
May 24, 2025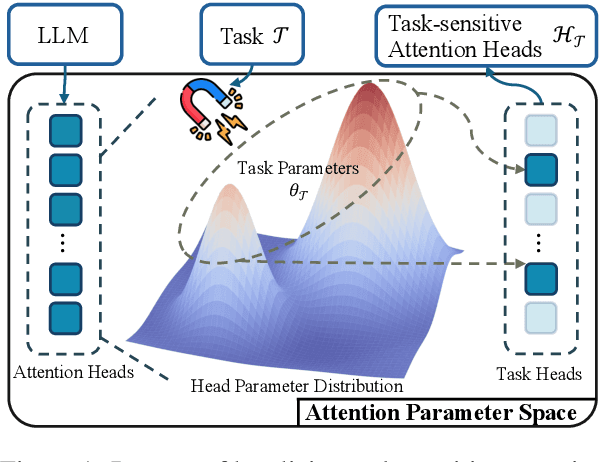
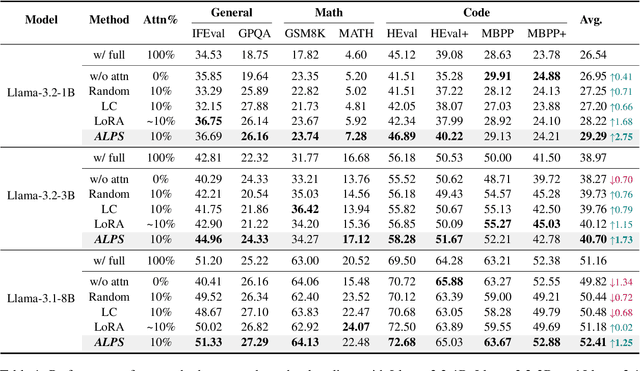
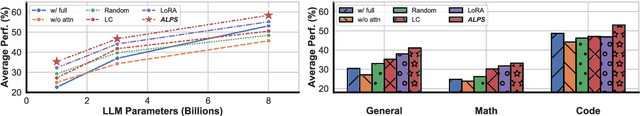
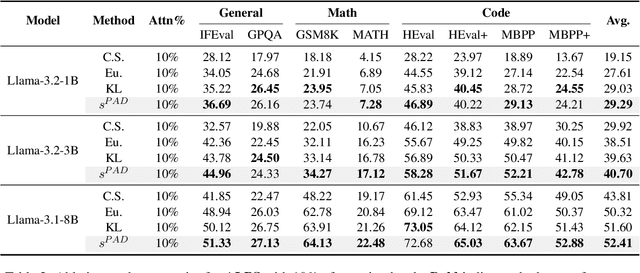
Abstract:Aligning general-purpose large language models (LLMs) to downstream tasks often incurs significant costs, including constructing task-specific instruction pairs and extensive training adjustments. Prior research has explored various avenues to enhance alignment efficiency, primarily through minimal-data training or data-driven activations to identify key attention heads. However, these approaches inherently introduce data dependency, which hinders generalization and reusability. To address this issue and enhance model alignment efficiency, we propose the \textit{\textbf{A}ttention \textbf{L}ocalization and \textbf{P}runing \textbf{S}trategy (\textbf{ALPS})}, an efficient algorithm that localizes the most task-sensitive attention heads and prunes by restricting attention training updates to these heads, thereby reducing alignment costs. Experimental results demonstrate that our method activates only \textbf{10\%} of attention parameters during fine-tuning while achieving a \textbf{2\%} performance improvement over baselines on three tasks. Moreover, the identified task-specific heads are transferable across datasets and mitigate knowledge forgetting. Our work and findings provide a novel perspective on efficient LLM alignment.
Feature Matching Intervention: Leveraging Observational Data for Causal Representation Learning
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:A major challenge in causal discovery from observational data is the absence of perfect interventions, making it difficult to distinguish causal features from spurious ones. We propose an innovative approach, Feature Matching Intervention (FMI), which uses a matching procedure to mimic perfect interventions. We define causal latent graphs, extending structural causal models to latent feature space, providing a framework that connects FMI with causal graph learning. Our feature matching procedure emulates perfect interventions within these causal latent graphs. Theoretical results demonstrate that FMI exhibits strong out-of-distribution (OOD) generalizability. Experiments further highlight FMI's superior performance in effectively identifying causal features solely from observational data.
The role of inhibitory control in garden-path sentence processing: A Chinese-English bilingual perspective
Dec 13, 2024Abstract:In reading garden-path sentences, people must resolve competing interpretations, though initial misinterpretations can linger despite reanalysis. This study examines the role of inhibitory control (IC) in managing these misinterpretations among Chinese-English bilinguals. Using self-paced reading tasks, we investigated how IC influences recovery from garden-path sentences in Chinese (L1) and its interaction with language proficiency during English (L2) processing. Results indicate that IC does not affect garden-path recovery in Chinese, suggesting reliance on semantic context may reduce the need for IC. In contrast, findings for English L2 learners reveal a complex relationship between language proficiency and IC: Participants with low L2 proficiency but high IC showed lingering misinterpretations, while those with high proficiency exhibited none. These results support and extend the Model of Cognitive Control (Ness et al., 2023). Moreover, our comparison of three Stroop task versions identifies L1 colour-word Stroop task as the preferred measure of IC in bilingual research.
TableGPT2: A Large Multimodal Model with Tabular Data Integration
Nov 04, 2024Abstract:The emergence of models like GPTs, Claude, LLaMA, and Qwen has reshaped AI applications, presenting vast new opportunities across industries. Yet, the integration of tabular data remains notably underdeveloped, despite its foundational role in numerous real-world domains. This gap is critical for three main reasons. First, database or data warehouse data integration is essential for advanced applications; second, the vast and largely untapped resource of tabular data offers immense potential for analysis; and third, the business intelligence domain specifically demands adaptable, precise solutions that many current LLMs may struggle to provide. In response, we introduce TableGPT2, a model rigorously pre-trained and fine-tuned with over 593.8K tables and 2.36M high-quality query-table-output tuples, a scale of table-related data unprecedented in prior research. This extensive training enables TableGPT2 to excel in table-centric tasks while maintaining strong general language and coding abilities. One of TableGPT2's key innovations is its novel table encoder, specifically designed to capture schema-level and cell-level information. This encoder strengthens the model's ability to handle ambiguous queries, missing column names, and irregular tables commonly encountered in real-world applications. Similar to visual language models, this pioneering approach integrates with the decoder to form a robust large multimodal model. We believe the results are compelling: over 23 benchmarking metrics, TableGPT2 achieves an average performance improvement of 35.20% in the 7B model and 49.32% in the 72B model over prior benchmark-neutral LLMs, with robust general-purpose capabilities intact.
PyXAB -- A Python Library for $\mathcal{X}$-Armed Bandit and Online Blackbox Optimization Algorithms
Mar 07, 2023Abstract:We introduce a Python open-source library for $\mathcal{X}$-armed bandit and online blackbox optimization named PyXAB. PyXAB contains the implementations for more than 10 $\mathcal{X}$-armed bandit algorithms, such as HOO, StoSOO, HCT, and the most recent works GPO and VHCT. PyXAB also provides the most commonly-used synthetic objectives to evaluate the performance of different algorithms and the various choices of the hierarchical partitions on the parameter space. The online documentation for PyXAB includes clear instructions for installation, straight-forward examples, detailed feature descriptions, and a complete reference of the API. PyXAB is released under the MIT license in order to encourage both academic and industrial usage. The library can be directly installed from PyPI with its source code available at https://github.com/WilliamLwj/PyXAB
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge