Haobo Wang
Stop Unnecessary Reflection: Training LRMs for Efficient Reasoning with Adaptive Reflection and Length Coordinated Penalty
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance on complex reasoning tasks by employing test-time scaling. However, they often generate over-long chains-of-thought that, driven by substantial reflections such as repetitive self-questioning and circular reasoning, lead to high token consumption, substantial computational overhead, and increased latency without improving accuracy, particularly in smaller models. Our observation reveals that increasing problem complexity induces more excessive and unnecessary reflection, which in turn reduces accuracy and increases token overhead. To address this challenge, we propose Adaptive Reflection and Length Coordinated Penalty (ARLCP), a novel reinforcement learning framework designed to dynamically balance reasoning efficiency and solution accuracy. ARLCP introduces two key innovations: (1) a reflection penalty that adaptively curtails unnecessary reflective steps while preserving essential reasoning, and (2) a length penalty calibrated to the estimated complexity of the problem. By coordinating these penalties, ARLCP encourages the model to generate more concise and effective reasoning paths. We evaluate our method on five mathematical reasoning benchmarks using DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B and DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B models. Experimental results show that ARLCP achieves a superior efficiency-accuracy trade-off compared to existing approaches. For the 1.5B model, it reduces the average response length by 53.1% while simultaneously improving accuracy by 5.8%. For the 7B model, it achieves a 35.0% reduction in length with a 2.7% accuracy gain. The code is released at https://github.com/ZeweiYu1/ARLCP .
SGHA-Attack: Semantic-Guided Hierarchical Alignment for Transferable Targeted Attacks on Vision-Language Models
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Large vision-language models (VLMs) are vulnerable to transfer-based adversarial perturbations, enabling attackers to optimize on surrogate models and manipulate black-box VLM outputs. Prior targeted transfer attacks often overfit surrogate-specific embedding space by relying on a single reference and emphasizing final-layer alignment, which underutilizes intermediate semantics and degrades transfer across heterogeneous VLMs. To address this, we propose SGHA-Attack, a Semantic-Guided Hierarchical Alignment framework that adopts multiple target references and enforces intermediate-layer consistency. Concretely, we generate a visually grounded reference pool by sampling a frozen text-to-image model conditioned on the target prompt, and then carefully select the Top-K most semantically relevant anchors under the surrogate to form a weighted mixture for stable optimization guidance. Building on these anchors, SGHA-Attack injects target semantics throughout the feature hierarchy by aligning intermediate visual representations at both global and spatial granularities across multiple depths, and by synchronizing intermediate visual and textual features in a shared latent subspace to provide early cross-modal supervision before the final projection. Extensive experiments on open-source and commercial black-box VLMs show that SGHA-Attack achieves stronger targeted transferability than prior methods and remains robust under preprocessing and purification defenses.
Supervised Fine-Tuning Needs to Unlock the Potential of Token Priority
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:The transition from fitting empirical data to achieving true human utility is fundamentally constrained by a granularity mismatch, where fine-grained autoregressive generation is often supervised by coarse or uniform signals. This position paper advocates Token Priority as the essential bridge, formalizing Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) not as simple optimization but as a precise distribution reshaping process that aligns raw data with the ideal alignment manifold. We analyze recent breakthroughs through this unified lens, categorizing them into two distinct regimes: Positive Priority for noise filtration and Signed Priority for toxic modes unlearning. We revisit existing progress and limitations, identify key challenges, and suggest directions for future research.
Harnessing Reasoning Trajectories for Hallucination Detection via Answer-agreement Representation Shaping
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Large reasoning models (LRMs) often generate long, seemingly coherent reasoning traces yet still produce incorrect answers, making hallucination detection challenging. Although trajectories contain useful signals, directly using trace text or vanilla hidden states for detection is brittle: traces vary in form and detectors can overfit to superficial patterns rather than answer validity. We introduce Answer-agreement Representation Shaping (ARS), which learns detection-friendly trace-conditioned representations by explicitly encoding answer stability. ARS generates counterfactual answers through small latent interventions, specifically, perturbing the trace-boundary embedding, and labels each perturbation by whether the resulting answer agrees with the original. It then learns representations that bring answer-agreeing states together and separate answer-disagreeing ones, exposing latent instability indicative of hallucination risk. The shaped embeddings are plug-and-play with existing embedding-based detectors and require no human annotations during training. Experiments demonstrate that ARS consistently improves detection and achieves substantial gains over strong baselines.
A Syllogistic Probe: Tracing the Evolution of Logic Reasoning in Large Language Models
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Human logic has gradually shifted from intuition-driven inference to rigorous formal systems. Motivated by recent advances in large language models (LLMs), we explore whether LLMs exhibit a similar evolution in the underlying logical framework. Using existential import as a probe, we for evaluate syllogism under traditional and modern logic. Through extensive experiments of testing SOTA LLMs on a new syllogism dataset, we have some interesting findings: (i) Model size scaling promotes the shift toward modern logic; (ii) Thinking serves as an efficient accelerator beyond parameter scaling; (iii) the Base model plays a crucial role in determining how easily and stably this shift can emerge. Beyond these core factors, we conduct additional experiments for in-depth analysis of properties of current LLMs on syllogistic reasoning.
TableGPT-R1: Advancing Tabular Reasoning Through Reinforcement Learning
Dec 23, 2025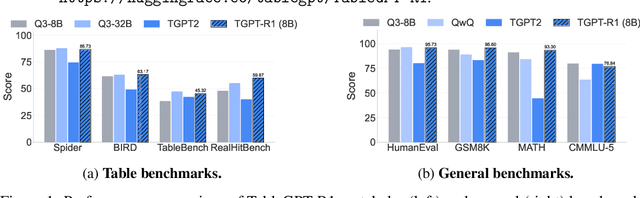
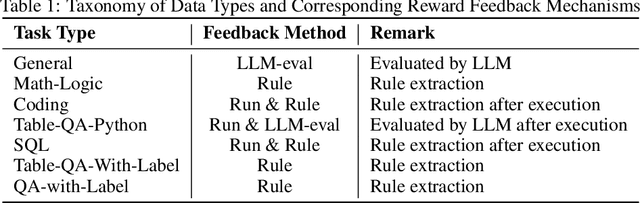
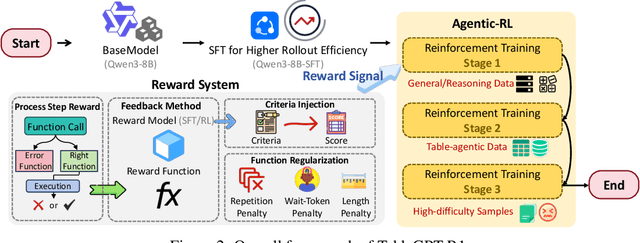
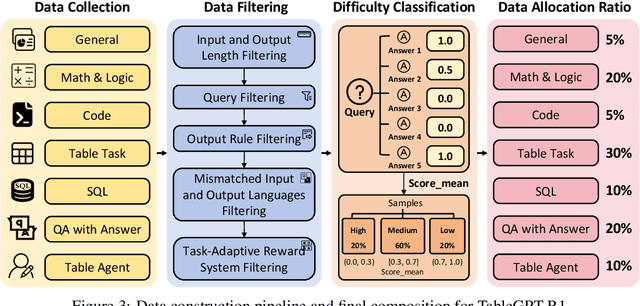
Abstract:Tabular data serves as the backbone of modern data analysis and scientific research. While Large Language Models (LLMs) fine-tuned via Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) have significantly improved natural language interaction with such structured data, they often fall short in handling the complex, multi-step reasoning and robust code execution required for real-world table tasks. Reinforcement Learning (RL) offers a promising avenue to enhance these capabilities, yet its application in the tabular domain faces three critical hurdles: the scarcity of high-quality agentic trajectories with closed-loop code execution and environment feedback on diverse table structures, the extreme heterogeneity of feedback signals ranging from rigid SQL execution to open-ended data interpretation, and the risk of catastrophic forgetting of general knowledge during vertical specialization. To overcome these challenges and unlock advanced reasoning on complex tables, we introduce \textbf{TableGPT-R1}, a specialized tabular model built on a systematic RL framework. Our approach integrates a comprehensive data engineering pipeline that synthesizes difficulty-stratified agentic trajectories for both supervised alignment and RL rollouts, a task-adaptive reward system that combines rule-based verification with a criteria-injected reward model and incorporates process-level step reward shaping with behavioral regularization, and a multi-stage training framework that progressively stabilizes reasoning before specializing in table-specific tasks. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that TableGPT-R1 achieves state-of-the-art performance on authoritative benchmarks, significantly outperforming baseline models while retaining robust general capabilities. Our model is available at https://huggingface.co/tablegpt/TableGPT-R1.
TraPO: A Semi-Supervised Reinforcement Learning Framework for Boosting LLM Reasoning
Dec 15, 2025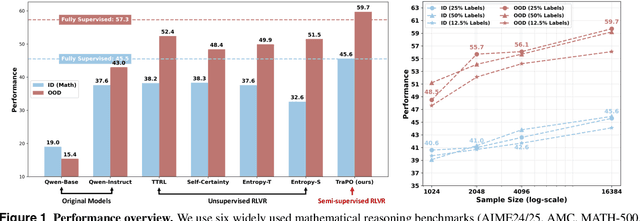
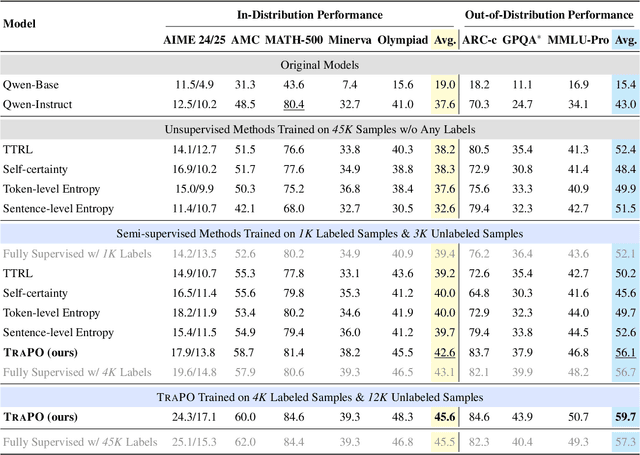
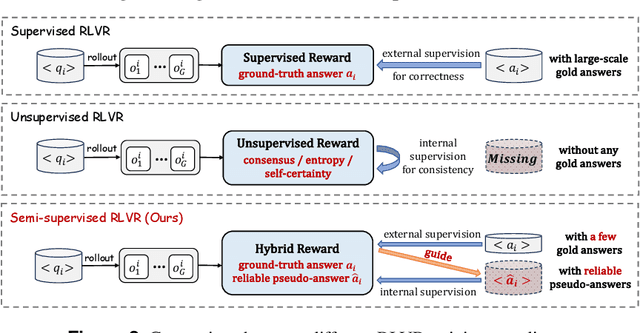
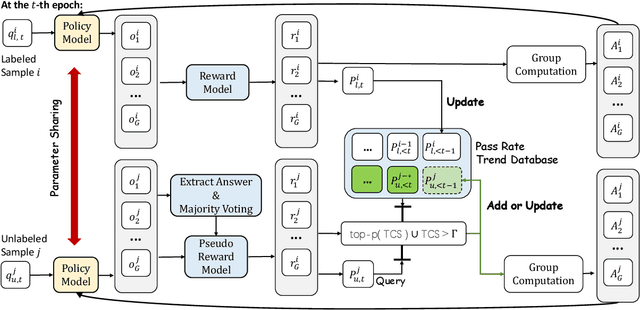
Abstract:Reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR) has proven effective in training large reasoning models (LRMs) by leveraging answer-verifiable signals to guide policy optimization, which, however, suffers from high annotation costs. To alleviate this problem, recent work has explored unsupervised RLVR methods that derive rewards solely from the model's internal consistency, such as through entropy and majority voting. While seemingly promising, these methods often suffer from model collapse in the later stages of training, which may arise from the reinforcement of incorrect reasoning patterns in the absence of external supervision. In this work, we investigate a novel semi-supervised RLVR paradigm that utilizes a small labeled set to guide RLVR training on unlabeled samples. Our key insight is that supervised rewards are essential for stabilizing consistency-based training on unlabeled samples, ensuring that only reasoning patterns verified on labeled instances are incorporated into RL training. Technically, we propose an effective policy optimization algorithm, TraPO, that identifies reliable unlabeled samples by matching their learning trajectory similarity to labeled ones. Building on this, TraPO achieves remarkable data efficiency and strong generalization on six widely used mathematical reasoning benchmarks (AIME24/25, AMC, MATH-500, Minerva, and Olympiad) and three out-of-distribution tasks (ARC-c, GPQA-diamond, and MMLU-pro). With only 1K labeled and 3K unlabeled samples, TraPO reaches 42.6% average accuracy, surpassing the best unsupervised method trained on 45K unlabeled samples (38.3%). Notably, when using 4K labeled and 12K unlabeled samples, TraPO even outperforms the fully supervised model trained on the full 45K labeled samples on all benchmarks, while using only 10% of the labeled data. The code is available via https://github.com/ShenzhiYang2000/TRAPO.
CrowdAgent: Multi-Agent Managed Multi-Source Annotation System
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:High-quality annotated data is a cornerstone of modern Natural Language Processing (NLP). While recent methods begin to leverage diverse annotation sources-including Large Language Models (LLMs), Small Language Models (SLMs), and human experts-they often focus narrowly on the labeling step itself. A critical gap remains in the holistic process control required to manage these sources dynamically, addressing complex scheduling and quality-cost trade-offs in a unified manner. Inspired by real-world crowdsourcing companies, we introduce CrowdAgent, a multi-agent system that provides end-to-end process control by integrating task assignment, data annotation, and quality/cost management. It implements a novel methodology that rationally assigns tasks, enabling LLMs, SLMs, and human experts to advance synergistically in a collaborative annotation workflow. We demonstrate the effectiveness of CrowdAgent through extensive experiments on six diverse multimodal classification tasks. The source code and video demo are available at https://github.com/QMMMS/CrowdAgent.
SPA++: Generalized Graph Spectral Alignment for Versatile Domain Adaptation
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Domain Adaptation (DA) aims to transfer knowledge from a labeled source domain to an unlabeled or sparsely labeled target domain under domain shifts. Most prior works focus on capturing the inter-domain transferability but largely overlook rich intra-domain structures, which empirically results in even worse discriminability. To tackle this tradeoff, we propose a generalized graph SPectral Alignment framework, SPA++. Its core is briefly condensed as follows: (1)-by casting the DA problem to graph primitives, it composes a coarse graph alignment mechanism with a novel spectral regularizer toward aligning the domain graphs in eigenspaces; (2)-we further develop a fine-grained neighbor-aware propagation mechanism for enhanced discriminability in the target domain; (3)-by incorporating data augmentation and consistency regularization, SPA++ can adapt to complex scenarios including most DA settings and even challenging distribution scenarios. Furthermore, we also provide theoretical analysis to support our method, including the generalization bound of graph-based DA and the role of spectral alignment and smoothing consistency. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that SPA++ consistently outperforms existing cutting-edge methods, achieving superior robustness and adaptability across various challenging adaptation scenarios.
RealHiTBench: A Comprehensive Realistic Hierarchical Table Benchmark for Evaluating LLM-Based Table Analysis
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:With the rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs), there is an increasing need for challenging benchmarks to evaluate their capabilities in handling complex tabular data. However, existing benchmarks are either based on outdated data setups or focus solely on simple, flat table structures. In this paper, we introduce RealHiTBench, a comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate the performance of both LLMs and Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) across a variety of input formats for complex tabular data, including LaTeX, HTML, and PNG. RealHiTBench also includes a diverse collection of tables with intricate structures, spanning a wide range of task types. Our experimental results, using 25 state-of-the-art LLMs, demonstrate that RealHiTBench is indeed a challenging benchmark. Moreover, we also develop TreeThinker, a tree-based pipeline that organizes hierarchical headers into a tree structure for enhanced tabular reasoning, validating the importance of improving LLMs' perception of table hierarchies. We hope that our work will inspire further research on tabular data reasoning and the development of more robust models. The code and data are available at https://github.com/cspzyy/RealHiTBench.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge