Ning Wang
Pruning Minimal Reasoning Graphs for Efficient Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) is now standard for knowledge-intensive LLM tasks, but most systems still treat every query as fresh, repeatedly re-retrieving long passages and re-reasoning from scratch, inflating tokens, latency, and cost. We present AutoPrunedRetriever, a graph-style RAG system that persists the minimal reasoning subgraph built for earlier questions and incrementally extends it for later ones. AutoPrunedRetriever stores entities and relations in a compact, ID-indexed codebook and represents questions, facts, and answers as edge sequences, enabling retrieval and prompting over symbolic structure instead of raw text. To keep the graph compact, we apply a two-layer consolidation policy (fast ANN/KNN alias detection plus selective $k$-means once a memory threshold is reached) and prune low-value structure, while prompts retain only overlap representatives and genuinely new evidence. We instantiate two front ends: AutoPrunedRetriever-REBEL, which uses REBEL as a triplet parser, and AutoPrunedRetriever-llm, which swaps in an LLM extractor. On GraphRAG-Benchmark (Medical and Novel), both variants achieve state-of-the-art complex reasoning accuracy, improving over HippoRAG2 by roughly 9--11 points, and remain competitive on contextual summarize and generation. On our harder STEM and TV benchmarks, AutoPrunedRetriever again ranks first, while using up to two orders of magnitude fewer tokens than graph-heavy baselines, making it a practical substrate for long-running sessions, evolving corpora, and multi-agent pipelines.
SparVAR: Exploring Sparsity in Visual AutoRegressive Modeling for Training-Free Acceleration
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Visual AutoRegressive (VAR) modeling has garnered significant attention for its innovative next-scale prediction paradigm. However, mainstream VAR paradigms attend to all tokens across historical scales at each autoregressive step. As the next scale resolution grows, the computational complexity of attention increases quartically with resolution, causing substantial latency. Prior accelerations often skip high-resolution scales, which speeds up inference but discards high-frequency details and harms image quality. To address these problems, we present SparVAR, a training-free acceleration framework that exploits three properties of VAR attention: (i) strong attention sinks, (ii) cross-scale activation similarity, and (iii) pronounced locality. Specifically, we dynamically predict the sparse attention pattern of later high-resolution scales from a sparse decision scale, and construct scale self-similar sparse attention via an efficient index-mapping mechanism, enabling high-efficiency sparse attention computation at large scales. Furthermore, we propose cross-scale local sparse attention and implement an efficient block-wise sparse kernel, which achieves $\mathbf{> 5\times}$ faster forward speed than FlashAttention. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed SparseVAR can reduce the generation time of an 8B model producing $1024\times1024$ high-resolution images to the 1s, without skipping the last scales. Compared with the VAR baseline accelerated by FlashAttention, our method achieves a $\mathbf{1.57\times}$ speed-up while preserving almost all high-frequency details. When combined with existing scale-skipping strategies, SparseVAR attains up to a $\mathbf{2.28\times}$ acceleration, while maintaining competitive visual generation quality. Code is available at https://github.com/CAS-CLab/SparVAR.
TableGPT-R1: Advancing Tabular Reasoning Through Reinforcement Learning
Dec 23, 2025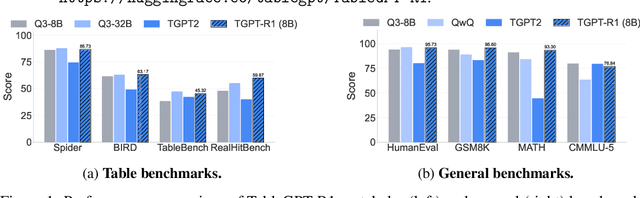
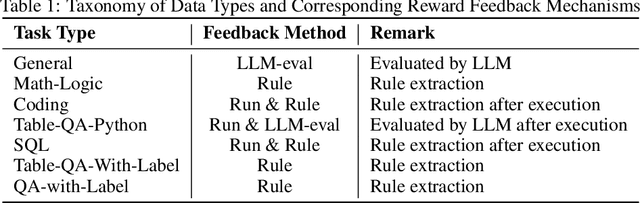
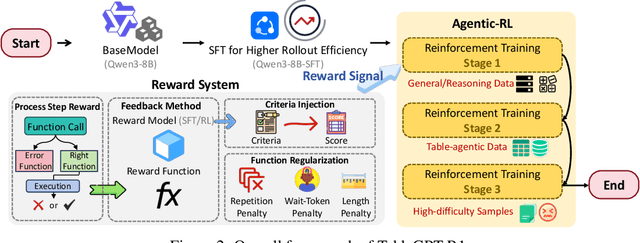
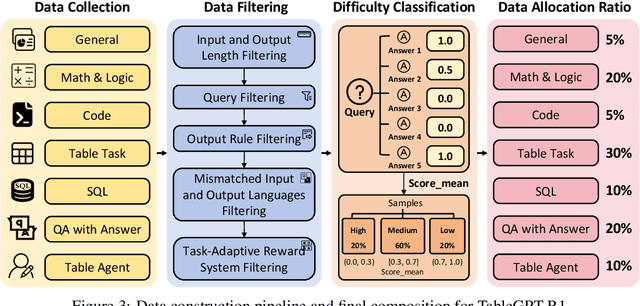
Abstract:Tabular data serves as the backbone of modern data analysis and scientific research. While Large Language Models (LLMs) fine-tuned via Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) have significantly improved natural language interaction with such structured data, they often fall short in handling the complex, multi-step reasoning and robust code execution required for real-world table tasks. Reinforcement Learning (RL) offers a promising avenue to enhance these capabilities, yet its application in the tabular domain faces three critical hurdles: the scarcity of high-quality agentic trajectories with closed-loop code execution and environment feedback on diverse table structures, the extreme heterogeneity of feedback signals ranging from rigid SQL execution to open-ended data interpretation, and the risk of catastrophic forgetting of general knowledge during vertical specialization. To overcome these challenges and unlock advanced reasoning on complex tables, we introduce \textbf{TableGPT-R1}, a specialized tabular model built on a systematic RL framework. Our approach integrates a comprehensive data engineering pipeline that synthesizes difficulty-stratified agentic trajectories for both supervised alignment and RL rollouts, a task-adaptive reward system that combines rule-based verification with a criteria-injected reward model and incorporates process-level step reward shaping with behavioral regularization, and a multi-stage training framework that progressively stabilizes reasoning before specializing in table-specific tasks. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that TableGPT-R1 achieves state-of-the-art performance on authoritative benchmarks, significantly outperforming baseline models while retaining robust general capabilities. Our model is available at https://huggingface.co/tablegpt/TableGPT-R1.
Step-GUI Technical Report
Dec 19, 2025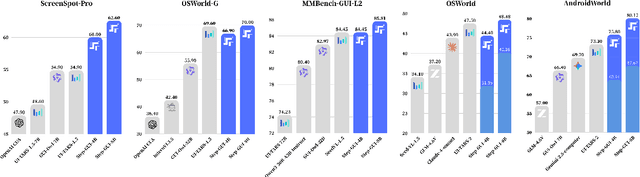
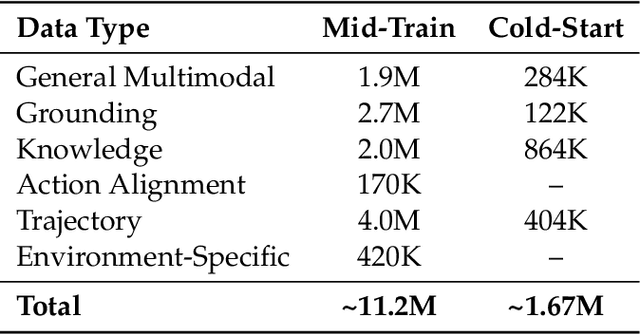
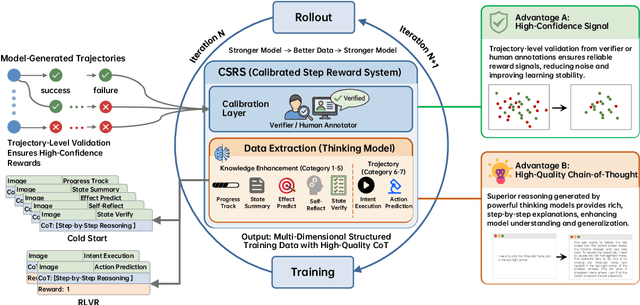

Abstract:Recent advances in multimodal large language models unlock unprecedented opportunities for GUI automation. However, a fundamental challenge remains: how to efficiently acquire high-quality training data while maintaining annotation reliability? We introduce a self-evolving training pipeline powered by the Calibrated Step Reward System, which converts model-generated trajectories into reliable training signals through trajectory-level calibration, achieving >90% annotation accuracy with 10-100x lower cost. Leveraging this pipeline, we introduce Step-GUI, a family of models (4B/8B) that achieves state-of-the-art GUI performance (8B: 80.2% AndroidWorld, 48.5% OSWorld, 62.6% ScreenShot-Pro) while maintaining robust general capabilities. As GUI agent capabilities improve, practical deployment demands standardized interfaces across heterogeneous devices while protecting user privacy. To this end, we propose GUI-MCP, the first Model Context Protocol for GUI automation with hierarchical architecture that combines low-level atomic operations and high-level task delegation to local specialist models, enabling high-privacy execution where sensitive data stays on-device. Finally, to assess whether agents can handle authentic everyday usage, we introduce AndroidDaily, a benchmark grounded in real-world mobile usage patterns with 3146 static actions and 235 end-to-end tasks across high-frequency daily scenarios (8B: static 89.91%, end-to-end 52.50%). Our work advances the development of practical GUI agents and demonstrates strong potential for real-world deployment in everyday digital interactions.
The Triple-C Paradigm: Cooperative, Complementary, and Competitive Modes for TBS-HAPS-LEO Integration
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:The growing demands of ubiquitous and resilient global coverage have pushed existing networks to their operational limits, making it increasingly difficult to meet all requirements on their own. Integrating \emph{Terrestrial Base Stations (TBS), High Altitude Platform Stations (HAPS)} and \emph{Low-Earth-Orbit (LEO)} satellites is envisioned as a promising solution, yet the coordination across these heterogeneous platforms remains an open challenge. This paper proposes a novel unifying \emph{Triple-C framework: Cooperation, Complementarity, and Competition}, that systematically defines the TBS-HAPS-LEO interaction to deliver seamless resilient and scalable connectivity. For each C, we detail the architectural methodology, required pre-requisites, and measurable deliverables that govern when and how the three layers should collaborate, complement each other, or contend. We further identify the enabling technologies across physical, logical, and cognitive layers to operationalize the proposed 3C paradigm. A rich portfolio of use cases and targeted applications demonstrates how this technological leap will make such integration both feasible and impactful. Comprehensive performance analysis and emulation results quantify the trade-offs of such integrated networks. In addition, we examine the economical, environmental, safety, privacy, standardization, and regulatory implications that shape the real-world implementation of the proposed framework. eventually, we provide the gap analysis, outline key technical/non-technical challenges, and a road-map of future research directions needed to unlock the full potential of Cooperation, Complementarity, and Competition operations in TBS-HAPS-LEO integrated networks.
REAP: Enhancing RAG with Recursive Evaluation and Adaptive Planning for Multi-Hop Question Answering
Nov 13, 2025



Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has been extensively employed to mitigate hallucinations in large language models (LLMs). However, existing methods for multi-hop reasoning tasks often lack global planning, increasing the risk of falling into local reasoning impasses. Insufficient exploitation of retrieved content and the neglect of latent clues fail to ensure the accuracy of reasoning outcomes. To overcome these limitations, we propose Recursive Evaluation and Adaptive Planning (REAP), whose core idea is to explicitly maintain structured sub-tasks and facts related to the current task through the Sub-task Planner (SP) and Fact Extractor (FE) modules. SP maintains a global perspective, guiding the overall reasoning direction and evaluating the task state based on the outcomes of FE, enabling dynamic optimization of the task-solving trajectory. FE performs fine-grained analysis over retrieved content to extract reliable answers and clues. These two modules incrementally enrich a logically coherent representation of global knowledge, enhancing the reliability and the traceability of the reasoning process. Furthermore, we propose a unified task paradigm design that enables effective multi-task fine-tuning, significantly enhancing SP's performance on complex, data-scarce tasks. We conduct extensive experiments on multiple public multi-hop datasets, and the results demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing RAG methods in both in-domain and out-of-domain settings, validating its effectiveness in complex multi-hop reasoning tasks.
Multi-Granularity Mutual Refinement Network for Zero-Shot Learning
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:Zero-shot learning (ZSL) aims to recognize unseen classes with zero samples by transferring semantic knowledge from seen classes. Current approaches typically correlate global visual features with semantic information (i.e., attributes) or align local visual region features with corresponding attributes to enhance visual-semantic interactions. Although effective, these methods often overlook the intrinsic interactions between local region features, which can further improve the acquisition of transferable and explicit visual features. In this paper, we propose a network named Multi-Granularity Mutual Refinement Network (Mg-MRN), which refine discriminative and transferable visual features by learning decoupled multi-granularity features and cross-granularity feature interactions. Specifically, we design a multi-granularity feature extraction module to learn region-level discriminative features through decoupled region feature mining. Then, a cross-granularity feature fusion module strengthens the inherent interactions between region features of varying granularities. This module enhances the discriminability of representations at each granularity level by integrating region representations from adjacent hierarchies, further improving ZSL recognition performance. Extensive experiments on three popular ZSL benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority and competitiveness of our proposed Mg-MRN method. Our code is available at https://github.com/NingWang2049/Mg-MRN.
PolygMap: A Perceptive Locomotion Framework for Humanoid Robot Stair Climbing
Oct 14, 2025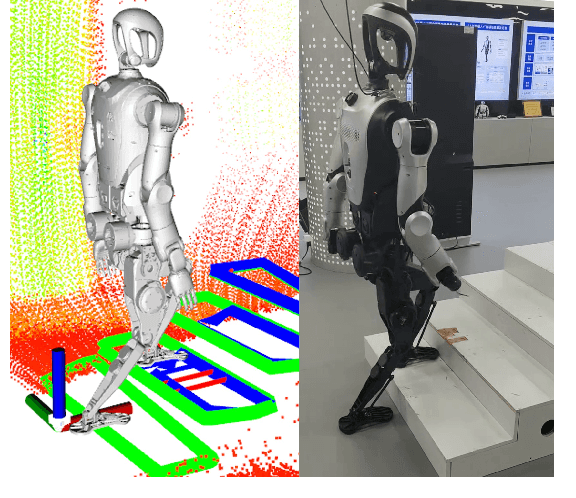
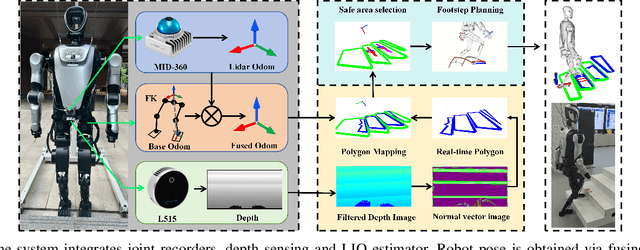
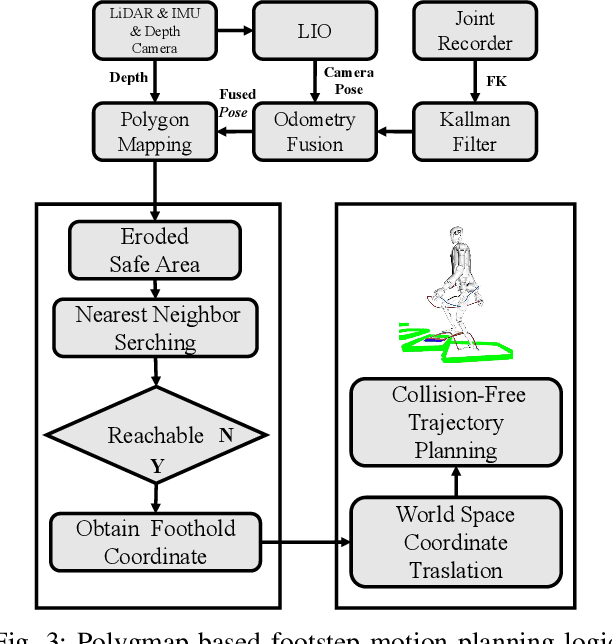
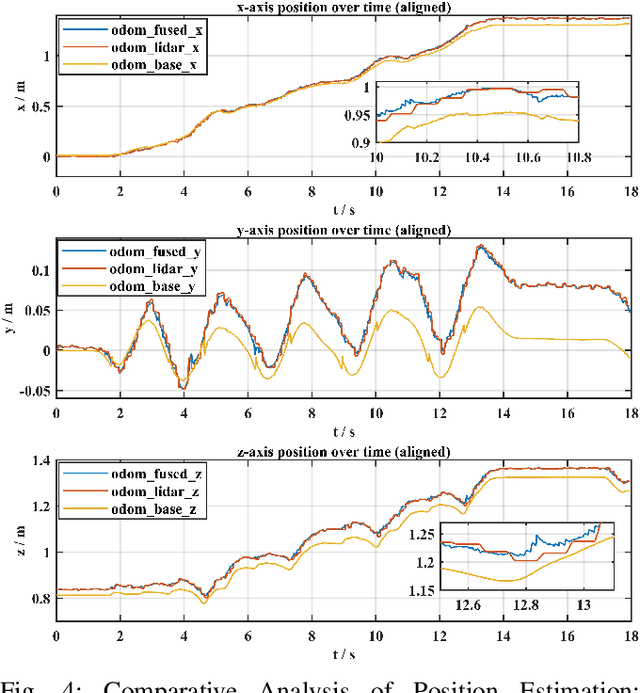
Abstract:Recently, biped robot walking technology has been significantly developed, mainly in the context of a bland walking scheme. To emulate human walking, robots need to step on the positions they see in unknown spaces accurately. In this paper, we present PolyMap, a perception-based locomotion planning framework for humanoid robots to climb stairs. Our core idea is to build a real-time polygonal staircase plane semantic map, followed by a footstep planar using these polygonal plane segments. These plane segmentation and visual odometry are done by multi-sensor fusion(LiDAR, RGB-D camera and IMUs). The proposed framework is deployed on a NVIDIA Orin, which performs 20-30 Hz whole-body motion planning output. Both indoor and outdoor real-scene experiments indicate that our method is efficient and robust for humanoid robot stair climbing.
Comparative Performance Analysis of Different Hybrid NOMA Schemes
Sep 18, 2025



Abstract:Hybrid non-orthogonal multiple access (H-NOMA), which combines the advantages of pure NOMA and conventional OMA organically, has emerged as a highly promising multiple access technology for future wireless networks. Recent studies have proposed various H-NOMA systems by employing different successive interference cancellation (SIC) methods for the NOMA transmission phase. However, existing analyses typically assume a fixed channel gain order between paired users, despite the fact that channel coefficients follow random distribution, leading to their magnitude relationships inherently stochastic and time varying. This paper analyzes the performance of three H-NOMA schemes under stochastic channel gain ordering: a) fixed order SIC (FSIC) aided H-NOMA scheme; b) hybrid SIC with non-power adaptation (HSIC-NPA) aided H-NOMA scheme; c) hybrid SIC with power adaptation (HSIC-PA) aided H-NOMA scheme. Theoretical analysis derives closed-form expressions for the probability that H-NOMA schemes underperform conventional OMA. Asymptotic results in the high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) regime are also developed. Simulation results validate our analysis and demonstrate the performance of H-NOMA schemes across different SNR scenarios, providing a theoretical foundation for the deployment of H-NOMA in next-generation wireless systems.
FR-Mamba: Time-Series Physical Field Reconstruction Based on State Space Model
May 21, 2025Abstract:Physical field reconstruction (PFR) aims to predict the state distribution of physical quantities (e.g., velocity, pressure, and temperature) based on limited sensor measurements. It plays a critical role in domains such as fluid dynamics and thermodynamics. However, existing deep learning methods often fail to capture long-range temporal dependencies, resulting in suboptimal performance on time-evolving physical systems. To address this, we propose FR-Mamba, a novel spatiotemporal flow field reconstruction framework based on state space modeling. Specifically, we design a hybrid neural network architecture that combines Fourier Neural Operator (FNO) and State Space Model (SSM) to capture both global spatial features and long-range temporal dependencies. We adopt Mamba, a recently proposed efficient SSM architecture, to model long-range temporal dependencies with linear time complexity. In parallel, the FNO is employed to capture non-local spatial features by leveraging frequency-domain transformations. The spatiotemporal representations extracted by these two components are then fused to reconstruct the full-field distribution of the physical system. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms existing PFR methods in flow field reconstruction tasks, achieving high-accuracy performance on long sequences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge