Yimin Chen
Kimi K2.5: Visual Agentic Intelligence
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:We introduce Kimi K2.5, an open-source multimodal agentic model designed to advance general agentic intelligence. K2.5 emphasizes the joint optimization of text and vision so that two modalities enhance each other. This includes a series of techniques such as joint text-vision pre-training, zero-vision SFT, and joint text-vision reinforcement learning. Building on this multimodal foundation, K2.5 introduces Agent Swarm, a self-directed parallel agent orchestration framework that dynamically decomposes complex tasks into heterogeneous sub-problems and executes them concurrently. Extensive evaluations show that Kimi K2.5 achieves state-of-the-art results across various domains including coding, vision, reasoning, and agentic tasks. Agent Swarm also reduces latency by up to $4.5\times$ over single-agent baselines. We release the post-trained Kimi K2.5 model checkpoint to facilitate future research and real-world applications of agentic intelligence.
REACT-LLM: A Benchmark for Evaluating LLM Integration with Causal Features in Clinical Prognostic Tasks
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) and causal learning each hold strong potential for clinical decision making (CDM). However, their synergy remains poorly understood, largely due to the lack of systematic benchmarks evaluating their integration in clinical risk prediction. In real-world healthcare, identifying features with causal influence on outcomes is crucial for actionable and trustworthy predictions. While recent work highlights LLMs' emerging causal reasoning abilities, there lacks comprehensive benchmarks to assess their causal learning and performance informed by causal features in clinical risk prediction. To address this, we introduce REACT-LLM, a benchmark designed to evaluate whether combining LLMs with causal features can enhance clinical prognostic performance and potentially outperform traditional machine learning (ML) methods. Unlike existing LLM-clinical benchmarks that often focus on a limited set of outcomes, REACT-LLM evaluates 7 clinical outcomes across 2 real-world datasets, comparing 15 prominent LLMs, 6 traditional ML models, and 3 causal discovery (CD) algorithms. Our findings indicate that while LLMs perform reasonably in clinical prognostics, they have not yet outperformed traditional ML models. Integrating causal features derived from CD algorithms into LLMs offers limited performance gains, primarily due to the strict assumptions of many CD methods, which are often violated in complex clinical data. While the direct integration yields limited improvement, our benchmark reveals a more promising synergy.
Kimi-VL Technical Report
Apr 10, 2025
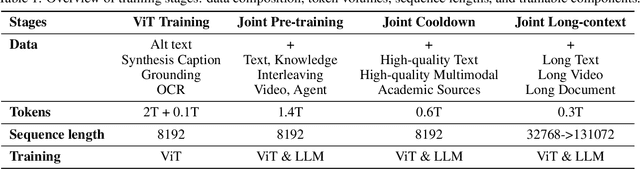
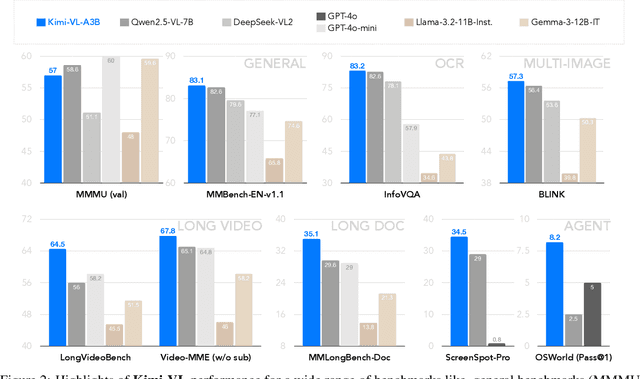
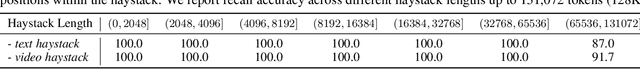
Abstract:We present Kimi-VL, an efficient open-source Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) vision-language model (VLM) that offers advanced multimodal reasoning, long-context understanding, and strong agent capabilities - all while activating only 2.8B parameters in its language decoder (Kimi-VL-A3B). Kimi-VL demonstrates strong performance across challenging domains: as a general-purpose VLM, Kimi-VL excels in multi-turn agent tasks (e.g., OSWorld), matching flagship models. Furthermore, it exhibits remarkable capabilities across diverse challenging vision language tasks, including college-level image and video comprehension, OCR, mathematical reasoning, and multi-image understanding. In comparative evaluations, it effectively competes with cutting-edge efficient VLMs such as GPT-4o-mini, Qwen2.5-VL-7B, and Gemma-3-12B-IT, while surpassing GPT-4o in several key domains. Kimi-VL also advances in processing long contexts and perceiving clearly. With a 128K extended context window, Kimi-VL can process diverse long inputs, achieving impressive scores of 64.5 on LongVideoBench and 35.1 on MMLongBench-Doc. Its native-resolution vision encoder, MoonViT, further allows it to see and understand ultra-high-resolution visual inputs, achieving 83.2 on InfoVQA and 34.5 on ScreenSpot-Pro, while maintaining lower computational cost for common tasks. Building upon Kimi-VL, we introduce an advanced long-thinking variant: Kimi-VL-Thinking. Developed through long chain-of-thought (CoT) supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and reinforcement learning (RL), this model exhibits strong long-horizon reasoning capabilities. It achieves scores of 61.7 on MMMU, 36.8 on MathVision, and 71.3 on MathVista while maintaining the compact 2.8B activated LLM parameters, setting a new standard for efficient multimodal thinking models. Code and models are publicly accessible at https://github.com/MoonshotAI/Kimi-VL.
Buffer is All You Need: Defending Federated Learning against Backdoor Attacks under Non-iids via Buffering
Mar 30, 2025



Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) is a popular paradigm enabling clients to jointly train a global model without sharing raw data. However, FL is known to be vulnerable towards backdoor attacks due to its distributed nature. As participants, attackers can upload model updates that effectively compromise FL. What's worse, existing defenses are mostly designed under independent-and-identically-distributed (iid) settings, hence neglecting the fundamental non-iid characteristic of FL. Here we propose FLBuff for tackling backdoor attacks even under non-iids. The main challenge for such defenses is that non-iids bring benign and malicious updates closer, hence harder to separate. FLBuff is inspired by our insight that non-iids can be modeled as omni-directional expansion in representation space while backdoor attacks as uni-directional. This leads to the key design of FLBuff, i.e., a supervised-contrastive-learning model extracting penultimate-layer representations to create a large in-between buffer layer. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that FLBuff consistently outperforms state-of-the-art defenses.
Two Heads Are Better than One: Model-Weight and Latent-Space Analysis for Federated Learning on Non-iid Data against Poisoning Attacks
Mar 30, 2025



Abstract:Federated Learning is a popular paradigm that enables remote clients to jointly train a global model without sharing their raw data. However, FL has been shown to be vulnerable towards model poisoning attacks due to its distributed nature. Particularly, attackers acting as participants can upload arbitrary model updates that effectively compromise the global model of FL. While extensive research has been focusing on fighting against these attacks, we find that most of them assume data at remote clients are under iid while in practice they are inevitably non-iid. Our benchmark evaluations reveal that existing defenses generally fail to live up to their reputation when applied to various non-iid scenarios. In this paper, we propose a novel approach, GeminiGuard, that aims to address such a significant gap. We design GeminiGuard to be lightweight, versatile, and unsupervised so that it aligns well with the practical requirements of deploying such defenses. The key challenge from non-iids is that they make benign model updates look more similar to malicious ones. GeminiGuard is mainly built on two fundamental observations: (1) existing defenses based on either model-weight analysis or latent-space analysis face limitations in covering different MPAs and non-iid scenarios, and (2) model-weight and latent-space analysis are sufficiently different yet potentially complementary methods as MPA defenses. We hence incorporate a novel model-weight analysis component as well as a custom latent-space analysis component in GeminiGuard, aiming to further enhance its defense performance. We conduct extensive experiments to evaluate our defense across various settings, demonstrating its effectiveness in countering multiple types of untargeted and targeted MPAs, including adaptive ones. Our comprehensive evaluations show that GeminiGuard consistently outperforms SOTA defenses under various settings.
BoBa: Boosting Backdoor Detection through Data Distribution Inference in Federated Learning
Jul 12, 2024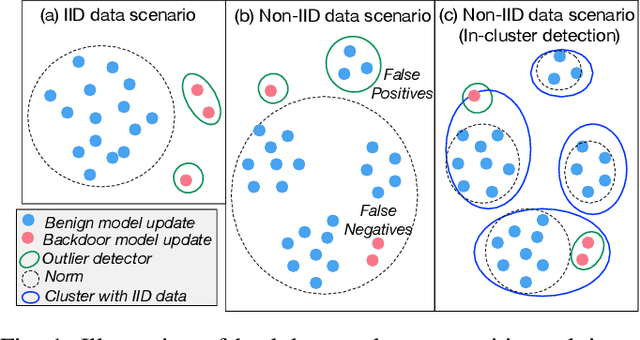
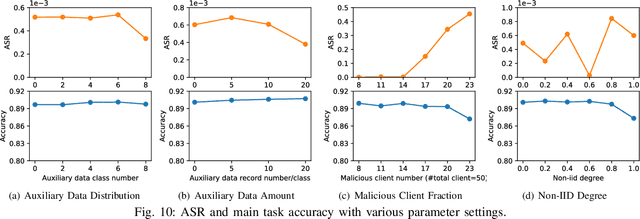
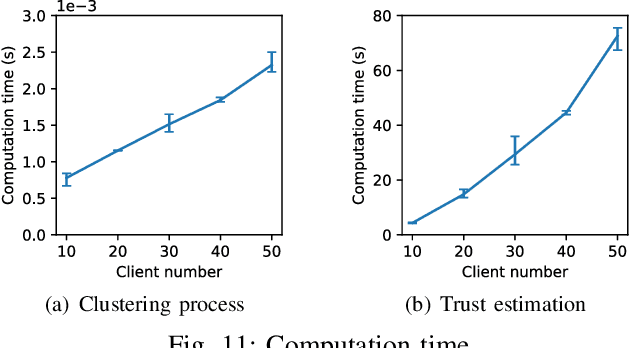
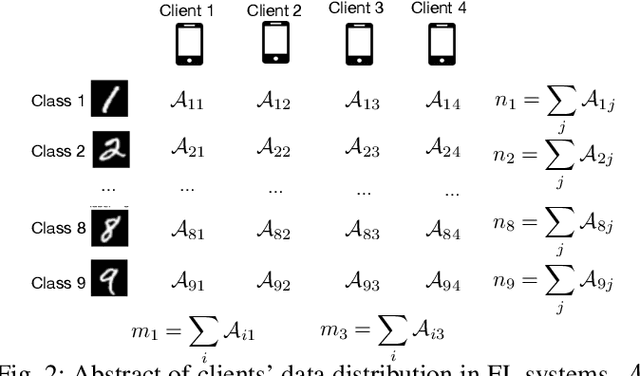
Abstract:Federated learning, while being a promising approach for collaborative model training, is susceptible to poisoning attacks due to its decentralized nature. Backdoor attacks, in particular, have shown remarkable stealthiness, as they selectively compromise predictions for inputs containing triggers. Previous endeavors to detect and mitigate such attacks are based on the Independent and Identically Distributed (IID) data assumption where benign model updates exhibit high-level similarity in multiple feature spaces due to IID data. Thus, outliers are detected as backdoor attacks. Nevertheless, non-IID data presents substantial challenges in backdoor attack detection, as the data variety introduces variance among benign models, making outlier detection-based mechanisms less effective. We propose a novel distribution-aware anomaly detection mechanism, BoBa, to address this problem. In order to differentiate outliers arising from data variety versus backdoor attack, we propose to break down the problem into two steps: clustering clients utilizing their data distribution followed by a voting-based detection. Based on the intuition that clustering and subsequent backdoor detection can drastically benefit from knowing client data distributions, we propose a novel data distribution inference mechanism. To improve detection robustness, we introduce an overlapping clustering method, where each client is associated with multiple clusters, ensuring that the trustworthiness of a model update is assessed collectively by multiple clusters rather than a single cluster. Through extensive evaluations, we demonstrate that BoBa can reduce the attack success rate to lower than 0.001 while maintaining high main task accuracy across various attack strategies and experimental settings.
Revisiting Domain Generalized Stereo Matching Networks from a Feature Consistency Perspective
Mar 21, 2022



Abstract:Despite recent stereo matching networks achieving impressive performance given sufficient training data, they suffer from domain shifts and generalize poorly to unseen domains. We argue that maintaining feature consistency between matching pixels is a vital factor for promoting the generalization capability of stereo matching networks, which has not been adequately considered. Here we address this issue by proposing a simple pixel-wise contrastive learning across the viewpoints. The stereo contrastive feature loss function explicitly constrains the consistency between learned features of matching pixel pairs which are observations of the same 3D points. A stereo selective whitening loss is further introduced to better preserve the stereo feature consistency across domains, which decorrelates stereo features from stereo viewpoint-specific style information. Counter-intuitively, the generalization of feature consistency between two viewpoints in the same scene translates to the generalization of stereo matching performance to unseen domains. Our method is generic in nature as it can be easily embedded into existing stereo networks and does not require access to the samples in the target domain. When trained on synthetic data and generalized to four real-world testing sets, our method achieves superior performance over several state-of-the-art networks.
Uncertainty Estimation via Response Scaling for Pseudo-mask Noise Mitigation in Weakly-supervised Semantic Segmentation
Dec 14, 2021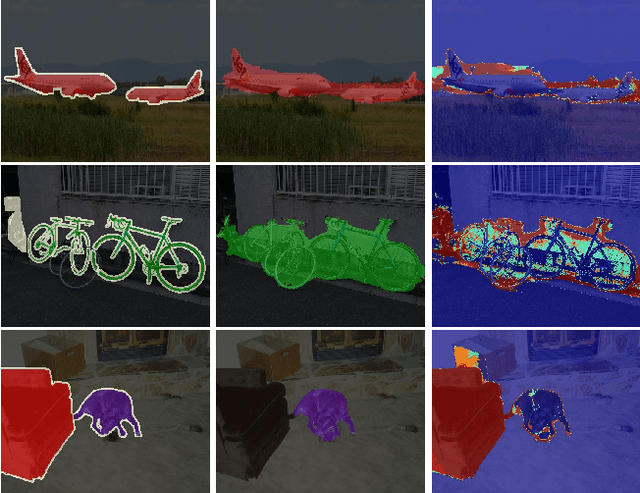
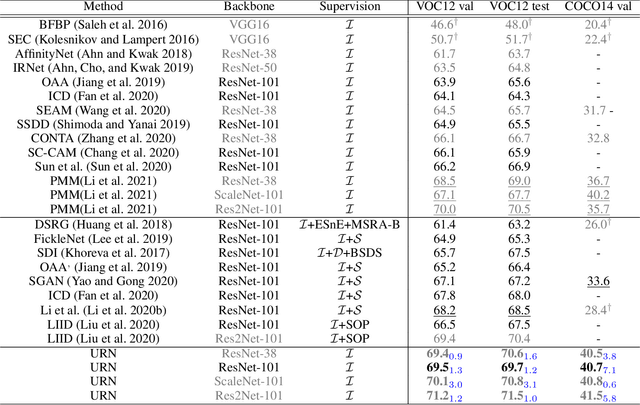
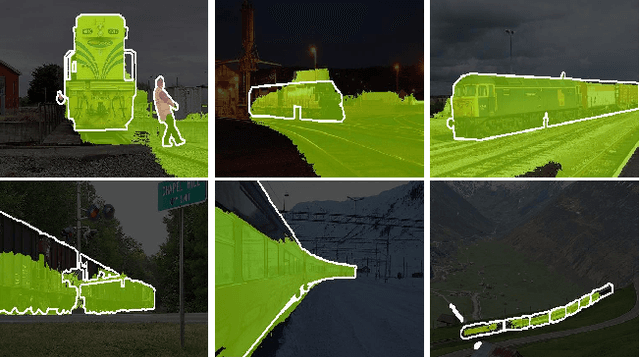

Abstract:Weakly-Supervised Semantic Segmentation (WSSS) segments objects without a heavy burden of dense annotation. While as a price, generated pseudo-masks exist obvious noisy pixels, which result in sub-optimal segmentation models trained over these pseudo-masks. But rare studies notice or work on this problem, even these noisy pixels are inevitable after their improvements on pseudo-mask. So we try to improve WSSS in the aspect of noise mitigation. And we observe that many noisy pixels are of high confidence, especially when the response range is too wide or narrow, presenting an uncertain status. Thus, in this paper, we simulate noisy variations of response by scaling the prediction map multiple times for uncertainty estimation. The uncertainty is then used to weight the segmentation loss to mitigate noisy supervision signals. We call this method URN, abbreviated from Uncertainty estimation via Response scaling for Noise mitigation. Experiments validate the benefits of URN, and our method achieves state-of-the-art results at 71.2% and 41.5% on PASCAL VOC 2012 and MS COCO 2014 respectively, without extra models like saliency detection. Code is available at https://github.com/XMed-Lab/URN.
Pseudo-mask Matters in Weakly-supervised Semantic Segmentation
Sep 07, 2021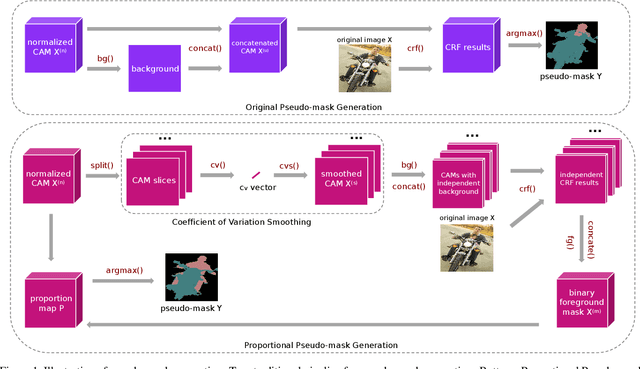

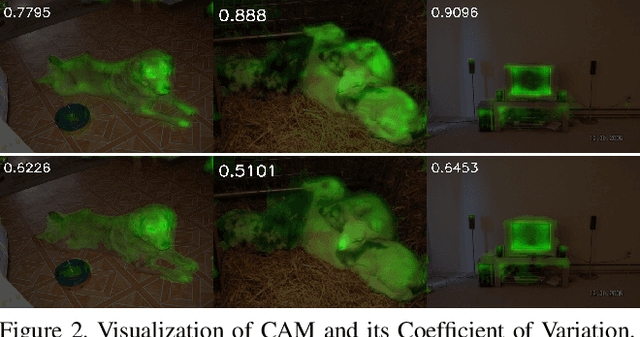

Abstract:Most weakly supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) methods follow the pipeline that generates pseudo-masks initially and trains the segmentation model with the pseudo-masks in fully supervised manner after. However, we find some matters related to the pseudo-masks, including high quality pseudo-masks generation from class activation maps (CAMs), and training with noisy pseudo-mask supervision. For these matters, we propose the following designs to push the performance to new state-of-art: (i) Coefficient of Variation Smoothing to smooth the CAMs adaptively; (ii) Proportional Pseudo-mask Generation to project the expanded CAMs to pseudo-mask based on a new metric indicating the importance of each class on each location, instead of the scores trained from binary classifiers. (iii) Pretended Under-Fitting strategy to suppress the influence of noise in pseudo-mask; (iv) Cyclic Pseudo-mask to boost the pseudo-masks during training of fully supervised semantic segmentation (FSSS). Experiments based on our methods achieve new state-of-art results on two changeling weakly supervised semantic segmentation datasets, pushing the mIoU to 70.0% and 40.2% on PAS-CAL VOC 2012 and MS COCO 2014 respectively. Codes including segmentation framework are released at https://github.com/Eli-YiLi/PMM
Group Fisher Pruning for Practical Network Compression
Aug 02, 2021



Abstract:Network compression has been widely studied since it is able to reduce the memory and computation cost during inference. However, previous methods seldom deal with complicated structures like residual connections, group/depth-wise convolution and feature pyramid network, where channels of multiple layers are coupled and need to be pruned simultaneously. In this paper, we present a general channel pruning approach that can be applied to various complicated structures. Particularly, we propose a layer grouping algorithm to find coupled channels automatically. Then we derive a unified metric based on Fisher information to evaluate the importance of a single channel and coupled channels. Moreover, we find that inference speedup on GPUs is more correlated with the reduction of memory rather than FLOPs, and thus we employ the memory reduction of each channel to normalize the importance. Our method can be used to prune any structures including those with coupled channels. We conduct extensive experiments on various backbones, including the classic ResNet and ResNeXt, mobile-friendly MobileNetV2, and the NAS-based RegNet, both on image classification and object detection which is under-explored. Experimental results validate that our method can effectively prune sophisticated networks, boosting inference speed without sacrificing accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge