Lin Gu
Denoising the Deep Sky: Physics-Based CCD Noise Formation for Astronomical Imaging
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Astronomical imaging remains noise-limited under practical observing constraints, while standard calibration pipelines mainly remove structured artifacts and leave stochastic noise largely unresolved. Learning-based denoising is promising, yet progress is hindered by scarce paired training data and the need for physically interpretable and reproducible models in scientific workflows. We propose a physics-based noise synthesis framework tailored to CCD noise formation. The pipeline models photon shot noise, photo-response non-uniformity, dark-current noise, readout effects, and localized outliers arising from cosmic-ray hits and hot pixels. To obtain low-noise inputs for synthesis, we average multiple unregistered exposures to produce high-SNR bases. Realistic noisy counterparts synthesized from these bases using our noise model enable the construction of abundant paired datasets for supervised learning. We further introduce a real-world dataset across multi-bands acquired with two twin ground-based telescopes, providing paired raw frames and instrument-pipeline calibrated frames, together with calibration data and stacked high-SNR bases for real-world evaluation.
Large-scale EM Benchmark for Multi-Organelle Instance Segmentation in the Wild
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Accurate instance-level segmentation of organelles in electron microscopy (EM) is critical for quantitative analysis of subcellular morphology and inter-organelle interactions. However, current benchmarks, based on small, curated datasets, fail to capture the inherent heterogeneity and large spatial context of in-the-wild EM data, imposing fundamental limitations on current patch-based methods. To address these limitations, we developed a large-scale, multi-source benchmark for multi-organelle instance segmentation, comprising over 100,000 2D EM images across variety cell types and five organelle classes that capture real-world variability. Dataset annotations were generated by our designed connectivity-aware Label Propagation Algorithm (3D LPA) with expert refinement. We further benchmarked several state-of-the-art models, including U-Net, SAM variants, and Mask2Former. Our results show several limitations: current models struggle to generalize across heterogeneous EM data and perform poorly on organelles with global, distributed morphologies (e.g., Endoplasmic Reticulum). These findings underscore the fundamental mismatch between local-context models and the challenge of modeling long-range structural continuity in the presence of real-world variability. The benchmark dataset and labeling tool will be publicly released soon.
RFAssigner: A Generic Label Assignment Strategy for Dense Object Detection
Jan 03, 2026Abstract:Label assignment is a critical component in training dense object detectors. State-of-the-art methods typically assign each training sample a positive and a negative weight, optimizing the assignment scheme during training. However, these strategies often assign an insufficient number of positive samples to small objects, leading to a scale imbalance during training. To address this limitation, we introduce RFAssigner, a novel assignment strategy designed to enhance the multi-scale learning capabilities of dense detectors. RFAssigner first establishes an initial set of positive samples using a point-based prior. It then leverages a Gaussian Receptive Field (GRF) distance to measure the similarity between the GRFs of unassigned candidate locations and the ground-truth objects. Based on this metric, RFAssigner adaptively selects supplementary positive samples from the unassigned pool, promoting a more balanced learning process across object scales. Comprehensive experiments on three datasets with distinct object scale distributions validate the effectiveness and generalizability of our method. Notably, a single FCOS-ResNet-50 detector equipped with RFAssigner achieves state-of-the-art performance across all object scales, consistently outperforming existing strategies without requiring auxiliary modules or heuristics.
RealX3D: A Physically-Degraded 3D Benchmark for Multi-view Visual Restoration and Reconstruction
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:We introduce RealX3D, a real-capture benchmark for multi-view visual restoration and 3D reconstruction under diverse physical degradations. RealX3D groups corruptions into four families, including illumination, scattering, occlusion, and blurring, and captures each at multiple severity levels using a unified acquisition protocol that yields pixel-aligned LQ/GT views. Each scene includes high-resolution capture, RAW images, and dense laser scans, from which we derive world-scale meshes and metric depth. Benchmarking a broad range of optimization-based and feed-forward methods shows substantial degradation in reconstruction quality under physical corruptions, underscoring the fragility of current multi-view pipelines in real-world challenging environments.
Perception-Inspired Color Space Design for Photo White Balance Editing
Dec 11, 2025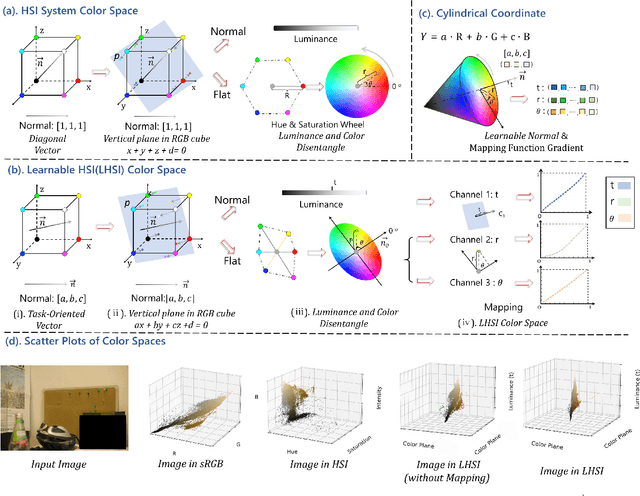
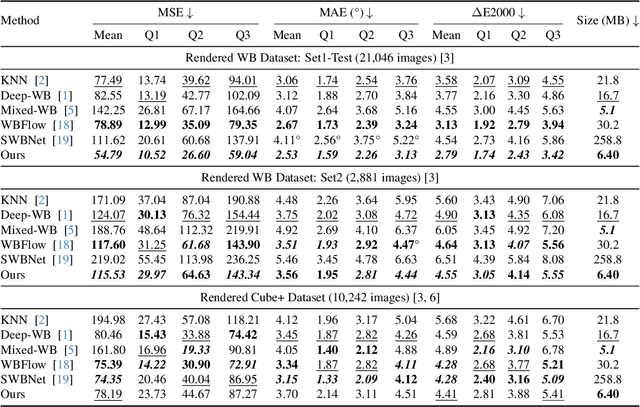
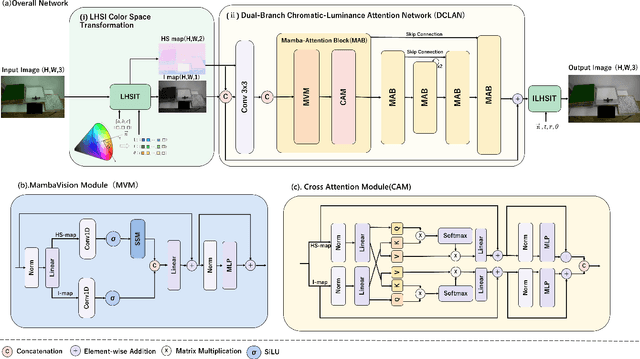
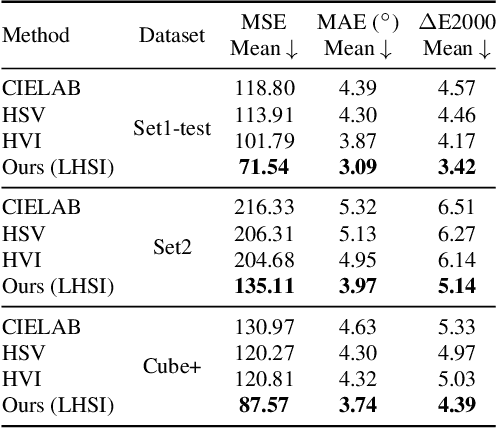
Abstract:White balance (WB) is a key step in the image signal processor (ISP) pipeline that mitigates color casts caused by varying illumination and restores the scene's true colors. Currently, sRGB-based WB editing for post-ISP WB correction is widely used to address color constancy failures in the ISP pipeline when the original camera RAW is unavailable. However, additive color models (e.g., sRGB) are inherently limited by fixed nonlinear transformations and entangled color channels, which often impede their generalization to complex lighting conditions. To address these challenges, we propose a novel framework for WB correction that leverages a perception-inspired Learnable HSI (LHSI) color space. Built upon a cylindrical color model that naturally separates luminance from chromatic components, our framework further introduces dedicated parameters to enhance this disentanglement and learnable mapping to adaptively refine the flexibility. Moreover, a new Mamba-based network is introduced, which is tailored to the characteristics of the proposed LHSI color space. Experimental results on benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of our method, highlighting the potential of perception-inspired color space design in computational photography. The source code is available at https://github.com/YangCheng58/WB_Color_Space.
EGTM: Event-guided Efficient Turbulence Mitigation
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:Turbulence mitigation (TM) aims to remove the stochastic distortions and blurs introduced by atmospheric turbulence into frame cameras. Existing state-of-the-art deep-learning TM methods extract turbulence cues from multiple degraded frames to find the so-called "lucky'', not distorted patch, for "lucky fusion''. However, it requires high-capacity network to learn from coarse-grained turbulence dynamics between synchronous frames with limited frame-rate, thus fall short in computational and storage efficiency. Event cameras, with microsecond-level temporal resolution, have the potential to fundamentally address this bottleneck with efficient sparse and asynchronous imaging mechanism. In light of this, we (i) present the fundamental \textbf{``event-lucky insight''} to reveal the correlation between turbulence distortions and inverse spatiotemporal distribution of event streams. Then, build upon this insight, we (ii) propose a novel EGTM framework that extracts pixel-level reliable turbulence-free guidance from the explicit but noisy turbulent events for temporal lucky fusion. Moreover, we (iii) build the first turbulence data acquisition system to contribute the first real-world event-driven TM dataset. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our approach significantly surpass the existing SOTA TM method by 710 times, 214 times and 224 times in model size, inference latency and model complexity respectively, while achieving the state-of-the-art in restoration quality (+0.94 PSNR and +0.08 SSIM) on our real-world EGTM dataset. This demonstrating the great efficiency merit of introducing event modality into TM task. Demo code and data have been uploaded in supplementary material and will be released once accepted.
ToolGrad: Efficient Tool-use Dataset Generation with Textual "Gradients"
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Prior work synthesizes tool-use LLM datasets by first generating a user query, followed by complex tool-use annotations like DFS. This leads to inevitable annotation failures and low efficiency in data generation. We introduce ToolGrad, an agentic framework that inverts this paradigm. ToolGrad first constructs valid tool-use chains through an iterative process guided by textual "gradients", and then synthesizes corresponding user queries. This "answer-first" approach led to ToolGrad-5k, a dataset generated with more complex tool use, lower cost, and 100% pass rate. Experiments show that models trained on ToolGrad-5k outperform those on expensive baseline datasets and proprietary LLMs, even on OOD benchmarks.
Spatial Frequency Modulation for Semantic Segmentation
Jul 16, 2025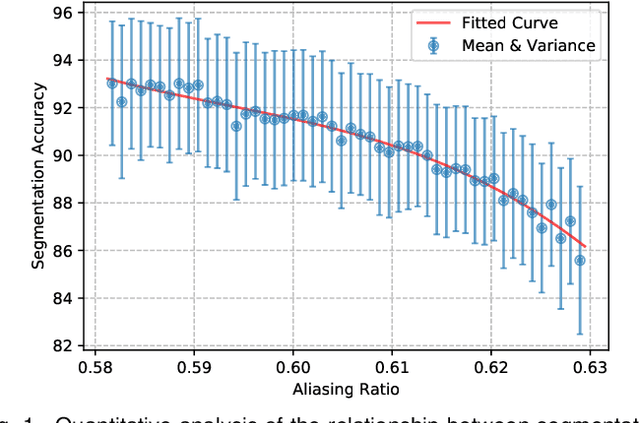
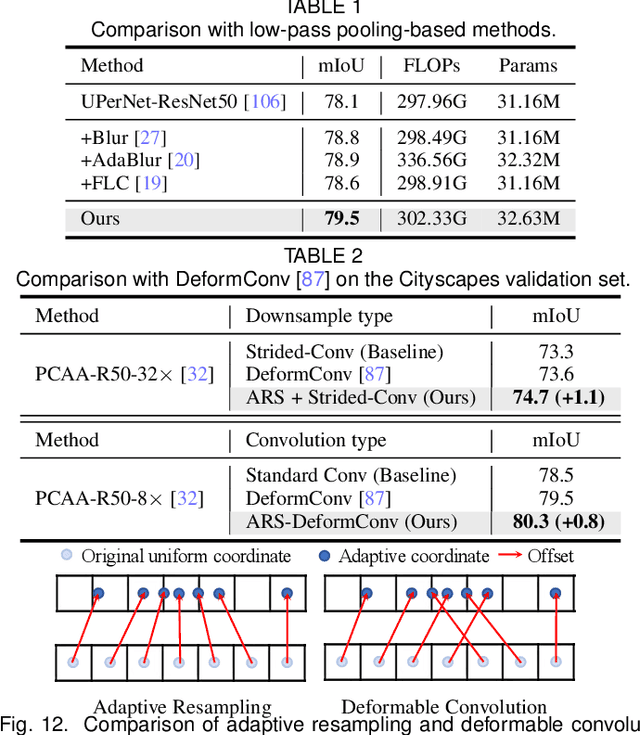
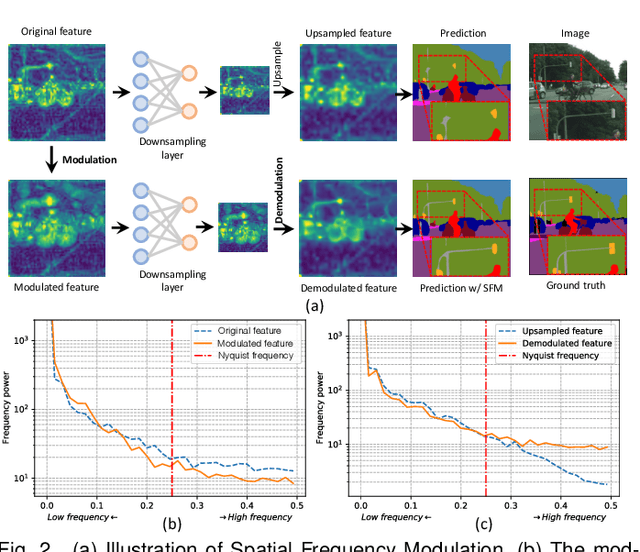
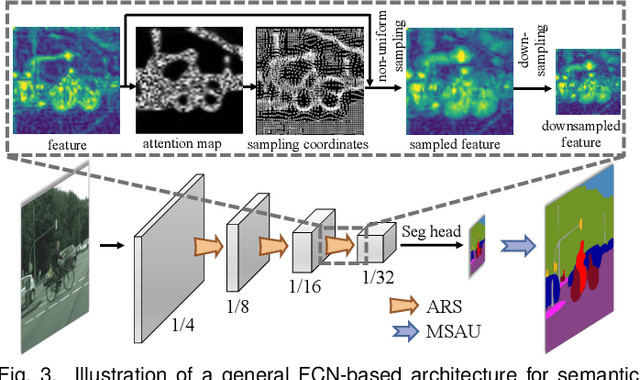
Abstract:High spatial frequency information, including fine details like textures, significantly contributes to the accuracy of semantic segmentation. However, according to the Nyquist-Shannon Sampling Theorem, high-frequency components are vulnerable to aliasing or distortion when propagating through downsampling layers such as strided-convolution. Here, we propose a novel Spatial Frequency Modulation (SFM) that modulates high-frequency features to a lower frequency before downsampling and then demodulates them back during upsampling. Specifically, we implement modulation through adaptive resampling (ARS) and design a lightweight add-on that can densely sample the high-frequency areas to scale up the signal, thereby lowering its frequency in accordance with the Frequency Scaling Property. We also propose Multi-Scale Adaptive Upsampling (MSAU) to demodulate the modulated feature and recover high-frequency information through non-uniform upsampling This module further improves segmentation by explicitly exploiting information interaction between densely and sparsely resampled areas at multiple scales. Both modules can seamlessly integrate with various architectures, extending from convolutional neural networks to transformers. Feature visualization and analysis confirm that our method effectively alleviates aliasing while successfully retaining details after demodulation. Finally, we validate the broad applicability and effectiveness of SFM by extending it to image classification, adversarial robustness, instance segmentation, and panoptic segmentation tasks. The code is available at \href{https://github.com/Linwei-Chen/SFM}{https://github.com/Linwei-Chen/SFM}.
Frequency-Dynamic Attention Modulation for Dense Prediction
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViTs) have significantly advanced computer vision, demonstrating strong performance across various tasks. However, the attention mechanism in ViTs makes each layer function as a low-pass filter, and the stacked-layer architecture in existing transformers suffers from frequency vanishing. This leads to the loss of critical details and textures. We propose a novel, circuit-theory-inspired strategy called Frequency-Dynamic Attention Modulation (FDAM), which can be easily plugged into ViTs. FDAM directly modulates the overall frequency response of ViTs and consists of two techniques: Attention Inversion (AttInv) and Frequency Dynamic Scaling (FreqScale). Since circuit theory uses low-pass filters as fundamental elements, we introduce AttInv, a method that generates complementary high-pass filtering by inverting the low-pass filter in the attention matrix, and dynamically combining the two. We further design FreqScale to weight different frequency components for fine-grained adjustments to the target response function. Through feature similarity analysis and effective rank evaluation, we demonstrate that our approach avoids representation collapse, leading to consistent performance improvements across various models, including SegFormer, DeiT, and MaskDINO. These improvements are evident in tasks such as semantic segmentation, object detection, and instance segmentation. Additionally, we apply our method to remote sensing detection, achieving state-of-the-art results in single-scale settings. The code is available at \href{https://github.com/Linwei-Chen/FDAM}{https://github.com/Linwei-Chen/FDAM}.
Frequency Dynamic Convolution for Dense Image Prediction
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:While Dynamic Convolution (DY-Conv) has shown promising performance by enabling adaptive weight selection through multiple parallel weights combined with an attention mechanism, the frequency response of these weights tends to exhibit high similarity, resulting in high parameter costs but limited adaptability. In this work, we introduce Frequency Dynamic Convolution (FDConv), a novel approach that mitigates these limitations by learning a fixed parameter budget in the Fourier domain. FDConv divides this budget into frequency-based groups with disjoint Fourier indices, enabling the construction of frequency-diverse weights without increasing the parameter cost. To further enhance adaptability, we propose Kernel Spatial Modulation (KSM) and Frequency Band Modulation (FBM). KSM dynamically adjusts the frequency response of each filter at the spatial level, while FBM decomposes weights into distinct frequency bands in the frequency domain and modulates them dynamically based on local content. Extensive experiments on object detection, segmentation, and classification validate the effectiveness of FDConv. We demonstrate that when applied to ResNet-50, FDConv achieves superior performance with a modest increase of +3.6M parameters, outperforming previous methods that require substantial increases in parameter budgets (e.g., CondConv +90M, KW +76.5M). Moreover, FDConv seamlessly integrates into a variety of architectures, including ConvNeXt, Swin-Transformer, offering a flexible and efficient solution for modern vision tasks. The code is made publicly available at https://github.com/Linwei-Chen/FDConv.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge