Paleoinspired Vision: From Exploring Colour Vision Evolution to Inspiring Camera Design
Paper and Code
Dec 27, 2024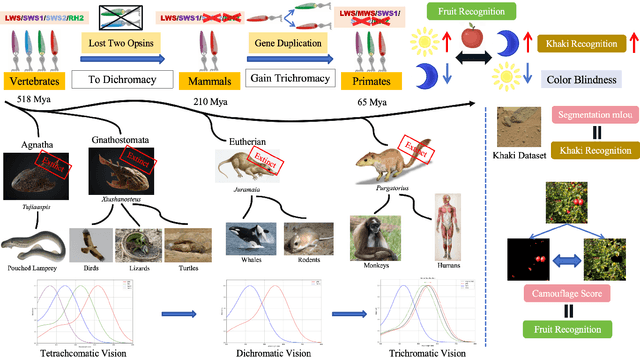
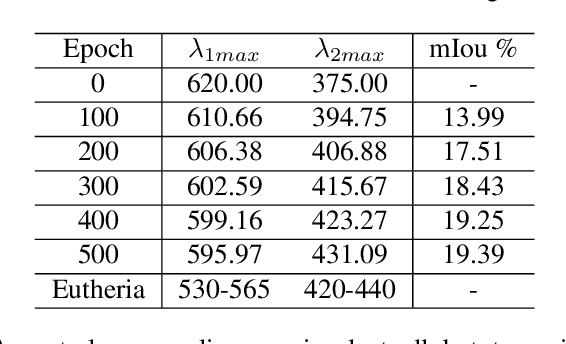
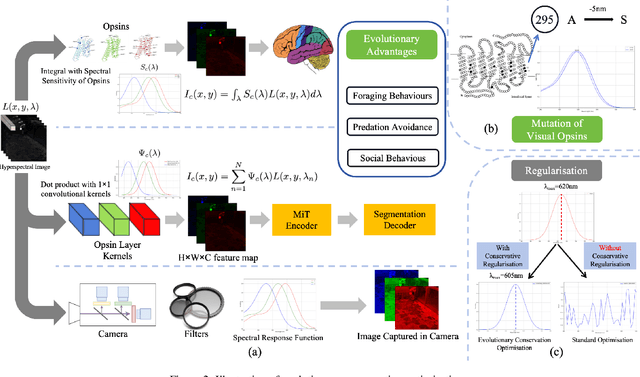
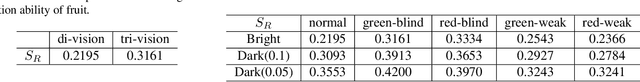
The evolution of colour vision is captivating, as it reveals the adaptive strategies of extinct species while simultaneously inspiring innovations in modern imaging technology. In this study, we present a simplified model of visual transduction in the retina, introducing a novel opsin layer. We quantify evolutionary pressures by measuring machine vision recognition accuracy on colour images shaped by specific opsins. Building on this, we develop an evolutionary conservation optimisation algorithm to reconstruct the spectral sensitivity of opsins, enabling mutation-driven adaptations to to more effectively spot fruits or predators. This model condenses millions of years of evolution within seconds on GPU, providing an experimental framework to test long-standing hypotheses in evolutionary biology , such as vision of early mammals, primate trichromacy from gene duplication, retention of colour blindness, blue-shift of fish rod and multiple rod opsins with bioluminescence. Moreover, the model enables speculative explorations of hypothetical species, such as organisms with eyes adapted to the conditions on Mars. Our findings suggest a minimalist yet effective approach to task-specific camera filter design, optimising the spectral response function to meet application-driven demands. The code will be made publicly available upon acceptance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge