Xiaohan Yu
M$^3$Searcher: Modular Multimodal Information Seeking Agency with Retrieval-Oriented Reasoning
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in DeepResearch-style agents have demonstrated strong capabilities in autonomous information acquisition and synthesize from real-world web environments. However, existing approaches remain fundamentally limited to text modality. Extending autonomous information-seeking agents to multimodal settings introduces critical challenges: the specialization-generalization trade-off that emerges when training models for multimodal tool-use at scale, and the severe scarcity of training data capturing complex, multi-step multimodal search trajectories. To address these challenges, we propose M$^3$Searcher, a modular multimodal information-seeking agent that explicitly decouples information acquisition from answer derivation. M$^3$Searcher is optimized with a retrieval-oriented multi-objective reward that jointly encourages factual accuracy, reasoning soundness, and retrieval fidelity. In addition, we develop MMSearchVQA, a multimodal multi-hop dataset to support retrieval centric RL training. Experimental results demonstrate that M$^3$Searcher outperforms existing approaches, exhibits strong transfer adaptability and effective reasoning in complex multimodal tasks.
SCE-SLAM: Scale-Consistent Monocular SLAM via Scene Coordinate Embeddings
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Monocular visual SLAM enables 3D reconstruction from internet video and autonomous navigation on resource-constrained platforms, yet suffers from scale drift, i.e., the gradual divergence of estimated scale over long sequences. Existing frame-to-frame methods achieve real-time performance through local optimization but accumulate scale drift due to the lack of global constraints among independent windows. To address this, we propose SCE-SLAM, an end-to-end SLAM system that maintains scale consistency through scene coordinate embeddings, which are learned patch-level representations encoding 3D geometric relationships under a canonical scale reference. The framework consists of two key modules: geometry-guided aggregation that leverages 3D spatial proximity to propagate scale information from historical observations through geometry-modulated attention, and scene coordinate bundle adjustment that anchors current estimates to the reference scale through explicit 3D coordinate constraints decoded from the scene coordinate embeddings. Experiments on KITTI, Waymo, and vKITTI demonstrate substantial improvements: our method reduces absolute trajectory error by 8.36m on KITTI compared to the best prior approach, while maintaining 36 FPS and achieving scale consistency across large-scale scenes.
SparseSurf: Sparse-View 3D Gaussian Splatting for Surface Reconstruction
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in optimizing Gaussian Splatting for scene geometry have enabled efficient reconstruction of detailed surfaces from images. However, when input views are sparse, such optimization is prone to overfitting, leading to suboptimal reconstruction quality. Existing approaches address this challenge by employing flattened Gaussian primitives to better fit surface geometry, combined with depth regularization to alleviate geometric ambiguities under limited viewpoints. Nevertheless, the increased anisotropy inherent in flattened Gaussians exacerbates overfitting in sparse-view scenarios, hindering accurate surface fitting and degrading novel view synthesis performance. In this paper, we propose \net{}, a method that reconstructs more accurate and detailed surfaces while preserving high-quality novel view rendering. Our key insight is to introduce Stereo Geometry-Texture Alignment, which bridges rendering quality and geometry estimation, thereby jointly enhancing both surface reconstruction and view synthesis. In addition, we present a Pseudo-Feature Enhanced Geometry Consistency that enforces multi-view geometric consistency by incorporating both training and unseen views, effectively mitigating overfitting caused by sparse supervision. Extensive experiments on the DTU, BlendedMVS, and Mip-NeRF360 datasets demonstrate that our method achieves the state-of-the-art performance.
TableRAG: A Retrieval Augmented Generation Framework for Heterogeneous Document Reasoning
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has demonstrated considerable effectiveness in open-domain question answering. However, when applied to heterogeneous documents, comprising both textual and tabular components, existing RAG approaches exhibit critical limitations. The prevailing practice of flattening tables and chunking strategies disrupts the intrinsic tabular structure, leads to information loss, and undermines the reasoning capabilities of LLMs in multi-hop, global queries. To address these challenges, we propose TableRAG, an hybrid framework that unifies textual understanding and complex manipulations over tabular data. TableRAG iteratively operates in four steps: context-sensitive query decomposition, text retrieval, SQL programming and execution, and compositional intermediate answer generation. We also develop HeteQA, a novel benchmark designed to evaluate the multi-hop heterogeneous reasoning capabilities. Experimental results demonstrate that TableRAG consistently outperforms existing baselines on both public datasets and our HeteQA, establishing a new state-of-the-art for heterogeneous document question answering. We release TableRAG at https://github.com/yxh-y/TableRAG/tree/main.
Improving Medical Visual Representation Learning with Pathological-level Cross-Modal Alignment and Correlation Exploration
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Learning medical visual representations from image-report pairs through joint learning has garnered increasing research attention due to its potential to alleviate the data scarcity problem in the medical domain. The primary challenges stem from the lengthy reports that feature complex discourse relations and semantic pathologies. Previous works have predominantly focused on instance-wise or token-wise cross-modal alignment, often neglecting the importance of pathological-level consistency. This paper presents a novel framework PLACE that promotes the Pathological-Level Alignment and enriches the fine-grained details via Correlation Exploration without additional human annotations. Specifically, we propose a novel pathological-level cross-modal alignment (PCMA) approach to maximize the consistency of pathology observations from both images and reports. To facilitate this, a Visual Pathology Observation Extractor is introduced to extract visual pathological observation representations from localized tokens. The PCMA module operates independently of any external disease annotations, enhancing the generalizability and robustness of our methods. Furthermore, we design a proxy task that enforces the model to identify correlations among image patches, thereby enriching the fine-grained details crucial for various downstream tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed framework achieves new state-of-the-art performance on multiple downstream tasks, including classification, image-to-text retrieval, semantic segmentation, object detection and report generation.
X2C: A Dataset Featuring Nuanced Facial Expressions for Realistic Humanoid Imitation
May 16, 2025Abstract:The ability to imitate realistic facial expressions is essential for humanoid robots engaged in affective human-robot communication. However, the lack of datasets containing diverse humanoid facial expressions with proper annotations hinders progress in realistic humanoid facial expression imitation. To address these challenges, we introduce X2C (Anything to Control), a dataset featuring nuanced facial expressions for realistic humanoid imitation. With X2C, we contribute: 1) a high-quality, high-diversity, large-scale dataset comprising 100,000 (image, control value) pairs. Each image depicts a humanoid robot displaying a diverse range of facial expressions, annotated with 30 control values representing the ground-truth expression configuration; 2) X2CNet, a novel human-to-humanoid facial expression imitation framework that learns the correspondence between nuanced humanoid expressions and their underlying control values from X2C. It enables facial expression imitation in the wild for different human performers, providing a baseline for the imitation task, showcasing the potential value of our dataset; 3) real-world demonstrations on a physical humanoid robot, highlighting its capability to advance realistic humanoid facial expression imitation. Code and Data: https://lipzh5.github.io/X2CNet/
LGD: Leveraging Generative Descriptions for Zero-Shot Referring Image Segmentation
Apr 20, 2025



Abstract:Zero-shot referring image segmentation aims to locate and segment the target region based on a referring expression, with the primary challenge of aligning and matching semantics across visual and textual modalities without training. Previous works address this challenge by utilizing Vision-Language Models and mask proposal networks for region-text matching. However, this paradigm may lead to incorrect target localization due to the inherent ambiguity and diversity of free-form referring expressions. To alleviate this issue, we present LGD (Leveraging Generative Descriptions), a framework that utilizes the advanced language generation capabilities of Multi-Modal Large Language Models to enhance region-text matching performance in Vision-Language Models. Specifically, we first design two kinds of prompts, the attribute prompt and the surrounding prompt, to guide the Multi-Modal Large Language Models in generating descriptions related to the crucial attributes of the referent object and the details of surrounding objects, referred to as attribute description and surrounding description, respectively. Secondly, three visual-text matching scores are introduced to evaluate the similarity between instance-level visual features and textual features, which determines the mask most associated with the referring expression. The proposed method achieves new state-of-the-art performance on three public datasets RefCOCO, RefCOCO+ and RefCOCOg, with maximum improvements of 9.97% in oIoU and 11.29% in mIoU compared to previous methods.
Visual and Semantic Prompt Collaboration for Generalized Zero-Shot Learning
Mar 29, 2025Abstract:Generalized zero-shot learning aims to recognize both seen and unseen classes with the help of semantic information that is shared among different classes. It inevitably requires consistent visual-semantic alignment. Existing approaches fine-tune the visual backbone by seen-class data to obtain semantic-related visual features, which may cause overfitting on seen classes with a limited number of training images. This paper proposes a novel visual and semantic prompt collaboration framework, which utilizes prompt tuning techniques for efficient feature adaptation. Specifically, we design a visual prompt to integrate the visual information for discriminative feature learning and a semantic prompt to integrate the semantic formation for visualsemantic alignment. To achieve effective prompt information integration, we further design a weak prompt fusion mechanism for the shallow layers and a strong prompt fusion mechanism for the deep layers in the network. Through the collaboration of visual and semantic prompts, we can obtain discriminative semantic-related features for generalized zero-shot image recognition. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our framework consistently achieves favorable performance in both conventional zero-shot learning and generalized zero-shot learning benchmarks compared to other state-of-the-art methods.
Unveiling the Potential of Multimodal Retrieval Augmented Generation with Planning
Jan 26, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Retrieval Augmented Generation (MRAG) systems, while promising for enhancing Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), often rely on rigid, single-step retrieval methods. This limitation hinders their ability to effectively address real-world scenarios that demand adaptive information acquisition and query refinement. To overcome this, we introduce the novel task of Multimodal Retrieval Augmented Generation Planning (MRAG Planning), focusing on optimizing MLLM performance while minimizing computational overhead. We present CogPlanner, a versatile framework inspired by human cognitive processes. CogPlanner iteratively refines queries and selects retrieval strategies, enabling both parallel and sequential modeling approaches. To rigorously evaluate MRAG Planning, we introduce CogBench, a new benchmark specifically designed for this task. CogBench facilitates the integration of lightweight CogPlanner with resource-efficient MLLMs. Our experimental findings demonstrate that CogPlanner surpasses existing MRAG baselines, achieving significant improvements in both accuracy and efficiency with minimal computational overhead.
Explainable CTR Prediction via LLM Reasoning
Dec 03, 2024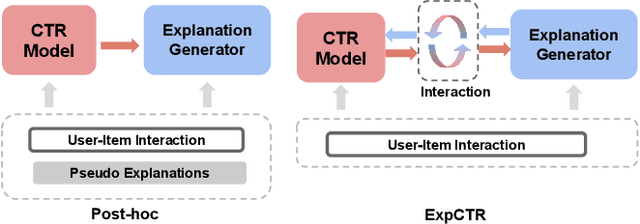
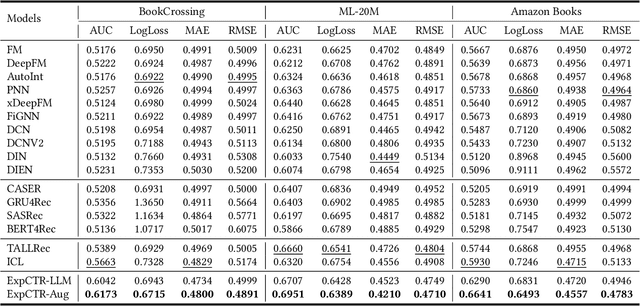
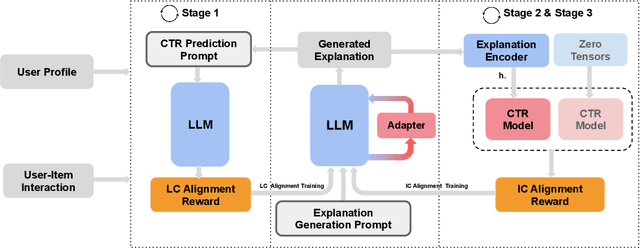
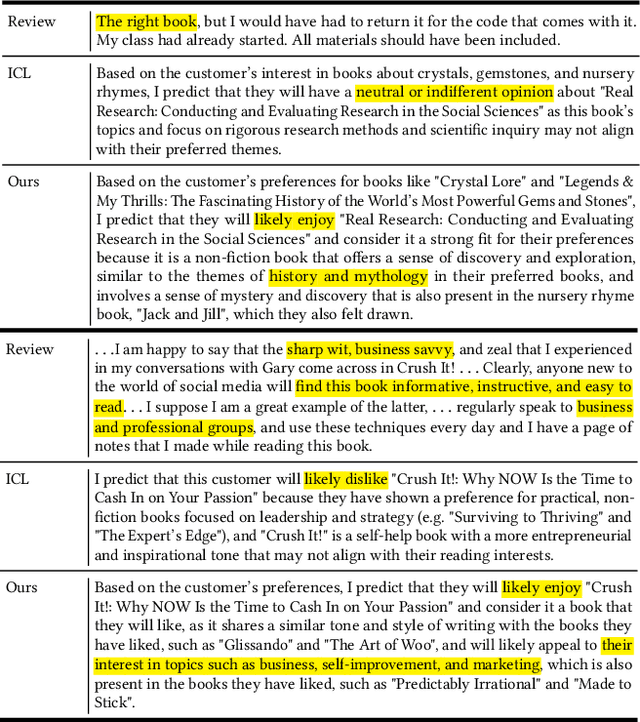
Abstract:Recommendation Systems have become integral to modern user experiences, but lack transparency in their decision-making processes. Existing explainable recommendation methods are hindered by reliance on a post-hoc paradigm, wherein explanation generators are trained independently of the underlying recommender models. This paradigm necessitates substantial human effort in data construction and raises concerns about explanation reliability. In this paper, we present ExpCTR, a novel framework that integrates large language model based explanation generation directly into the CTR prediction process. Inspired by recent advances in reinforcement learning, we employ two carefully designed reward mechanisms, LC alignment, which ensures explanations reflect user intentions, and IC alignment, which maintains consistency with traditional ID-based CTR models. Our approach incorporates an efficient training paradigm with LoRA and a three-stage iterative process. ExpCTR circumvents the need for extensive explanation datasets while fostering synergy between CTR prediction and explanation generation. Experimental results demonstrate that ExpCTR significantly enhances both recommendation accuracy and interpretability across three real-world datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge