Huajie Jiang
Visual and Semantic Prompt Collaboration for Generalized Zero-Shot Learning
Mar 29, 2025Abstract:Generalized zero-shot learning aims to recognize both seen and unseen classes with the help of semantic information that is shared among different classes. It inevitably requires consistent visual-semantic alignment. Existing approaches fine-tune the visual backbone by seen-class data to obtain semantic-related visual features, which may cause overfitting on seen classes with a limited number of training images. This paper proposes a novel visual and semantic prompt collaboration framework, which utilizes prompt tuning techniques for efficient feature adaptation. Specifically, we design a visual prompt to integrate the visual information for discriminative feature learning and a semantic prompt to integrate the semantic formation for visualsemantic alignment. To achieve effective prompt information integration, we further design a weak prompt fusion mechanism for the shallow layers and a strong prompt fusion mechanism for the deep layers in the network. Through the collaboration of visual and semantic prompts, we can obtain discriminative semantic-related features for generalized zero-shot image recognition. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our framework consistently achieves favorable performance in both conventional zero-shot learning and generalized zero-shot learning benchmarks compared to other state-of-the-art methods.
Adapter-Enhanced Semantic Prompting for Continual Learning
Dec 15, 2024



Abstract:Continual learning (CL) enables models to adapt to evolving data streams. A major challenge of CL is catastrophic forgetting, where new knowledge will overwrite previously acquired knowledge. Traditional methods usually retain the past data for replay or add additional branches in the model to learn new knowledge, which has high memory requirements. In this paper, we propose a novel lightweight CL framework, Adapter-Enhanced Semantic Prompting (AESP), which integrates prompt tuning and adapter techniques. Specifically, we design semantic-guided prompts to enhance the generalization ability of visual features and utilize adapters to efficiently fuse the semantic information, aiming to learn more adaptive features for the continual learning task. Furthermore, to choose the right task prompt for feature adaptation, we have developed a novel matching mechanism for prompt selection. Extensive experiments on three CL datasets demonstrate that our approach achieves favorable performance across multiple metrics, showing its potential for advancing CL.
Query-Enhanced Adaptive Semantic Path Reasoning for Inductive Knowledge Graph Completion
Jun 04, 2024Abstract:Conventional Knowledge graph completion (KGC) methods aim to infer missing information in incomplete Knowledge Graphs (KGs) by leveraging existing information, which struggle to perform effectively in scenarios involving emerging entities. Inductive KGC methods can handle the emerging entities and relations in KGs, offering greater dynamic adaptability. While existing inductive KGC methods have achieved some success, they also face challenges, such as susceptibility to noisy structural information during reasoning and difficulty in capturing long-range dependencies in reasoning paths. To address these challenges, this paper proposes the Query-Enhanced Adaptive Semantic Path Reasoning (QASPR) framework, which simultaneously captures both the structural and semantic information of KGs to enhance the inductive KGC task. Specifically, the proposed QASPR employs a query-dependent masking module to adaptively mask noisy structural information while retaining important information closely related to the targets. Additionally, QASPR introduces a global semantic scoring module that evaluates both the individual contributions and the collective impact of nodes along the reasoning path within KGs. The experimental results demonstrate that QASPR achieves state-of-the-art performance.
Unsupervised Coherent Video Cartoonization with Perceptual Motion Consistency
Apr 02, 2022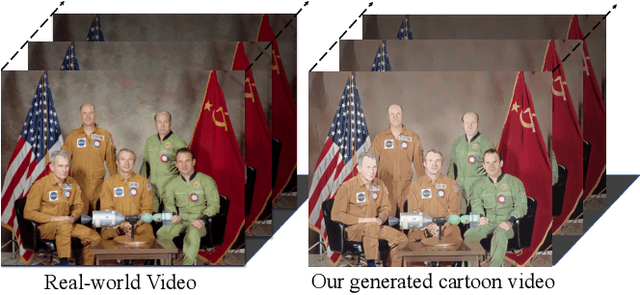
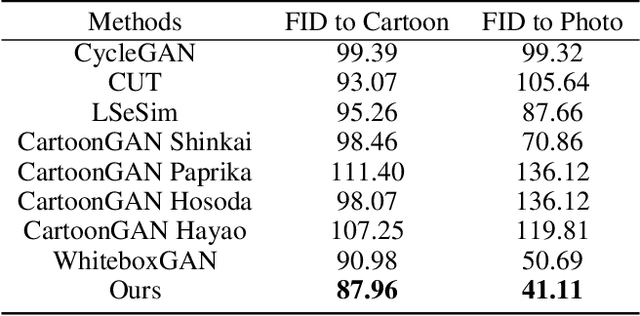

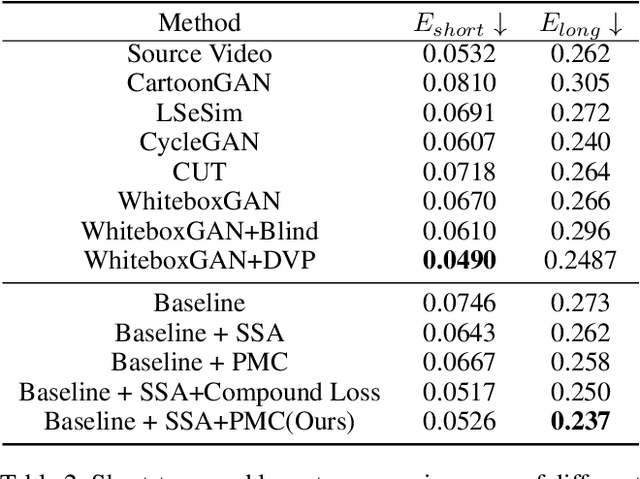
Abstract:In recent years, creative content generations like style transfer and neural photo editing have attracted more and more attention. Among these, cartoonization of real-world scenes has promising applications in entertainment and industry. Different from image translations focusing on improving the style effect of generated images, video cartoonization has additional requirements on the temporal consistency. In this paper, we propose a spatially-adaptive semantic alignment framework with perceptual motion consistency for coherent video cartoonization in an unsupervised manner. The semantic alignment module is designed to restore deformation of semantic structure caused by spatial information lost in the encoder-decoder architecture. Furthermore, we devise the spatio-temporal correlative map as a style-independent, global-aware regularization on the perceptual motion consistency. Deriving from similarity measurement of high-level features in photo and cartoon frames, it captures global semantic information beyond raw pixel-value in optical flow. Besides, the similarity measurement disentangles temporal relationships from domain-specific style properties, which helps regularize the temporal consistency without hurting style effects of cartoon images. Qualitative and quantitative experiments demonstrate our method is able to generate highly stylistic and temporal consistent cartoon videos.
Transferable Contrastive Network for Generalized Zero-Shot Learning
Aug 16, 2019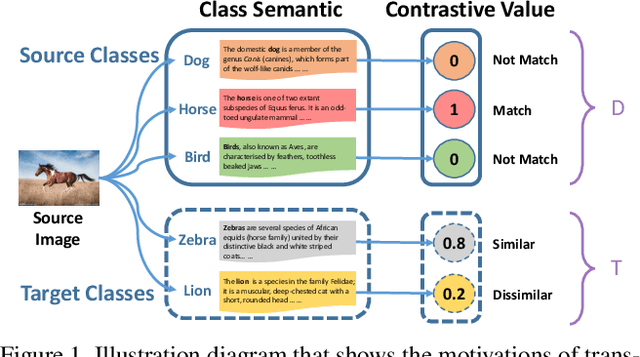
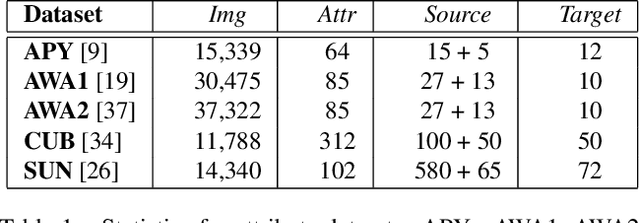
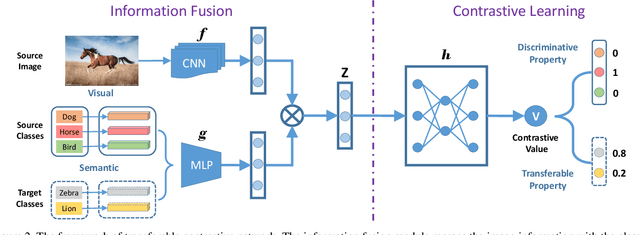
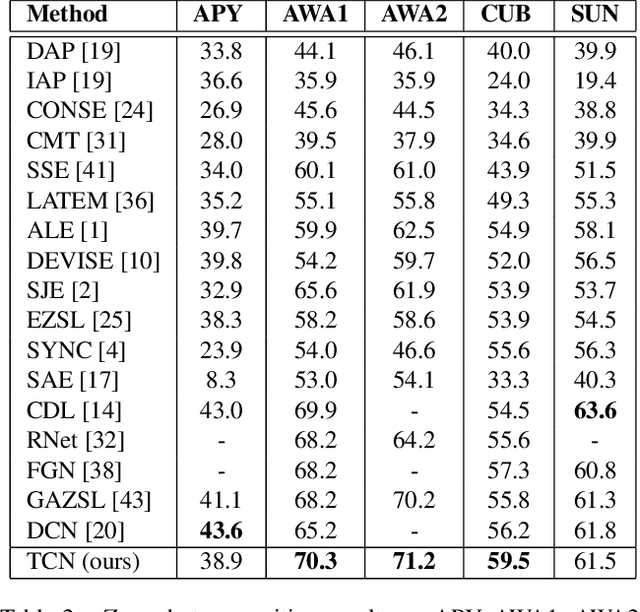
Abstract:Zero-shot learning (ZSL) is a challenging problem that aims to recognize the target categories without seen data, where semantic information is leveraged to transfer knowledge from some source classes. Although ZSL has made great progress in recent years, most existing approaches are easy to overfit the sources classes in generalized zero-shot learning (GZSL) task, which indicates that they learn little knowledge about target classes. To tackle such problem, we propose a novel Transferable Contrastive Network (TCN) that explicitly transfers knowledge from the source classes to the target classes. It automatically contrasts one image with different classes to judge whether they are consistent or not. By exploiting the class similarities to make knowledge transfer from source images to similar target classes, our approach is more robust to recognize the target images. Experiments on five benchmark datasets show the superiority of our approach for GZSL.
Learning Class Prototypes via Structure Alignment for Zero-Shot Recognition
Jul 24, 2018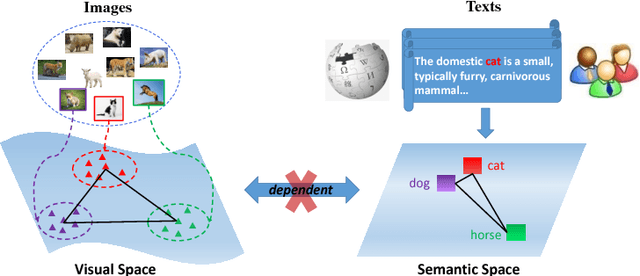
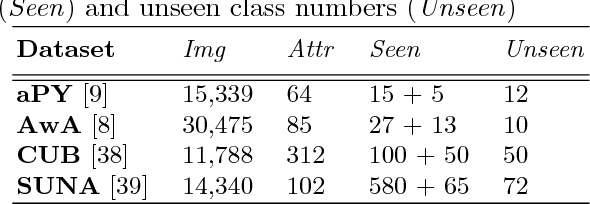
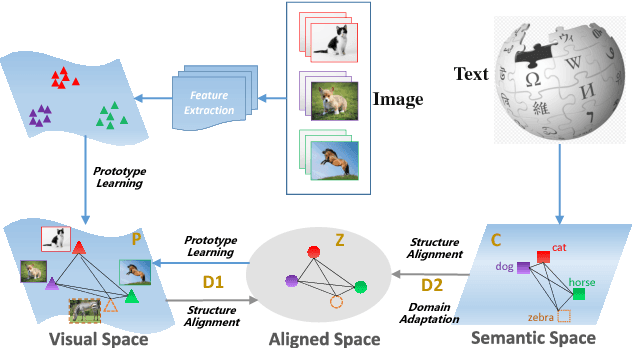
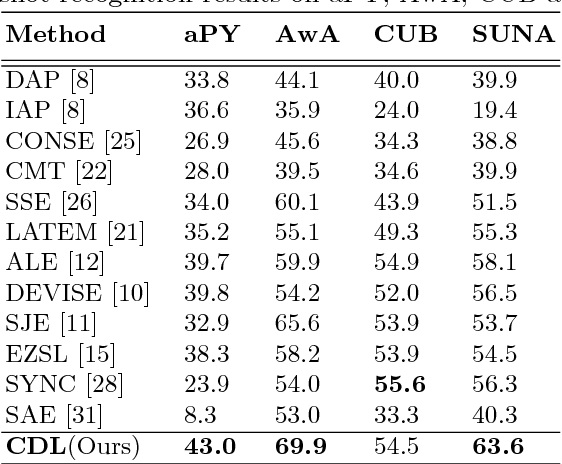
Abstract:Zero-shot learning (ZSL) aims to recognize objects of novel classes without any training samples of specific classes, which is achieved by exploiting the semantic information and auxiliary datasets. Recently most ZSL approaches focus on learning visual-semantic embeddings to transfer knowledge from the auxiliary datasets to the novel classes. However, few works study whether the semantic information is discriminative or not for the recognition task. To tackle such problem, we propose a coupled dictionary learning approach to align the visual-semantic structures using the class prototypes, where the discriminative information lying in the visual space is utilized to improve the less discriminative semantic space. Then, zero-shot recognition can be performed in different spaces by the simple nearest neighbor approach using the learned class prototypes. Extensive experiments on four benchmark datasets show the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge