Ming-Hsuan Yang
Context Forcing: Consistent Autoregressive Video Generation with Long Context
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Recent approaches to real-time long video generation typically employ streaming tuning strategies, attempting to train a long-context student using a short-context (memoryless) teacher. In these frameworks, the student performs long rollouts but receives supervision from a teacher limited to short 5-second windows. This structural discrepancy creates a critical \textbf{student-teacher mismatch}: the teacher's inability to access long-term history prevents it from guiding the student on global temporal dependencies, effectively capping the student's context length. To resolve this, we propose \textbf{Context Forcing}, a novel framework that trains a long-context student via a long-context teacher. By ensuring the teacher is aware of the full generation history, we eliminate the supervision mismatch, enabling the robust training of models capable of long-term consistency. To make this computationally feasible for extreme durations (e.g., 2 minutes), we introduce a context management system that transforms the linearly growing context into a \textbf{Slow-Fast Memory} architecture, significantly reducing visual redundancy. Extensive results demonstrate that our method enables effective context lengths exceeding 20 seconds -- 2 to 10 times longer than state-of-the-art methods like LongLive and Infinite-RoPE. By leveraging this extended context, Context Forcing preserves superior consistency across long durations, surpassing state-of-the-art baselines on various long video evaluation metrics.
Unlocking Prototype Potential: An Efficient Tuning Framework for Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Few-shot class-incremental learning (FSCIL) seeks to continuously learn new classes from very limited samples while preserving previously acquired knowledge. Traditional methods often utilize a frozen pre-trained feature extractor to generate static class prototypes, which suffer from the inherent representation bias of the backbone. While recent prompt-based tuning methods attempt to adapt the backbone via minimal parameter updates, given the constraint of extreme data scarcity, the model's capacity to assimilate novel information and substantively enhance its global discriminative power is inherently limited. In this paper, we propose a novel shift in perspective: freezing the feature extractor while fine-tuning the prototypes. We argue that the primary challenge in FSCIL is not feature acquisition, but rather the optimization of decision regions within a static, high-quality feature space. To this end, we introduce an efficient prototype fine-tuning framework that evolves static centroids into dynamic, learnable components. The framework employs a dual-calibration method consisting of class-specific and task-aware offsets. These components function synergistically to improve the discriminative capacity of prototypes for ongoing incremental classes. Extensive results demonstrate that our method attains superior performance across multiple benchmarks while requiring minimal learnable parameters.
ProjDevBench: Benchmarking AI Coding Agents on End-to-End Project Development
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Recent coding agents can generate complete codebases from simple prompts, yet existing evaluations focus on issue-level bug fixing and lag behind end-to-end development. We introduce ProjDevBench, an end-to-end benchmark that provides project requirements to coding agents and evaluates the resulting repositories. Combining Online Judge (OJ) testing with LLM-assisted code review, the benchmark evaluates agents on (1) system architecture design, (2) functional correctness, and (3) iterative solution refinement. We curate 20 programming problems across 8 categories, covering both concept-oriented tasks and real-world application scenarios, and evaluate six coding agents built on different LLM backends. Our evaluation reports an overall acceptance rate of 27.38%: agents handle basic functionality and data structures but struggle with complex system design, time complexity optimization, and resource management. Our benchmark is available at https://github.com/zsworld6/projdevbench.
Prism: Efficient Test-Time Scaling via Hierarchical Search and Self-Verification for Discrete Diffusion Language Models
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Inference-time compute has re-emerged as a practical way to improve LLM reasoning. Most test-time scaling (TTS) algorithms rely on autoregressive decoding, which is ill-suited to discrete diffusion language models (dLLMs) due to their parallel decoding over the entire sequence. As a result, developing effective and efficient TTS methods to unlock dLLMs' full generative potential remains an underexplored challenge. To address this, we propose Prism (Pruning, Remasking, and Integrated Self-verification Method), an efficient TTS framework for dLLMs that (i) performs Hierarchical Trajectory Search (HTS) which dynamically prunes and reallocates compute in an early-to-mid denoising window, (ii) introduces Local branching with partial remasking to explore diverse implementations while preserving high-confidence tokens, and (iii) replaces external verifiers with Self-Verified Feedback (SVF) obtained via self-evaluation prompts on intermediate completions. Across four mathematical reasoning and code generation benchmarks on three dLLMs, including LLaDA 8B Instruct, Dream 7B Instruct, and LLaDA 2.0-mini, our Prism achieves a favorable performance-efficiency trade-off, matching best-of-N performance with substantially fewer function evaluations (NFE). The code is released at https://github.com/viiika/Prism.
Multimodal Visual Surrogate Compression for Alzheimer's Disease Classification
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:High-dimensional structural MRI (sMRI) images are widely used for Alzheimer's Disease (AD) diagnosis. Most existing methods for sMRI representation learning rely on 3D architectures (e.g., 3D CNNs), slice-wise feature extraction with late aggregation, or apply training-free feature extractions using 2D foundation models (e.g., DINO). However, these three paradigms suffer from high computational cost, loss of cross-slice relations, and limited ability to extract discriminative features, respectively. To address these challenges, we propose Multimodal Visual Surrogate Compression (MVSC). It learns to compress and adapt large 3D sMRI volumes into compact 2D features, termed as visual surrogates, which are better aligned with frozen 2D foundation models to extract powerful representations for final AD classification. MVSC has two key components: a Volume Context Encoder that captures global cross-slice context under textual guidance, and an Adaptive Slice Fusion module that aggregates slice-level information in a text-enhanced, patch-wise manner. Extensive experiments on three large-scale Alzheimer's disease benchmarks demonstrate our MVSC performs favourably on both binary and multi-class classification tasks compared against state-of-the-art methods.
Edit3r: Instant 3D Scene Editing from Sparse Unposed Images
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:We present Edit3r, a feed-forward framework that reconstructs and edits 3D scenes in a single pass from unposed, view-inconsistent, instruction-edited images. Unlike prior methods requiring per-scene optimization, Edit3r directly predicts instruction-aligned 3D edits, enabling fast and photorealistic rendering without optimization or pose estimation. A key challenge in training such a model lies in the absence of multi-view consistent edited images for supervision. We address this with (i) a SAM2-based recoloring strategy that generates reliable, cross-view-consistent supervision, and (ii) an asymmetric input strategy that pairs a recolored reference view with raw auxiliary views, encouraging the network to fuse and align disparate observations. At inference, our model effectively handles images edited by 2D methods such as InstructPix2Pix, despite not being exposed to such edits during training. For large-scale quantitative evaluation, we introduce DL3DV-Edit-Bench, a benchmark built on the DL3DV test split, featuring 20 diverse scenes, 4 edit types and 100 edits in total. Comprehensive quantitative and qualitative results show that Edit3r achieves superior semantic alignment and enhanced 3D consistency compared to recent baselines, while operating at significantly higher inference speed, making it promising for real-time 3D editing applications.
KnowVal: A Knowledge-Augmented and Value-Guided Autonomous Driving System
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Visual-language reasoning, driving knowledge, and value alignment are essential for advanced autonomous driving systems. However, existing approaches largely rely on data-driven learning, making it difficult to capture the complex logic underlying decision-making through imitation or limited reinforcement rewards. To address this, we propose KnowVal, a new autonomous driving system that enables visual-language reasoning through the synergistic integration of open-world perception and knowledge retrieval. Specifically, we construct a comprehensive driving knowledge graph that encodes traffic laws, defensive driving principles, and ethical norms, complemented by an efficient LLM-based retrieval mechanism tailored for driving scenarios. Furthermore, we develop a human-preference dataset and train a Value Model to guide interpretable, value-aligned trajectory assessment. Experimental results show that our method substantially improves planning performance while remaining compatible with existing architectures. Notably, KnowVal achieves the lowest collision rate on nuScenes and state-of-the-art results on Bench2Drive.
Depth Any Panoramas: A Foundation Model for Panoramic Depth Estimation
Dec 18, 2025
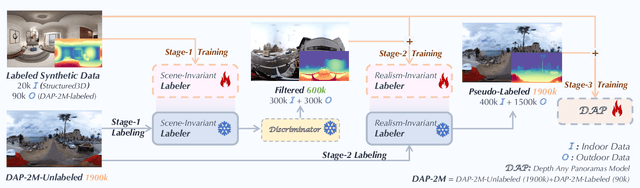

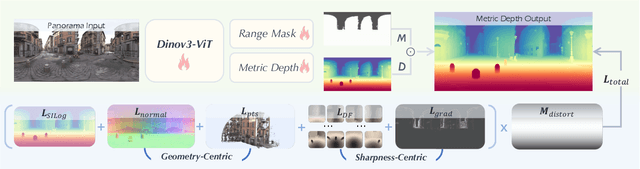
Abstract:In this work, we present a panoramic metric depth foundation model that generalizes across diverse scene distances. We explore a data-in-the-loop paradigm from the view of both data construction and framework design. We collect a large-scale dataset by combining public datasets, high-quality synthetic data from our UE5 simulator and text-to-image models, and real panoramic images from the web. To reduce domain gaps between indoor/outdoor and synthetic/real data, we introduce a three-stage pseudo-label curation pipeline to generate reliable ground truth for unlabeled images. For the model, we adopt DINOv3-Large as the backbone for its strong pre-trained generalization, and introduce a plug-and-play range mask head, sharpness-centric optimization, and geometry-centric optimization to improve robustness to varying distances and enforce geometric consistency across views. Experiments on multiple benchmarks (e.g., Stanford2D3D, Matterport3D, and Deep360) demonstrate strong performance and zero-shot generalization, with particularly robust and stable metric predictions in diverse real-world scenes. The project page can be found at: \href{https://insta360-research-team.github.io/DAP_website/} {https://insta360-research-team.github.io/DAP\_website/}
Image Diffusion Preview with Consistency Solver
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:The slow inference process of image diffusion models significantly degrades interactive user experiences. To address this, we introduce Diffusion Preview, a novel paradigm employing rapid, low-step sampling to generate preliminary outputs for user evaluation, deferring full-step refinement until the preview is deemed satisfactory. Existing acceleration methods, including training-free solvers and post-training distillation, struggle to deliver high-quality previews or ensure consistency between previews and final outputs. We propose ConsistencySolver derived from general linear multistep methods, a lightweight, trainable high-order solver optimized via Reinforcement Learning, that enhances preview quality and consistency. Experimental results demonstrate that ConsistencySolver significantly improves generation quality and consistency in low-step scenarios, making it ideal for efficient preview-and-refine workflows. Notably, it achieves FID scores on-par with Multistep DPM-Solver using 47% fewer steps, while outperforming distillation baselines. Furthermore, user studies indicate our approach reduces overall user interaction time by nearly 50% while maintaining generation quality. Code is available at https://github.com/G-U-N/consolver.
Teaching Prompts to Coordinate: Hierarchical Layer-Grouped Prompt Tuning for Continual Learning
Nov 15, 2025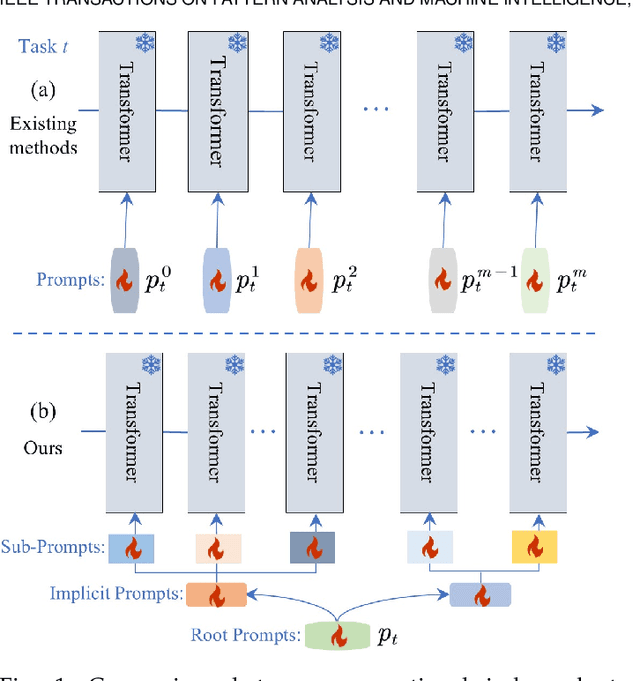
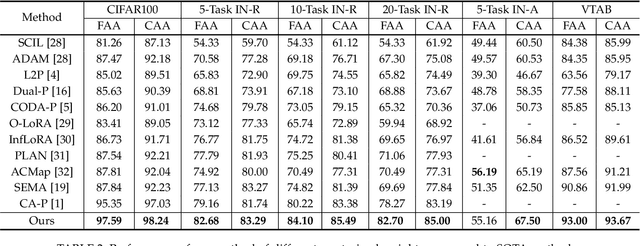
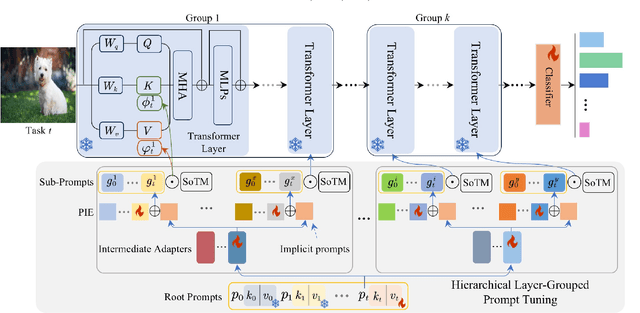
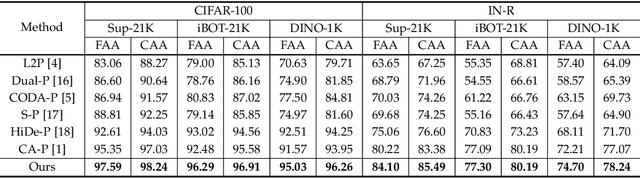
Abstract:Prompt-based continual learning methods fine-tune only a small set of additional learnable parameters while keeping the pre-trained model's parameters frozen. It enables efficient adaptation to new tasks while mitigating the risk of catastrophic forgetting. These methods typically attach one independent task-specific prompt to each layer of pre-trained models to locally modulate its features, ensuring that the layer's representation aligns with the requirements of the new task. However, although introducing learnable prompts independently at each layer provides high flexibility for adapting to new tasks, this overly flexible tuning could make certain layers susceptible to unnecessary updates. As all prompts till the current task are added together as a final prompt for all seen tasks, the model may easily overwrite feature representations essential to previous tasks, which increases the risk of catastrophic forgetting. To address this issue, we propose a novel hierarchical layer-grouped prompt tuning method for continual learning. It improves model stability in two ways: (i) Layers in the same group share roughly the same prompts, which are adjusted by position encoding. This helps preserve the intrinsic feature relationships and propagation pathways of the pre-trained model within each group. (ii) It utilizes a single task-specific root prompt to learn to generate sub-prompts for each layer group. In this way, all sub-prompts are conditioned on the same root prompt, enhancing their synergy and reducing independence. Extensive experiments across four benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves favorable performance compared with several state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge