Xiaoshui Huang
Masked Clustering Prediction for Unsupervised Point Cloud Pre-training
Aug 12, 2025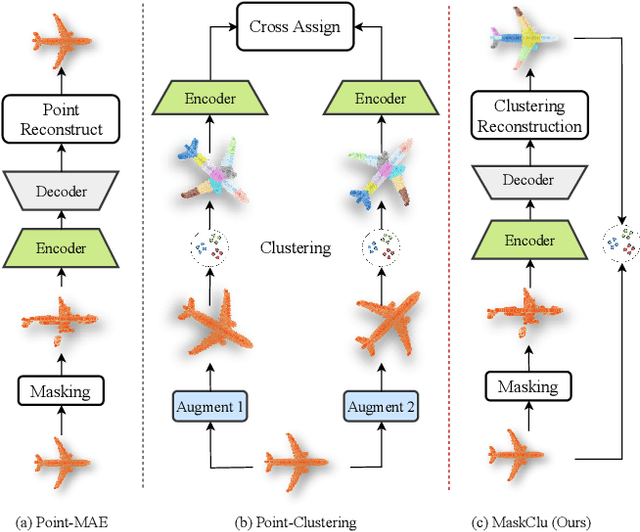
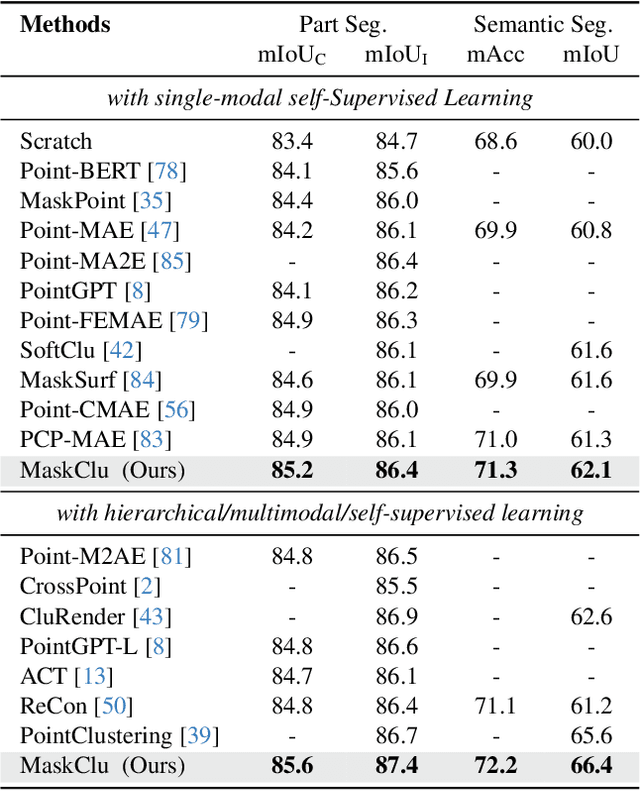
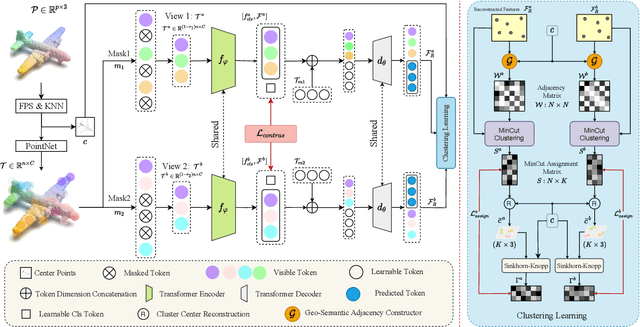
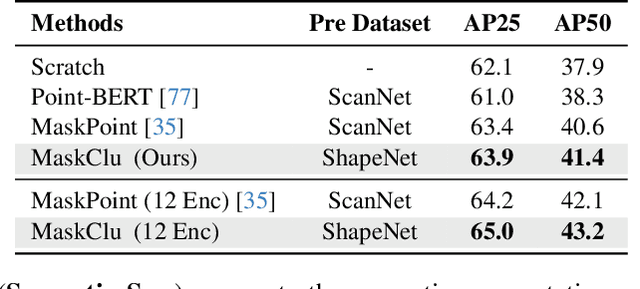
Abstract:Vision transformers (ViTs) have recently been widely applied to 3D point cloud understanding, with masked autoencoding as the predominant pre-training paradigm. However, the challenge of learning dense and informative semantic features from point clouds via standard ViTs remains underexplored. We propose MaskClu, a novel unsupervised pre-training method for ViTs on 3D point clouds that integrates masked point modeling with clustering-based learning. MaskClu is designed to reconstruct both cluster assignments and cluster centers from masked point clouds, thus encouraging the model to capture dense semantic information. Additionally, we introduce a global contrastive learning mechanism that enhances instance-level feature learning by contrasting different masked views of the same point cloud. By jointly optimizing these complementary objectives, i.e., dense semantic reconstruction, and instance-level contrastive learning. MaskClu enables ViTs to learn richer and more semantically meaningful representations from 3D point clouds. We validate the effectiveness of our method via multiple 3D tasks, including part segmentation, semantic segmentation, object detection, and classification, where MaskClu sets new competitive results. The code and models will be released at:https://github.com/Amazingren/maskclu.
Self-Supervised and Generalizable Tokenization for CLIP-Based 3D Understanding
May 24, 2025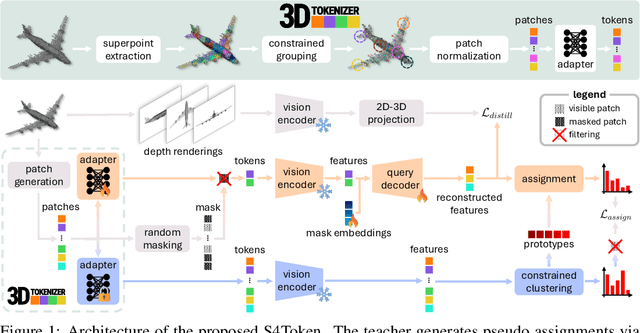

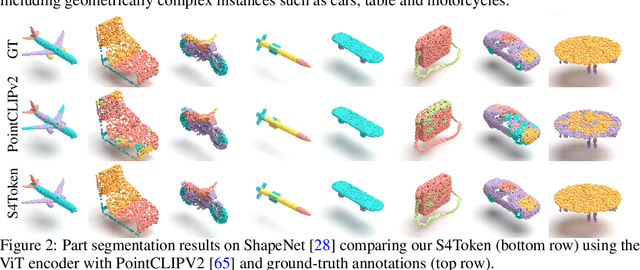
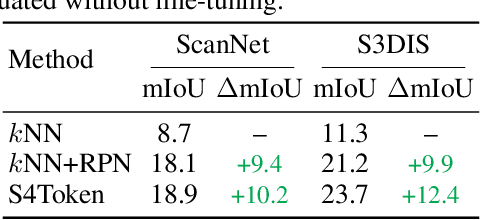
Abstract:Vision-language models like CLIP can offer a promising foundation for 3D scene understanding when extended with 3D tokenizers. However, standard approaches, such as k-nearest neighbor or radius-based tokenization, struggle with cross-domain generalization due to sensitivity to dataset-specific spatial scales. We present a universal 3D tokenizer designed for scale-invariant representation learning with a frozen CLIP backbone. We show that combining superpoint-based grouping with coordinate scale normalization consistently outperforms conventional methods through extensive experimental analysis. Specifically, we introduce S4Token, a tokenization pipeline that produces semantically-informed tokens regardless of scene scale. Our tokenizer is trained without annotations using masked point modeling and clustering-based objectives, along with cross-modal distillation to align 3D tokens with 2D multi-view image features. For dense prediction tasks, we propose a superpoint-level feature propagation module to recover point-level detail from sparse tokens.
BRepFormer: Transformer-Based B-rep Geometric Feature Recognition
Apr 10, 2025



Abstract:Recognizing geometric features on B-rep models is a cornerstone technique for multimedia content-based retrieval and has been widely applied in intelligent manufacturing. However, previous research often merely focused on Machining Feature Recognition (MFR), falling short in effectively capturing the intricate topological and geometric characteristics of complex geometry features. In this paper, we propose BRepFormer, a novel transformer-based model to recognize both machining feature and complex CAD models' features. BRepFormer encodes and fuses the geometric and topological features of the models. Afterwards, BRepFormer utilizes a transformer architecture for feature propagation and a recognition head to identify geometry features. During each iteration of the transformer, we incorporate a bias that combines edge features and topology features to reinforce geometric constraints on each face. In addition, we also proposed a dataset named Complex B-rep Feature Dataset (CBF), comprising 20,000 B-rep models. By covering more complex B-rep models, it is better aligned with industrial applications. The experimental results demonstrate that BRepFormer achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on the MFInstSeg, MFTRCAD, and our CBF datasets.
MeshCraft: Exploring Efficient and Controllable Mesh Generation with Flow-based DiTs
Mar 29, 2025Abstract:In the domain of 3D content creation, achieving optimal mesh topology through AI models has long been a pursuit for 3D artists. Previous methods, such as MeshGPT, have explored the generation of ready-to-use 3D objects via mesh auto-regressive techniques. While these methods produce visually impressive results, their reliance on token-by-token predictions in the auto-regressive process leads to several significant limitations. These include extremely slow generation speeds and an uncontrollable number of mesh faces. In this paper, we introduce MeshCraft, a novel framework for efficient and controllable mesh generation, which leverages continuous spatial diffusion to generate discrete triangle faces. Specifically, MeshCraft consists of two core components: 1) a transformer-based VAE that encodes raw meshes into continuous face-level tokens and decodes them back to the original meshes, and 2) a flow-based diffusion transformer conditioned on the number of faces, enabling the generation of high-quality 3D meshes with a predefined number of faces. By utilizing the diffusion model for the simultaneous generation of the entire mesh topology, MeshCraft achieves high-fidelity mesh generation at significantly faster speeds compared to auto-regressive methods. Specifically, MeshCraft can generate an 800-face mesh in just 3.2 seconds (35$\times$ faster than existing baselines). Extensive experiments demonstrate that MeshCraft outperforms state-of-the-art techniques in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations on ShapeNet dataset and demonstrates superior performance on Objaverse dataset. Moreover, it integrates seamlessly with existing conditional guidance strategies, showcasing its potential to relieve artists from the time-consuming manual work involved in mesh creation.
PSReg: Prior-guided Sparse Mixture of Experts for Point Cloud Registration
Jan 14, 2025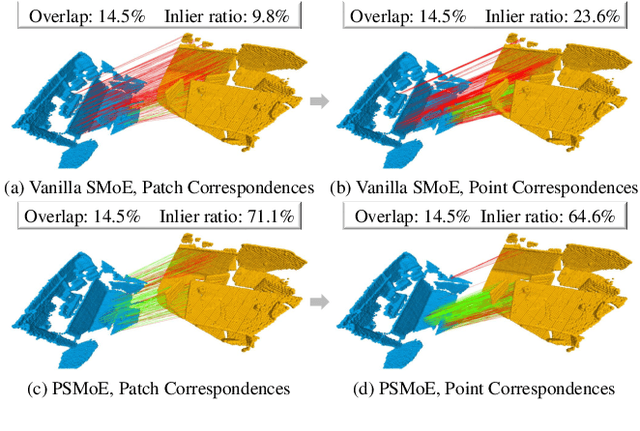
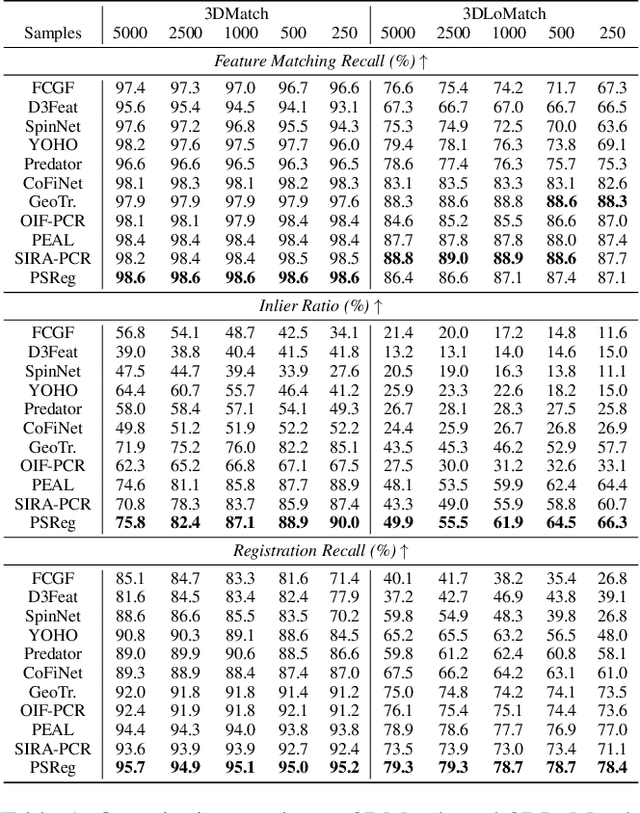
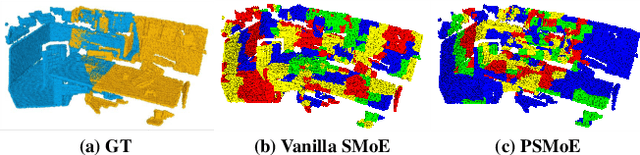
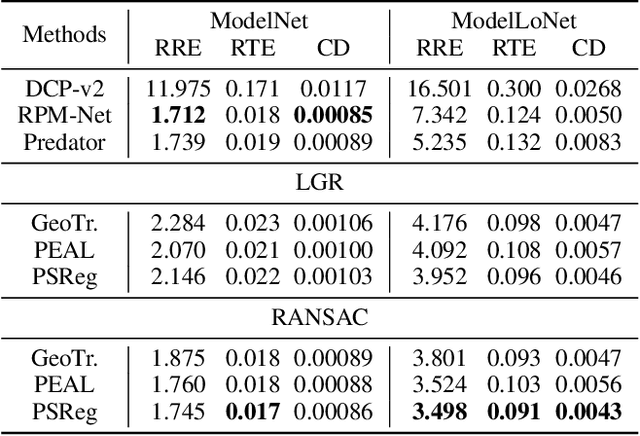
Abstract:The discriminative feature is crucial for point cloud registration. Recent methods improve the feature discriminative by distinguishing between non-overlapping and overlapping region points. However, they still face challenges in distinguishing the ambiguous structures in the overlapping regions. Therefore, the ambiguous features they extracted resulted in a significant number of outlier matches from overlapping regions. To solve this problem, we propose a prior-guided SMoE-based registration method to improve the feature distinctiveness by dispatching the potential correspondences to the same experts. Specifically, we propose a prior-guided SMoE module by fusing prior overlap and potential correspondence embeddings for routing, assigning tokens to the most suitable experts for processing. In addition, we propose a registration framework by a specific combination of Transformer layer and prior-guided SMoE module. The proposed method not only pays attention to the importance of locating the overlapping areas of point clouds, but also commits to finding more accurate correspondences in overlapping areas. Our extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, achieving state-of-the-art registration recall (95.7\%/79.3\%) on the 3DMatch/3DLoMatch benchmark. Moreover, we also test the performance on ModelNet40 and demonstrate excellent performance.
Synergizing Motion and Appearance: Multi-Scale Compensatory Codebooks for Talking Head Video Generation
Dec 01, 2024



Abstract:Talking head video generation aims to generate a realistic talking head video that preserves the person's identity from a source image and the motion from a driving video. Despite the promising progress made in the field, it remains a challenging and critical problem to generate videos with accurate poses and fine-grained facial details simultaneously. Essentially, facial motion is often highly complex to model precisely, and the one-shot source face image cannot provide sufficient appearance guidance during generation due to dynamic pose changes. To tackle the problem, we propose to jointly learn motion and appearance codebooks and perform multi-scale codebook compensation to effectively refine both the facial motion conditions and appearance features for talking face image decoding. Specifically, the designed multi-scale motion and appearance codebooks are learned simultaneously in a unified framework to store representative global facial motion flow and appearance patterns. Then, we present a novel multi-scale motion and appearance compensation module, which utilizes a transformer-based codebook retrieval strategy to query complementary information from the two codebooks for joint motion and appearance compensation. The entire process produces motion flows of greater flexibility and appearance features with fewer distortions across different scales, resulting in a high-quality talking head video generation framework. Extensive experiments on various benchmarks validate the effectiveness of our approach and demonstrate superior generation results from both qualitative and quantitative perspectives when compared to state-of-the-art competitors.
An End-to-End Robust Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation Network with Single-Step Conditional Diffusion Models
Nov 25, 2024



Abstract:Existing conditional Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPMs) with a Noise-Conditional Framework (NCF) remain challenging for 3D scene understanding tasks, as the complex geometric details in scenes increase the difficulty of fitting the gradients of the data distribution (the scores) from semantic labels. This also results in longer training and inference time for DDPMs compared to non-DDPMs. From a different perspective, we delve deeply into the model paradigm dominated by the Conditional Network. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end robust semantic \textbf{Seg}mentation \textbf{Net}work based on a \textbf{C}onditional-Noise Framework (CNF) of D\textbf{D}PMs, named \textbf{CDSegNet}. Specifically, CDSegNet models the Noise Network (NN) as a learnable noise-feature generator. This enables the Conditional Network (CN) to understand 3D scene semantics under multi-level feature perturbations, enhancing the generalization in unseen scenes. Meanwhile, benefiting from the noise system of DDPMs, CDSegNet exhibits strong noise and sparsity robustness in experiments. Moreover, thanks to CNF, CDSegNet can generate the semantic labels in a single-step inference like non-DDPMs, due to avoiding directly fitting the scores from semantic labels in the dominant network of CDSegNet. On public indoor and outdoor benchmarks, CDSegNet significantly outperforms existing methods, achieving state-of-the-art performance.
DATAP-SfM: Dynamic-Aware Tracking Any Point for Robust Structure from Motion in the Wild
Nov 20, 2024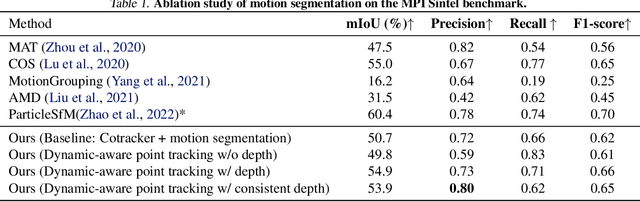
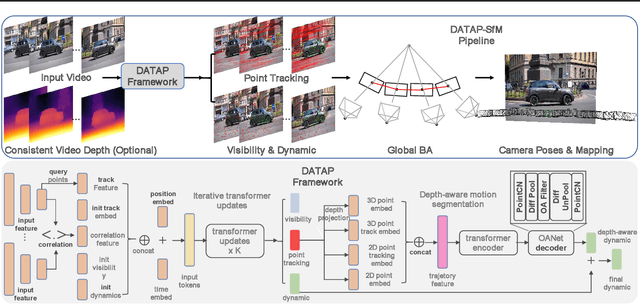
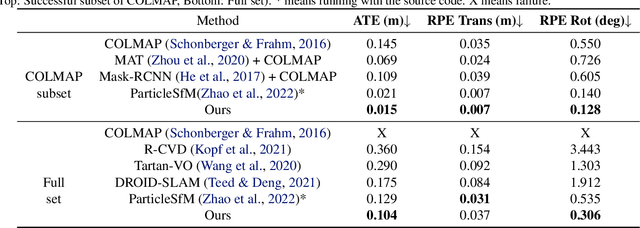
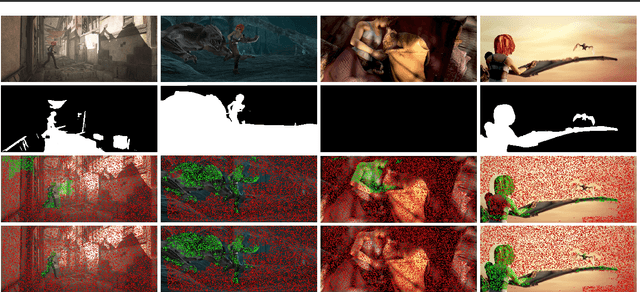
Abstract:This paper proposes a concise, elegant, and robust pipeline to estimate smooth camera trajectories and obtain dense point clouds for casual videos in the wild. Traditional frameworks, such as ParticleSfM~\cite{zhao2022particlesfm}, address this problem by sequentially computing the optical flow between adjacent frames to obtain point trajectories. They then remove dynamic trajectories through motion segmentation and perform global bundle adjustment. However, the process of estimating optical flow between two adjacent frames and chaining the matches can introduce cumulative errors. Additionally, motion segmentation combined with single-view depth estimation often faces challenges related to scale ambiguity. To tackle these challenges, we propose a dynamic-aware tracking any point (DATAP) method that leverages consistent video depth and point tracking. Specifically, our DATAP addresses these issues by estimating dense point tracking across the video sequence and predicting the visibility and dynamics of each point. By incorporating the consistent video depth prior, the performance of motion segmentation is enhanced. With the integration of DATAP, it becomes possible to estimate and optimize all camera poses simultaneously by performing global bundle adjustments for point tracking classified as static and visible, rather than relying on incremental camera registration. Extensive experiments on dynamic sequences, e.g., Sintel and TUM RGBD dynamic sequences, and on the wild video, e.g., DAVIS, demonstrate that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance in terms of camera pose estimation even in complex dynamic challenge scenes.
DiffPano: Scalable and Consistent Text to Panorama Generation with Spherical Epipolar-Aware Diffusion
Oct 31, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion-based methods have achieved remarkable achievements in 2D image or 3D object generation, however, the generation of 3D scenes and even $360^{\circ}$ images remains constrained, due to the limited number of scene datasets, the complexity of 3D scenes themselves, and the difficulty of generating consistent multi-view images. To address these issues, we first establish a large-scale panoramic video-text dataset containing millions of consecutive panoramic keyframes with corresponding panoramic depths, camera poses, and text descriptions. Then, we propose a novel text-driven panoramic generation framework, termed DiffPano, to achieve scalable, consistent, and diverse panoramic scene generation. Specifically, benefiting from the powerful generative capabilities of stable diffusion, we fine-tune a single-view text-to-panorama diffusion model with LoRA on the established panoramic video-text dataset. We further design a spherical epipolar-aware multi-view diffusion model to ensure the multi-view consistency of the generated panoramic images. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DiffPano can generate scalable, consistent, and diverse panoramic images with given unseen text descriptions and camera poses.
LLaMA-Berry: Pairwise Optimization for O1-like Olympiad-Level Mathematical Reasoning
Oct 03, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents an advanced mathematical problem-solving framework, LLaMA-Berry, for enhancing the mathematical reasoning ability of Large Language Models (LLMs). The framework combines Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) with iterative Self-Refine to optimize the reasoning path and utilizes a pairwise reward model to evaluate different paths globally. By leveraging the self-critic and rewriting capabilities of LLMs, Self-Refine applied to MCTS (SR-MCTS) overcomes the inefficiencies and limitations of conventional step-wise and greedy search algorithms by fostering a more efficient exploration of solution spaces. Pairwise Preference Reward Model~(PPRM), inspired by Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), is then used to model pairwise preferences between solutions, utilizing an Enhanced Borda Count (EBC) method to synthesize these preferences into a global ranking score to find better answers. This approach addresses the challenges of scoring variability and non-independent distributions in mathematical reasoning tasks. The framework has been tested on general and advanced benchmarks, showing superior performance in terms of search efficiency and problem-solving capability compared to existing methods like ToT and rStar, particularly in complex Olympiad-level benchmarks, including GPQA, AIME24 and AMC23.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge