Guofeng Zhang
LightCity: An Urban Dataset for Outdoor Inverse Rendering and Reconstruction under Multi-illumination Conditions
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Inverse rendering in urban scenes is pivotal for applications like autonomous driving and digital twins. Yet, it faces significant challenges due to complex illumination conditions, including multi-illumination and indirect light and shadow effects. However, the effects of these challenges on intrinsic decomposition and 3D reconstruction have not been explored due to the lack of appropriate datasets. In this paper, we present LightCity, a novel high-quality synthetic urban dataset featuring diverse illumination conditions with realistic indirect light and shadow effects. LightCity encompasses over 300 sky maps with highly controllable illumination, varying scales with street-level and aerial perspectives over 50K images, and rich properties such as depth, normal, material components, light and indirect light, etc. Besides, we leverage LightCity to benchmark three fundamental tasks in the urban environments and conduct a comprehensive analysis of these benchmarks, laying a robust foundation for advancing related research.
FaceSnap: Enhanced ID-fidelity Network for Tuning-free Portrait Customization
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Benefiting from the significant advancements in text-to-image diffusion models, research in personalized image generation, particularly customized portrait generation, has also made great strides recently. However, existing methods either require time-consuming fine-tuning and lack generalizability or fail to achieve high fidelity in facial details. To address these issues, we propose FaceSnap, a novel method based on Stable Diffusion (SD) that requires only a single reference image and produces extremely consistent results in a single inference stage. This method is plug-and-play and can be easily extended to different SD models. Specifically, we design a new Facial Attribute Mixer that can extract comprehensive fused information from both low-level specific features and high-level abstract features, providing better guidance for image generation. We also introduce a Landmark Predictor that maintains reference identity across landmarks with different poses, providing diverse yet detailed spatial control conditions for image generation. Then we use an ID-preserving module to inject these into the UNet. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach performs remarkably in personalized and customized portrait generation, surpassing other state-of-the-art methods in this domain.
One-Shot Refiner: Boosting Feed-forward Novel View Synthesis via One-Step Diffusion
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:We present a novel framework for high-fidelity novel view synthesis (NVS) from sparse images, addressing key limitations in recent feed-forward 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) methods built on Vision Transformer (ViT) backbones. While ViT-based pipelines offer strong geometric priors, they are often constrained by low-resolution inputs due to computational costs. Moreover, existing generative enhancement methods tend to be 3D-agnostic, resulting in inconsistent structures across views, especially in unseen regions. To overcome these challenges, we design a Dual-Domain Detail Perception Module, which enables handling high-resolution images without being limited by the ViT backbone, and endows Gaussians with additional features to store high-frequency details. We develop a feature-guided diffusion network, which can preserve high-frequency details during the restoration process. We introduce a unified training strategy that enables joint optimization of the ViT-based geometric backbone and the diffusion-based refinement module. Experiments demonstrate that our method can maintain superior generation quality across multiple datasets.
CoProSketch: Controllable and Progressive Sketch Generation with Diffusion Model
Apr 11, 2025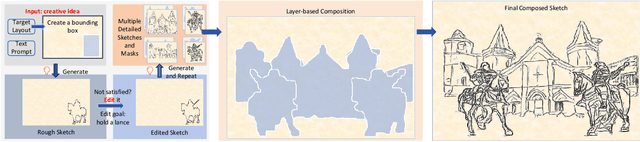
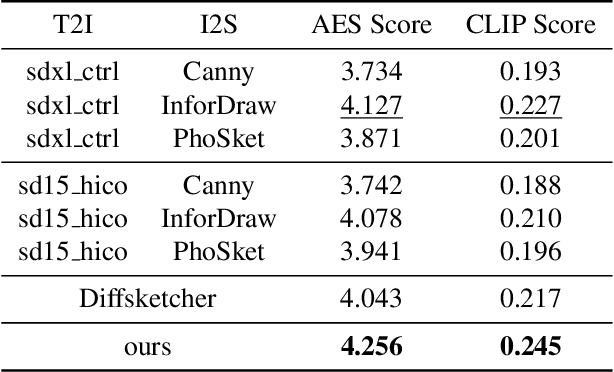
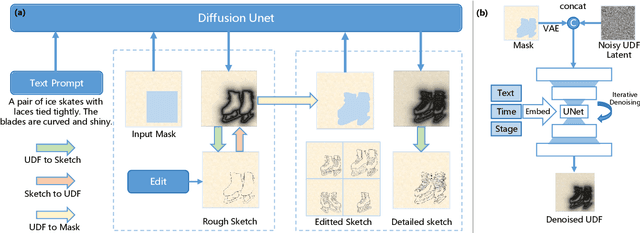
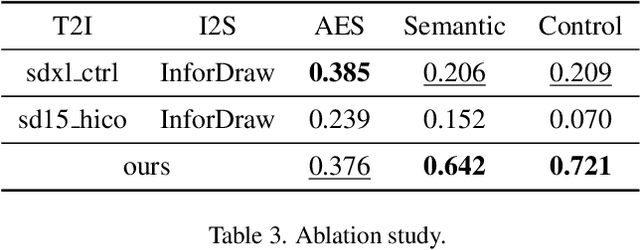
Abstract:Sketches serve as fundamental blueprints in artistic creation because sketch editing is easier and more intuitive than pixel-level RGB image editing for painting artists, yet sketch generation remains unexplored despite advancements in generative models. We propose a novel framework CoProSketch, providing prominent controllability and details for sketch generation with diffusion models. A straightforward method is fine-tuning a pretrained image generation diffusion model with binarized sketch images. However, we find that the diffusion models fail to generate clear binary images, which makes the produced sketches chaotic. We thus propose to represent the sketches by unsigned distance field (UDF), which is continuous and can be easily decoded to sketches through a lightweight network. With CoProSketch, users generate a rough sketch from a bounding box and a text prompt. The rough sketch can be manually edited and fed back into the model for iterative refinement and will be decoded to a detailed sketch as the final result. Additionally, we curate the first large-scale text-sketch paired dataset as the training data. Experiments demonstrate superior semantic consistency and controllability over baselines, offering a practical solution for integrating user feedback into generative workflows.
Free360: Layered Gaussian Splatting for Unbounded 360-Degree View Synthesis from Extremely Sparse and Unposed Views
Mar 31, 2025

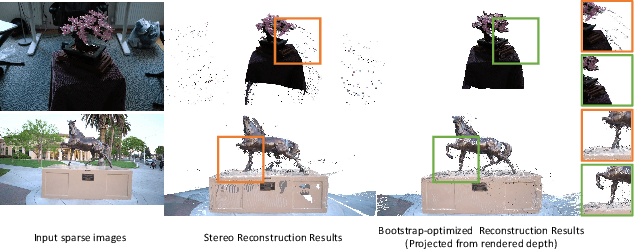

Abstract:Neural rendering has demonstrated remarkable success in high-quality 3D neural reconstruction and novel view synthesis with dense input views and accurate poses. However, applying it to extremely sparse, unposed views in unbounded 360{\deg} scenes remains a challenging problem. In this paper, we propose a novel neural rendering framework to accomplish the unposed and extremely sparse-view 3D reconstruction in unbounded 360{\deg} scenes. To resolve the spatial ambiguity inherent in unbounded scenes with sparse input views, we propose a layered Gaussian-based representation to effectively model the scene with distinct spatial layers. By employing a dense stereo reconstruction model to recover coarse geometry, we introduce a layer-specific bootstrap optimization to refine the noise and fill occluded regions in the reconstruction. Furthermore, we propose an iterative fusion of reconstruction and generation alongside an uncertainty-aware training approach to facilitate mutual conditioning and enhancement between these two processes. Comprehensive experiments show that our approach outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in terms of rendering quality and surface reconstruction accuracy. Project page: https://zju3dv.github.io/free360/
DINeMo: Learning Neural Mesh Models with no 3D Annotations
Mar 26, 2025



Abstract:Category-level 3D/6D pose estimation is a crucial step towards comprehensive 3D scene understanding, which would enable a broad range of applications in robotics and embodied AI. Recent works explored neural mesh models that approach a range of 2D and 3D tasks from an analysis-by-synthesis perspective. Despite the largely enhanced robustness to partial occlusion and domain shifts, these methods depended heavily on 3D annotations for part-contrastive learning, which confines them to a narrow set of categories and hinders efficient scaling. In this work, we present DINeMo, a novel neural mesh model that is trained with no 3D annotations by leveraging pseudo-correspondence obtained from large visual foundation models. We adopt a bidirectional pseudo-correspondence generation method, which produce pseudo correspondence utilize both local appearance features and global context information. Experimental results on car datasets demonstrate that our DINeMo outperforms previous zero- and few-shot 3D pose estimation by a wide margin, narrowing the gap with fully-supervised methods by 67.3%. Our DINeMo also scales effectively and efficiently when incorporating more unlabeled images during training, which demonstrate the advantages over supervised learning methods that rely on 3D annotations. Our project page is available at https://analysis-by-synthesis.github.io/DINeMo/.
From Sparse to Dense: Camera Relocalization with Scene-Specific Detector from Feature Gaussian Splatting
Mar 25, 2025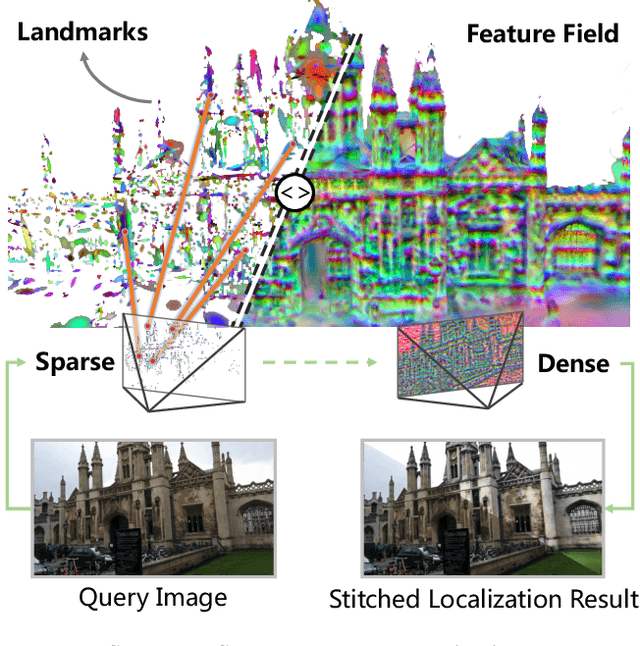
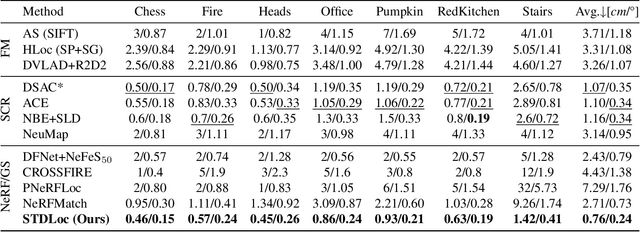
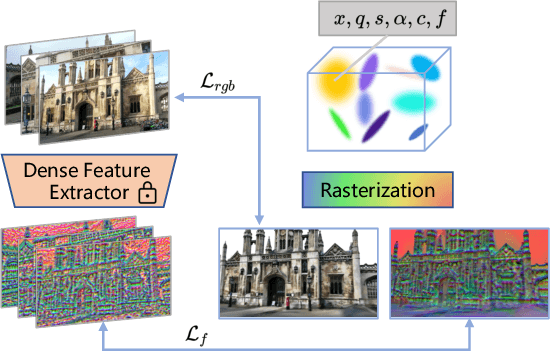

Abstract:This paper presents a novel camera relocalization method, STDLoc, which leverages Feature Gaussian as scene representation. STDLoc is a full relocalization pipeline that can achieve accurate relocalization without relying on any pose prior. Unlike previous coarse-to-fine localization methods that require image retrieval first and then feature matching, we propose a novel sparse-to-dense localization paradigm. Based on this scene representation, we introduce a novel matching-oriented Gaussian sampling strategy and a scene-specific detector to achieve efficient and robust initial pose estimation. Furthermore, based on the initial localization results, we align the query feature map to the Gaussian feature field by dense feature matching to enable accurate localization. The experiments on indoor and outdoor datasets show that STDLoc outperforms current state-of-the-art localization methods in terms of localization accuracy and recall.
SGFormer: Satellite-Ground Fusion for 3D Semantic Scene Completion
Mar 21, 2025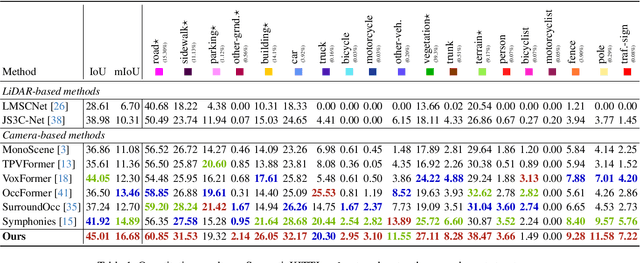
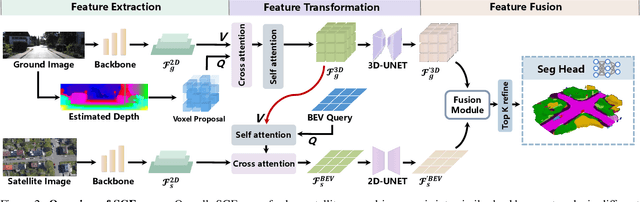
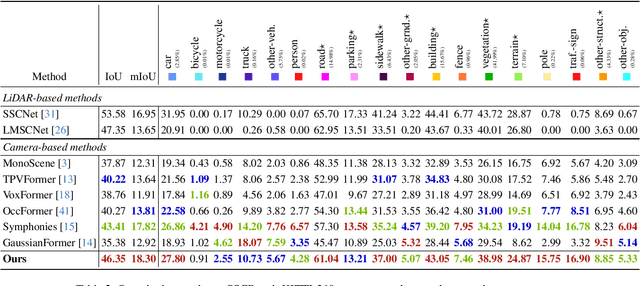
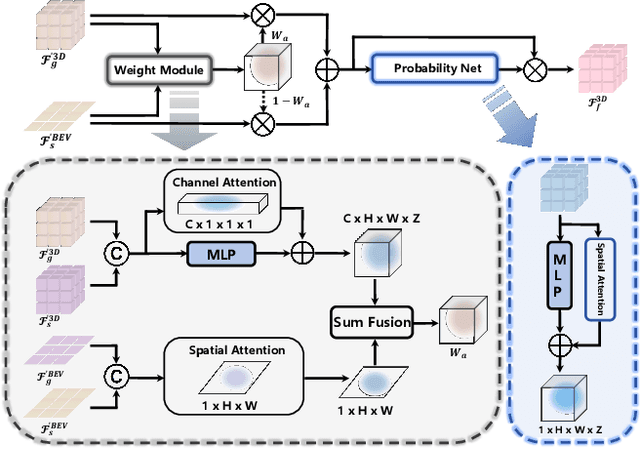
Abstract:Recently, camera-based solutions have been extensively explored for scene semantic completion (SSC). Despite their success in visible areas, existing methods struggle to capture complete scene semantics due to frequent visual occlusions. To address this limitation, this paper presents the first satellite-ground cooperative SSC framework, i.e., SGFormer, exploring the potential of satellite-ground image pairs in the SSC task. Specifically, we propose a dual-branch architecture that encodes orthogonal satellite and ground views in parallel, unifying them into a common domain. Additionally, we design a ground-view guidance strategy that corrects satellite image biases during feature encoding, addressing misalignment between satellite and ground views. Moreover, we develop an adaptive weighting strategy that balances contributions from satellite and ground views. Experiments demonstrate that SGFormer outperforms the state of the art on SemanticKITTI and SSCBench-KITTI-360 datasets. Our code is available on https://github.com/gxytcrc/SGFormer.
Creation-MMBench: Assessing Context-Aware Creative Intelligence in MLLM
Mar 19, 2025



Abstract:Creativity is a fundamental aspect of intelligence, involving the ability to generate novel and appropriate solutions across diverse contexts. While Large Language Models (LLMs) have been extensively evaluated for their creative capabilities, the assessment of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) in this domain remains largely unexplored. To address this gap, we introduce Creation-MMBench, a multimodal benchmark specifically designed to evaluate the creative capabilities of MLLMs in real-world, image-based tasks. The benchmark comprises 765 test cases spanning 51 fine-grained tasks. To ensure rigorous evaluation, we define instance-specific evaluation criteria for each test case, guiding the assessment of both general response quality and factual consistency with visual inputs. Experimental results reveal that current open-source MLLMs significantly underperform compared to proprietary models in creative tasks. Furthermore, our analysis demonstrates that visual fine-tuning can negatively impact the base LLM's creative abilities. Creation-MMBench provides valuable insights for advancing MLLM creativity and establishes a foundation for future improvements in multimodal generative intelligence. Full data and evaluation code is released on https://github.com/open-compass/Creation-MMBench.
X-LRM: X-ray Large Reconstruction Model for Extremely Sparse-View Computed Tomography Recovery in One Second
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Sparse-view 3D CT reconstruction aims to recover volumetric structures from a limited number of 2D X-ray projections. Existing feedforward methods are constrained by the limited capacity of CNN-based architectures and the scarcity of large-scale training datasets. In this paper, we propose an X-ray Large Reconstruction Model (X-LRM) for extremely sparse-view (<10 views) CT reconstruction. X-LRM consists of two key components: X-former and X-triplane. Our X-former can handle an arbitrary number of input views using an MLP-based image tokenizer and a Transformer-based encoder. The output tokens are then upsampled into our X-triplane representation, which models the 3D radiodensity as an implicit neural field. To support the training of X-LRM, we introduce Torso-16K, a large-scale dataset comprising over 16K volume-projection pairs of various torso organs. Extensive experiments demonstrate that X-LRM outperforms the state-of-the-art method by 1.5 dB and achieves 27x faster speed and better flexibility. Furthermore, the downstream evaluation of lung segmentation tasks also suggests the practical value of our approach. Our code, pre-trained models, and dataset will be released at https://github.com/caiyuanhao1998/X-LRM
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge