Songyou Peng
Selfi: Self Improving Reconstruction Engine via 3D Geometric Feature Alignment
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:Novel View Synthesis (NVS) has traditionally relied on models with explicit 3D inductive biases combined with known camera parameters from Structure-from-Motion (SfM) beforehand. Recent vision foundation models like VGGT take an orthogonal approach -- 3D knowledge is gained implicitly through training data and loss objectives, enabling feed-forward prediction of both camera parameters and 3D representations directly from a set of uncalibrated images. While flexible, VGGT features lack explicit multi-view geometric consistency, and we find that improving such 3D feature consistency benefits both NVS and pose estimation tasks. We introduce Selfi, a self-improving 3D reconstruction pipeline via feature alignment, transforming a VGGT backbone into a high-fidelity 3D reconstruction engine by leveraging its own outputs as pseudo-ground-truth. Specifically, we train a lightweight feature adapter using a reprojection-based consistency loss, which distills VGGT outputs into a new geometrically-aligned feature space that captures spatial proximity in 3D. This enables state-of-the-art performance in both NVS and camera pose estimation, demonstrating that feature alignment is a highly beneficial step for downstream 3D reasoning.
Splat4D: Diffusion-Enhanced 4D Gaussian Splatting for Temporally and Spatially Consistent Content Creation
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Generating high-quality 4D content from monocular videos for applications such as digital humans and AR/VR poses challenges in ensuring temporal and spatial consistency, preserving intricate details, and incorporating user guidance effectively. To overcome these challenges, we introduce Splat4D, a novel framework enabling high-fidelity 4D content generation from a monocular video. Splat4D achieves superior performance while maintaining faithful spatial-temporal coherence by leveraging multi-view rendering, inconsistency identification, a video diffusion model, and an asymmetric U-Net for refinement. Through extensive evaluations on public benchmarks, Splat4D consistently demonstrates state-of-the-art performance across various metrics, underscoring the efficacy of our approach. Additionally, the versatility of Splat4D is validated in various applications such as text/image conditioned 4D generation, 4D human generation, and text-guided content editing, producing coherent outcomes following user instructions.
LODGE: Level-of-Detail Large-Scale Gaussian Splatting with Efficient Rendering
May 29, 2025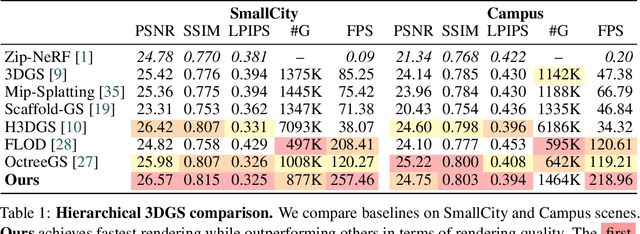
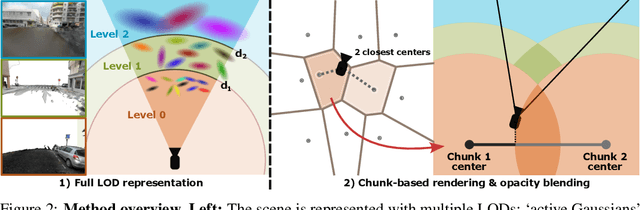
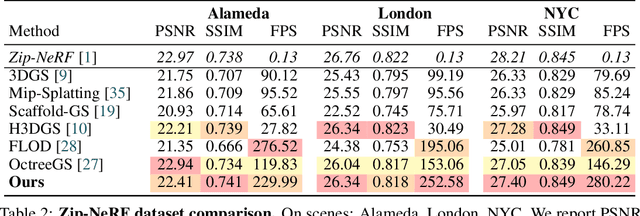
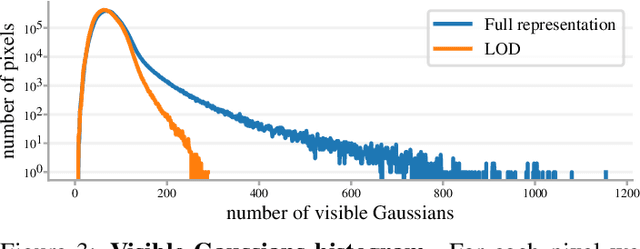
Abstract:In this work, we present a novel level-of-detail (LOD) method for 3D Gaussian Splatting that enables real-time rendering of large-scale scenes on memory-constrained devices. Our approach introduces a hierarchical LOD representation that iteratively selects optimal subsets of Gaussians based on camera distance, thus largely reducing both rendering time and GPU memory usage. We construct each LOD level by applying a depth-aware 3D smoothing filter, followed by importance-based pruning and fine-tuning to maintain visual fidelity. To further reduce memory overhead, we partition the scene into spatial chunks and dynamically load only relevant Gaussians during rendering, employing an opacity-blending mechanism to avoid visual artifacts at chunk boundaries. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on both outdoor (Hierarchical 3DGS) and indoor (Zip-NeRF) datasets, delivering high-quality renderings with reduced latency and memory requirements.
Visual Chronicles: Using Multimodal LLMs to Analyze Massive Collections of Images
Apr 14, 2025
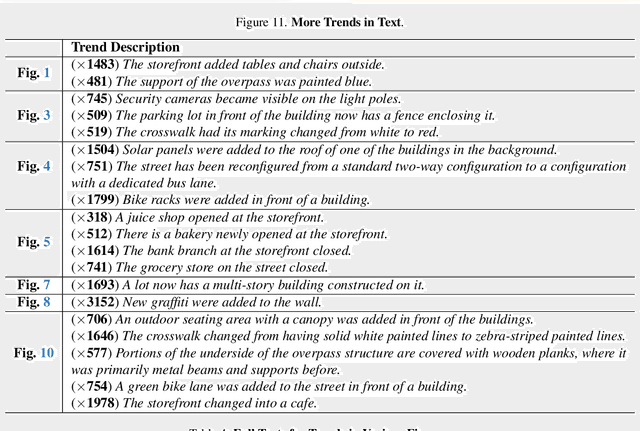
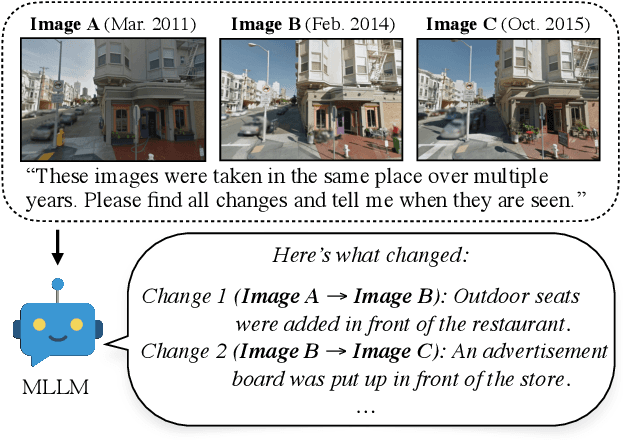
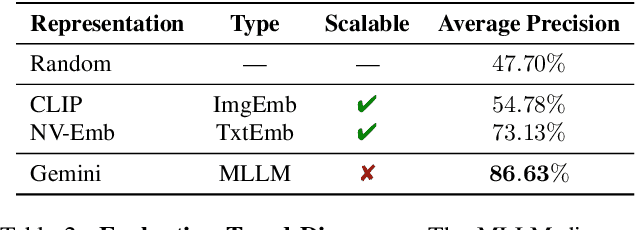
Abstract:We present a system using Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) to analyze a large database with tens of millions of images captured at different times, with the aim of discovering patterns in temporal changes. Specifically, we aim to capture frequent co-occurring changes ("trends") across a city over a certain period. Unlike previous visual analyses, our analysis answers open-ended queries (e.g., "what are the frequent types of changes in the city?") without any predetermined target subjects or training labels. These properties cast prior learning-based or unsupervised visual analysis tools unsuitable. We identify MLLMs as a novel tool for their open-ended semantic understanding capabilities. Yet, our datasets are four orders of magnitude too large for an MLLM to ingest as context. So we introduce a bottom-up procedure that decomposes the massive visual analysis problem into more tractable sub-problems. We carefully design MLLM-based solutions to each sub-problem. During experiments and ablation studies with our system, we find it significantly outperforms baselines and is able to discover interesting trends from images captured in large cities (e.g., "addition of outdoor dining,", "overpass was painted blue," etc.). See more results and interactive demos at https://boyangdeng.com/visual-chronicles.
WildGS-SLAM: Monocular Gaussian Splatting SLAM in Dynamic Environments
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:We present WildGS-SLAM, a robust and efficient monocular RGB SLAM system designed to handle dynamic environments by leveraging uncertainty-aware geometric mapping. Unlike traditional SLAM systems, which assume static scenes, our approach integrates depth and uncertainty information to enhance tracking, mapping, and rendering performance in the presence of moving objects. We introduce an uncertainty map, predicted by a shallow multi-layer perceptron and DINOv2 features, to guide dynamic object removal during both tracking and mapping. This uncertainty map enhances dense bundle adjustment and Gaussian map optimization, improving reconstruction accuracy. Our system is evaluated on multiple datasets and demonstrates artifact-free view synthesis. Results showcase WildGS-SLAM's superior performance in dynamic environments compared to state-of-the-art methods.
Free360: Layered Gaussian Splatting for Unbounded 360-Degree View Synthesis from Extremely Sparse and Unposed Views
Mar 31, 2025

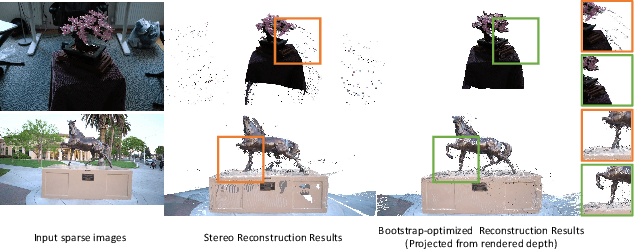

Abstract:Neural rendering has demonstrated remarkable success in high-quality 3D neural reconstruction and novel view synthesis with dense input views and accurate poses. However, applying it to extremely sparse, unposed views in unbounded 360{\deg} scenes remains a challenging problem. In this paper, we propose a novel neural rendering framework to accomplish the unposed and extremely sparse-view 3D reconstruction in unbounded 360{\deg} scenes. To resolve the spatial ambiguity inherent in unbounded scenes with sparse input views, we propose a layered Gaussian-based representation to effectively model the scene with distinct spatial layers. By employing a dense stereo reconstruction model to recover coarse geometry, we introduce a layer-specific bootstrap optimization to refine the noise and fill occluded regions in the reconstruction. Furthermore, we propose an iterative fusion of reconstruction and generation alongside an uncertainty-aware training approach to facilitate mutual conditioning and enhancement between these two processes. Comprehensive experiments show that our approach outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in terms of rendering quality and surface reconstruction accuracy. Project page: https://zju3dv.github.io/free360/
SplatTalk: 3D VQA with Gaussian Splatting
Mar 08, 2025Abstract:Language-guided 3D scene understanding is important for advancing applications in robotics, AR/VR, and human-computer interaction, enabling models to comprehend and interact with 3D environments through natural language. While 2D vision-language models (VLMs) have achieved remarkable success in 2D VQA tasks, progress in the 3D domain has been significantly slower due to the complexity of 3D data and the high cost of manual annotations. In this work, we introduce SplatTalk, a novel method that uses a generalizable 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) framework to produce 3D tokens suitable for direct input into a pretrained LLM, enabling effective zero-shot 3D visual question answering (3D VQA) for scenes with only posed images. During experiments on multiple benchmarks, our approach outperforms both 3D models trained specifically for the task and previous 2D-LMM-based models utilizing only images (our setting), while achieving competitive performance with state-of-the-art 3D LMMs that additionally utilize 3D inputs.
Prompting Depth Anything for 4K Resolution Accurate Metric Depth Estimation
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:Prompts play a critical role in unleashing the power of language and vision foundation models for specific tasks. For the first time, we introduce prompting into depth foundation models, creating a new paradigm for metric depth estimation termed Prompt Depth Anything. Specifically, we use a low-cost LiDAR as the prompt to guide the Depth Anything model for accurate metric depth output, achieving up to 4K resolution. Our approach centers on a concise prompt fusion design that integrates the LiDAR at multiple scales within the depth decoder. To address training challenges posed by limited datasets containing both LiDAR depth and precise GT depth, we propose a scalable data pipeline that includes synthetic data LiDAR simulation and real data pseudo GT depth generation. Our approach sets new state-of-the-arts on the ARKitScenes and ScanNet++ datasets and benefits downstream applications, including 3D reconstruction and generalized robotic grasping.
No Pose, No Problem: Surprisingly Simple 3D Gaussian Splats from Sparse Unposed Images
Oct 31, 2024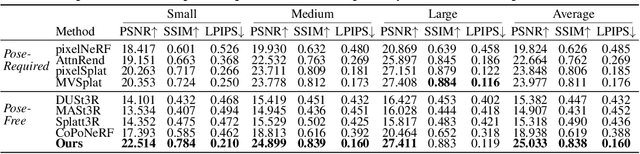
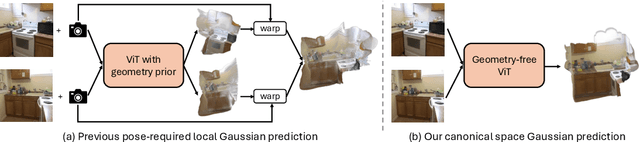
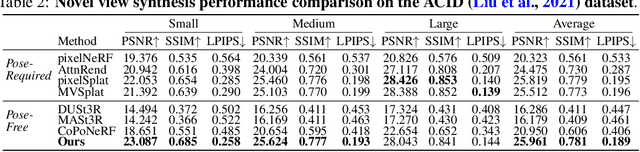
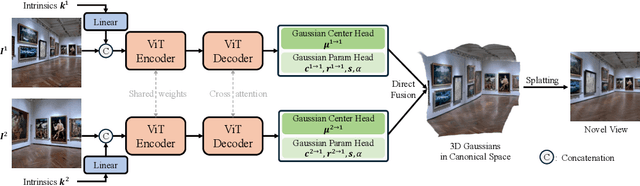
Abstract:We introduce NoPoSplat, a feed-forward model capable of reconstructing 3D scenes parameterized by 3D Gaussians from \textit{unposed} sparse multi-view images. Our model, trained exclusively with photometric loss, achieves real-time 3D Gaussian reconstruction during inference. To eliminate the need for accurate pose input during reconstruction, we anchor one input view's local camera coordinates as the canonical space and train the network to predict Gaussian primitives for all views within this space. This approach obviates the need to transform Gaussian primitives from local coordinates into a global coordinate system, thus avoiding errors associated with per-frame Gaussians and pose estimation. To resolve scale ambiguity, we design and compare various intrinsic embedding methods, ultimately opting to convert camera intrinsics into a token embedding and concatenate it with image tokens as input to the model, enabling accurate scene scale prediction. We utilize the reconstructed 3D Gaussians for novel view synthesis and pose estimation tasks and propose a two-stage coarse-to-fine pipeline for accurate pose estimation. Experimental results demonstrate that our pose-free approach can achieve superior novel view synthesis quality compared to pose-required methods, particularly in scenarios with limited input image overlap. For pose estimation, our method, trained without ground truth depth or explicit matching loss, significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art methods with substantial improvements. This work makes significant advances in pose-free generalizable 3D reconstruction and demonstrates its applicability to real-world scenarios. Code and trained models are available at https://noposplat.github.io/.
DepthSplat: Connecting Gaussian Splatting and Depth
Oct 17, 2024



Abstract:Gaussian splatting and single/multi-view depth estimation are typically studied in isolation. In this paper, we present DepthSplat to connect Gaussian splatting and depth estimation and study their interactions. More specifically, we first contribute a robust multi-view depth model by leveraging pre-trained monocular depth features, leading to high-quality feed-forward 3D Gaussian splatting reconstructions. We also show that Gaussian splatting can serve as an unsupervised pre-training objective for learning powerful depth models from large-scale unlabelled datasets. We validate the synergy between Gaussian splatting and depth estimation through extensive ablation and cross-task transfer experiments. Our DepthSplat achieves state-of-the-art performance on ScanNet, RealEstate10K and DL3DV datasets in terms of both depth estimation and novel view synthesis, demonstrating the mutual benefits of connecting both tasks. Our code, models, and video results are available at https://haofeixu.github.io/depthsplat/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge