Xiaowei Zhou
Zhejiang University
InfiniDepth: Arbitrary-Resolution and Fine-Grained Depth Estimation with Neural Implicit Fields
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Existing depth estimation methods are fundamentally limited to predicting depth on discrete image grids. Such representations restrict their scalability to arbitrary output resolutions and hinder the geometric detail recovery. This paper introduces InfiniDepth, which represents depth as neural implicit fields. Through a simple yet effective local implicit decoder, we can query depth at continuous 2D coordinates, enabling arbitrary-resolution and fine-grained depth estimation. To better assess our method's capabilities, we curate a high-quality 4K synthetic benchmark from five different games, spanning diverse scenes with rich geometric and appearance details. Extensive experiments demonstrate that InfiniDepth achieves state-of-the-art performance on both synthetic and real-world benchmarks across relative and metric depth estimation tasks, particularly excelling in fine-detail regions. It also benefits the task of novel view synthesis under large viewpoint shifts, producing high-quality results with fewer holes and artifacts.
Split4D: Decomposed 4D Scene Reconstruction Without Video Segmentation
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of decomposed 4D scene reconstruction from multi-view videos. Recent methods achieve this by lifting video segmentation results to a 4D representation through differentiable rendering techniques. Therefore, they heavily rely on the quality of video segmentation maps, which are often unstable, leading to unreliable reconstruction results. To overcome this challenge, our key idea is to represent the decomposed 4D scene with the Freetime FeatureGS and design a streaming feature learning strategy to accurately recover it from per-image segmentation maps, eliminating the need for video segmentation. Freetime FeatureGS models the dynamic scene as a set of Gaussian primitives with learnable features and linear motion ability, allowing them to move to neighboring regions over time. We apply a contrastive loss to Freetime FeatureGS, forcing primitive features to be close or far apart based on whether their projections belong to the same instance in the 2D segmentation map. As our Gaussian primitives can move across time, it naturally extends the feature learning to the temporal dimension, achieving 4D segmentation. Furthermore, we sample observations for training in a temporally ordered manner, enabling the streaming propagation of features over time and effectively avoiding local minima during the optimization process. Experimental results on several datasets show that the reconstruction quality of our method outperforms recent methods by a large margin.
SpatialTree: How Spatial Abilities Branch Out in MLLMs
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Cognitive science suggests that spatial ability develops progressively-from perception to reasoning and interaction. Yet in multimodal LLMs (MLLMs), this hierarchy remains poorly understood, as most studies focus on a narrow set of tasks. We introduce SpatialTree, a cognitive-science-inspired hierarchy that organizes spatial abilities into four levels: low-level perception (L1), mental mapping (L2), simulation (L3), and agentic competence (L4). Based on this taxonomy, we construct the first capability-centric hierarchical benchmark, thoroughly evaluating mainstream MLLMs across 27 sub-abilities. The evaluation results reveal a clear structure: L1 skills are largely orthogonal, whereas higher-level skills are strongly correlated, indicating increasing interdependency. Through targeted supervised fine-tuning, we uncover a surprising transfer dynamic-negative transfer within L1, but strong cross-level transfer from low- to high-level abilities with notable synergy. Finally, we explore how to improve the entire hierarchy. We find that naive RL that encourages extensive "thinking" is unreliable: it helps complex reasoning but hurts intuitive perception. We propose a simple auto-think strategy that suppresses unnecessary deliberation, enabling RL to consistently improve performance across all levels. By building SpatialTree, we provide a proof-of-concept framework for understanding and systematically scaling spatial abilities in MLLMs.
StreamingTalker: Audio-driven 3D Facial Animation with Autoregressive Diffusion Model
Nov 19, 2025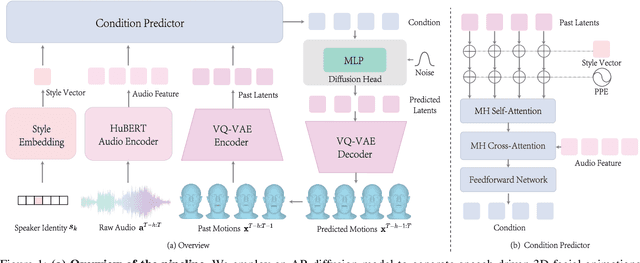
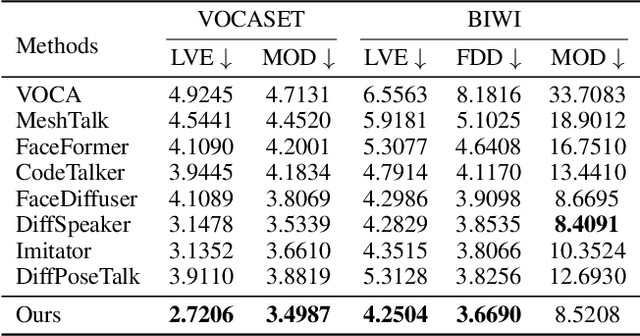
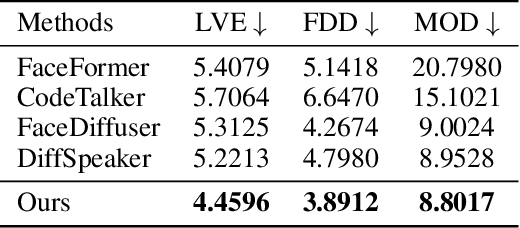
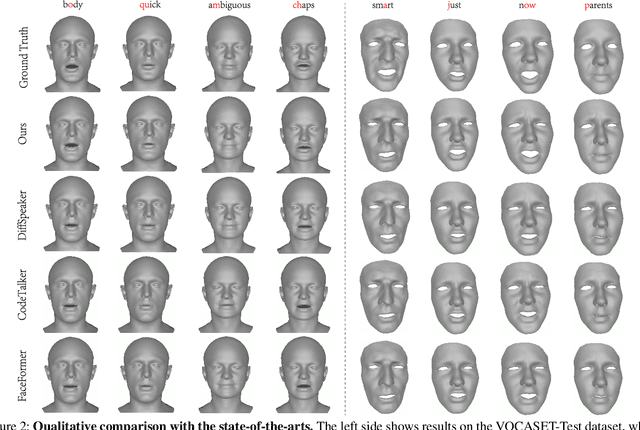
Abstract:This paper focuses on the task of speech-driven 3D facial animation, which aims to generate realistic and synchronized facial motions driven by speech inputs. Recent methods have employed audio-conditioned diffusion models for 3D facial animation, achieving impressive results in generating expressive and natural animations. However, these methods process the whole audio sequences in a single pass, which poses two major challenges: they tend to perform poorly when handling audio sequences that exceed the training horizon and will suffer from significant latency when processing long audio inputs. To address these limitations, we propose a novel autoregressive diffusion model that processes input audio in a streaming manner. This design ensures flexibility with varying audio lengths and achieves low latency independent of audio duration. Specifically, we select a limited number of past frames as historical motion context and combine them with the audio input to create a dynamic condition. This condition guides the diffusion process to iteratively generate facial motion frames, enabling real-time synthesis with high-quality results. Additionally, we implemented a real-time interactive demo, highlighting the effectiveness and efficiency of our approach. We will release the code at https://zju3dv.github.io/StreamingTalker/.
UniVerse: Unleashing the Scene Prior of Video Diffusion Models for Robust Radiance Field Reconstruction
Oct 02, 2025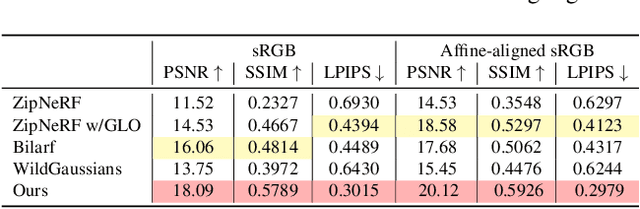
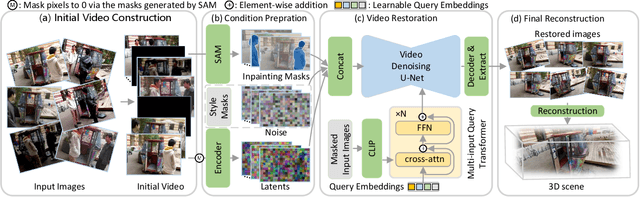
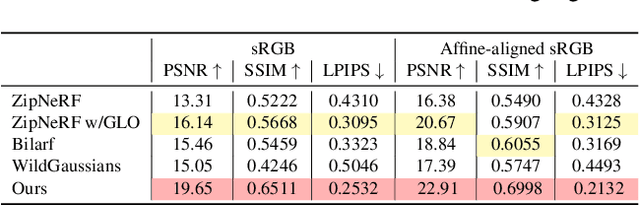

Abstract:This paper tackles the challenge of robust reconstruction, i.e., the task of reconstructing a 3D scene from a set of inconsistent multi-view images. Some recent works have attempted to simultaneously remove image inconsistencies and perform reconstruction by integrating image degradation modeling into neural 3D scene representations.However, these methods rely heavily on dense observations for robustly optimizing model parameters.To address this issue, we propose to decouple robust reconstruction into two subtasks: restoration and reconstruction, which naturally simplifies the optimization process.To this end, we introduce UniVerse, a unified framework for robust reconstruction based on a video diffusion model. Specifically, UniVerse first converts inconsistent images into initial videos, then uses a specially designed video diffusion model to restore them into consistent images, and finally reconstructs the 3D scenes from these restored images.Compared with case-by-case per-view degradation modeling, the diffusion model learns a general scene prior from large-scale data, making it applicable to diverse image inconsistencies.Extensive experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate the strong generalization capability and superior performance of our method in robust reconstruction. Moreover, UniVerse can control the style of the reconstructed 3D scene. Project page: https://jin-cao-tma.github.io/UniVerse.github.io/
Diffuman4D: 4D Consistent Human View Synthesis from Sparse-View Videos with Spatio-Temporal Diffusion Models
Jul 17, 2025Abstract:This paper addresses the challenge of high-fidelity view synthesis of humans with sparse-view videos as input. Previous methods solve the issue of insufficient observation by leveraging 4D diffusion models to generate videos at novel viewpoints. However, the generated videos from these models often lack spatio-temporal consistency, thus degrading view synthesis quality. In this paper, we propose a novel sliding iterative denoising process to enhance the spatio-temporal consistency of the 4D diffusion model. Specifically, we define a latent grid in which each latent encodes the image, camera pose, and human pose for a certain viewpoint and timestamp, then alternately denoising the latent grid along spatial and temporal dimensions with a sliding window, and finally decode the videos at target viewpoints from the corresponding denoised latents. Through the iterative sliding, information flows sufficiently across the latent grid, allowing the diffusion model to obtain a large receptive field and thus enhance the 4D consistency of the output, while making the GPU memory consumption affordable. The experiments on the DNA-Rendering and ActorsHQ datasets demonstrate that our method is able to synthesize high-quality and consistent novel-view videos and significantly outperforms the existing approaches. See our project page for interactive demos and video results: https://diffuman4d.github.io/ .
SpatialTrackerV2: 3D Point Tracking Made Easy
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:We present SpatialTrackerV2, a feed-forward 3D point tracking method for monocular videos. Going beyond modular pipelines built on off-the-shelf components for 3D tracking, our approach unifies the intrinsic connections between point tracking, monocular depth, and camera pose estimation into a high-performing and feedforward 3D point tracker. It decomposes world-space 3D motion into scene geometry, camera ego-motion, and pixel-wise object motion, with a fully differentiable and end-to-end architecture, allowing scalable training across a wide range of datasets, including synthetic sequences, posed RGB-D videos, and unlabeled in-the-wild footage. By learning geometry and motion jointly from such heterogeneous data, SpatialTrackerV2 outperforms existing 3D tracking methods by 30%, and matches the accuracy of leading dynamic 3D reconstruction approaches while running 50$\times$ faster.
Towards Depth Foundation Model: Recent Trends in Vision-Based Depth Estimation
Jul 15, 2025Abstract:Depth estimation is a fundamental task in 3D computer vision, crucial for applications such as 3D reconstruction, free-viewpoint rendering, robotics, autonomous driving, and AR/VR technologies. Traditional methods relying on hardware sensors like LiDAR are often limited by high costs, low resolution, and environmental sensitivity, limiting their applicability in real-world scenarios. Recent advances in vision-based methods offer a promising alternative, yet they face challenges in generalization and stability due to either the low-capacity model architectures or the reliance on domain-specific and small-scale datasets. The emergence of scaling laws and foundation models in other domains has inspired the development of "depth foundation models": deep neural networks trained on large datasets with strong zero-shot generalization capabilities. This paper surveys the evolution of deep learning architectures and paradigms for depth estimation across the monocular, stereo, multi-view, and monocular video settings. We explore the potential of these models to address existing challenges and provide a comprehensive overview of large-scale datasets that can facilitate their development. By identifying key architectures and training strategies, we aim to highlight the path towards robust depth foundation models, offering insights into their future research and applications.
4DGT: Learning a 4D Gaussian Transformer Using Real-World Monocular Videos
Jun 09, 2025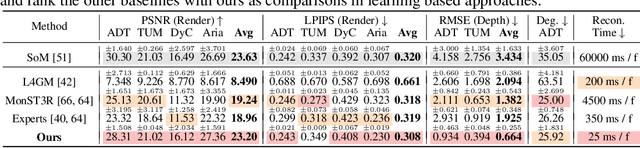
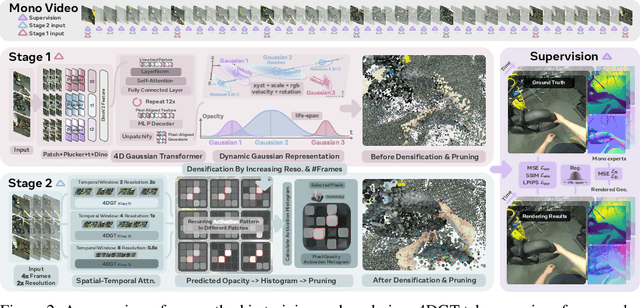

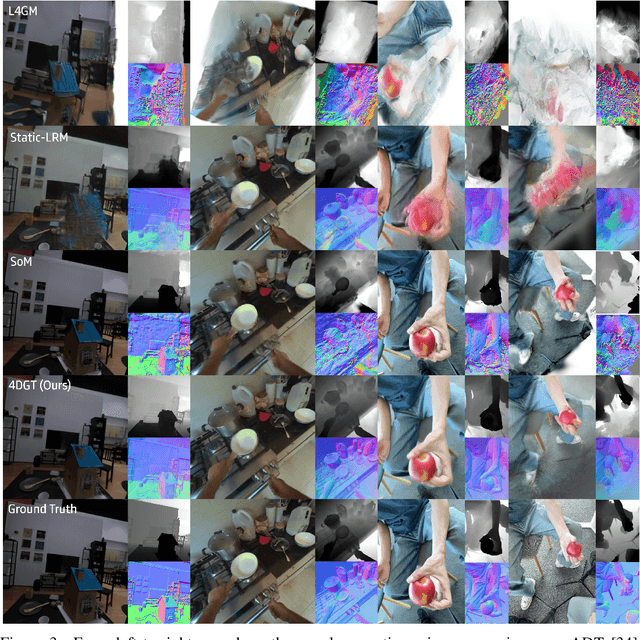
Abstract:We propose 4DGT, a 4D Gaussian-based Transformer model for dynamic scene reconstruction, trained entirely on real-world monocular posed videos. Using 4D Gaussian as an inductive bias, 4DGT unifies static and dynamic components, enabling the modeling of complex, time-varying environments with varying object lifespans. We proposed a novel density control strategy in training, which enables our 4DGT to handle longer space-time input and remain efficient rendering at runtime. Our model processes 64 consecutive posed frames in a rolling-window fashion, predicting consistent 4D Gaussians in the scene. Unlike optimization-based methods, 4DGT performs purely feed-forward inference, reducing reconstruction time from hours to seconds and scaling effectively to long video sequences. Trained only on large-scale monocular posed video datasets, 4DGT can outperform prior Gaussian-based networks significantly in real-world videos and achieve on-par accuracy with optimization-based methods on cross-domain videos. Project page: https://4dgt.github.io
FreeTimeGS: Free Gaussian Primitives at Anytime and Anywhere for Dynamic Scene Reconstruction
Jun 06, 2025



Abstract:This paper addresses the challenge of reconstructing dynamic 3D scenes with complex motions. Some recent works define 3D Gaussian primitives in the canonical space and use deformation fields to map canonical primitives to observation spaces, achieving real-time dynamic view synthesis. However, these methods often struggle to handle scenes with complex motions due to the difficulty of optimizing deformation fields. To overcome this problem, we propose FreeTimeGS, a novel 4D representation that allows Gaussian primitives to appear at arbitrary time and locations. In contrast to canonical Gaussian primitives, our representation possesses the strong flexibility, thus improving the ability to model dynamic 3D scenes. In addition, we endow each Gaussian primitive with an motion function, allowing it to move to neighboring regions over time, which reduces the temporal redundancy. Experiments results on several datasets show that the rendering quality of our method outperforms recent methods by a large margin. Project page: https://zju3dv.github.io/freetimegs/ .
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge