Ligang Liu
DeX-Portrait: Disentangled and Expressive Portrait Animation via Explicit and Latent Motion Representations
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Portrait animation from a single source image and a driving video is a long-standing problem. Recent approaches tend to adopt diffusion-based image/video generation models for realistic and expressive animation. However, none of these diffusion models realizes high-fidelity disentangled control between the head pose and facial expression, hindering applications like expression-only or pose-only editing and animation. To address this, we propose DeX-Portrait, a novel approach capable of generating expressive portrait animation driven by disentangled pose and expression signals. Specifically, we represent the pose as an explicit global transformation and the expression as an implicit latent code. First, we design a powerful motion trainer to learn both pose and expression encoders for extracting precise and decomposed driving signals. Then we propose to inject the pose transformation into the diffusion model through a dual-branch conditioning mechanism, and the expression latent through cross attention. Finally, we design a progressive hybrid classifier-free guidance for more faithful identity consistency. Experiments show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art baselines on both animation quality and disentangled controllability.
Co-Layout: LLM-driven Co-optimization for Interior Layout
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:We present a novel framework for automated interior design that combines large language models (LLMs) with grid-based integer programming to jointly optimize room layout and furniture placement. Given a textual prompt, the LLM-driven agent workflow extracts structured design constraints related to room configurations and furniture arrangements. These constraints are encoded into a unified grid-based representation inspired by ``Modulor". Our formulation accounts for key design requirements, including corridor connectivity, room accessibility, spatial exclusivity, and user-specified preferences. To improve computational efficiency, we adopt a coarse-to-fine optimization strategy that begins with a low-resolution grid to solve a simplified problem and guides the solution at the full resolution. Experimental results across diverse scenarios demonstrate that our joint optimization approach significantly outperforms existing two-stage design pipelines in solution quality, and achieves notable computational efficiency through the coarse-to-fine strategy.
Learning Sparse Approximate Inverse Preconditioners for Conjugate Gradient Solvers on GPUs
Oct 31, 2025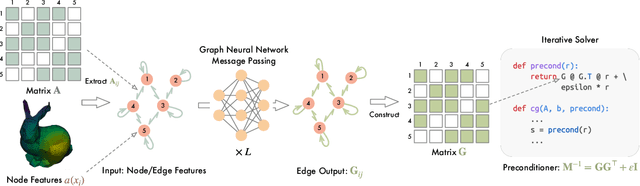
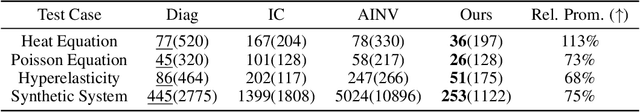
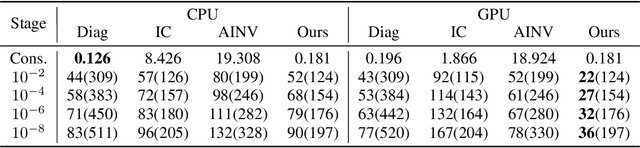
Abstract:The conjugate gradient solver (CG) is a prevalent method for solving symmetric and positive definite linear systems Ax=b, where effective preconditioners are crucial for fast convergence. Traditional preconditioners rely on prescribed algorithms to offer rigorous theoretical guarantees, while limiting their ability to exploit optimization from data. Existing learning-based methods often utilize Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) to improve the performance and speed up the construction. However, their reliance on incomplete factorization leads to significant challenges: the associated triangular solve hinders GPU parallelization in practice, and introduces long-range dependencies which are difficult for GNNs to model. To address these issues, we propose a learning-based method to generate GPU-friendly preconditioners, particularly using GNNs to construct Sparse Approximate Inverse (SPAI) preconditioners, which avoids triangular solves and requires only two matrix-vector products at each CG step. The locality of matrix-vector product is compatible with the local propagation mechanism of GNNs. The flexibility of GNNs also allows our approach to be applied in a wide range of scenarios. Furthermore, we introduce a statistics-based scale-invariant loss function. Its design matches CG's property that the convergence rate depends on the condition number, rather than the absolute scale of A, leading to improved performance of the learned preconditioner. Evaluations on three PDE-derived datasets and one synthetic dataset demonstrate that our method outperforms standard preconditioners (Diagonal, IC, and traditional SPAI) and previous learning-based preconditioners on GPUs. We reduce solution time on GPUs by 40%-53% (68%-113% faster), along with better condition numbers and superior generalization performance. Source code available at https://github.com/Adversarr/LearningSparsePreconditioner4GPU
Drawing2CAD: Sequence-to-Sequence Learning for CAD Generation from Vectorized Drawings
Aug 26, 2025



Abstract:Computer-Aided Design (CAD) generative modeling is driving significant innovations across industrial applications. Recent works have shown remarkable progress in creating solid models from various inputs such as point clouds, meshes, and text descriptions. However, these methods fundamentally diverge from traditional industrial workflows that begin with 2D engineering drawings. The automatic generation of parametric CAD models from these 2D vector drawings remains underexplored despite being a critical step in engineering design. To address this gap, our key insight is to reframe CAD generation as a sequence-to-sequence learning problem where vector drawing primitives directly inform the generation of parametric CAD operations, preserving geometric precision and design intent throughout the transformation process. We propose Drawing2CAD, a framework with three key technical components: a network-friendly vector primitive representation that preserves precise geometric information, a dual-decoder transformer architecture that decouples command type and parameter generation while maintaining precise correspondence, and a soft target distribution loss function accommodating inherent flexibility in CAD parameters. To train and evaluate Drawing2CAD, we create CAD-VGDrawing, a dataset of paired engineering drawings and parametric CAD models, and conduct thorough experiments to demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. Code and dataset are available at https://github.com/lllssc/Drawing2CAD.
AvatarMakeup: Realistic Makeup Transfer for 3D Animatable Head Avatars
Jul 03, 2025Abstract:Similar to facial beautification in real life, 3D virtual avatars require personalized customization to enhance their visual appeal, yet this area remains insufficiently explored. Although current 3D Gaussian editing methods can be adapted for facial makeup purposes, these methods fail to meet the fundamental requirements for achieving realistic makeup effects: 1) ensuring a consistent appearance during drivable expressions, 2) preserving the identity throughout the makeup process, and 3) enabling precise control over fine details. To address these, we propose a specialized 3D makeup method named AvatarMakeup, leveraging a pretrained diffusion model to transfer makeup patterns from a single reference photo of any individual. We adopt a coarse-to-fine idea to first maintain the consistent appearance and identity, and then to refine the details. In particular, the diffusion model is employed to generate makeup images as supervision. Due to the uncertainties in diffusion process, the generated images are inconsistent across different viewpoints and expressions. Therefore, we propose a Coherent Duplication method to coarsely apply makeup to the target while ensuring consistency across dynamic and multiview effects. Coherent Duplication optimizes a global UV map by recoding the averaged facial attributes among the generated makeup images. By querying the global UV map, it easily synthesizes coherent makeup guidance from arbitrary views and expressions to optimize the target avatar. Given the coarse makeup avatar, we further enhance the makeup by incorporating a Refinement Module into the diffusion model to achieve high makeup quality. Experiments demonstrate that AvatarMakeup achieves state-of-the-art makeup transfer quality and consistency throughout animation.
SUPRA: Subspace Parameterized Attention for Neural Operator on General Domains
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:Neural operators are efficient surrogate models for solving partial differential equations (PDEs), but their key components face challenges: (1) in order to improve accuracy, attention mechanisms suffer from computational inefficiency on large-scale meshes, and (2) spectral convolutions rely on the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) on regular grids and assume a flat geometry, which causes accuracy degradation on irregular domains. To tackle these problems, we regard the matrix-vector operations in the standard attention mechanism on vectors in Euclidean space as bilinear forms and linear operators in vector spaces and generalize the attention mechanism to function spaces. This new attention mechanism is fully equivalent to the standard attention but impossible to compute due to the infinite dimensionality of function spaces. To address this, inspired by model reduction techniques, we propose a Subspace Parameterized Attention (SUPRA) neural operator, which approximates the attention mechanism within a finite-dimensional subspace. To construct a subspace on irregular domains for SUPRA, we propose using the Laplacian eigenfunctions, which naturally adapt to domains' geometry and guarantee the optimal approximation for smooth functions. Experiments show that the SUPRA neural operator reduces error rates by up to 33% on various PDE datasets while maintaining state-of-the-art computational efficiency.
MASH: Masked Anchored SpHerical Distances for 3D Shape Representation and Generation
Apr 12, 2025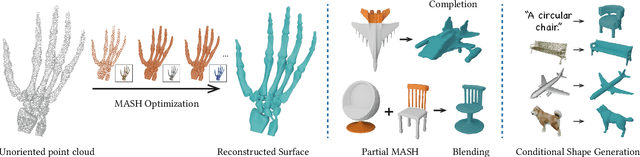
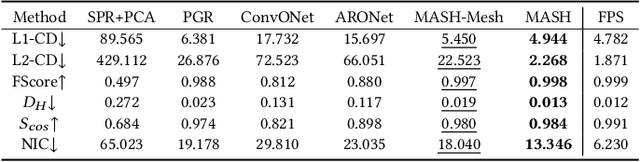
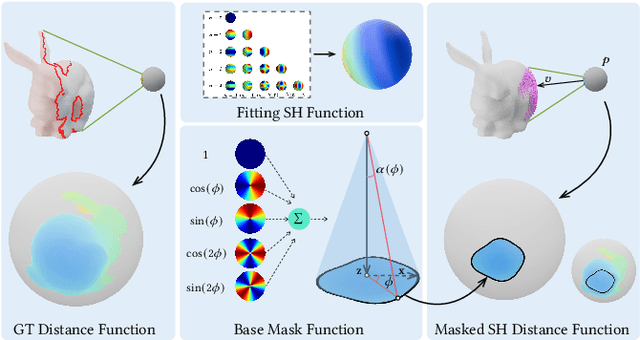

Abstract:We introduce Masked Anchored SpHerical Distances (MASH), a novel multi-view and parametrized representation of 3D shapes. Inspired by multi-view geometry and motivated by the importance of perceptual shape understanding for learning 3D shapes, MASH represents a 3D shape as a collection of observable local surface patches, each defined by a spherical distance function emanating from an anchor point. We further leverage the compactness of spherical harmonics to encode the MASH functions, combined with a generalized view cone with a parameterized base that masks the spatial extent of the spherical function to attain locality. We develop a differentiable optimization algorithm capable of converting any point cloud into a MASH representation accurately approximating ground-truth surfaces with arbitrary geometry and topology. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MASH is versatile for multiple applications including surface reconstruction, shape generation, completion, and blending, achieving superior performance thanks to its unique representation encompassing both implicit and explicit features.
ArticulatedGS: Self-supervised Digital Twin Modeling of Articulated Objects using 3D Gaussian Splatting
Mar 11, 2025



Abstract:We tackle the challenge of concurrent reconstruction at the part level with the RGB appearance and estimation of motion parameters for building digital twins of articulated objects using the 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) method. With two distinct sets of multi-view imagery, each depicting an object in separate static articulation configurations, we reconstruct the articulated object in 3D Gaussian representations with both appearance and geometry information at the same time. Our approach decoupled multiple highly interdependent parameters through a multi-step optimization process, thereby achieving a stable optimization procedure and high-quality outcomes. We introduce ArticulatedGS, a self-supervised, comprehensive framework that autonomously learns to model shapes and appearances at the part level and synchronizes the optimization of motion parameters, all without reliance on 3D supervision, motion cues, or semantic labels. Our experimental results demonstrate that, among comparable methodologies, our approach has achieved optimal outcomes in terms of part segmentation accuracy, motion estimation accuracy, and visual quality.
Text2VDM: Text to Vector Displacement Maps for Expressive and Interactive 3D Sculpting
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Professional 3D asset creation often requires diverse sculpting brushes to add surface details and geometric structures. Despite recent progress in 3D generation, producing reusable sculpting brushes compatible with artists' workflows remains an open and challenging problem. These sculpting brushes are typically represented as vector displacement maps (VDMs), which existing models cannot easily generate compared to natural images. This paper presents Text2VDM, a novel framework for text-to-VDM brush generation through the deformation of a dense planar mesh guided by score distillation sampling (SDS). The original SDS loss is designed for generating full objects and struggles with generating desirable sub-object structures from scratch in brush generation. We refer to this issue as semantic coupling, which we address by introducing classifier-free guidance (CFG) weighted blending of prompt tokens to SDS, resulting in a more accurate target distribution and semantic guidance. Experiments demonstrate that Text2VDM can generate diverse, high-quality VDM brushes for sculpting surface details and geometric structures. Our generated brushes can be seamlessly integrated into mainstream modeling software, enabling various applications such as mesh stylization and real-time interactive modeling.
No Parameters, No Problem: 3D Gaussian Splatting without Camera Intrinsics and Extrinsics
Feb 27, 2025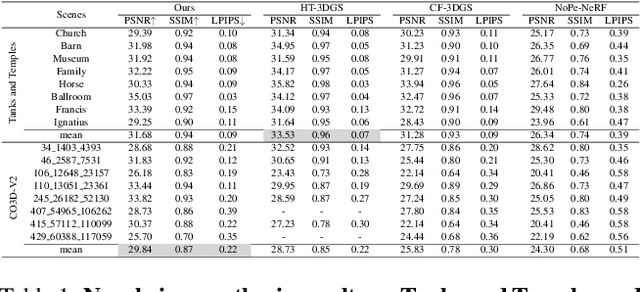
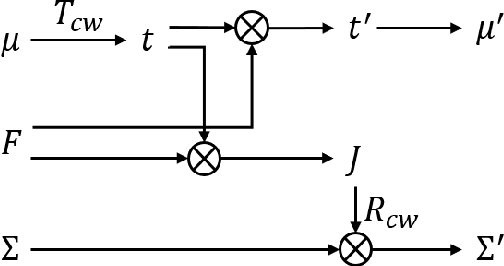
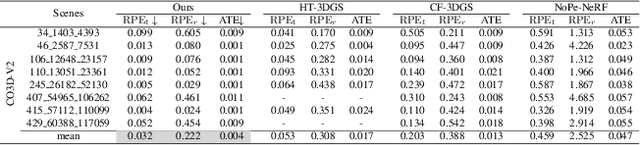
Abstract:While 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has made significant progress in scene reconstruction and novel view synthesis, it still heavily relies on accurately pre-computed camera intrinsics and extrinsics, such as focal length and camera poses. In order to mitigate this dependency, the previous efforts have focused on optimizing 3DGS without the need for camera poses, yet camera intrinsics remain necessary. To further loose the requirement, we propose a joint optimization method to train 3DGS from an image collection without requiring either camera intrinsics or extrinsics. To achieve this goal, we introduce several key improvements during the joint training of 3DGS. We theoretically derive the gradient of the camera intrinsics, allowing the camera intrinsics to be optimized simultaneously during training. Moreover, we integrate global track information and select the Gaussian kernels associated with each track, which will be trained and automatically rescaled to an infinitesimally small size, closely approximating surface points, and focusing on enforcing multi-view consistency and minimizing reprojection errors, while the remaining kernels continue to serve their original roles. This hybrid training strategy nicely unifies the camera parameters estimation and 3DGS training. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on both public and synthetic datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge