Jiaqi Gu
Democratizing Electronic-Photonic AI Systems: An Open-Source AI-Infused Cross-Layer Co-Design and Design Automation Toolflow
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Photonics is becoming a cornerstone technology for high-performance AI systems and scientific computing, offering unparalleled speed, parallelism, and energy efficiency. Despite this promise, the design and deployment of electronic-photonic AI systems remain highly challenging due to a steep learning curve across multiple layers, spanning device physics, circuit design, system architecture, and AI algorithms. The absence of a mature electronic-photonic design automation (EPDA) toolchain leads to long, inefficient design cycles and limits cross-disciplinary innovation and co-evolution. In this work, we present a cross-layer co-design and automation framework aimed at democratizing photonic AI system development. We begin by introducing our architecture designs for scalable photonic edge AI and Transformer inference, followed by SimPhony, an open-source modeling tool for rapid EPIC AI system evaluation and design-space exploration. We then highlight advances in AI-enabled photonic design automation, including physical AI-based Maxwell solvers, a fabrication-aware inverse design framework, and a scalable inverse training algorithm for meta-optical neural networks, enabling a scalable EPDA stack for next-generation electronic-photonic AI systems.
Toward Large-Scale Photonics-Empowered AI Systems: From Physical Design Automation to System-Algorithm Co-Exploration
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:In this work, we identify three considerations that are essential for realizing practical photonic AI systems at scale: (1) dynamic tensor operation support for modern models rather than only weight-static kernels, especially for attention/Transformer-style workloads; (2) systematic management of conversion, control, and data-movement overheads, where multiplexing and dataflow must amortize electronic costs instead of letting ADC/DAC and I/O dominate; and (3) robustness under hardware non-idealities that become more severe as integration density grows. To study these coupled tradeoffs quantitatively, and to ensure they remain meaningful under real implementation constraints, we build a cross-layer toolchain that supports photonic AI design from early exploration to physical realization. SimPhony provides implementation-aware modeling and rapid cross-layer evaluation, translating physical costs into system-level metrics so architectural decisions are grounded in realistic assumptions. ADEPT and ADEPT-Z enable end-to-end circuit and topology exploration, connecting system objectives to feasible photonic fabrics under practical device and circuit constraints. Finally, Apollo and LiDAR provide scalable photonic physical design automation, turning candidate circuits into manufacturable layouts while accounting for routing, thermal, and crosstalk constraints.
Sketch-in-Latents: Eliciting Unified Reasoning in MLLMs
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:While Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) excel at visual understanding tasks through text reasoning, they often fall short in scenarios requiring visual imagination. Unlike current works that take predefined external toolkits or generate images during thinking, however, humans can form flexible visual-text imagination and interactions during thinking without predefined toolkits, where one important reason is that humans construct the visual-text thinking process in a unified space inside the brain. Inspired by this capability, given that current MLLMs already encode visual and text information in the same feature space, we hold that visual tokens can be seamlessly inserted into the reasoning process carried by text tokens, where ideally, all visual imagination processes can be encoded by the latent features. To achieve this goal, we propose Sketch-in-Latents (SkiLa), a novel paradigm for unified multi-modal reasoning that expands the auto-regressive capabilities of MLLMs to natively generate continuous visual embeddings, termed latent sketch tokens, as visual thoughts. During multi-step reasoning, the model dynamically alternates between textual thinking mode for generating textual think tokens and visual sketching mode for generating latent sketch tokens. A latent visual semantics reconstruction mechanism is proposed to ensure these latent sketch tokens are semantically grounded. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SkiLa achieves superior performance on vision-centric tasks while exhibiting strong generalization to diverse general multi-modal benchmarks. Codes will be released at https://github.com/TungChintao/SkiLa.
Toward Lifelong-Sustainable Electronic-Photonic AI Systems via Extreme Efficiency, Reconfigurability, and Robustness
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:The relentless growth of large-scale artificial intelligence (AI) has created unprecedented demand for computational power, straining the energy, bandwidth, and scaling limits of conventional electronic platforms. Electronic-photonic integrated circuits (EPICs) have emerged as a compelling platform for next-generation AI systems, offering inherent advantages in ultra-high bandwidth, low latency, and energy efficiency for computing and interconnection. Beyond performance, EPICs also hold unique promises for sustainability. Fabricated in relaxed process nodes with fewer metal layers and lower defect densities, photonic devices naturally reduce embodied carbon footprint (CFP) compared to advanced digital electronic integrated circuits, while delivering orders-of-magnitude higher computing performance and interconnect bandwidth. To further advance the sustainability of photonic AI systems, we explore how electronic-photonic design automation (EPDA) and cross-layer co-design methodologies can amplify these inherent benefits. We present how advanced EPDA tools enable more compact layout generation, reducing both chip area and metal layer usage. We will also demonstrate how cross-layer device-circuit-architecture co-design unlocks new sustainability gains for photonic hardware: ultra-compact photonic circuit designs that minimize chip area cost, reconfigurable hardware topology that adapts to evolving AI workloads, and intelligent resilience mechanisms that prolong lifetime by tolerating variations and faults. By uniting intrinsic photonic efficiency with EPDA- and co-design-driven gains in area efficiency, reconfigurability, and robustness, we outline a vision for lifelong-sustainable electronic-photonic AI systems. This perspective highlights how EPIC AI systems can simultaneously meet the performance demands of modern AI and the urgent imperative for sustainable computing.
SparseC-AFM: a deep learning method for fast and accurate characterization of MoS$_2$ with C-AFM
Jul 17, 2025Abstract:The increasing use of two-dimensional (2D) materials in nanoelectronics demands robust metrology techniques for electrical characterization, especially for large-scale production. While atomic force microscopy (AFM) techniques like conductive AFM (C-AFM) offer high accuracy, they suffer from slow data acquisition speeds due to the raster scanning process. To address this, we introduce SparseC-AFM, a deep learning model that rapidly and accurately reconstructs conductivity maps of 2D materials like MoS$_2$ from sparse C-AFM scans. Our approach is robust across various scanning modes, substrates, and experimental conditions. We report a comparison between (a) classic flow implementation, where a high pixel density C-AFM image (e.g., 15 minutes to collect) is manually parsed to extract relevant material parameters, and (b) our SparseC-AFM method, which achieves the same operation using data that requires substantially less acquisition time (e.g., under 5 minutes). SparseC-AFM enables efficient extraction of critical material parameters in MoS$_2$, including film coverage, defect density, and identification of crystalline island boundaries, edges, and cracks. We achieve over 11x reduction in acquisition time compared to manual extraction from a full-resolution C-AFM image. Moreover, we demonstrate that our model-predicted samples exhibit remarkably similar electrical properties to full-resolution data gathered using classic-flow scanning. This work represents a significant step toward translating AI-assisted 2D material characterization from laboratory research to industrial fabrication. Code and model weights are available at github.com/UNITES-Lab/sparse-cafm.
SP2RINT: Spatially-Decoupled Physics-Inspired Progressive Inverse Optimization for Scalable, PDE-Constrained Meta-Optical Neural Network Training
May 23, 2025Abstract:DONNs harness the physics of light propagation for efficient analog computation, with applications in AI and signal processing. Advances in nanophotonic fabrication and metasurface-based wavefront engineering have opened new pathways to realize high-capacity DONNs across various spectral regimes. Training such DONN systems to determine the metasurface structures remains challenging. Heuristic methods are fast but oversimplify metasurfaces modulation, often resulting in physically unrealizable designs and significant performance degradation. Simulation-in-the-loop training methods directly optimize a physically implementable metasurface using adjoint methods during end-to-end DONN training, but are inherently computationally prohibitive and unscalable.To address these limitations, we propose SP2RINT, a spatially decoupled, progressive training framework that formulates DONN training as a PDE-constrained learning problem. Metasurface responses are first relaxed into freely trainable transfer matrices with a banded structure. We then progressively enforce physical constraints by alternating between transfer matrix training and adjoint-based inverse design, avoiding per-iteration PDE solves while ensuring final physical realizability. To further reduce runtime, we introduce a physics-inspired, spatially decoupled inverse design strategy based on the natural locality of field interactions. This approach partitions the metasurface into independently solvable patches, enabling scalable and parallel inverse design with system-level calibration. Evaluated across diverse DONN training tasks, SP2RINT achieves digital-comparable accuracy while being 1825 times faster than simulation-in-the-loop approaches. By bridging the gap between abstract DONN models and implementable photonic hardware, SP2RINT enables scalable, high-performance training of physically realizable meta-optical neural systems.
MAPS: Multi-Fidelity AI-Augmented Photonic Simulation and Inverse Design Infrastructure
Mar 02, 2025



Abstract:Inverse design has emerged as a transformative approach for photonic device optimization, enabling the exploration of high-dimensional, non-intuitive design spaces to create ultra-compact devices and advance photonic integrated circuits (PICs) in computing and interconnects. However, practical challenges, such as suboptimal device performance, limited manufacturability, high sensitivity to variations, computational inefficiency, and lack of interpretability, have hindered its adoption in commercial hardware. Recent advancements in AI-assisted photonic simulation and design offer transformative potential, accelerating simulations and design generation by orders of magnitude over traditional numerical methods. Despite these breakthroughs, the lack of an open-source, standardized infrastructure and evaluation benchmark limits accessibility and cross-disciplinary collaboration. To address this, we introduce MAPS, a multi-fidelity AI-augmented photonic simulation and inverse design infrastructure designed to bridge this gap. MAPS features three synergistic components: (1) MAPS-Data: A dataset acquisition framework for generating multi-fidelity, richly labeled devices, providing high-quality data for AI-for-optics research. (2) MAPS-Train: A flexible AI-for-photonics training framework offering a hierarchical data loading pipeline, customizable model construction, support for data- and physics-driven losses, and comprehensive evaluations. (3) MAPS-InvDes: An advanced adjoint inverse design toolkit that abstracts complex physics but exposes flexible optimization steps, integrates pre-trained AI models, and incorporates fabrication variation models. This infrastructure MAPS provides a unified, open-source platform for developing, benchmarking, and advancing AI-assisted photonic design workflows, accelerating innovation in photonic hardware optimization and scientific machine learning.
PTZ-Calib: Robust Pan-Tilt-Zoom Camera Calibration
Feb 13, 2025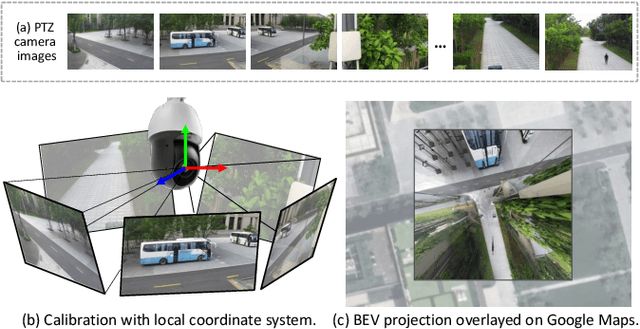
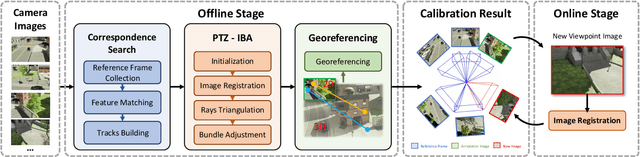
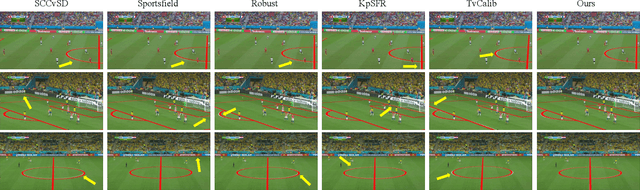
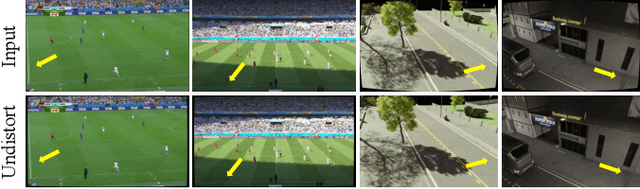
Abstract:In this paper, we present PTZ-Calib, a robust two-stage PTZ camera calibration method, that efficiently and accurately estimates camera parameters for arbitrary viewpoints. Our method includes an offline and an online stage. In the offline stage, we first uniformly select a set of reference images that sufficiently overlap to encompass a complete 360{\deg} view. We then utilize the novel PTZ-IBA (PTZ Incremental Bundle Adjustment) algorithm to automatically calibrate the cameras within a local coordinate system. Additionally, for practical application, we can further optimize camera parameters and align them with the geographic coordinate system using extra global reference 3D information. In the online stage, we formulate the calibration of any new viewpoints as a relocalization problem. Our approach balances the accuracy and computational efficiency to meet real-world demands. Extensive evaluations demonstrate our robustness and superior performance over state-of-the-art methods on various real and synthetic datasets. Datasets and source code can be accessed online at https://github.com/gjgjh/PTZ-Calib
HybridGS: Decoupling Transients and Statics with 2D and 3D Gaussian Splatting
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:Generating high-quality novel view renderings of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) in scenes featuring transient objects is challenging. We propose a novel hybrid representation, termed as HybridGS, using 2D Gaussians for transient objects per image and maintaining traditional 3D Gaussians for the whole static scenes. Note that, the 3DGS itself is better suited for modeling static scenes that assume multi-view consistency, but the transient objects appear occasionally and do not adhere to the assumption, thus we model them as planar objects from a single view, represented with 2D Gaussians. Our novel representation decomposes the scene from the perspective of fundamental viewpoint consistency, making it more reasonable. Additionally, we present a novel multi-view regulated supervision method for 3DGS that leverages information from co-visible regions, further enhancing the distinctions between the transients and statics. Then, we propose a straightforward yet effective multi-stage training strategy to ensure robust training and high-quality view synthesis across various settings. Experiments on benchmark datasets show our state-of-the-art performance of novel view synthesis in both indoor and outdoor scenes, even in the presence of distracting elements.
SimPhony: A Device-Circuit-Architecture Cross-Layer Modeling and Simulation Framework for Heterogeneous Electronic-Photonic AI System
Nov 20, 2024



Abstract:Electronic-photonic integrated circuits (EPICs) offer transformative potential for next-generation high-performance AI but require interdisciplinary advances across devices, circuits, architecture, and design automation. The complexity of hybrid systems makes it challenging even for domain experts to understand distinct behaviors and interactions across design stack. The lack of a flexible, accurate, fast, and easy-to-use EPIC AI system simulation framework significantly limits the exploration of hardware innovations and system evaluations on common benchmarks. To address this gap, we propose SimPhony, a cross-layer modeling and simulation framework for heterogeneous electronic-photonic AI systems. SimPhony offers a platform that enables (1) generic, extensible hardware topology representation that supports heterogeneous multi-core architectures with diverse photonic tensor core designs; (2) optics-specific dataflow modeling with unique multi-dimensional parallelism and reuse beyond spatial/temporal dimensions; (3) data-aware energy modeling with realistic device responses, layout-aware area estimation, link budget analysis, and bandwidth-adaptive memory modeling; and (4) seamless integration with model training framework for hardware/software co-simulation. By providing a unified, versatile, and high-fidelity simulation platform, SimPhony enables researchers to innovate and evaluate EPIC AI hardware across multiple domains, facilitating the next leap in emerging AI hardware. We open-source our codes at https://github.com/ScopeX-ASU/SimPhony
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge