Shen Cao
No Parameters, No Problem: 3D Gaussian Splatting without Camera Intrinsics and Extrinsics
Feb 27, 2025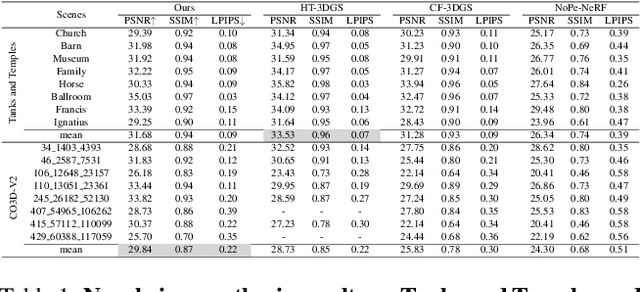
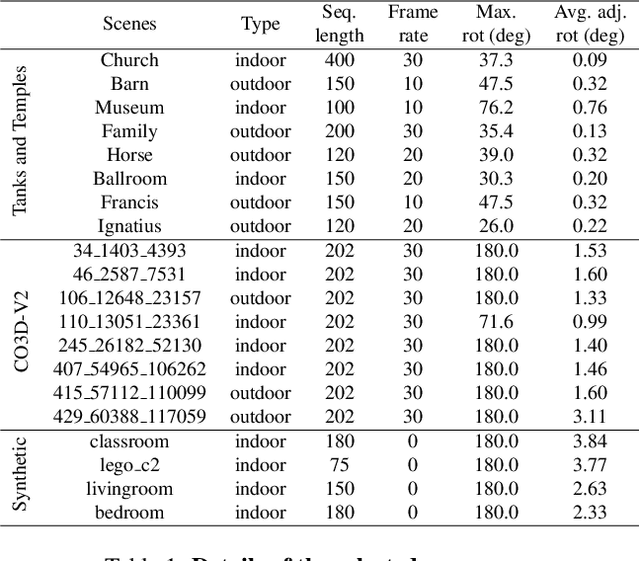
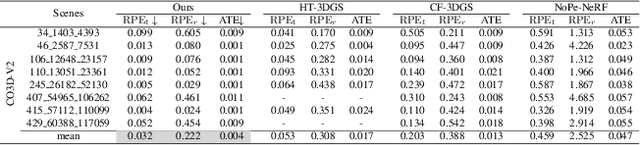
Abstract:While 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has made significant progress in scene reconstruction and novel view synthesis, it still heavily relies on accurately pre-computed camera intrinsics and extrinsics, such as focal length and camera poses. In order to mitigate this dependency, the previous efforts have focused on optimizing 3DGS without the need for camera poses, yet camera intrinsics remain necessary. To further loose the requirement, we propose a joint optimization method to train 3DGS from an image collection without requiring either camera intrinsics or extrinsics. To achieve this goal, we introduce several key improvements during the joint training of 3DGS. We theoretically derive the gradient of the camera intrinsics, allowing the camera intrinsics to be optimized simultaneously during training. Moreover, we integrate global track information and select the Gaussian kernels associated with each track, which will be trained and automatically rescaled to an infinitesimally small size, closely approximating surface points, and focusing on enforcing multi-view consistency and minimizing reprojection errors, while the remaining kernels continue to serve their original roles. This hybrid training strategy nicely unifies the camera parameters estimation and 3DGS training. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on both public and synthetic datasets.
CoL3D: Collaborative Learning of Single-view Depth and Camera Intrinsics for Metric 3D Shape Recovery
Feb 13, 2025



Abstract:Recovering the metric 3D shape from a single image is particularly relevant for robotics and embodied intelligence applications, where accurate spatial understanding is crucial for navigation and interaction with environments. Usually, the mainstream approaches achieve it through monocular depth estimation. However, without camera intrinsics, the 3D metric shape can not be recovered from depth alone. In this study, we theoretically demonstrate that depth serves as a 3D prior constraint for estimating camera intrinsics and uncover the reciprocal relations between these two elements. Motivated by this, we propose a collaborative learning framework for jointly estimating depth and camera intrinsics, named CoL3D, to learn metric 3D shapes from single images. Specifically, CoL3D adopts a unified network and performs collaborative optimization at three levels: depth, camera intrinsics, and 3D point clouds. For camera intrinsics, we design a canonical incidence field mechanism as a prior that enables the model to learn the residual incident field for enhanced calibration. Additionally, we incorporate a shape similarity measurement loss in the point cloud space, which improves the quality of 3D shapes essential for robotic applications. As a result, when training and testing on a single dataset with in-domain settings, CoL3D delivers outstanding performance in both depth estimation and camera calibration across several indoor and outdoor benchmark datasets, which leads to remarkable 3D shape quality for the perception capabilities of robots.
PTZ-Calib: Robust Pan-Tilt-Zoom Camera Calibration
Feb 13, 2025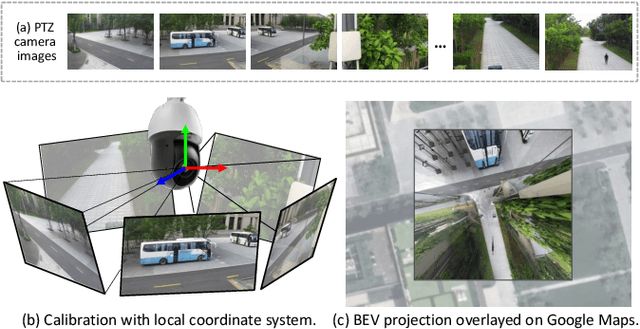
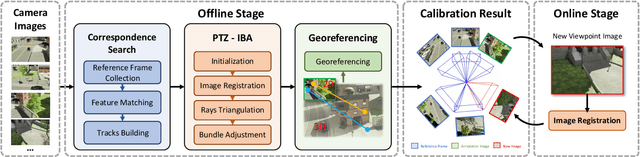
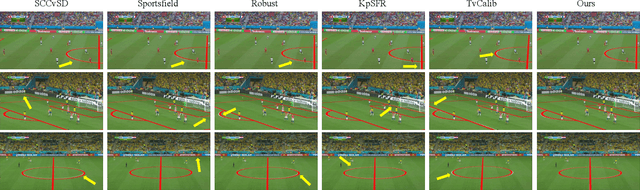
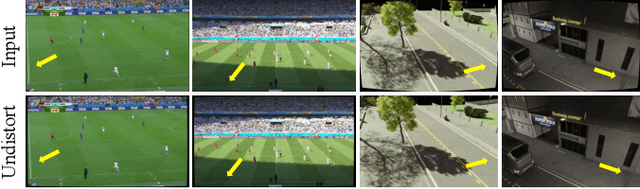
Abstract:In this paper, we present PTZ-Calib, a robust two-stage PTZ camera calibration method, that efficiently and accurately estimates camera parameters for arbitrary viewpoints. Our method includes an offline and an online stage. In the offline stage, we first uniformly select a set of reference images that sufficiently overlap to encompass a complete 360{\deg} view. We then utilize the novel PTZ-IBA (PTZ Incremental Bundle Adjustment) algorithm to automatically calibrate the cameras within a local coordinate system. Additionally, for practical application, we can further optimize camera parameters and align them with the geographic coordinate system using extra global reference 3D information. In the online stage, we formulate the calibration of any new viewpoints as a relocalization problem. Our approach balances the accuracy and computational efficiency to meet real-world demands. Extensive evaluations demonstrate our robustness and superior performance over state-of-the-art methods on various real and synthetic datasets. Datasets and source code can be accessed online at https://github.com/gjgjh/PTZ-Calib
Enhancing, Refining, and Fusing: Towards Robust Multi-Scale and Dense Ship Detection
Jan 10, 2025



Abstract:Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imaging, celebrated for its high resolution, all-weather capability, and day-night operability, is indispensable for maritime applications. However, ship detection in SAR imagery faces significant challenges, including complex backgrounds, densely arranged targets, and large scale variations. To address these issues, we propose a novel framework, Center-Aware SAR Ship Detector (CASS-Det), designed for robust multi-scale and densely packed ship detection. CASS-Det integrates three key innovations: (1) a center enhancement module (CEM) that employs rotational convolution to emphasize ship centers, improving localization while suppressing background interference; (2) a neighbor attention module (NAM) that leverages cross-layer dependencies to refine ship boundaries in densely populated scenes; and (3) a cross-connected feature pyramid network (CC-FPN) that enhances multi-scale feature fusion by integrating shallow and deep features. Extensive experiments on the SSDD, HRSID, and LS-SSDD-v1.0 datasets demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of CASS-Det, excelling at detecting multi-scale and densely arranged ships.
Homography Loss for Monocular 3D Object Detection
Apr 02, 2022
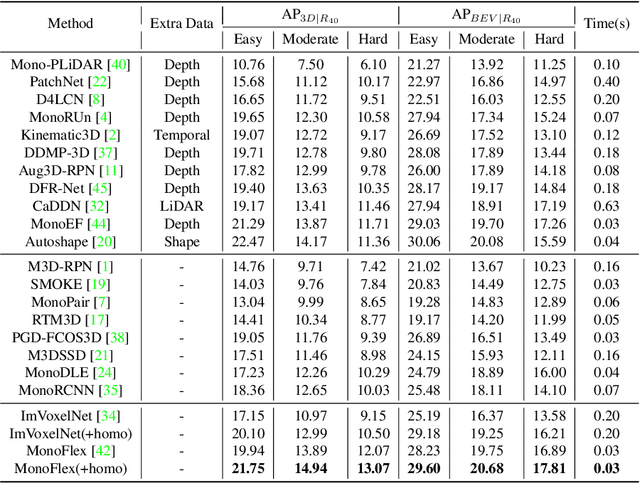
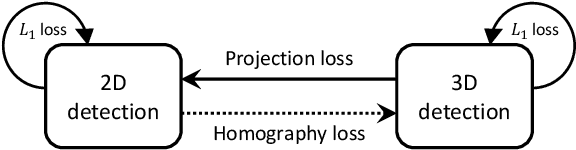
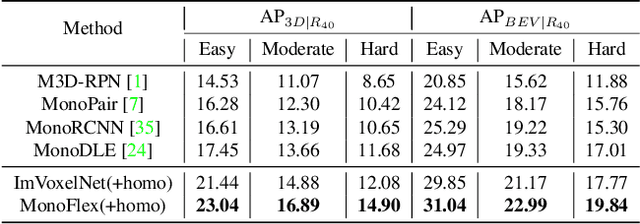
Abstract:Monocular 3D object detection is an essential task in autonomous driving. However, most current methods consider each 3D object in the scene as an independent training sample, while ignoring their inherent geometric relations, thus inevitably resulting in a lack of leveraging spatial constraints. In this paper, we propose a novel method that takes all the objects into consideration and explores their mutual relationships to help better estimate the 3D boxes. Moreover, since 2D detection is more reliable currently, we also investigate how to use the detected 2D boxes as guidance to globally constrain the optimization of the corresponding predicted 3D boxes. To this end, a differentiable loss function, termed as Homography Loss, is proposed to achieve the goal, which exploits both 2D and 3D information, aiming at balancing the positional relationships between different objects by global constraints, so as to obtain more accurately predicted 3D boxes. Thanks to the concise design, our loss function is universal and can be plugged into any mature monocular 3D detector, while significantly boosting the performance over their baseline. Experiments demonstrate that our method yields the best performance (Nov. 2021) compared with the other state-of-the-arts by a large margin on KITTI 3D datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge