Nicholas Gangi
Toward Large-Scale Photonics-Empowered AI Systems: From Physical Design Automation to System-Algorithm Co-Exploration
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:In this work, we identify three considerations that are essential for realizing practical photonic AI systems at scale: (1) dynamic tensor operation support for modern models rather than only weight-static kernels, especially for attention/Transformer-style workloads; (2) systematic management of conversion, control, and data-movement overheads, where multiplexing and dataflow must amortize electronic costs instead of letting ADC/DAC and I/O dominate; and (3) robustness under hardware non-idealities that become more severe as integration density grows. To study these coupled tradeoffs quantitatively, and to ensure they remain meaningful under real implementation constraints, we build a cross-layer toolchain that supports photonic AI design from early exploration to physical realization. SimPhony provides implementation-aware modeling and rapid cross-layer evaluation, translating physical costs into system-level metrics so architectural decisions are grounded in realistic assumptions. ADEPT and ADEPT-Z enable end-to-end circuit and topology exploration, connecting system objectives to feasible photonic fabrics under practical device and circuit constraints. Finally, Apollo and LiDAR provide scalable photonic physical design automation, turning candidate circuits into manufacturable layouts while accounting for routing, thermal, and crosstalk constraints.
SP2RINT: Spatially-Decoupled Physics-Inspired Progressive Inverse Optimization for Scalable, PDE-Constrained Meta-Optical Neural Network Training
May 23, 2025Abstract:DONNs harness the physics of light propagation for efficient analog computation, with applications in AI and signal processing. Advances in nanophotonic fabrication and metasurface-based wavefront engineering have opened new pathways to realize high-capacity DONNs across various spectral regimes. Training such DONN systems to determine the metasurface structures remains challenging. Heuristic methods are fast but oversimplify metasurfaces modulation, often resulting in physically unrealizable designs and significant performance degradation. Simulation-in-the-loop training methods directly optimize a physically implementable metasurface using adjoint methods during end-to-end DONN training, but are inherently computationally prohibitive and unscalable.To address these limitations, we propose SP2RINT, a spatially decoupled, progressive training framework that formulates DONN training as a PDE-constrained learning problem. Metasurface responses are first relaxed into freely trainable transfer matrices with a banded structure. We then progressively enforce physical constraints by alternating between transfer matrix training and adjoint-based inverse design, avoiding per-iteration PDE solves while ensuring final physical realizability. To further reduce runtime, we introduce a physics-inspired, spatially decoupled inverse design strategy based on the natural locality of field interactions. This approach partitions the metasurface into independently solvable patches, enabling scalable and parallel inverse design with system-level calibration. Evaluated across diverse DONN training tasks, SP2RINT achieves digital-comparable accuracy while being 1825 times faster than simulation-in-the-loop approaches. By bridging the gap between abstract DONN models and implementable photonic hardware, SP2RINT enables scalable, high-performance training of physically realizable meta-optical neural systems.
SCATTER: Algorithm-Circuit Co-Sparse Photonic Accelerator with Thermal-Tolerant, Power-Efficient In-situ Light Redistribution
Jul 07, 2024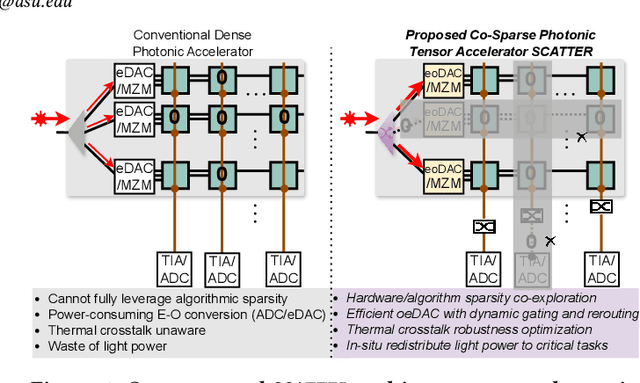
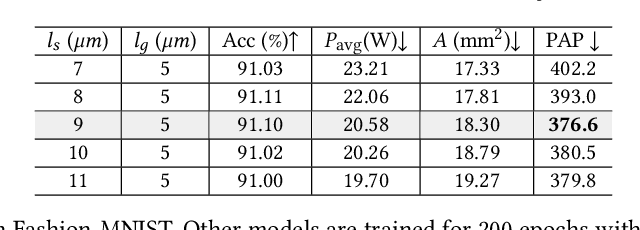
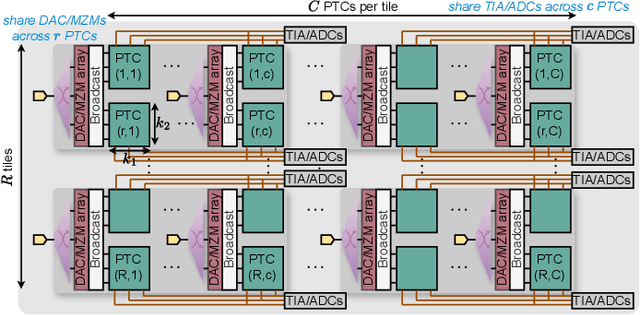
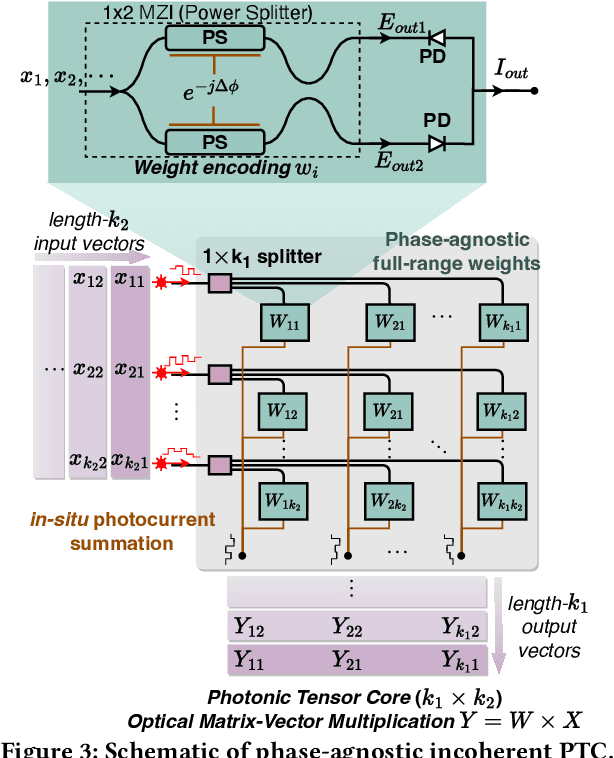
Abstract:Photonic computing has emerged as a promising solution for accelerating computation-intensive artificial intelligence (AI) workloads. However, limited reconfigurability, high electrical-optical conversion cost, and thermal sensitivity limit the deployment of current optical analog computing engines to support power-restricted, performance-sensitive AI workloads at scale. Sparsity provides a great opportunity for hardware-efficient AI accelerators. However, current dense photonic accelerators fail to fully exploit the power-saving potential of algorithmic sparsity. It requires sparsity-aware hardware specialization with a fundamental re-design of photonic tensor core topology and cross-layer device-circuit-architecture-algorithm co-optimization aware of hardware non-ideality and power bottleneck. To trim down the redundant power consumption while maximizing robustness to thermal variations, we propose SCATTER, a novel algorithm-circuit co-sparse photonic accelerator featuring dynamically reconfigurable signal path via thermal-tolerant, power-efficient in-situ light redistribution and power gating. A power-optimized, crosstalk-aware dynamic sparse training framework is introduced to explore row-column structured sparsity and ensure marginal accuracy loss and maximum power efficiency. The extensive evaluation shows that our cross-stacked optimized accelerator SCATTER achieves a 511X area reduction and 12.4X power saving with superior crosstalk tolerance that enables unprecedented circuit layout compactness and on-chip power efficiency.
TeMPO: Efficient Time-Multiplexed Dynamic Photonic Tensor Core for Edge AI with Compact Slow-Light Electro-Optic Modulator
Feb 12, 2024Abstract:Electronic-photonic computing systems offer immense potential in energy-efficient artificial intelligence (AI) acceleration tasks due to the superior computing speed and efficiency of optics, especially for real-time, low-energy deep neural network (DNN) inference tasks on resource-restricted edge platforms. However, current optical neural accelerators based on foundry-available devices and conventional system architecture still encounter a performance gap compared to highly customized electronic counterparts. To bridge the performance gap due to lack of domain specialization, we present a time-multiplexed dynamic photonic tensor accelerator, dubbed TeMPO, with cross-layer device/circuit/architecture customization. At the device level, we present foundry-compatible, customized photonic devices, including a slow-light electro-optic modulator with experimental demonstration, optical splitters, and phase shifters that significantly reduce the footprint and power in input encoding and dot-product calculation. At the circuit level, partial products are hierarchically accumulated via parallel photocurrent aggregation, lightweight capacitive temporal integration, and sequential digital summation, considerably relieving the analog-to-digital conversion bottleneck. We also employ a multi-tile, multi-core architecture to maximize hardware sharing for higher efficiency. Across diverse edge AI workloads, TeMPO delivers digital-comparable task accuracy with superior quantization/noise tolerance. We achieve a 368.6 TOPS peak performance, 22.3 TOPS/W energy efficiency, and 1.2 TOPS/mm$^2$ compute density, pushing the Pareto frontier in edge AI hardware. This work signifies the power of cross-layer co-design and domain-specific customization, paving the way for future electronic-photonic accelerators with even greater performance and efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge