Wenming Wu
Advancing Architectural Floorplan Design with Geometry-enhanced Graph Diffusion
Aug 29, 2024



Abstract:Automating architectural floorplan design is vital for housing and interior design, offering a faster, cost-effective alternative to manual sketches by architects. However, existing methods, including rule-based and learning-based approaches, face challenges in design complexity and constrained generation with extensive post-processing, and tend to obvious geometric inconsistencies such as misalignment, overlap, and gaps. In this work, we propose a novel generative framework for vector floorplan design via structural graph generation, called GSDiff, focusing on wall junction generation and wall segment prediction to capture both geometric and semantic aspects of structural graphs. To improve the geometric rationality of generated structural graphs, we propose two innovative geometry enhancement methods. In wall junction generation, we propose a novel alignment loss function to improve geometric consistency. In wall segment prediction, we propose a random self-supervision method to enhance the model's perception of the overall geometric structure, thereby promoting the generation of reasonable geometric structures. Employing the diffusion model and the Transformer model, as well as the geometry enhancement strategies, our framework can generate wall junctions, wall segments and room polygons with structural and semantic information, resulting in structural graphs that accurately represent floorplans. Extensive experiments show that the proposed method surpasses existing techniques, enabling free generation and constrained generation, marking a shift towards structure generation in architectural design.
Guided Diffusion for Fast Inverse Design of Density-based Mechanical Metamaterials
Jan 24, 2024Abstract:Mechanical metamaterial is a synthetic material that can possess extraordinary physical characteristics, such as abnormal elasticity, stiffness, and stability, by carefully designing its internal structure. To make metamaterials contain delicate local structures with unique mechanical properties, it is a potential method to represent them through high-resolution voxels. However, it brings a substantial computational burden. To this end, this paper proposes a fast inverse design method, whose core is an advanced deep generative AI algorithm, to generate voxel-based mechanical metamaterials. Specifically, we use the self-conditioned diffusion model, capable of generating a microstructure with a resolution of $128^3$ to approach the specified homogenized tensor matrix in just 3 seconds. Accordingly, this rapid reverse design tool facilitates the exploration of extreme metamaterials, the sequence interpolation in metamaterials, and the generation of diverse microstructures for multi-scale design. This flexible and adaptive generative tool is of great value in structural engineering or other mechanical systems and can stimulate more subsequent research.
Breast Tumor Classification Based on Decision Information Genes and Inverse Projection Sparse Representation
Apr 17, 2018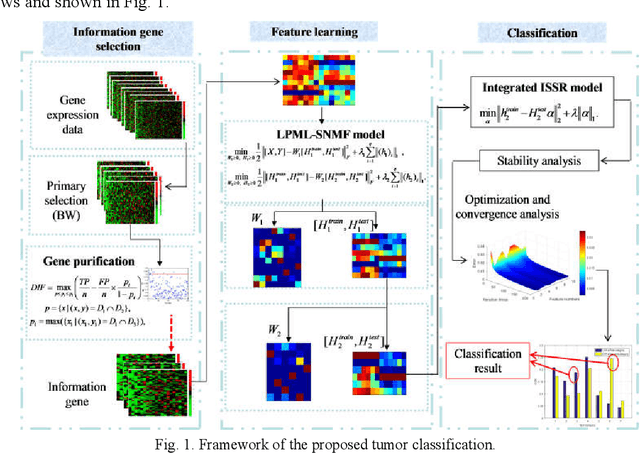
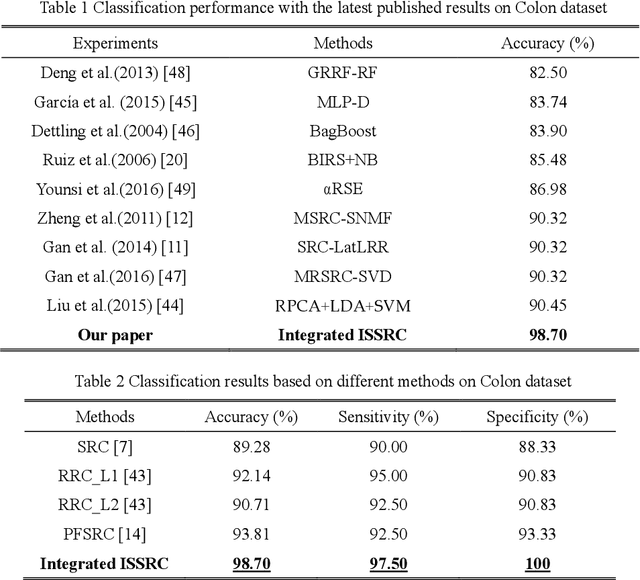
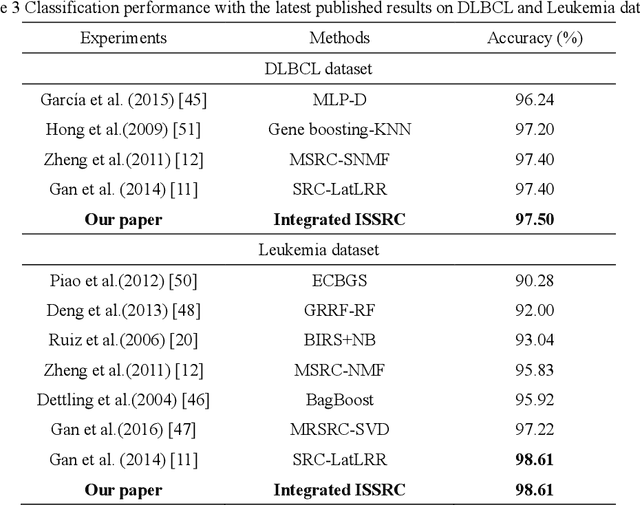
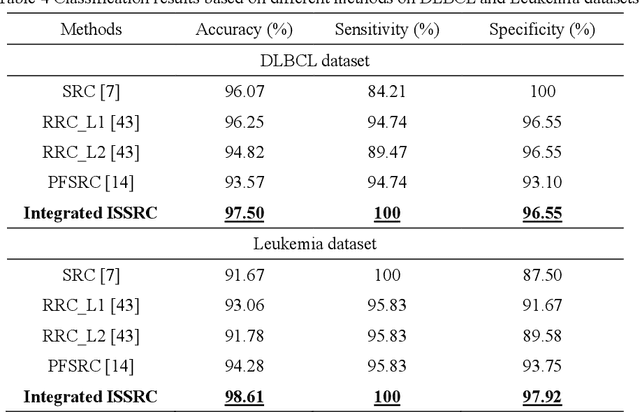
Abstract:Microarray gene expression data-based breast tumor classification is an active and challenging issue. In this paper, a robust framework of breast tumor recognition is presented aiming at reducing clinical misdiagnosis rate and exploiting available information in existing samples. A wrapper gene selection method is established from a new perspective of reducing clinical misdiagnosis rate. The further feature selection of information genes is achieved using the modified NMF model, which is rooted in the use of hierarchical learning and layer-wise pre-training strategy in deep learning. For completing the classification, an inverse projection sparse representation (IPSR) model is constructed to exploit information embedded in existing samples, especially in the test ones. Moreover, the IPSR model is optimized through generalized ADMM and the corresponding convergence is analyzed. Extensive experiments on public microarray gene expression datasets show that the proposed method is stable and effective for breast tumor classification. Compared to the latest open literature, there is 14% higher in classification accuracy. Specificity and sensitivity achieve 94.17% and 97.5%, respectively.
Low Rank Variation Dictionary and Inverse Projection Group Sparse Representation Model for Breast Tumor Classification
Mar 10, 2018


Abstract:Sparse representation classification achieves good results by addressing recognition problem with sufficient training samples per subject. However, SRC performs not very well for small sample data. In this paper, an inverse-projection group sparse representation model is presented for breast tumor classification, which is based on constructing low-rank variation dictionary. The proposed low-rank variation dictionary tackles tumor recognition problem from the viewpoint of detecting and using variations in gene expression profiles of normal and patients, rather than directly using these samples. The inverse projection group sparsity representation model is constructed based on taking full using of exist samples and group effect of microarray gene data. Extensive experiments on public breast tumor microarray gene expression datasets demonstrate the proposed technique is competitive with state-of-the-art methods. The results of Breast-1, Breast-2 and Breast-3 databases are 80.81%, 89.10% and 100% respectively, which are better than the latest literature.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge