Jiaming Sun
FreeTimeGS: Free Gaussian Primitives at Anytime and Anywhere for Dynamic Scene Reconstruction
Jun 06, 2025



Abstract:This paper addresses the challenge of reconstructing dynamic 3D scenes with complex motions. Some recent works define 3D Gaussian primitives in the canonical space and use deformation fields to map canonical primitives to observation spaces, achieving real-time dynamic view synthesis. However, these methods often struggle to handle scenes with complex motions due to the difficulty of optimizing deformation fields. To overcome this problem, we propose FreeTimeGS, a novel 4D representation that allows Gaussian primitives to appear at arbitrary time and locations. In contrast to canonical Gaussian primitives, our representation possesses the strong flexibility, thus improving the ability to model dynamic 3D scenes. In addition, we endow each Gaussian primitive with an motion function, allowing it to move to neighboring regions over time, which reduces the temporal redundancy. Experiments results on several datasets show that the rendering quality of our method outperforms recent methods by a large margin. Project page: https://zju3dv.github.io/freetimegs/ .
Prompting Depth Anything for 4K Resolution Accurate Metric Depth Estimation
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:Prompts play a critical role in unleashing the power of language and vision foundation models for specific tasks. For the first time, we introduce prompting into depth foundation models, creating a new paradigm for metric depth estimation termed Prompt Depth Anything. Specifically, we use a low-cost LiDAR as the prompt to guide the Depth Anything model for accurate metric depth output, achieving up to 4K resolution. Our approach centers on a concise prompt fusion design that integrates the LiDAR at multiple scales within the depth decoder. To address training challenges posed by limited datasets containing both LiDAR depth and precise GT depth, we propose a scalable data pipeline that includes synthetic data LiDAR simulation and real data pseudo GT depth generation. Our approach sets new state-of-the-arts on the ARKitScenes and ScanNet++ datasets and benefits downstream applications, including 3D reconstruction and generalized robotic grasping.
Representing Long Volumetric Video with Temporal Gaussian Hierarchy
Dec 12, 2024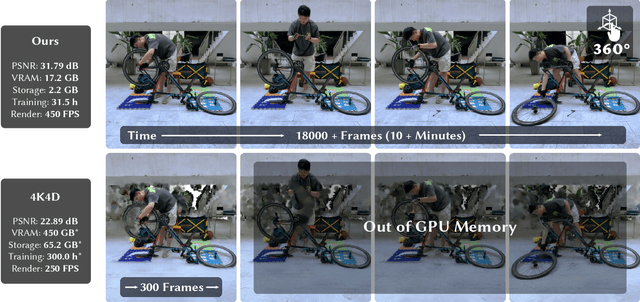
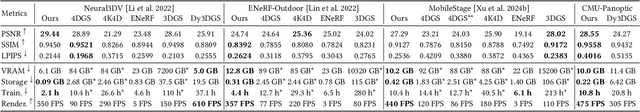
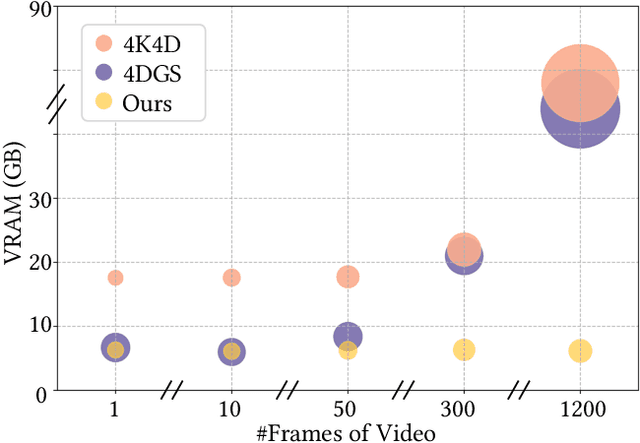
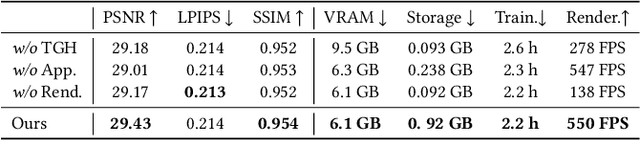
Abstract:This paper aims to address the challenge of reconstructing long volumetric videos from multi-view RGB videos. Recent dynamic view synthesis methods leverage powerful 4D representations, like feature grids or point cloud sequences, to achieve high-quality rendering results. However, they are typically limited to short (1~2s) video clips and often suffer from large memory footprints when dealing with longer videos. To solve this issue, we propose a novel 4D representation, named Temporal Gaussian Hierarchy, to compactly model long volumetric videos. Our key observation is that there are generally various degrees of temporal redundancy in dynamic scenes, which consist of areas changing at different speeds. Motivated by this, our approach builds a multi-level hierarchy of 4D Gaussian primitives, where each level separately describes scene regions with different degrees of content change, and adaptively shares Gaussian primitives to represent unchanged scene content over different temporal segments, thus effectively reducing the number of Gaussian primitives. In addition, the tree-like structure of the Gaussian hierarchy allows us to efficiently represent the scene at a particular moment with a subset of Gaussian primitives, leading to nearly constant GPU memory usage during the training or rendering regardless of the video length. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our method over alternative methods in terms of training cost, rendering speed, and storage usage. To our knowledge, this work is the first approach capable of efficiently handling minutes of volumetric video data while maintaining state-of-the-art rendering quality. Our project page is available at: https://zju3dv.github.io/longvolcap.
EasyVolcap: Accelerating Neural Volumetric Video Research
Dec 11, 2023



Abstract:Volumetric video is a technology that digitally records dynamic events such as artistic performances, sporting events, and remote conversations. When acquired, such volumography can be viewed from any viewpoint and timestamp on flat screens, 3D displays, or VR headsets, enabling immersive viewing experiences and more flexible content creation in a variety of applications such as sports broadcasting, video conferencing, gaming, and movie productions. With the recent advances and fast-growing interest in neural scene representations for volumetric video, there is an urgent need for a unified open-source library to streamline the process of volumetric video capturing, reconstruction, and rendering for both researchers and non-professional users to develop various algorithms and applications of this emerging technology. In this paper, we present EasyVolcap, a Python & Pytorch library for accelerating neural volumetric video research with the goal of unifying the process of multi-view data processing, 4D scene reconstruction, and efficient dynamic volumetric video rendering. Our source code is available at https://github.com/zju3dv/EasyVolcap.
4K4D: Real-Time 4D View Synthesis at 4K Resolution
Oct 28, 2023



Abstract:This paper targets high-fidelity and real-time view synthesis of dynamic 3D scenes at 4K resolution. Recently, some methods on dynamic view synthesis have shown impressive rendering quality. However, their speed is still limited when rendering high-resolution images. To overcome this problem, we propose 4K4D, a 4D point cloud representation that supports hardware rasterization and enables unprecedented rendering speed. Our representation is built on a 4D feature grid so that the points are naturally regularized and can be robustly optimized. In addition, we design a novel hybrid appearance model that significantly boosts the rendering quality while preserving efficiency. Moreover, we develop a differentiable depth peeling algorithm to effectively learn the proposed model from RGB videos. Experiments show that our representation can be rendered at over 400 FPS on the DNA-Rendering dataset at 1080p resolution and 80 FPS on the ENeRF-Outdoor dataset at 4K resolution using an RTX 4090 GPU, which is 30x faster than previous methods and achieves the state-of-the-art rendering quality. Our project page is available at https://zju3dv.github.io/4k4d/.
CPPF: A contextual and post-processing-free model for automatic speech recognition
Sep 21, 2023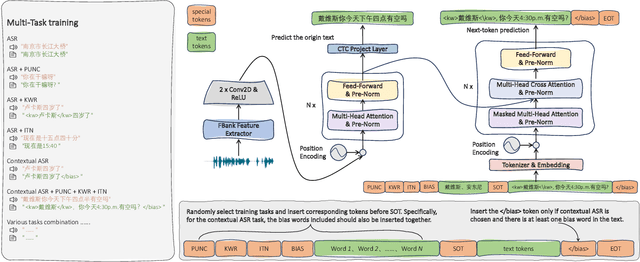
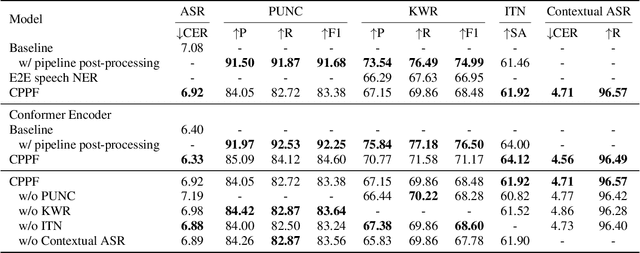
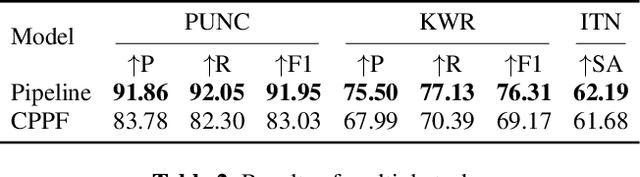
Abstract:ASR systems have become increasingly widespread in recent years. However, their textual outputs often require post-processing tasks before they can be practically utilized. To address this issue, we draw inspiration from the multifaceted capabilities of LLMs and Whisper, and focus on integrating multiple ASR text processing tasks related to speech recognition into the ASR model. This integration not only shortens the multi-stage pipeline, but also prevents the propagation of cascading errors, resulting in direct generation of post-processed text. In this study, we focus on ASR-related processing tasks, including Contextual ASR and multiple ASR post processing tasks. To achieve this objective, we introduce the CPPF model, which offers a versatile and highly effective alternative to ASR processing. CPPF seamlessly integrates these tasks without any significant loss in recognition performance.
Relightable and Animatable Neural Avatar from Sparse-View Video
Aug 17, 2023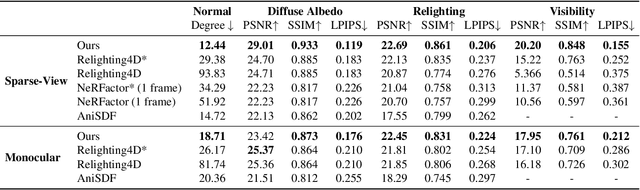
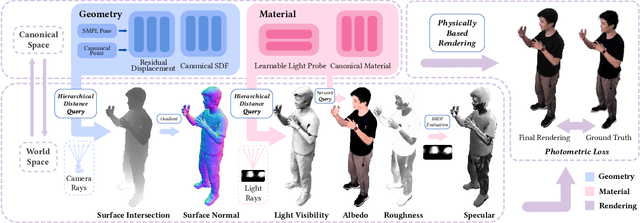
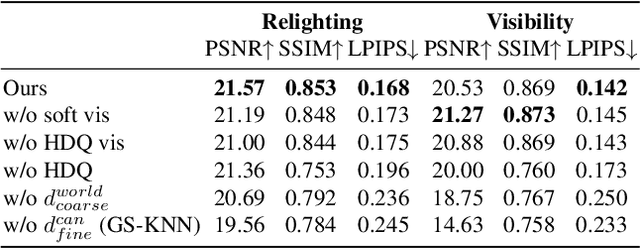
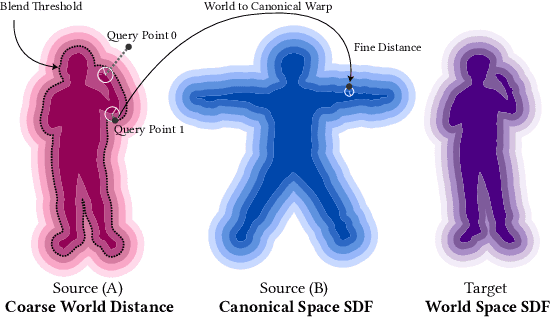
Abstract:This paper tackles the challenge of creating relightable and animatable neural avatars from sparse-view (or even monocular) videos of dynamic humans under unknown illumination. Compared to studio environments, this setting is more practical and accessible but poses an extremely challenging ill-posed problem. Previous neural human reconstruction methods are able to reconstruct animatable avatars from sparse views using deformed Signed Distance Fields (SDF) but cannot recover material parameters for relighting. While differentiable inverse rendering-based methods have succeeded in material recovery of static objects, it is not straightforward to extend them to dynamic humans as it is computationally intensive to compute pixel-surface intersection and light visibility on deformed SDFs for inverse rendering. To solve this challenge, we propose a Hierarchical Distance Query (HDQ) algorithm to approximate the world space distances under arbitrary human poses. Specifically, we estimate coarse distances based on a parametric human model and compute fine distances by exploiting the local deformation invariance of SDF. Based on the HDQ algorithm, we leverage sphere tracing to efficiently estimate the surface intersection and light visibility. This allows us to develop the first system to recover animatable and relightable neural avatars from sparse view (or monocular) inputs. Experiments demonstrate that our approach is able to produce superior results compared to state-of-the-art methods. Our code will be released for reproducibility.
Detector-Free Structure from Motion
Jun 27, 2023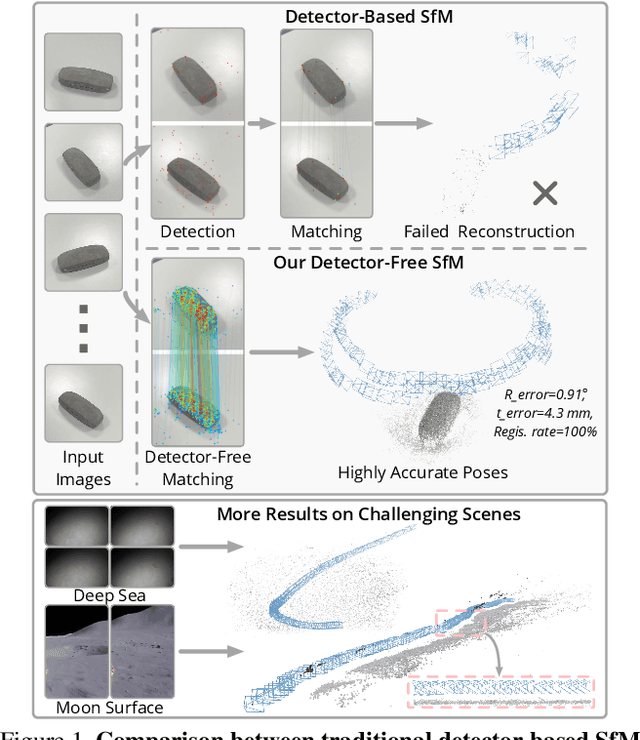
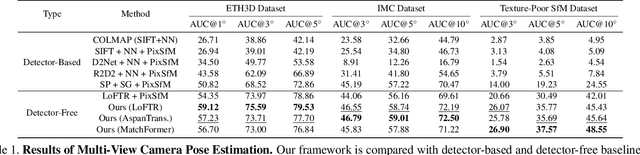
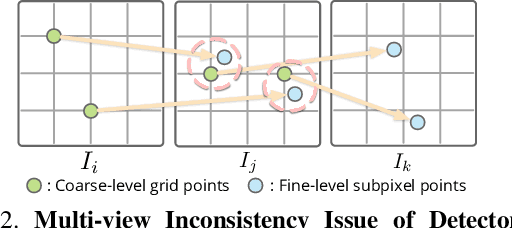
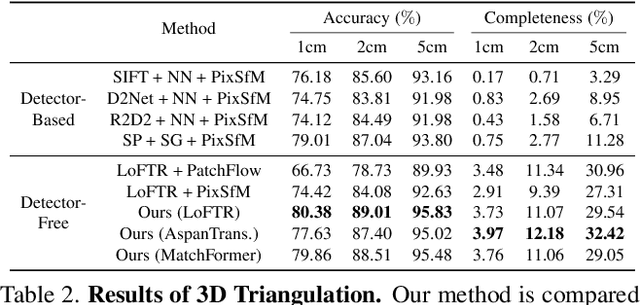
Abstract:We propose a new structure-from-motion framework to recover accurate camera poses and point clouds from unordered images. Traditional SfM systems typically rely on the successful detection of repeatable keypoints across multiple views as the first step, which is difficult for texture-poor scenes, and poor keypoint detection may break down the whole SfM system. We propose a new detector-free SfM framework to draw benefits from the recent success of detector-free matchers to avoid the early determination of keypoints, while solving the multi-view inconsistency issue of detector-free matchers. Specifically, our framework first reconstructs a coarse SfM model from quantized detector-free matches. Then, it refines the model by a novel iterative refinement pipeline, which iterates between an attention-based multi-view matching module to refine feature tracks and a geometry refinement module to improve the reconstruction accuracy. Experiments demonstrate that the proposed framework outperforms existing detector-based SfM systems on common benchmark datasets. We also collect a texture-poor SfM dataset to demonstrate the capability of our framework to reconstruct texture-poor scenes. Based on this framework, we take $\textit{first place}$ in Image Matching Challenge 2023.
OnePose++: Keypoint-Free One-Shot Object Pose Estimation without CAD Models
Jan 18, 2023

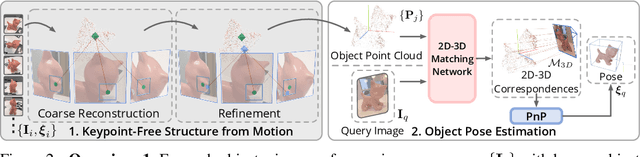

Abstract:We propose a new method for object pose estimation without CAD models. The previous feature-matching-based method OnePose has shown promising results under a one-shot setting which eliminates the need for CAD models or object-specific training. However, OnePose relies on detecting repeatable image keypoints and is thus prone to failure on low-textured objects. We propose a keypoint-free pose estimation pipeline to remove the need for repeatable keypoint detection. Built upon the detector-free feature matching method LoFTR, we devise a new keypoint-free SfM method to reconstruct a semi-dense point-cloud model for the object. Given a query image for object pose estimation, a 2D-3D matching network directly establishes 2D-3D correspondences between the query image and the reconstructed point-cloud model without first detecting keypoints in the image. Experiments show that the proposed pipeline outperforms existing one-shot CAD-model-free methods by a large margin and is comparable to CAD-model-based methods on LINEMOD even for low-textured objects. We also collect a new dataset composed of 80 sequences of 40 low-textured objects to facilitate future research on one-shot object pose estimation. The supplementary material, code and dataset are available on the project page: https://zju3dv.github.io/onepose_plus_plus/.
Reconstructing Hand-Held Objects from Monocular Video
Nov 30, 2022
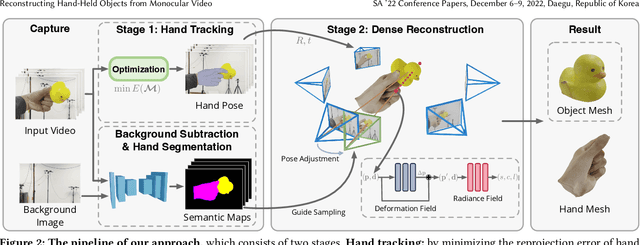
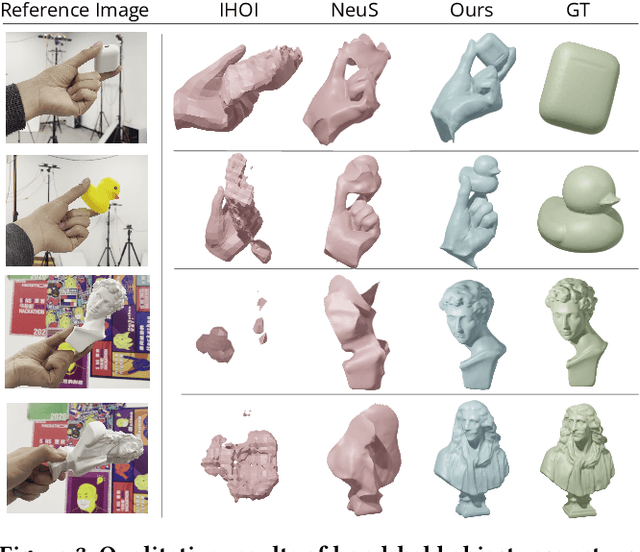
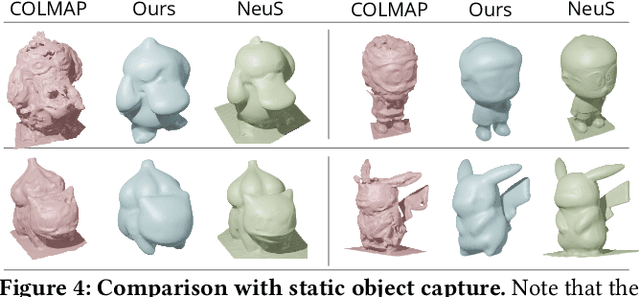
Abstract:This paper presents an approach that reconstructs a hand-held object from a monocular video. In contrast to many recent methods that directly predict object geometry by a trained network, the proposed approach does not require any learned prior about the object and is able to recover more accurate and detailed object geometry. The key idea is that the hand motion naturally provides multiple views of the object and the motion can be reliably estimated by a hand pose tracker. Then, the object geometry can be recovered by solving a multi-view reconstruction problem. We devise an implicit neural representation-based method to solve the reconstruction problem and address the issues of imprecise hand pose estimation, relative hand-object motion, and insufficient geometry optimization for small objects. We also provide a newly collected dataset with 3D ground truth to validate the proposed approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge