Hongyu Xiang
CPPF: A contextual and post-processing-free model for automatic speech recognition
Sep 21, 2023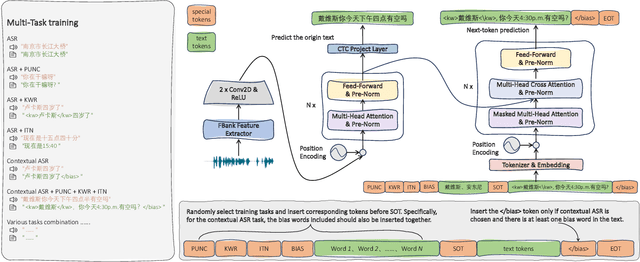
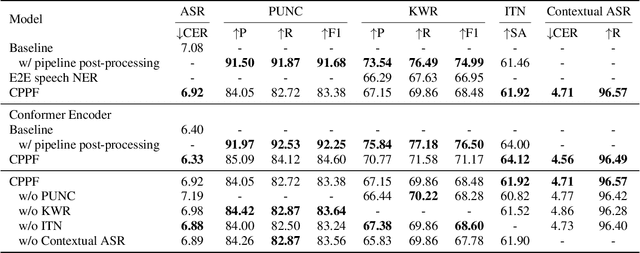
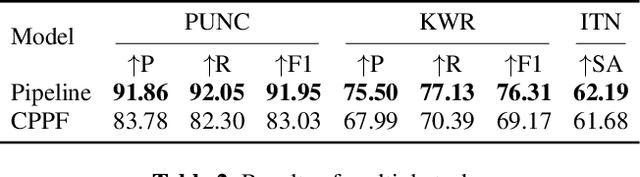
Abstract:ASR systems have become increasingly widespread in recent years. However, their textual outputs often require post-processing tasks before they can be practically utilized. To address this issue, we draw inspiration from the multifaceted capabilities of LLMs and Whisper, and focus on integrating multiple ASR text processing tasks related to speech recognition into the ASR model. This integration not only shortens the multi-stage pipeline, but also prevents the propagation of cascading errors, resulting in direct generation of post-processed text. In this study, we focus on ASR-related processing tasks, including Contextual ASR and multiple ASR post processing tasks. To achieve this objective, we introduce the CPPF model, which offers a versatile and highly effective alternative to ASR processing. CPPF seamlessly integrates these tasks without any significant loss in recognition performance.
Peak-First CTC: Reducing the Peak Latency of CTC Models by Applying Peak-First Regularization
Nov 07, 2022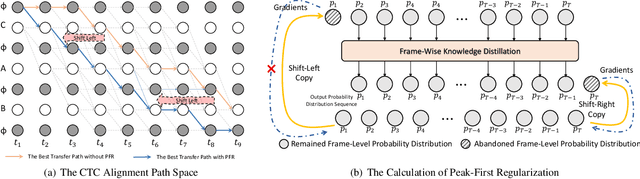
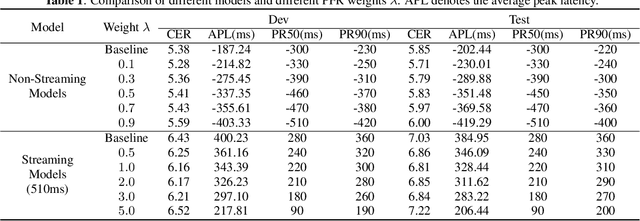
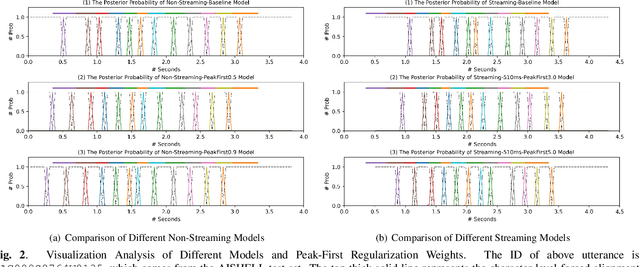
Abstract:The CTC model has been widely applied to many application scenarios because of its simple structure, excellent performance, and fast inference speed. There are many peaks in the probability distribution predicted by the CTC models, and each peak represents a non-blank token. The recognition latency of CTC models can be reduced by encouraging the model to predict peaks earlier. Existing methods to reduce latency require modifying the transition relationship between tokens in the forward-backward algorithm, and the gradient calculation. Some of these methods even depend on the forced alignment results provided by other pretrained models. The above methods are complex to implement. To reduce the peak latency, we propose a simple and novel method named peak-first regularization, which utilizes a frame-wise knowledge distillation function to force the probability distribution of the CTC model to shift left along the time axis instead of directly modifying the calculation process of CTC loss and gradients. All the experiments are conducted on a Chinese Mandarin dataset AISHELL-1. We have verified the effectiveness of the proposed regularization on both streaming and non-streaming CTC models respectively. The results show that the proposed method can reduce the average peak latency by about 100 to 200 milliseconds with almost no degradation of recognition accuracy.
CUSIDE: Chunking, Simulating Future Context and Decoding for Streaming ASR
Mar 31, 2022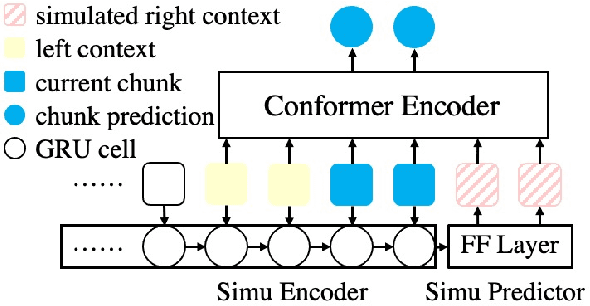
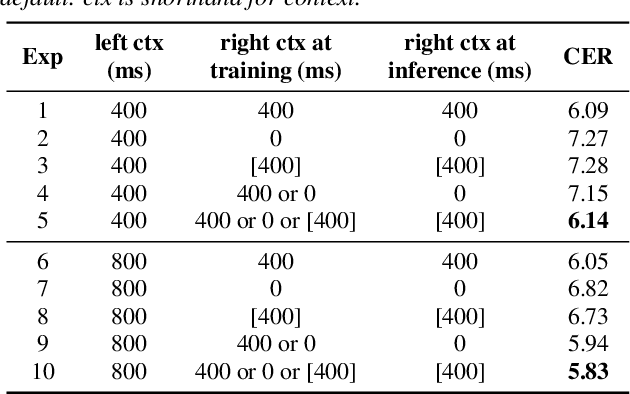
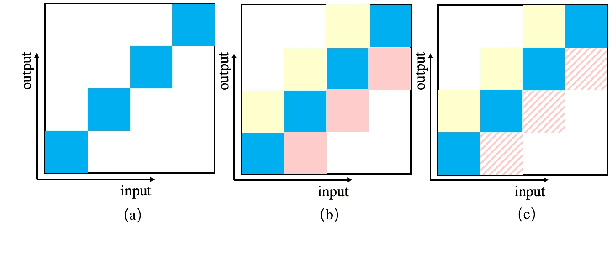
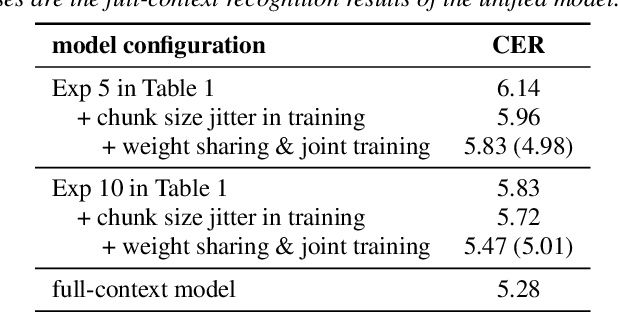
Abstract:History and future contextual information are known to be important for accurate acoustic modeling. However, acquiring future context brings latency for streaming ASR. In this paper, we propose a new framework - Chunking, Simulating Future Context and Decoding (CUSIDE) for streaming speech recognition. A new simulation module is introduced to recursively simulate the future contextual frames, without waiting for future context. The simulation module is jointly trained with the ASR model using a self-supervised loss; the ASR model is optimized with the usual ASR loss, e.g., CTC-CRF as used in our experiments. Experiments show that, compared to using real future frames as right context, using simulated future context can drastically reduce latency while maintaining recognition accuracy. With CUSIDE, we obtain new state-of-the-art streaming ASR results on the AISHELL-1 dataset.
CAT: A CTC-CRF based ASR Toolkit Bridging the Hybrid and the End-to-end Approaches towards Data Efficiency and Low Latency
May 27, 2020
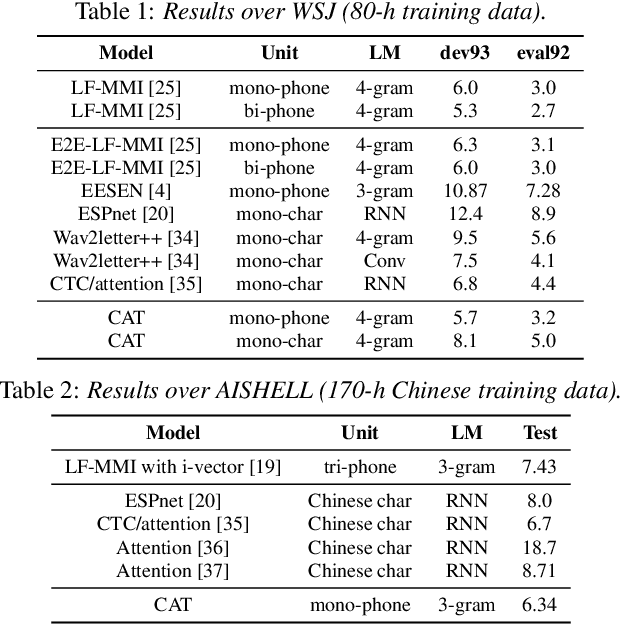


Abstract:In this paper, we present a new open source toolkit for speech recognition, named CAT (CTC-CRF based ASR Toolkit). CAT inherits the data-efficiency of the hybrid approach and the simplicity of the E2E approach, providing a full-fledged implementation of CTC-CRFs and complete training and testing scripts for a number of English and Chinese benchmarks. Experiments show CAT obtains state-of-the-art results, which are comparable to the fine-tuned hybrid models in Kaldi but with a much simpler training pipeline. Compared to existing non-modularized E2E models, CAT performs better on limited-scale datasets, demonstrating its data efficiency. Furthermore, we propose a new method called contextualized soft forgetting, which enables CAT to do streaming ASR without accuracy degradation. We hope CAT, especially the CTC-CRF based framework and software, will be of broad interest to the community, and can be further explored and improved.
CAT: CRF-based ASR Toolkit
Nov 20, 2019



Abstract:In this paper, we present a new open source toolkit for automatic speech recognition (ASR), named CAT (CRF-based ASR Toolkit). A key feature of CAT is discriminative training in the framework of conditional random field (CRF), particularly with connectionist temporal classification (CTC) inspired state topology. CAT contains a full-fledged implementation of CTC-CRF and provides a complete workflow for CRF-based end-to-end speech recognition. Evaluation results on Chinese and English benchmarks such as Switchboard and Aishell show that CAT obtains the state-of-the-art results among existing end-to-end models with less parameters, and is competitive compared with the hybrid DNN-HMM models. Towards flexibility, we show that i-vector based speaker-adapted recognition and latency control mechanism can be explored easily and effectively in CAT. We hope CAT, especially the CRF-based framework and software, will be of broad interest to the community, and can be further explored and improved.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge