Feifei Lin
Peak-First CTC: Reducing the Peak Latency of CTC Models by Applying Peak-First Regularization
Nov 07, 2022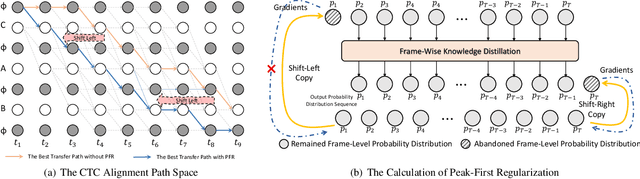
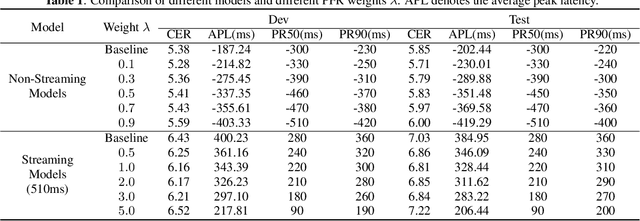
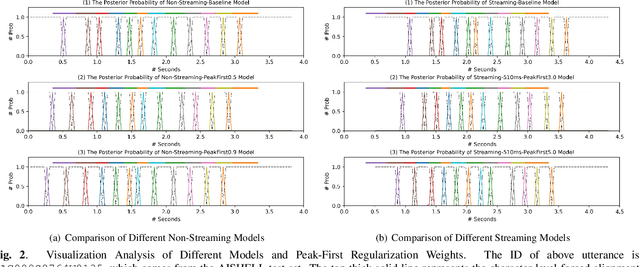
Abstract:The CTC model has been widely applied to many application scenarios because of its simple structure, excellent performance, and fast inference speed. There are many peaks in the probability distribution predicted by the CTC models, and each peak represents a non-blank token. The recognition latency of CTC models can be reduced by encouraging the model to predict peaks earlier. Existing methods to reduce latency require modifying the transition relationship between tokens in the forward-backward algorithm, and the gradient calculation. Some of these methods even depend on the forced alignment results provided by other pretrained models. The above methods are complex to implement. To reduce the peak latency, we propose a simple and novel method named peak-first regularization, which utilizes a frame-wise knowledge distillation function to force the probability distribution of the CTC model to shift left along the time axis instead of directly modifying the calculation process of CTC loss and gradients. All the experiments are conducted on a Chinese Mandarin dataset AISHELL-1. We have verified the effectiveness of the proposed regularization on both streaming and non-streaming CTC models respectively. The results show that the proposed method can reduce the average peak latency by about 100 to 200 milliseconds with almost no degradation of recognition accuracy.
SubCharacter Chinese-English Neural Machine Translation with Wubi encoding
Nov 07, 2019



Abstract:Neural machine translation (NMT) is one of the best methods for understanding the differences in semantic rules between two languages. Especially for Indo-European languages, subword-level models have achieved impressive results. However, when the translation task involves Chinese, semantic granularity remains at the word and character level, so there is still need more fine-grained translation model of Chinese. In this paper, we introduce a simple and effective method for Chinese translation at the sub-character level. Our approach uses the Wubi method to translate Chinese into English; byte-pair encoding (BPE) is then applied. Our method for Chinese-English translation eliminates the need for a complicated word segmentation algorithm during preprocessing. Furthermore, our method allows for sub-character-level neural translation based on recurrent neural network (RNN) architecture, without preprocessing. The empirical results show that for Chinese-English translation tasks, our sub-character-level model has a comparable BLEU score to the subword model, despite having a much smaller vocabulary. Additionally, the small vocabulary is highly advantageous for NMT model compression.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge