Minghuan Liu
Scalable and General Whole-Body Control for Cross-Humanoid Locomotion
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Learning-based whole-body controllers have become a key driver for humanoid robots, yet most existing approaches require robot-specific training. In this paper, we study the problem of cross-embodiment humanoid control and show that a single policy can robustly generalize across a wide range of humanoid robot designs with one-time training. We introduce XHugWBC, a novel cross-embodiment training framework that enables generalist humanoid control through: (1) physics-consistent morphological randomization, (2) semantically aligned observation and action spaces across diverse humanoid robots, and (3) effective policy architectures modeling morphological and dynamical properties. XHugWBC is not tied to any specific robot. Instead, it internalizes a broad distribution of morphological and dynamical characteristics during training. By learning motion priors from diverse randomized embodiments, the policy acquires a strong structural bias that supports zero-shot transfer to previously unseen robots. Experiments on twelve simulated humanoids and seven real-world robots demonstrate the strong generalization and robustness of the resulting universal controller.
RHINO: Learning Real-Time Humanoid-Human-Object Interaction from Human Demonstrations
Feb 18, 2025



Abstract:Humanoid robots have shown success in locomotion and manipulation. Despite these basic abilities, humanoids are still required to quickly understand human instructions and react based on human interaction signals to become valuable assistants in human daily life. Unfortunately, most existing works only focus on multi-stage interactions, treating each task separately, and neglecting real-time feedback. In this work, we aim to empower humanoid robots with real-time reaction abilities to achieve various tasks, allowing human to interrupt robots at any time, and making robots respond to humans immediately. To support such abilities, we propose a general humanoid-human-object interaction framework, named RHINO, i.e., Real-time Humanoid-human Interaction and Object manipulation. RHINO provides a unified view of reactive motion, instruction-based manipulation, and safety concerns, over multiple human signal modalities, such as languages, images, and motions. RHINO is a hierarchical learning framework, enabling humanoids to learn reaction skills from human-human-object demonstrations and teleoperation data. In particular, it decouples the interaction process into two levels: 1) a high-level planner inferring human intentions from real-time human behaviors; and 2) a low-level controller achieving reactive motion behaviors and object manipulation skills based on the predicted intentions. We evaluate the proposed framework on a real humanoid robot and demonstrate its effectiveness, flexibility, and safety in various scenarios.
Re$^3$Sim: Generating High-Fidelity Simulation Data via 3D-Photorealistic Real-to-Sim for Robotic Manipulation
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:Real-world data collection for robotics is costly and resource-intensive, requiring skilled operators and expensive hardware. Simulations offer a scalable alternative but often fail to achieve sim-to-real generalization due to geometric and visual gaps. To address these challenges, we propose a 3D-photorealistic real-to-sim system, namely, RE$^3$SIM, addressing geometric and visual sim-to-real gaps. RE$^3$SIM employs advanced 3D reconstruction and neural rendering techniques to faithfully recreate real-world scenarios, enabling real-time rendering of simulated cross-view cameras within a physics-based simulator. By utilizing privileged information to collect expert demonstrations efficiently in simulation, and train robot policies with imitation learning, we validate the effectiveness of the real-to-sim-to-real pipeline across various manipulation task scenarios. Notably, with only simulated data, we can achieve zero-shot sim-to-real transfer with an average success rate exceeding 58%. To push the limit of real-to-sim, we further generate a large-scale simulation dataset, demonstrating how a robust policy can be built from simulation data that generalizes across various objects. Codes and demos are available at: http://xshenhan.github.io/Re3Sim/.
A Unified and General Humanoid Whole-Body Controller for Fine-Grained Locomotion
Feb 06, 2025Abstract:Locomotion is a fundamental skill for humanoid robots. However, most existing works made locomotion a single, tedious, unextendable, and passive movement. This limits the kinematic capabilities of humanoid robots. In contrast, humans possess versatile athletic abilities-running, jumping, hopping, and finely adjusting walking parameters such as frequency, and foot height. In this paper, we investigate solutions to bring such versatility into humanoid locomotion and thereby propose HUGWBC: a unified and general humanoid whole-body controller for fine-grained locomotion. By designing a general command space in the aspect of tasks and behaviors, along with advanced techniques like symmetrical loss and intervention training for learning a whole-body humanoid controlling policy in simulation, HugWBC enables real-world humanoid robots to produce various natural gaits, including walking (running), jumping, standing, and hopping, with customizable parameters such as frequency, foot swing height, further combined with different body height, waist rotation, and body pitch, all in one single policy. Beyond locomotion, HUGWBC also supports real-time interventions from external upper-body controllers like teleoperation, enabling loco-manipulation while maintaining precise control under any locomotive behavior. Our experiments validate the high tracking accuracy and robustness of HUGWBC with/without upper-body intervention for all commands, and we further provide an in-depth analysis of how the various commands affect humanoid movement and offer insights into the relationships between these commands. To our knowledge, HugWBC is the first humanoid whole-body controller that supports such fine-grained locomotion behaviors with high robustness and flexibility.
Towards Generalist Robot Policies: What Matters in Building Vision-Language-Action Models
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:Foundation Vision Language Models (VLMs) exhibit strong capabilities in multi-modal representation learning, comprehension, and reasoning. By injecting action components into the VLMs, Vision-Language-Action Models (VLAs) can be naturally formed and also show promising performance. Existing work has demonstrated the effectiveness and generalization of VLAs in multiple scenarios and tasks. Nevertheless, the transfer from VLMs to VLAs is not trivial since existing VLAs differ in their backbones, action-prediction formulations, data distributions, and training recipes. This leads to a missing piece for a systematic understanding of the design choices of VLAs. In this work, we disclose the key factors that significantly influence the performance of VLA and focus on answering three essential design choices: which backbone to select, how to formulate the VLA architectures, and when to add cross-embodiment data. The obtained results convince us firmly to explain why we need VLA and develop a new family of VLAs, RoboVLMs, which require very few manual designs and achieve a new state-of-the-art performance in three simulation tasks and real-world experiments. Through our extensive experiments, which include over 8 VLM backbones, 4 policy architectures, and over 600 distinct designed experiments, we provide a detailed guidebook for the future design of VLAs. In addition to the study, the highly flexible RoboVLMs framework, which supports easy integrations of new VLMs and free combinations of various design choices, is made public to facilitate future research. We open-source all details, including codes, models, datasets, and toolkits, along with detailed training and evaluation recipes at: robovlms.github.io.
Prompting Depth Anything for 4K Resolution Accurate Metric Depth Estimation
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:Prompts play a critical role in unleashing the power of language and vision foundation models for specific tasks. For the first time, we introduce prompting into depth foundation models, creating a new paradigm for metric depth estimation termed Prompt Depth Anything. Specifically, we use a low-cost LiDAR as the prompt to guide the Depth Anything model for accurate metric depth output, achieving up to 4K resolution. Our approach centers on a concise prompt fusion design that integrates the LiDAR at multiple scales within the depth decoder. To address training challenges posed by limited datasets containing both LiDAR depth and precise GT depth, we propose a scalable data pipeline that includes synthetic data LiDAR simulation and real data pseudo GT depth generation. Our approach sets new state-of-the-arts on the ARKitScenes and ScanNet++ datasets and benefits downstream applications, including 3D reconstruction and generalized robotic grasping.
WildLMa: Long Horizon Loco-Manipulation in the Wild
Nov 22, 2024



Abstract:`In-the-wild' mobile manipulation aims to deploy robots in diverse real-world environments, which requires the robot to (1) have skills that generalize across object configurations; (2) be capable of long-horizon task execution in diverse environments; and (3) perform complex manipulation beyond pick-and-place. Quadruped robots with manipulators hold promise for extending the workspace and enabling robust locomotion, but existing results do not investigate such a capability. This paper proposes WildLMa with three components to address these issues: (1) adaptation of learned low-level controller for VR-enabled whole-body teleoperation and traversability; (2) WildLMa-Skill -- a library of generalizable visuomotor skills acquired via imitation learning or heuristics and (3) WildLMa-Planner -- an interface of learned skills that allow LLM planners to coordinate skills for long-horizon tasks. We demonstrate the importance of high-quality training data by achieving higher grasping success rate over existing RL baselines using only tens of demonstrations. WildLMa exploits CLIP for language-conditioned imitation learning that empirically generalizes to objects unseen in training demonstrations. Besides extensive quantitative evaluation, we qualitatively demonstrate practical robot applications, such as cleaning up trash in university hallways or outdoor terrains, operating articulated objects, and rearranging items on a bookshelf.
D4W: Dependable Data-Driven Dynamics for Wheeled Robots
Nov 14, 2024Abstract:Wheeled robots have gained significant attention due to their wide range of applications in manufacturing, logistics, and service industries. However, due to the difficulty of building a highly accurate dynamics model for wheeled robots, developing and testing control algorithms for them remains challenging and time-consuming, requiring extensive physical experimentation. To address this problem, we propose D4W, i.e., Dependable Data-Driven Dynamics for Wheeled Robots, a simulation framework incorporating data-driven methods to accelerate the development and evaluation of algorithms for wheeled robots. The key contribution of D4W is a solution that utilizes real-world sensor data to learn accurate models of robot dynamics. The learned dynamics can capture complex robot behaviors and interactions with the environment throughout simulations, surpassing the limitations of analytical methods, which only work in simplified scenarios. Experimental results show that D4W achieves the best simulation accuracy compared to traditional approaches, allowing for rapid iteration of wheel robot algorithms with less or no need for fine-tuning in reality. We further verify the usability and practicality of the proposed framework through integration with existing simulators and controllers.
GenSim2: Scaling Robot Data Generation with Multi-modal and Reasoning LLMs
Oct 04, 2024



Abstract:Robotic simulation today remains challenging to scale up due to the human efforts required to create diverse simulation tasks and scenes. Simulation-trained policies also face scalability issues as many sim-to-real methods focus on a single task. To address these challenges, this work proposes GenSim2, a scalable framework that leverages coding LLMs with multi-modal and reasoning capabilities for complex and realistic simulation task creation, including long-horizon tasks with articulated objects. To automatically generate demonstration data for these tasks at scale, we propose planning and RL solvers that generalize within object categories. The pipeline can generate data for up to 100 articulated tasks with 200 objects and reduce the required human efforts. To utilize such data, we propose an effective multi-task language-conditioned policy architecture, dubbed proprioceptive point-cloud transformer (PPT), that learns from the generated demonstrations and exhibits strong sim-to-real zero-shot transfer. Combining the proposed pipeline and the policy architecture, we show a promising usage of GenSim2 that the generated data can be used for zero-shot transfer or co-train with real-world collected data, which enhances the policy performance by 20% compared with training exclusively on limited real data.
ACE: A Cross-Platform Visual-Exoskeletons System for Low-Cost Dexterous Teleoperation
Aug 21, 2024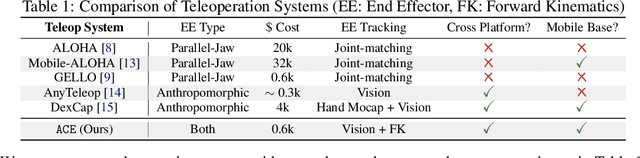

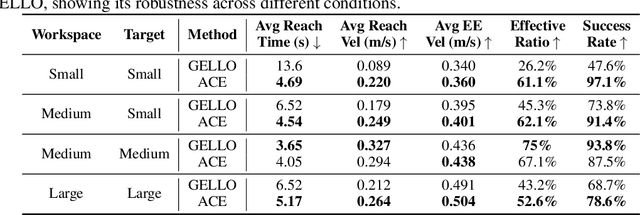

Abstract:Learning from demonstrations has shown to be an effective approach to robotic manipulation, especially with the recently collected large-scale robot data with teleoperation systems. Building an efficient teleoperation system across diverse robot platforms has become more crucial than ever. However, there is a notable lack of cost-effective and user-friendly teleoperation systems for different end-effectors, e.g., anthropomorphic robot hands and grippers, that can operate across multiple platforms. To address this issue, we develop ACE, a cross-platform visual-exoskeleton system for low-cost dexterous teleoperation. Our system utilizes a hand-facing camera to capture 3D hand poses and an exoskeleton mounted on a portable base, enabling accurate real-time capture of both finger and wrist poses. Compared to previous systems, which often require hardware customization according to different robots, our single system can generalize to humanoid hands, arm-hands, arm-gripper, and quadruped-gripper systems with high-precision teleoperation. This enables imitation learning for complex manipulation tasks on diverse platforms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge