Jiahang Cao
Fast and Safe Trajectory Optimization for Mobile Manipulators With Neural Configuration Space Distance Field
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Mobile manipulators promise agile, long-horizon behavior by coordinating base and arm motion, yet whole-body trajectory optimization in cluttered, confined spaces remains difficult due to high-dimensional nonconvexity and the need for fast, accurate collision reasoning. Configuration Space Distance Fields (CDF) enable fixed-base manipulators to model collisions directly in configuration space via smooth, implicit distances. This representation holds strong potential to bypass the nonlinear configuration-to-workspace mapping while preserving accurate whole-body geometry and providing optimization-friendly collision costs. Yet, extending this capability to mobile manipulators is hindered by unbounded workspaces and tighter base-arm coupling. We lift this promise to mobile manipulation with Generalized Configuration Space Distance Fields (GCDF), extending CDF to robots with both translational and rotational joints in unbounded workspaces with tighter base-arm coupling. We prove that GCDF preserves Euclidean-like local distance structure and accurately encodes whole-body geometry in configuration space, and develop a data generation and training pipeline that yields continuous neural GCDFs with accurate values and gradients, supporting efficient GPU-batched queries. Building on this representation, we develop a high-performance sequential convex optimization framework centered on GCDF-based collision reasoning. The solver scales to large numbers of implicit constraints through (i) online specification of neural constraints, (ii) sparsity-aware active-set detection with parallel batched evaluation across thousands of constraints, and (iii) incremental constraint management for rapid replanning under scene changes.
DEGS: Deformable Event-based 3D Gaussian Splatting from RGB and Event Stream
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:Reconstructing Dynamic 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) from low-framerate RGB videos is challenging. This is because large inter-frame motions will increase the uncertainty of the solution space. For example, one pixel in the first frame might have more choices to reach the corresponding pixel in the second frame. Event cameras can asynchronously capture rapid visual changes and are robust to motion blur, but they do not provide color information. Intuitively, the event stream can provide deterministic constraints for the inter-frame large motion by the event trajectories. Hence, combining low-temporal-resolution images with high-framerate event streams can address this challenge. However, it is challenging to jointly optimize Dynamic 3DGS using both RGB and event modalities due to the significant discrepancy between these two data modalities. This paper introduces a novel framework that jointly optimizes dynamic 3DGS from the two modalities. The key idea is to adopt event motion priors to guide the optimization of the deformation fields. First, we extract the motion priors encoded in event streams by using the proposed LoCM unsupervised fine-tuning framework to adapt an event flow estimator to a certain unseen scene. Then, we present the geometry-aware data association method to build the event-Gaussian motion correspondence, which is the primary foundation of the pipeline, accompanied by two useful strategies, namely motion decomposition and inter-frame pseudo-label. Extensive experiments show that our method outperforms existing image and event-based approaches across synthetic and real scenes and prove that our method can effectively optimize dynamic 3DGS with the help of event data.
DPL: Depth-only Perceptive Humanoid Locomotion via Realistic Depth Synthesis and Cross-Attention Terrain Reconstruction
Oct 08, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in legged robot perceptive locomotion have shown promising progress. However, terrain-aware humanoid locomotion remains largely constrained to two paradigms: depth image-based end-to-end learning and elevation map-based methods. The former suffers from limited training efficiency and a significant sim-to-real gap in depth perception, while the latter depends heavily on multiple vision sensors and localization systems, resulting in latency and reduced robustness. To overcome these challenges, we propose a novel framework that tightly integrates three key components: (1) Terrain-Aware Locomotion Policy with a Blind Backbone, which leverages pre-trained elevation map-based perception to guide reinforcement learning with minimal visual input; (2) Multi-Modality Cross-Attention Transformer, which reconstructs structured terrain representations from noisy depth images; (3) Realistic Depth Images Synthetic Method, which employs self-occlusion-aware ray casting and noise-aware modeling to synthesize realistic depth observations, achieving over 30\% reduction in terrain reconstruction error. This combination enables efficient policy training with limited data and hardware resources, while preserving critical terrain features essential for generalization. We validate our framework on a full-sized humanoid robot, demonstrating agile and adaptive locomotion across diverse and challenging terrains.
DACA-Net: A Degradation-Aware Conditional Diffusion Network for Underwater Image Enhancement
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:Underwater images typically suffer from severe colour distortions, low visibility, and reduced structural clarity due to complex optical effects such as scattering and absorption, which greatly degrade their visual quality and limit the performance of downstream visual perception tasks. Existing enhancement methods often struggle to adaptively handle diverse degradation conditions and fail to leverage underwater-specific physical priors effectively. In this paper, we propose a degradation-aware conditional diffusion model to enhance underwater images adaptively and robustly. Given a degraded underwater image as input, we first predict its degradation level using a lightweight dual-stream convolutional network, generating a continuous degradation score as semantic guidance. Based on this score, we introduce a novel conditional diffusion-based restoration network with a Swin UNet backbone, enabling adaptive noise scheduling and hierarchical feature refinement. To incorporate underwater-specific physical priors, we further propose a degradation-guided adaptive feature fusion module and a hybrid loss function that combines perceptual consistency, histogram matching, and feature-level contrast. Comprehensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method effectively restores underwater images with superior colour fidelity, perceptual quality, and structural details. Compared with SOTA approaches, our framework achieves significant improvements in both quantitative metrics and qualitative visual assessments.
Humanoid Occupancy: Enabling A Generalized Multimodal Occupancy Perception System on Humanoid Robots
Jul 27, 2025Abstract:Humanoid robot technology is advancing rapidly, with manufacturers introducing diverse heterogeneous visual perception modules tailored to specific scenarios. Among various perception paradigms, occupancy-based representation has become widely recognized as particularly suitable for humanoid robots, as it provides both rich semantic and 3D geometric information essential for comprehensive environmental understanding. In this work, we present Humanoid Occupancy, a generalized multimodal occupancy perception system that integrates hardware and software components, data acquisition devices, and a dedicated annotation pipeline. Our framework employs advanced multi-modal fusion techniques to generate grid-based occupancy outputs encoding both occupancy status and semantic labels, thereby enabling holistic environmental understanding for downstream tasks such as task planning and navigation. To address the unique challenges of humanoid robots, we overcome issues such as kinematic interference and occlusion, and establish an effective sensor layout strategy. Furthermore, we have developed the first panoramic occupancy dataset specifically for humanoid robots, offering a valuable benchmark and resource for future research and development in this domain. The network architecture incorporates multi-modal feature fusion and temporal information integration to ensure robust perception. Overall, Humanoid Occupancy delivers effective environmental perception for humanoid robots and establishes a technical foundation for standardizing universal visual modules, paving the way for the widespread deployment of humanoid robots in complex real-world scenarios.
LOVON: Legged Open-Vocabulary Object Navigator
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:Object navigation in open-world environments remains a formidable and pervasive challenge for robotic systems, particularly when it comes to executing long-horizon tasks that require both open-world object detection and high-level task planning. Traditional methods often struggle to integrate these components effectively, and this limits their capability to deal with complex, long-range navigation missions. In this paper, we propose LOVON, a novel framework that integrates large language models (LLMs) for hierarchical task planning with open-vocabulary visual detection models, tailored for effective long-range object navigation in dynamic, unstructured environments. To tackle real-world challenges including visual jittering, blind zones, and temporary target loss, we design dedicated solutions such as Laplacian Variance Filtering for visual stabilization. We also develop a functional execution logic for the robot that guarantees LOVON's capabilities in autonomous navigation, task adaptation, and robust task completion. Extensive evaluations demonstrate the successful completion of long-sequence tasks involving real-time detection, search, and navigation toward open-vocabulary dynamic targets. Furthermore, real-world experiments across different legged robots (Unitree Go2, B2, and H1-2) showcase the compatibility and appealing plug-and-play feature of LOVON.
Occupancy World Model for Robots
May 07, 2025Abstract:Understanding and forecasting the scene evolutions deeply affect the exploration and decision of embodied agents. While traditional methods simulate scene evolutions through trajectory prediction of potential instances, current works use the occupancy world model as a generative framework for describing fine-grained overall scene dynamics. However, existing methods cluster on the outdoor structured road scenes, while ignoring the exploration of forecasting 3D occupancy scene evolutions for robots in indoor scenes. In this work, we explore a new framework for learning the scene evolutions of observed fine-grained occupancy and propose an occupancy world model based on the combined spatio-temporal receptive field and guided autoregressive transformer to forecast the scene evolutions, called RoboOccWorld. We propose the Conditional Causal State Attention (CCSA), which utilizes camera poses of next state as conditions to guide the autoregressive transformer to adapt and understand the indoor robotics scenarios. In order to effectively exploit the spatio-temporal cues from historical observations, Hybrid Spatio-Temporal Aggregation (HSTA) is proposed to obtain the combined spatio-temporal receptive field based on multi-scale spatio-temporal windows. In addition, we restructure the OccWorld-ScanNet benchmark based on local annotations to facilitate the evaluation of the indoor 3D occupancy scene evolution prediction task. Experimental results demonstrate that our RoboOccWorld outperforms state-of-the-art methods in indoor 3D occupancy scene evolution prediction task. The code will be released soon.
Modality-Composable Diffusion Policy via Inference-Time Distribution-level Composition
Mar 16, 2025Abstract:Diffusion Policy (DP) has attracted significant attention as an effective method for policy representation due to its capacity to model multi-distribution dynamics. However, current DPs are often based on a single visual modality (e.g., RGB or point cloud), limiting their accuracy and generalization potential. Although training a generalized DP capable of handling heterogeneous multimodal data would enhance performance, it entails substantial computational and data-related costs. To address these challenges, we propose a novel policy composition method: by leveraging multiple pre-trained DPs based on individual visual modalities, we can combine their distributional scores to form a more expressive Modality-Composable Diffusion Policy (MCDP), without the need for additional training. Through extensive empirical experiments on the RoboTwin dataset, we demonstrate the potential of MCDP to improve both adaptability and performance. This exploration aims to provide valuable insights into the flexible composition of existing DPs, facilitating the development of generalizable cross-modality, cross-domain, and even cross-embodiment policies. Our code is open-sourced at https://github.com/AndyCao1125/MCDP.
EmbodiedVSR: Dynamic Scene Graph-Guided Chain-of-Thought Reasoning for Visual Spatial Tasks
Mar 14, 2025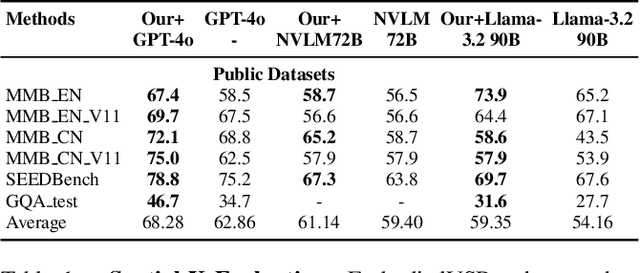
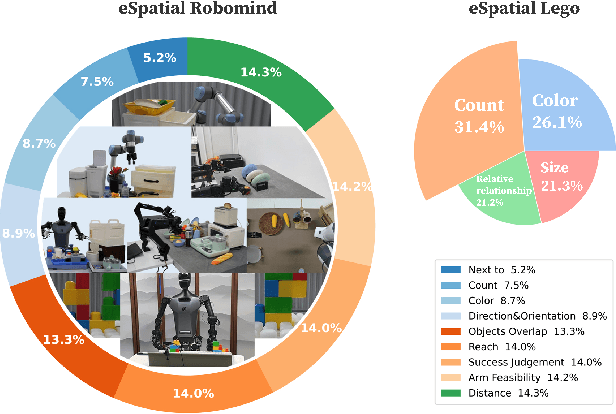
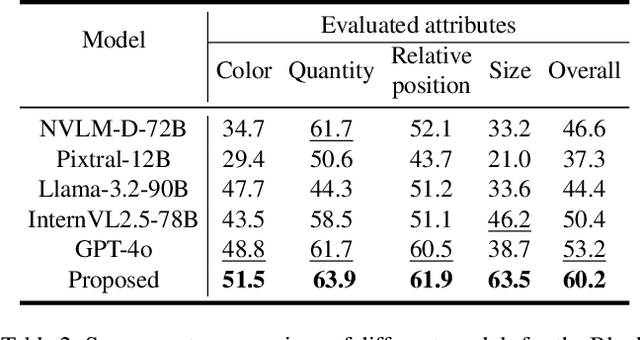
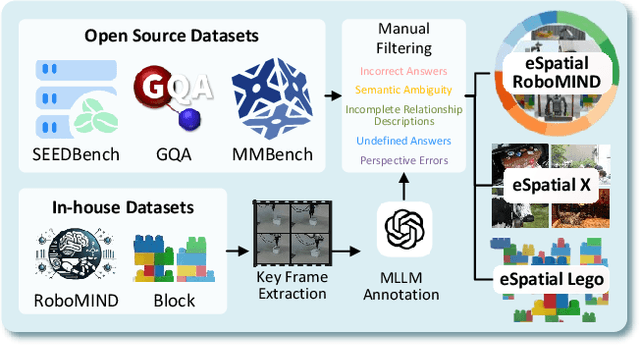
Abstract:While multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have made groundbreaking progress in embodied intelligence, they still face significant challenges in spatial reasoning for complex long-horizon tasks. To address this gap, we propose EmbodiedVSR (Embodied Visual Spatial Reasoning), a novel framework that integrates dynamic scene graph-guided Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning to enhance spatial understanding for embodied agents. By explicitly constructing structured knowledge representations through dynamic scene graphs, our method enables zero-shot spatial reasoning without task-specific fine-tuning. This approach not only disentangles intricate spatial relationships but also aligns reasoning steps with actionable environmental dynamics. To rigorously evaluate performance, we introduce the eSpatial-Benchmark, a comprehensive dataset including real-world embodied scenarios with fine-grained spatial annotations and adaptive task difficulty levels. Experiments demonstrate that our framework significantly outperforms existing MLLM-based methods in accuracy and reasoning coherence, particularly in long-horizon tasks requiring iterative environment interaction. The results reveal the untapped potential of MLLMs for embodied intelligence when equipped with structured, explainable reasoning mechanisms, paving the way for more reliable deployment in real-world spatial applications. The codes and datasets will be released soon.
ES-Parkour: Advanced Robot Parkour with Bio-inspired Event Camera and Spiking Neural Network
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:In recent years, quadruped robotics has advanced significantly, particularly in perception and motion control via reinforcement learning, enabling complex motions in challenging environments. Visual sensors like depth cameras enhance stability and robustness but face limitations, such as low operating frequencies relative to joint control and sensitivity to lighting, which hinder outdoor deployment. Additionally, deep neural networks in sensor and control systems increase computational demands. To address these issues, we introduce spiking neural networks (SNNs) and event cameras to perform a challenging quadruped parkour task. Event cameras capture dynamic visual data, while SNNs efficiently process spike sequences, mimicking biological perception. Experimental results demonstrate that this approach significantly outperforms traditional models, achieving excellent parkour performance with just 11.7% of the energy consumption of an artificial neural network (ANN)-based model, yielding an 88.3% energy reduction. By integrating event cameras with SNNs, our work advances robotic reinforcement learning and opens new possibilities for applications in demanding environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge