Zhiyuan Qin
BiManiBench: A Hierarchical Benchmark for Evaluating Bimanual Coordination of Multimodal Large Language Models
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have significantly advanced embodied AI, and using them to benchmark robotic intelligence has become a pivotal trend. However, existing frameworks remain predominantly confined to single-arm manipulation, failing to capture the spatio-temporal coordination required for bimanual tasks like lifting a heavy pot. To address this, we introduce BiManiBench, a hierarchical benchmark evaluating MLLMs across three tiers: fundamental spatial reasoning, high-level action planning, and low-level end-effector control. Our framework isolates unique bimanual challenges, such as arm reachability and kinematic constraints, thereby distinguishing perceptual hallucinations from planning failures. Analysis of over 30 state-of-the-art models reveals that despite high-level reasoning proficiency, MLLMs struggle with dual-arm spatial grounding and control, frequently resulting in mutual interference and sequencing errors. These findings suggest the current paradigm lacks a deep understanding of mutual kinematic constraints, highlighting the need for future research to focus on inter-arm collision-avoidance and fine-grained temporal sequencing.
TC-IDM: Grounding Video Generation for Executable Zero-shot Robot Motion
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:The vision-language-action (VLA) paradigm has enabled powerful robotic control by leveraging vision-language models, but its reliance on large-scale, high-quality robot data limits its generalization. Generative world models offer a promising alternative for general-purpose embodied AI, yet a critical gap remains between their pixel-level plans and physically executable actions. To this end, we propose the Tool-Centric Inverse Dynamics Model (TC-IDM). By focusing on the tool's imagined trajectory as synthesized by the world model, TC-IDM establishes a robust intermediate representation that bridges the gap between visual planning and physical control. TC-IDM extracts the tool's point cloud trajectories via segmentation and 3D motion estimation from generated videos. Considering diverse tool attributes, our architecture employs decoupled action heads to project these planned trajectories into 6-DoF end-effector motions and corresponding control signals. This plan-and-translate paradigm not only supports a wide range of end-effectors but also significantly improves viewpoint invariance. Furthermore, it exhibits strong generalization capabilities across long-horizon and out-of-distribution tasks, including interacting with deformable objects. In real-world evaluations, the world model with TC-IDM achieves an average success rate of 61.11 percent, with 77.7 percent on simple tasks and 38.46 percent on zero-shot deformable object tasks. It substantially outperforms end-to-end VLA-style baselines and other inverse dynamics models.
Wow, wo, val! A Comprehensive Embodied World Model Evaluation Turing Test
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:As world models gain momentum in Embodied AI, an increasing number of works explore using video foundation models as predictive world models for downstream embodied tasks like 3D prediction or interactive generation. However, before exploring these downstream tasks, video foundation models still have two critical questions unanswered: (1) whether their generative generalization is sufficient to maintain perceptual fidelity in the eyes of human observers, and (2) whether they are robust enough to serve as a universal prior for real-world embodied agents. To provide a standardized framework for answering these questions, we introduce the Embodied Turing Test benchmark: WoW-World-Eval (Wow,wo,val). Building upon 609 robot manipulation data, Wow-wo-val examines five core abilities, including perception, planning, prediction, generalization, and execution. We propose a comprehensive evaluation protocol with 22 metrics to assess the models' generation ability, which achieves a high Pearson Correlation between the overall score and human preference (>0.93) and establishes a reliable foundation for the Human Turing Test. On Wow-wo-val, models achieve only 17.27 on long-horizon planning and at best 68.02 on physical consistency, indicating limited spatiotemporal consistency and physical reasoning. For the Inverse Dynamic Model Turing Test, we first use an IDM to evaluate the video foundation models' execution accuracy in the real world. However, most models collapse to $\approx$ 0% success, while WoW maintains a 40.74% success rate. These findings point to a noticeable gap between the generated videos and the real world, highlighting the urgency and necessity of benchmarking World Model in Embodied AI.
WristWorld: Generating Wrist-Views via 4D World Models for Robotic Manipulation
Oct 08, 2025Abstract:Wrist-view observations are crucial for VLA models as they capture fine-grained hand-object interactions that directly enhance manipulation performance. Yet large-scale datasets rarely include such recordings, resulting in a substantial gap between abundant anchor views and scarce wrist views. Existing world models cannot bridge this gap, as they require a wrist-view first frame and thus fail to generate wrist-view videos from anchor views alone. Amid this gap, recent visual geometry models such as VGGT emerge with geometric and cross-view priors that make it possible to address extreme viewpoint shifts. Inspired by these insights, we propose WristWorld, the first 4D world model that generates wrist-view videos solely from anchor views. WristWorld operates in two stages: (i) Reconstruction, which extends VGGT and incorporates our Spatial Projection Consistency (SPC) Loss to estimate geometrically consistent wrist-view poses and 4D point clouds; (ii) Generation, which employs our video generation model to synthesize temporally coherent wrist-view videos from the reconstructed perspective. Experiments on Droid, Calvin, and Franka Panda demonstrate state-of-the-art video generation with superior spatial consistency, while also improving VLA performance, raising the average task completion length on Calvin by 3.81% and closing 42.4% of the anchor-wrist view gap.
WoW: Towards a World omniscient World model Through Embodied Interaction
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Humans develop an understanding of intuitive physics through active interaction with the world. This approach is in stark contrast to current video models, such as Sora, which rely on passive observation and therefore struggle with grasping physical causality. This observation leads to our central hypothesis: authentic physical intuition of the world model must be grounded in extensive, causally rich interactions with the real world. To test this hypothesis, we present WoW, a 14-billion-parameter generative world model trained on 2 million robot interaction trajectories. Our findings reveal that the model's understanding of physics is a probabilistic distribution of plausible outcomes, leading to stochastic instabilities and physical hallucinations. Furthermore, we demonstrate that this emergent capability can be actively constrained toward physical realism by SOPHIA, where vision-language model agents evaluate the DiT-generated output and guide its refinement by iteratively evolving the language instructions. In addition, a co-trained Inverse Dynamics Model translates these refined plans into executable robotic actions, thus closing the imagination-to-action loop. We establish WoWBench, a new benchmark focused on physical consistency and causal reasoning in video, where WoW achieves state-of-the-art performance in both human and autonomous evaluation, demonstrating strong ability in physical causality, collision dynamics, and object permanence. Our work provides systematic evidence that large-scale, real-world interaction is a cornerstone for developing physical intuition in AI. Models, data, and benchmarks will be open-sourced.
Follow-Your-Instruction: A Comprehensive MLLM Agent for World Data Synthesis
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:With the growing demands of AI-generated content (AIGC), the need for high-quality, diverse, and scalable data has become increasingly crucial. However, collecting large-scale real-world data remains costly and time-consuming, hindering the development of downstream applications. While some works attempt to collect task-specific data via a rendering process, most approaches still rely on manual scene construction, limiting their scalability and accuracy. To address these challenges, we propose Follow-Your-Instruction, a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM)-driven framework for automatically synthesizing high-quality 2D, 3D, and 4D data. Our \textbf{Follow-Your-Instruction} first collects assets and their associated descriptions through multimodal inputs using the MLLM-Collector. Then it constructs 3D layouts, and leverages Vision-Language Models (VLMs) for semantic refinement through multi-view scenes with the MLLM-Generator and MLLM-Optimizer, respectively. Finally, it uses MLLM-Planner to generate temporally coherent future frames. We evaluate the quality of the generated data through comprehensive experiments on the 2D, 3D, and 4D generative tasks. The results show that our synthetic data significantly boosts the performance of existing baseline models, demonstrating Follow-Your-Instruction's potential as a scalable and effective data engine for generative intelligence.
EmbodiedVSR: Dynamic Scene Graph-Guided Chain-of-Thought Reasoning for Visual Spatial Tasks
Mar 14, 2025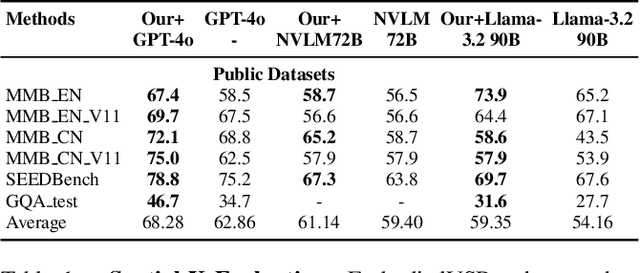
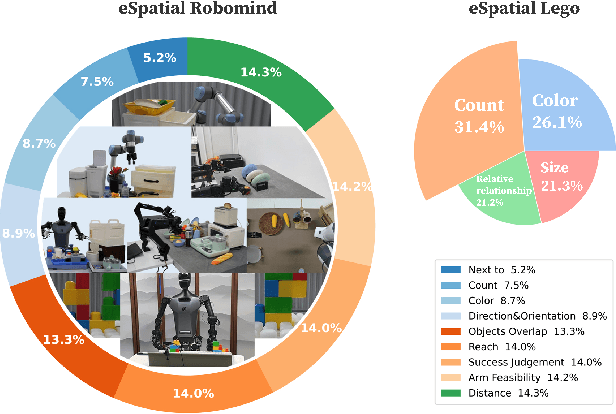
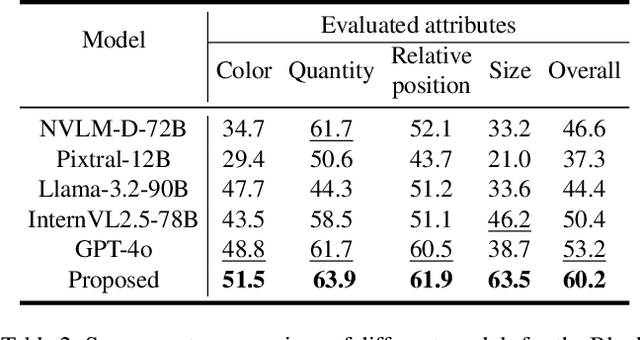
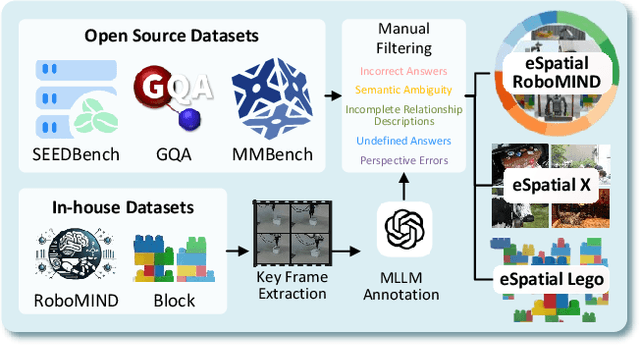
Abstract:While multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have made groundbreaking progress in embodied intelligence, they still face significant challenges in spatial reasoning for complex long-horizon tasks. To address this gap, we propose EmbodiedVSR (Embodied Visual Spatial Reasoning), a novel framework that integrates dynamic scene graph-guided Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning to enhance spatial understanding for embodied agents. By explicitly constructing structured knowledge representations through dynamic scene graphs, our method enables zero-shot spatial reasoning without task-specific fine-tuning. This approach not only disentangles intricate spatial relationships but also aligns reasoning steps with actionable environmental dynamics. To rigorously evaluate performance, we introduce the eSpatial-Benchmark, a comprehensive dataset including real-world embodied scenarios with fine-grained spatial annotations and adaptive task difficulty levels. Experiments demonstrate that our framework significantly outperforms existing MLLM-based methods in accuracy and reasoning coherence, particularly in long-horizon tasks requiring iterative environment interaction. The results reveal the untapped potential of MLLMs for embodied intelligence when equipped with structured, explainable reasoning mechanisms, paving the way for more reliable deployment in real-world spatial applications. The codes and datasets will be released soon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge