Xin Wu
SSR: Pushing the Limit of Spatial Intelligence with Structured Scene Reasoning
Feb 28, 2026Abstract:While Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) excel in semantic tasks, they frequently lack the "spatial sense" essential for sophisticated geometric reasoning. Current models typically suffer from exorbitant modality-alignment costs and deficiency in fine-grained structural modeling precision.We introduce SSR, a framework designed for Structured Scene Reasoning that seamlessly integrates 2D and 3D representations via a lightweight alignment mechanism. To minimize training overhead, our framework anchors 3D geometric features to the large language model's pre-aligned 2D visual semantics through cross-modal addition and token interleaving, effectively obviating the necessity for large-scale alignment pre-training. To underpin complex spatial reasoning, we propose a novel scene graph generation pipeline that represents global layouts as a chain of independent local triplets defined by relative coordinates. This is complemented by an incremental generation algorithm, enabling the model to construct "language-model-friendly" structural scaffolds for complex environments. Furthermore, we extend these capabilities to global-scale 3D global grounding task, achieving absolute metric precision across heterogeneous data sources. At a 7B parameter scale, SSR achieves state-of-the-art performance on multiple spatial intelligence benchmarks, notably scoring 73.9 on VSI-Bench. Our approach significantly outperforms much larger models, demonstrating that efficient feature alignment and structured scene reasoning are the cornerstones of authentic spatial intelligence.
Step 3.5 Flash: Open Frontier-Level Intelligence with 11B Active Parameters
Feb 11, 2026Abstract:We introduce Step 3.5 Flash, a sparse Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model that bridges frontier-level agentic intelligence and computational efficiency. We focus on what matters most when building agents: sharp reasoning and fast, reliable execution. Step 3.5 Flash pairs a 196B-parameter foundation with 11B active parameters for efficient inference. It is optimized with interleaved 3:1 sliding-window/full attention and Multi-Token Prediction (MTP-3) to reduce the latency and cost of multi-round agentic interactions. To reach frontier-level intelligence, we design a scalable reinforcement learning framework that combines verifiable signals with preference feedback, while remaining stable under large-scale off-policy training, enabling consistent self-improvement across mathematics, code, and tool use. Step 3.5 Flash demonstrates strong performance across agent, coding, and math tasks, achieving 85.4% on IMO-AnswerBench, 86.4% on LiveCodeBench-v6 (2024.08-2025.05), 88.2% on tau2-Bench, 69.0% on BrowseComp (with context management), and 51.0% on Terminal-Bench 2.0, comparable to frontier models such as GPT-5.2 xHigh and Gemini 3.0 Pro. By redefining the efficiency frontier, Step 3.5 Flash provides a high-density foundation for deploying sophisticated agents in real-world industrial environments.
BiManiBench: A Hierarchical Benchmark for Evaluating Bimanual Coordination of Multimodal Large Language Models
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have significantly advanced embodied AI, and using them to benchmark robotic intelligence has become a pivotal trend. However, existing frameworks remain predominantly confined to single-arm manipulation, failing to capture the spatio-temporal coordination required for bimanual tasks like lifting a heavy pot. To address this, we introduce BiManiBench, a hierarchical benchmark evaluating MLLMs across three tiers: fundamental spatial reasoning, high-level action planning, and low-level end-effector control. Our framework isolates unique bimanual challenges, such as arm reachability and kinematic constraints, thereby distinguishing perceptual hallucinations from planning failures. Analysis of over 30 state-of-the-art models reveals that despite high-level reasoning proficiency, MLLMs struggle with dual-arm spatial grounding and control, frequently resulting in mutual interference and sequencing errors. These findings suggest the current paradigm lacks a deep understanding of mutual kinematic constraints, highlighting the need for future research to focus on inter-arm collision-avoidance and fine-grained temporal sequencing.
DockSmith: Scaling Reliable Coding Environments via an Agentic Docker Builder
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Reliable Docker-based environment construction is a dominant bottleneck for scaling execution-grounded training and evaluation of software engineering agents. We introduce DockSmith, a specialized agentic Docker builder designed to address this challenge. DockSmith treats environment construction not only as a preprocessing step, but as a core agentic capability that exercises long-horizon tool use, dependency reasoning, and failure recovery, yielding supervision that transfers beyond Docker building itself. DockSmith is trained on large-scale, execution-grounded Docker-building trajectories produced by a SWE-Factory-style pipeline augmented with a loop-detection controller and a cross-task success memory. Training a 30B-A3B model on these trajectories achieves open-source state-of-the-art performance on Multi-Docker-Eval, with 39.72% Fail-to-Pass and 58.28% Commit Rate. Moreover, DockSmith improves out-of-distribution performance on SWE-bench Verified, SWE-bench Multilingual, and Terminal-Bench 2.0, demonstrating broader agentic benefits of environment construction.
STEP3-VL-10B Technical Report
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:We present STEP3-VL-10B, a lightweight open-source foundation model designed to redefine the trade-off between compact efficiency and frontier-level multimodal intelligence. STEP3-VL-10B is realized through two strategic shifts: first, a unified, fully unfrozen pre-training strategy on 1.2T multimodal tokens that integrates a language-aligned Perception Encoder with a Qwen3-8B decoder to establish intrinsic vision-language synergy; and second, a scaled post-training pipeline featuring over 1k iterations of reinforcement learning. Crucially, we implement Parallel Coordinated Reasoning (PaCoRe) to scale test-time compute, allocating resources to scalable perceptual reasoning that explores and synthesizes diverse visual hypotheses. Consequently, despite its compact 10B footprint, STEP3-VL-10B rivals or surpasses models 10$\times$-20$\times$ larger (e.g., GLM-4.6V-106B, Qwen3-VL-235B) and top-tier proprietary flagships like Gemini 2.5 Pro and Seed-1.5-VL. Delivering best-in-class performance, it records 92.2% on MMBench and 80.11% on MMMU, while excelling in complex reasoning with 94.43% on AIME2025 and 75.95% on MathVision. We release the full model suite to provide the community with a powerful, efficient, and reproducible baseline.
PaCoRe: Learning to Scale Test-Time Compute with Parallel Coordinated Reasoning
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:We introduce Parallel Coordinated Reasoning (PaCoRe), a training-and-inference framework designed to overcome a central limitation of contemporary language models: their inability to scale test-time compute (TTC) far beyond sequential reasoning under a fixed context window. PaCoRe departs from the traditional sequential paradigm by driving TTC through massive parallel exploration coordinated via a message-passing architecture in multiple rounds. Each round launches many parallel reasoning trajectories, compacts their findings into context-bounded messages, and synthesizes these messages to guide the next round and ultimately produce the final answer. Trained end-to-end with large-scale, outcome-based reinforcement learning, the model masters the synthesis abilities required by PaCoRe and scales to multi-million-token effective TTC without exceeding context limits. The approach yields strong improvements across diverse domains, and notably pushes reasoning beyond frontier systems in mathematics: an 8B model reaches 94.5% on HMMT 2025, surpassing GPT-5's 93.2% by scaling effective TTC to roughly two million tokens. We open-source model checkpoints, training data, and the full inference pipeline to accelerate follow-up work.
Spatial4D-Bench: A Versatile 4D Spatial Intelligence Benchmark
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:4D spatial intelligence involves perceiving and processing how objects move or change over time. Humans naturally possess 4D spatial intelligence, supporting a broad spectrum of spatial reasoning abilities. To what extent can Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) achieve human-level 4D spatial intelligence? In this work, we present Spatial4D-Bench, a versatile 4D spatial intelligence benchmark designed to comprehensively assess the 4D spatial reasoning abilities of MLLMs. Unlike existing spatial intelligence benchmarks that are often small-scale or limited in diversity, Spatial4D-Bench provides a large-scale, multi-task evaluation benchmark consisting of ~40,000 question-answer pairs covering 18 well-defined tasks. We systematically organize these tasks into six cognitive categories: object understanding, scene understanding, spatial relationship understanding, spatiotemporal relationship understanding, spatial reasoning and spatiotemporal reasoning. Spatial4D-Bench thereby offers a structured and comprehensive benchmark for evaluating the spatial cognition abilities of MLLMs, covering a broad spectrum of tasks that parallel the versatility of human spatial intelligence. We benchmark various state-of-the-art open-source and proprietary MLLMs on Spatial4D-Bench and reveal their substantial limitations in a wide variety of 4D spatial reasoning aspects, such as route plan, action recognition, and physical plausibility reasoning. We hope that the findings provided in this work offer valuable insights to the community and that our benchmark can facilitate the development of more capable MLLMs toward human-level 4D spatial intelligence. More resources can be found on our project page.
DialogueReason: Rule-Based RL Sparks Dialogue Reasoning in LLMs
May 11, 2025Abstract:We propose DialogueReason, a reasoning paradigm that uncovers the lost roles in monologue-style reasoning models, aiming to boost diversity and coherency of the reasoning process. Recent advances in RL-based large reasoning models have led to impressive long CoT capabilities and high performance on math and science benchmarks. However, these reasoning models rely mainly on monologue-style reasoning, which often limits reasoning diversity and coherency, frequently recycling fixed strategies or exhibiting unnecessary shifts in attention. Our work consists of an analysis of monologue reasoning patterns and the development of a dialogue-based reasoning approach. We first introduce the Compound-QA task, which concatenates multiple problems into a single prompt to assess both diversity and coherency of reasoning. Our analysis shows that Compound-QA exposes weaknesses in monologue reasoning, evidenced by both quantitative metrics and qualitative reasoning traces. Building on the analysis, we propose a dialogue-based reasoning, named DialogueReason, structured around agents, environment, and interactions. Using PPO with rule-based rewards, we train open-source LLMs (Qwen-QWQ and Qwen-Base) to adopt dialogue reasoning. We evaluate trained models on MATH, AIME, and GPQA datasets, showing that the dialogue reasoning model outperforms monologue models under more complex compound questions. Additionally, we discuss how dialogue-based reasoning helps enhance interpretability, facilitate more intuitive human interaction, and inspire advances in multi-agent system design.
Out-of-Distribution Generalization in Time Series: A Survey
Mar 18, 2025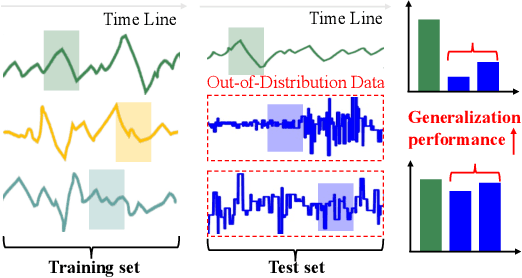
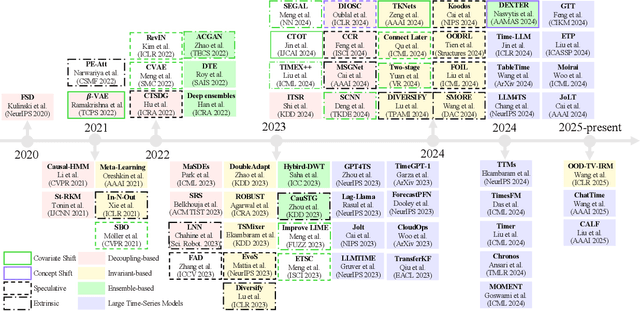
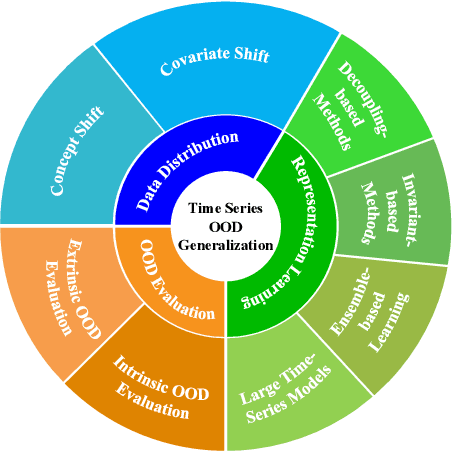
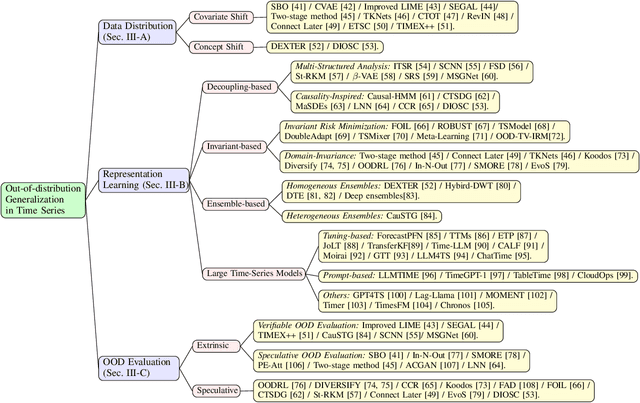
Abstract:Time series frequently manifest distribution shifts, diverse latent features, and non-stationary learning dynamics, particularly in open and evolving environments. These characteristics pose significant challenges for out-of-distribution (OOD) generalization. While substantial progress has been made, a systematic synthesis of advancements remains lacking. To address this gap, we present the first comprehensive review of OOD generalization methodologies for time series, organized to delineate the field's evolutionary trajectory and contemporary research landscape. We organize our analysis across three foundational dimensions: data distribution, representation learning, and OOD evaluation. For each dimension, we present several popular algorithms in detail. Furthermore, we highlight key application scenarios, emphasizing their real-world impact. Finally, we identify persistent challenges and propose future research directions. A detailed summary of the methods reviewed for the generalization of OOD in time series can be accessed at https://tsood-generalization.com.
Step-Audio: Unified Understanding and Generation in Intelligent Speech Interaction
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Real-time speech interaction, serving as a fundamental interface for human-machine collaboration, holds immense potential. However, current open-source models face limitations such as high costs in voice data collection, weakness in dynamic control, and limited intelligence. To address these challenges, this paper introduces Step-Audio, the first production-ready open-source solution. Key contributions include: 1) a 130B-parameter unified speech-text multi-modal model that achieves unified understanding and generation, with the Step-Audio-Chat version open-sourced; 2) a generative speech data engine that establishes an affordable voice cloning framework and produces the open-sourced lightweight Step-Audio-TTS-3B model through distillation; 3) an instruction-driven fine control system enabling dynamic adjustments across dialects, emotions, singing, and RAP; 4) an enhanced cognitive architecture augmented with tool calling and role-playing abilities to manage complex tasks effectively. Based on our new StepEval-Audio-360 evaluation benchmark, Step-Audio achieves state-of-the-art performance in human evaluations, especially in terms of instruction following. On open-source benchmarks like LLaMA Question, shows 9.3% average performance improvement, demonstrating our commitment to advancing the development of open-source multi-modal language technologies. Our code and models are available at https://github.com/stepfun-ai/Step-Audio.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge