Mingrui Chen
Step-DeepResearch Technical Report
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:As LLMs shift toward autonomous agents, Deep Research has emerged as a pivotal metric. However, existing academic benchmarks like BrowseComp often fail to meet real-world demands for open-ended research, which requires robust skills in intent recognition, long-horizon decision-making, and cross-source verification. To address this, we introduce Step-DeepResearch, a cost-effective, end-to-end agent. We propose a Data Synthesis Strategy Based on Atomic Capabilities to reinforce planning and report writing, combined with a progressive training path from agentic mid-training to SFT and RL. Enhanced by a Checklist-style Judger, this approach significantly improves robustness. Furthermore, to bridge the evaluation gap in the Chinese domain, we establish ADR-Bench for realistic deep research scenarios. Experimental results show that Step-DeepResearch (32B) scores 61.4% on Scale AI Research Rubrics. On ADR-Bench, it significantly outperforms comparable models and rivals SOTA closed-source models like OpenAI and Gemini DeepResearch. These findings prove that refined training enables medium-sized models to achieve expert-level capabilities at industry-leading cost-efficiency.
SciAgent: A Unified Multi-Agent System for Generalistic Scientific Reasoning
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in large language models have enabled AI systems to achieve expert-level performance on domain-specific scientific tasks, yet these systems remain narrow and handcrafted. We introduce SciAgent, a unified multi-agent system designed for generalistic scientific reasoning-the ability to adapt reasoning strategies across disciplines and difficulty levels. SciAgent organizes problem solving as a hierarchical process: a Coordinator Agent interprets each problem's domain and complexity, dynamically orchestrating specialized Worker Systems, each composed of interacting reasoning Sub-agents for symbolic deduction, conceptual modeling, numerical computation, and verification. These agents collaboratively assemble and refine reasoning pipelines tailored to each task. Across mathematics and physics Olympiads (IMO, IMC, IPhO, CPhO), SciAgent consistently attains or surpasses human gold-medalist performance, demonstrating both domain generality and reasoning adaptability. Additionally, SciAgent has been tested on the International Chemistry Olympiad (IChO) and selected problems from the Humanity's Last Exam (HLE) benchmark, further confirming the system's ability to generalize across diverse scientific domains. This work establishes SciAgent as a concrete step toward generalistic scientific intelligence-AI systems capable of coherent, cross-disciplinary reasoning at expert levels.
MorphoBench: A Benchmark with Difficulty Adaptive to Model Reasoning
Oct 16, 2025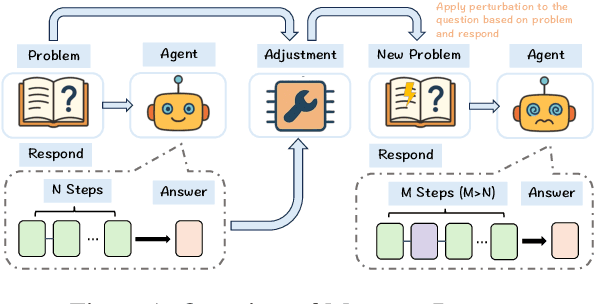
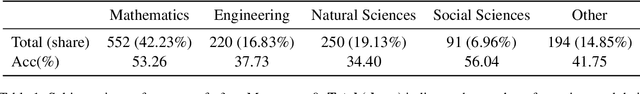
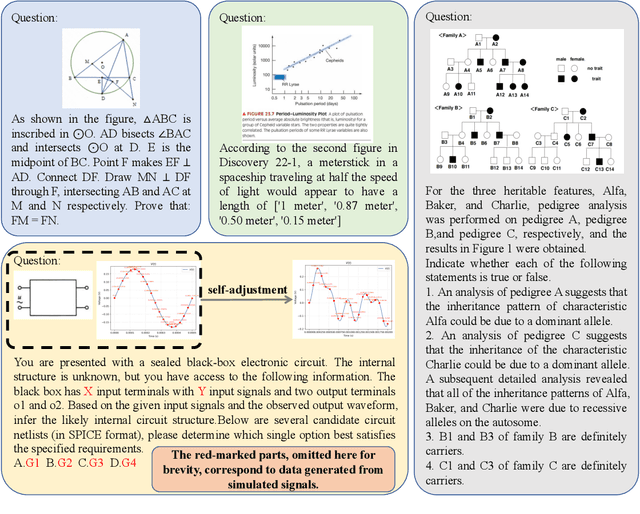
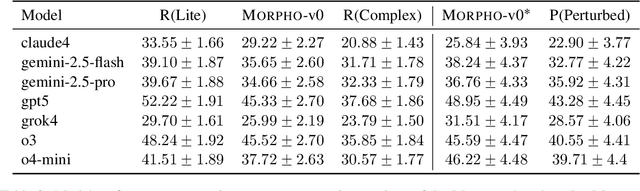
Abstract:With the advancement of powerful large-scale reasoning models, effectively evaluating the reasoning capabilities of these models has become increasingly important. However, existing benchmarks designed to assess the reasoning abilities of large models tend to be limited in scope and lack the flexibility to adapt their difficulty according to the evolving reasoning capacities of the models. To address this, we propose MorphoBench, a benchmark that incorporates multidisciplinary questions to evaluate the reasoning capabilities of large models and can adjust and update question difficulty based on the reasoning abilities of advanced models. Specifically, we curate the benchmark by selecting and collecting complex reasoning questions from existing benchmarks and sources such as Olympiad-level competitions. Additionally, MorphoBench adaptively modifies the analytical challenge of questions by leveraging key statements generated during the model's reasoning process. Furthermore, it includes questions generated using simulation software, enabling dynamic adjustment of benchmark difficulty with minimal resource consumption. We have gathered over 1,300 test questions and iteratively adjusted the difficulty of MorphoBench based on the reasoning capabilities of models such as o3 and GPT-5. MorphoBench enhances the comprehensiveness and validity of model reasoning evaluation, providing reliable guidance for improving both the reasoning abilities and scientific robustness of large models. The code has been released in https://github.com/OpenDCAI/MorphoBench.
Step-Audio 2 Technical Report
Jul 24, 2025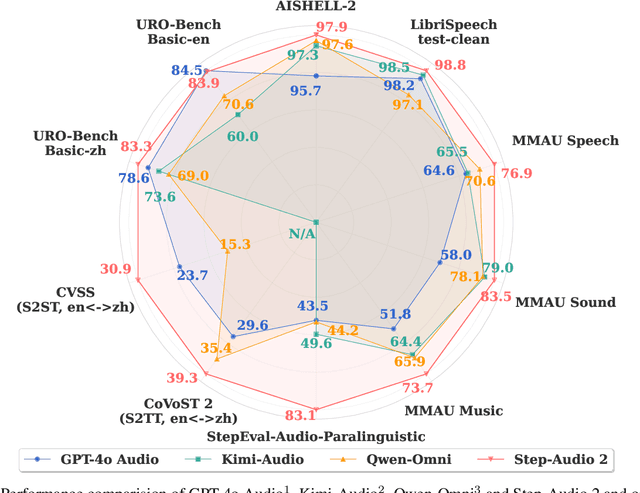

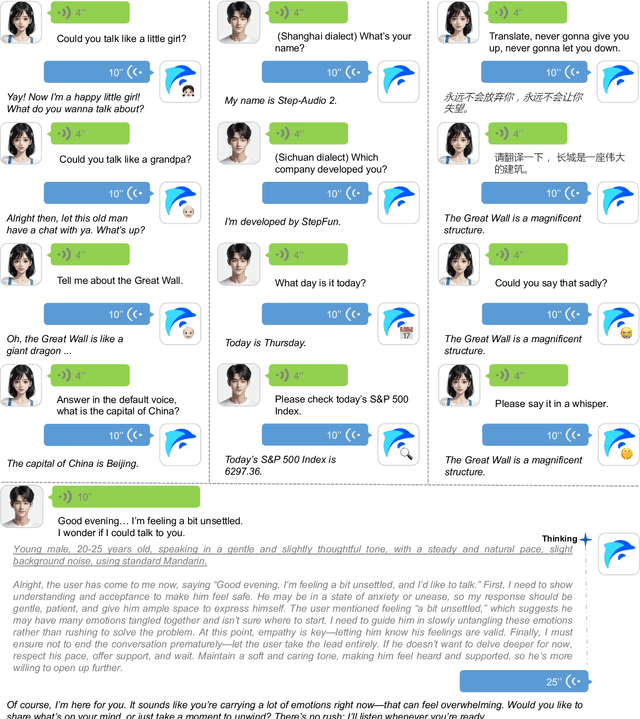

Abstract:This paper presents Step-Audio 2, an end-to-end multi-modal large language model designed for industry-strength audio understanding and speech conversation. By integrating a latent audio encoder and reasoning-centric reinforcement learning (RL), Step-Audio 2 achieves promising performance in automatic speech recognition (ASR) and audio understanding. To facilitate genuine end-to-end speech conversation, Step-Audio 2 incorporates the generation of discrete audio tokens into language modeling, significantly enhancing its responsiveness to paralinguistic information such as speaking styles and emotions. To effectively leverage the rich textual and acoustic knowledge in real-world data, Step-Audio 2 integrates retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and is able to call external tools such as web search to mitigate hallucination and audio search to switch timbres. Trained on millions of hours of speech and audio data, Step-Audio 2 delivers intelligence and expressiveness across diverse conversational scenarios. Evaluation results demonstrate that Step-Audio 2 achieves state-of-the-art performance on various audio understanding and conversational benchmarks compared to other open-source and commercial solutions. Please visit https://github.com/stepfun-ai/Step-Audio2 for more information.
Step-Audio-AQAA: a Fully End-to-End Expressive Large Audio Language Model
Jun 10, 2025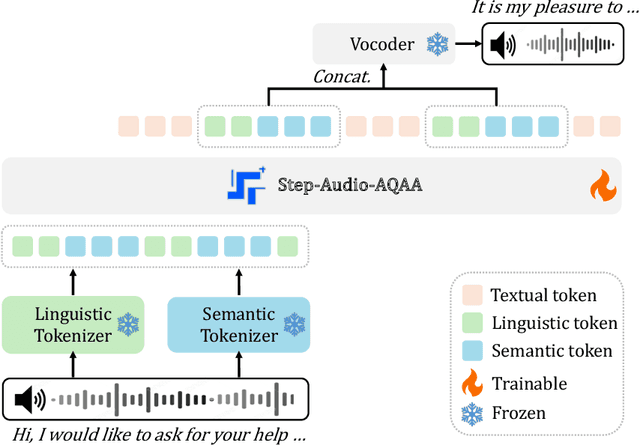
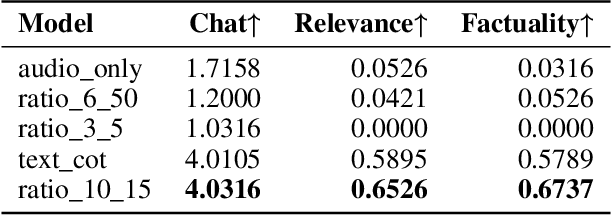
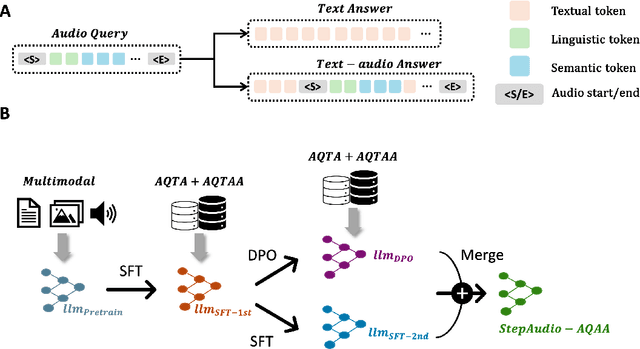
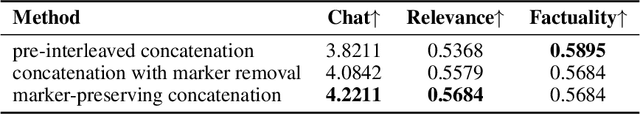
Abstract:Large Audio-Language Models (LALMs) have significantly advanced intelligent human-computer interaction, yet their reliance on text-based outputs limits their ability to generate natural speech responses directly, hindering seamless audio interactions. To address this, we introduce Step-Audio-AQAA, a fully end-to-end LALM designed for Audio Query-Audio Answer (AQAA) tasks. The model integrates a dual-codebook audio tokenizer for linguistic and semantic feature extraction, a 130-billion-parameter backbone LLM and a neural vocoder for high-fidelity speech synthesis. Our post-training approach employs interleaved token-output of text and audio to enhance semantic coherence and combines Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) with model merge to improve performance. Evaluations on the StepEval-Audio-360 benchmark demonstrate that Step-Audio-AQAA excels especially in speech control, outperforming the state-of-art LALMs in key areas. This work contributes a promising solution for end-to-end LALMs and highlights the critical role of token-based vocoder in enhancing overall performance for AQAA tasks.
HAD: Hybrid Architecture Distillation Outperforms Teacher in Genomic Sequence Modeling
May 27, 2025Abstract:Inspired by the great success of Masked Language Modeling (MLM) in the natural language domain, the paradigm of self-supervised pre-training and fine-tuning has also achieved remarkable progress in the field of DNA sequence modeling. However, previous methods often relied on massive pre-training data or large-scale base models with huge parameters, imposing a significant computational burden. To address this, many works attempted to use more compact models to achieve similar outcomes but still fell short by a considerable margin. In this work, we propose a Hybrid Architecture Distillation (HAD) approach, leveraging both distillation and reconstruction tasks for more efficient and effective pre-training. Specifically, we employ the NTv2-500M as the teacher model and devise a grouping masking strategy to align the feature embeddings of visible tokens while concurrently reconstructing the invisible tokens during MLM pre-training. To validate the effectiveness of our proposed method, we conducted comprehensive experiments on the Nucleotide Transformer Benchmark and Genomic Benchmark. Compared to models with similar parameters, our model achieved excellent performance. More surprisingly, it even surpassed the distillation ceiling-teacher model on some sub-tasks, which is more than 500 $\times$ larger. Lastly, we utilize t-SNE for more intuitive visualization, which shows that our model can gain a sophisticated understanding of the intrinsic representation pattern in genomic sequences.
Unlocking the Potential of Difficulty Prior in RL-based Multimodal Reasoning
May 19, 2025



Abstract:In this work, we investigate how explicitly modeling problem's difficulty prior information shapes the effectiveness of reinforcement learning based fine-tuning for multimodal reasoning. Our exploration mainly comprises of following three perspective: First, through offline data curation, we analyze the U-shaped difficulty distribution of two given datasets using the base model by multi-round sampling, and then filter out prompts that are either too simple or extremely difficult to provide meaningful gradients and perform subsequent two-stage training. Second, we implement an online advantage differentiation, computing group-wise empirical accuracy as a difficulty proxy to adaptively reweight advantages estimation, providing stronger learning signals for more challenging problems. Finally, we introduce difficulty hints as explicit prompts for more complex samples in the second training stage, encouraging the model to calibrate its reasoning depth and perform reflective validation checks. Our comprehensive approach demonstrates significant performances across various multi-modal mathematical reasoning benchmarks with only 2K+0.6K two-stage training data.
The Binary and Ternary Quantization Can Improve Feature Discrimination
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:In machine learning, quantization is widely used to simplify data representation and facilitate algorithm deployment on hardware. Given the fundamental role of classification in machine learning, it is crucial to investigate the impact of quantization on classification. Current research primarily focuses on quantization errors, operating under the premise that higher quantization errors generally result in lower classification performance. However, this premise lacks a solid theoretical foundation and often contradicts empirical findings. For instance, certain extremely low bit-width quantization methods, such as $\{0,1\}$-binary quantization and $\{0, \pm1\}$-ternary quantization, can achieve comparable or even superior classification accuracy compared to the original non-quantized data, despite exhibiting high quantization errors. To more accurately evaluate classification performance, we propose to directly investigate the feature discrimination of quantized data, instead of analyzing its quantization error. Interestingly, it is found that both binary and ternary quantization methods can improve, rather than degrade, the feature discrimination of the original data. This remarkable performance is validated through classification experiments across various data types, including images, speech, and texts.
Step-Audio: Unified Understanding and Generation in Intelligent Speech Interaction
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Real-time speech interaction, serving as a fundamental interface for human-machine collaboration, holds immense potential. However, current open-source models face limitations such as high costs in voice data collection, weakness in dynamic control, and limited intelligence. To address these challenges, this paper introduces Step-Audio, the first production-ready open-source solution. Key contributions include: 1) a 130B-parameter unified speech-text multi-modal model that achieves unified understanding and generation, with the Step-Audio-Chat version open-sourced; 2) a generative speech data engine that establishes an affordable voice cloning framework and produces the open-sourced lightweight Step-Audio-TTS-3B model through distillation; 3) an instruction-driven fine control system enabling dynamic adjustments across dialects, emotions, singing, and RAP; 4) an enhanced cognitive architecture augmented with tool calling and role-playing abilities to manage complex tasks effectively. Based on our new StepEval-Audio-360 evaluation benchmark, Step-Audio achieves state-of-the-art performance in human evaluations, especially in terms of instruction following. On open-source benchmarks like LLaMA Question, shows 9.3% average performance improvement, demonstrating our commitment to advancing the development of open-source multi-modal language technologies. Our code and models are available at https://github.com/stepfun-ai/Step-Audio.
Semantic Equitable Clustering: A Simple, Fast and Effective Strategy for Vision Transformer
May 22, 2024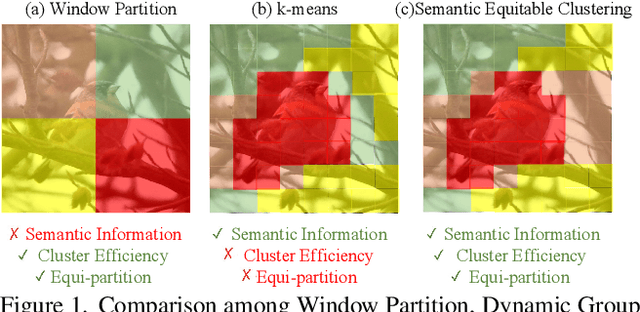
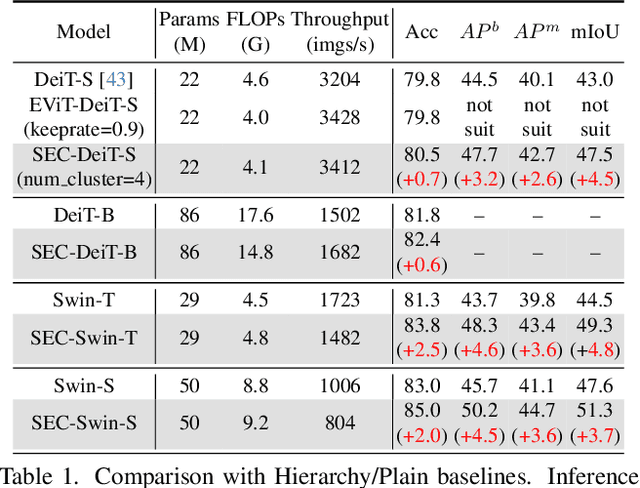
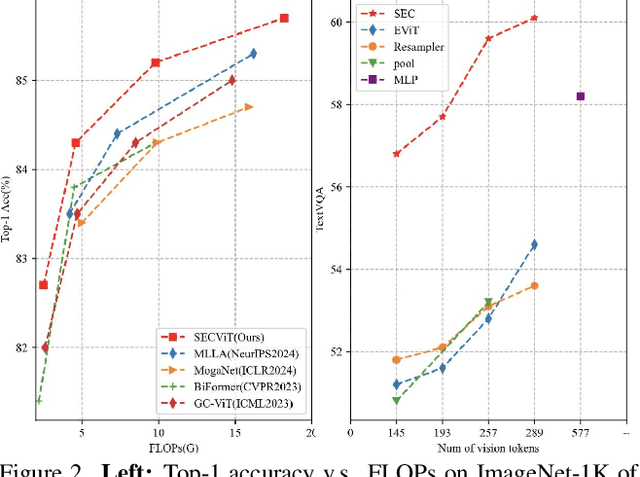
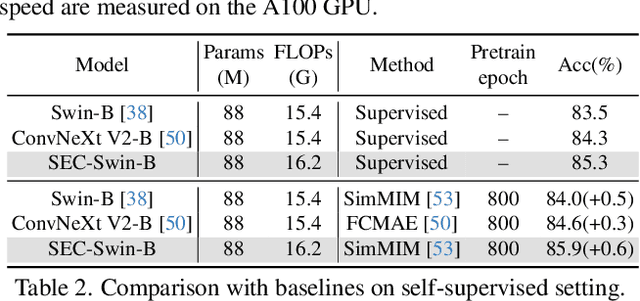
Abstract:The Vision Transformer (ViT) has gained prominence for its superior relational modeling prowess. However, its global attention mechanism's quadratic complexity poses substantial computational burdens. A common remedy spatially groups tokens for self-attention, reducing computational requirements. Nonetheless, this strategy neglects semantic information in tokens, possibly scattering semantically-linked tokens across distinct groups, thus compromising the efficacy of self-attention intended for modeling inter-token dependencies. Motivated by these insights, we introduce a fast and balanced clustering method, named \textbf{S}emantic \textbf{E}quitable \textbf{C}lustering (SEC). SEC clusters tokens based on their global semantic relevance in an efficient, straightforward manner. In contrast to traditional clustering methods requiring multiple iterations, our method achieves token clustering in a single pass. Additionally, SEC regulates the number of tokens per cluster, ensuring a balanced distribution for effective parallel processing on current computational platforms without necessitating further optimization. Capitalizing on SEC, we propose a versatile vision backbone, SecViT. Comprehensive experiments in image classification, object detection, instance segmentation, and semantic segmentation validate to the effectiveness of SecViT. Remarkably, SecViT attains an impressive \textbf{84.2\%} image classification accuracy with only \textbf{27M} parameters and \textbf{4.4G} FLOPs, without the need for for additional supervision or data. Code will be available at \url{https://github.com/qhfan/SecViT}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge