Chen Hu
SpotAgent: Grounding Visual Geo-localization in Large Vision-Language Models through Agentic Reasoning
Feb 11, 2026Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have demonstrated strong reasoning capabilities in geo-localization, yet they often struggle in real-world scenarios where visual cues are sparse, long-tailed, and highly ambiguous. Previous approaches, bound by internal knowledge, often fail to provide verifiable results, yielding confident but ungrounded predictions when faced with confounded evidence. To address these challenges, we propose SpotAgent, a framework that formalizes geo-localization into an agentic reasoning process that leverages expert-level reasoning to synergize visual interpretation with tool-assisted verification. SpotAgent actively explores and verifies visual cues by leveraging external tools (e.g., web search, maps) through a ReAct diagram. We introduce a 3-stage post-training pipeline starting with a Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) stage for basic alignment, followed by an Agentic Cold Start phase utilizing high-quality trajectories synthesized via a Multi-Agent framework, aiming to instill tool-calling expertise. Subsequently, the model's reasoning capabilities are refined through Reinforcement Learning. We propose a Spatially-Aware Dynamic Filtering strategy to enhance the efficiency of the RL stage by prioritizing learnable samples based on spatial difficulty. Extensive experiments on standard benchmarks demonstrate that SpotAgent achieves state-of-the-art performance, effectively mitigating hallucinations while delivering precise and verifiable geo-localization.
Step 3.5 Flash: Open Frontier-Level Intelligence with 11B Active Parameters
Feb 11, 2026Abstract:We introduce Step 3.5 Flash, a sparse Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model that bridges frontier-level agentic intelligence and computational efficiency. We focus on what matters most when building agents: sharp reasoning and fast, reliable execution. Step 3.5 Flash pairs a 196B-parameter foundation with 11B active parameters for efficient inference. It is optimized with interleaved 3:1 sliding-window/full attention and Multi-Token Prediction (MTP-3) to reduce the latency and cost of multi-round agentic interactions. To reach frontier-level intelligence, we design a scalable reinforcement learning framework that combines verifiable signals with preference feedback, while remaining stable under large-scale off-policy training, enabling consistent self-improvement across mathematics, code, and tool use. Step 3.5 Flash demonstrates strong performance across agent, coding, and math tasks, achieving 85.4% on IMO-AnswerBench, 86.4% on LiveCodeBench-v6 (2024.08-2025.05), 88.2% on tau2-Bench, 69.0% on BrowseComp (with context management), and 51.0% on Terminal-Bench 2.0, comparable to frontier models such as GPT-5.2 xHigh and Gemini 3.0 Pro. By redefining the efficiency frontier, Step 3.5 Flash provides a high-density foundation for deploying sophisticated agents in real-world industrial environments.
Step-DeepResearch Technical Report
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:As LLMs shift toward autonomous agents, Deep Research has emerged as a pivotal metric. However, existing academic benchmarks like BrowseComp often fail to meet real-world demands for open-ended research, which requires robust skills in intent recognition, long-horizon decision-making, and cross-source verification. To address this, we introduce Step-DeepResearch, a cost-effective, end-to-end agent. We propose a Data Synthesis Strategy Based on Atomic Capabilities to reinforce planning and report writing, combined with a progressive training path from agentic mid-training to SFT and RL. Enhanced by a Checklist-style Judger, this approach significantly improves robustness. Furthermore, to bridge the evaluation gap in the Chinese domain, we establish ADR-Bench for realistic deep research scenarios. Experimental results show that Step-DeepResearch (32B) scores 61.4% on Scale AI Research Rubrics. On ADR-Bench, it significantly outperforms comparable models and rivals SOTA closed-source models like OpenAI and Gemini DeepResearch. These findings prove that refined training enables medium-sized models to achieve expert-level capabilities at industry-leading cost-efficiency.
OVGrasp: Open-Vocabulary Grasping Assistance via Multimodal Intent Detection
Sep 04, 2025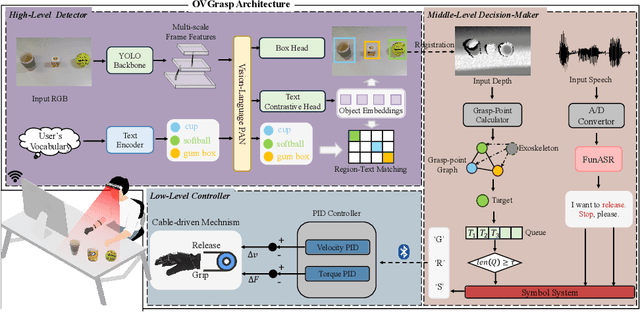
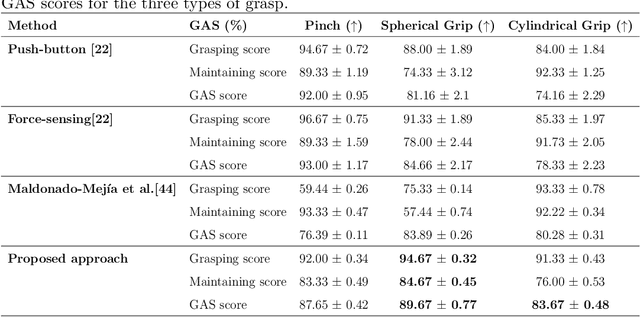
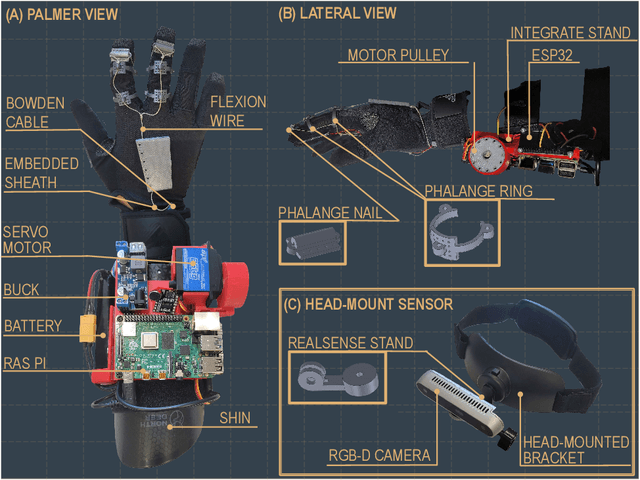
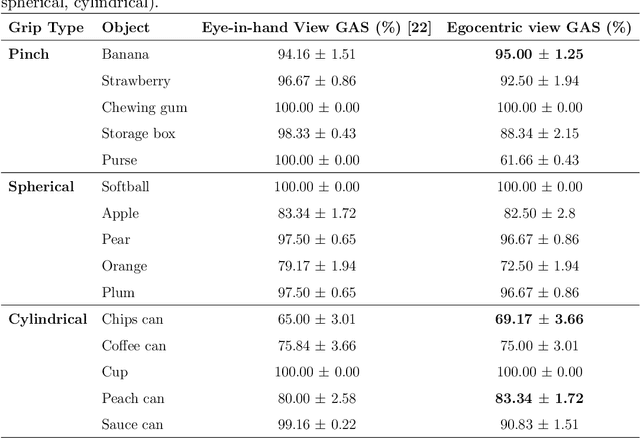
Abstract:Grasping assistance is essential for restoring autonomy in individuals with motor impairments, particularly in unstructured environments where object categories and user intentions are diverse and unpredictable. We present OVGrasp, a hierarchical control framework for soft exoskeleton-based grasp assistance that integrates RGB-D vision, open-vocabulary prompts, and voice commands to enable robust multimodal interaction. To enhance generalization in open environments, OVGrasp incorporates a vision-language foundation model with an open-vocabulary mechanism, allowing zero-shot detection of previously unseen objects without retraining. A multimodal decision-maker further fuses spatial and linguistic cues to infer user intent, such as grasp or release, in multi-object scenarios. We deploy the complete framework on a custom egocentric-view wearable exoskeleton and conduct systematic evaluations on 15 objects across three grasp types. Experimental results with ten participants demonstrate that OVGrasp achieves a grasping ability score (GAS) of 87.00%, outperforming state-of-the-art baselines and achieving improved kinematic alignment with natural hand motion.
GitTaskBench: A Benchmark for Code Agents Solving Real-World Tasks Through Code Repository Leveraging
Aug 26, 2025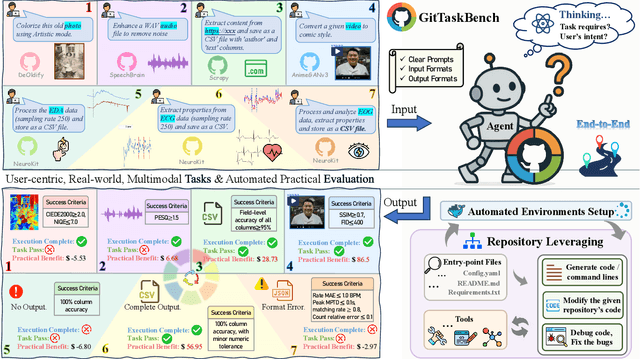
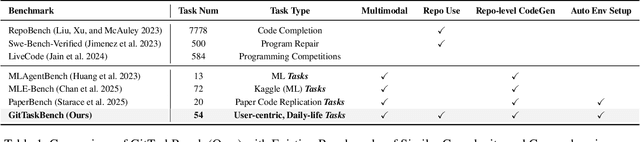
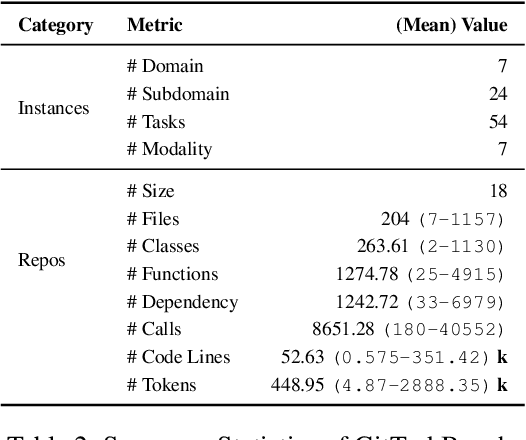
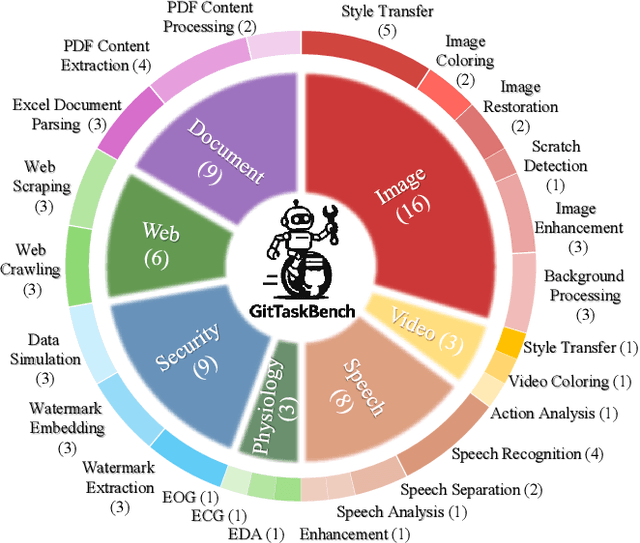
Abstract:Beyond scratch coding, exploiting large-scale code repositories (e.g., GitHub) for practical tasks is vital in real-world software development, yet current benchmarks rarely evaluate code agents in such authentic, workflow-driven scenarios. To bridge this gap, we introduce GitTaskBench, a benchmark designed to systematically assess this capability via 54 realistic tasks across 7 modalities and 7 domains. Each task pairs a relevant repository with an automated, human-curated evaluation harness specifying practical success criteria. Beyond measuring execution and task success, we also propose the alpha-value metric to quantify the economic benefit of agent performance, which integrates task success rates, token cost, and average developer salaries. Experiments across three state-of-the-art agent frameworks with multiple advanced LLMs show that leveraging code repositories for complex task solving remains challenging: even the best-performing system, OpenHands+Claude 3.7, solves only 48.15% of tasks. Error analysis attributes over half of failures to seemingly mundane yet critical steps like environment setup and dependency resolution, highlighting the need for more robust workflow management and increased timeout preparedness. By releasing GitTaskBench, we aim to drive progress and attention toward repository-aware code reasoning, execution, and deployment -- moving agents closer to solving complex, end-to-end real-world tasks. The benchmark and code are open-sourced at https://github.com/QuantaAlpha/GitTaskBench.
Step-Audio 2 Technical Report
Jul 24, 2025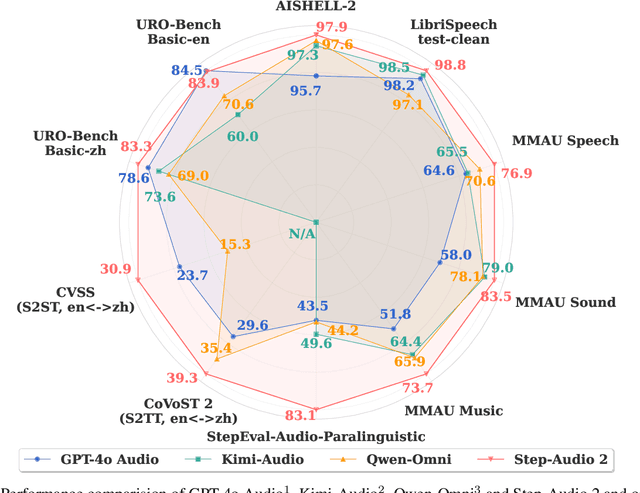

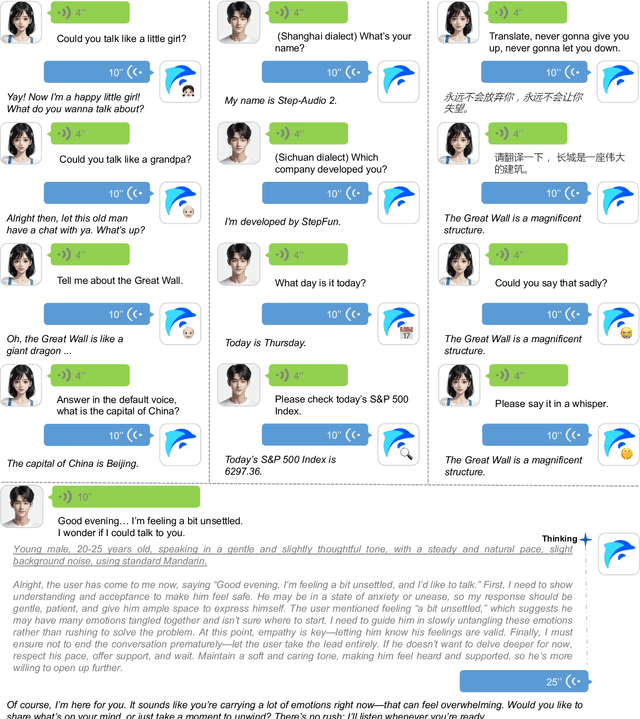

Abstract:This paper presents Step-Audio 2, an end-to-end multi-modal large language model designed for industry-strength audio understanding and speech conversation. By integrating a latent audio encoder and reasoning-centric reinforcement learning (RL), Step-Audio 2 achieves promising performance in automatic speech recognition (ASR) and audio understanding. To facilitate genuine end-to-end speech conversation, Step-Audio 2 incorporates the generation of discrete audio tokens into language modeling, significantly enhancing its responsiveness to paralinguistic information such as speaking styles and emotions. To effectively leverage the rich textual and acoustic knowledge in real-world data, Step-Audio 2 integrates retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and is able to call external tools such as web search to mitigate hallucination and audio search to switch timbres. Trained on millions of hours of speech and audio data, Step-Audio 2 delivers intelligence and expressiveness across diverse conversational scenarios. Evaluation results demonstrate that Step-Audio 2 achieves state-of-the-art performance on various audio understanding and conversational benchmarks compared to other open-source and commercial solutions. Please visit https://github.com/stepfun-ai/Step-Audio2 for more information.
Step-Audio-AQAA: a Fully End-to-End Expressive Large Audio Language Model
Jun 10, 2025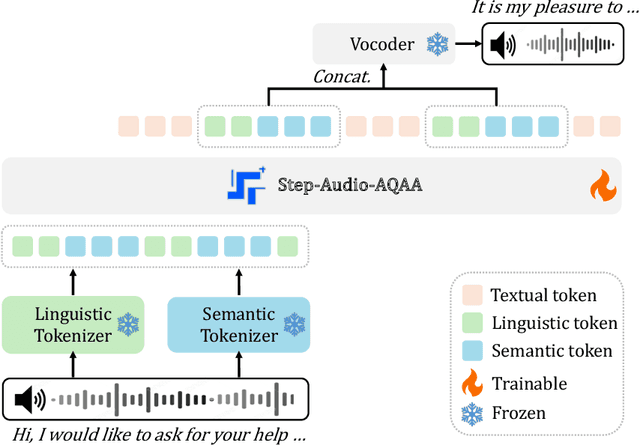
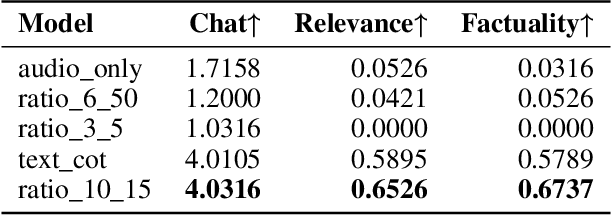
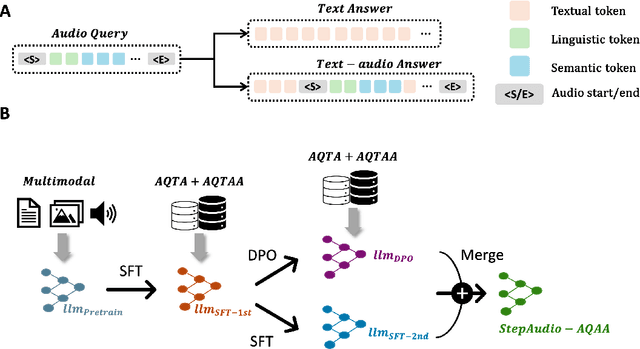
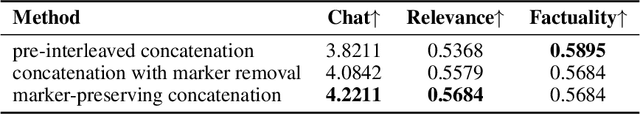
Abstract:Large Audio-Language Models (LALMs) have significantly advanced intelligent human-computer interaction, yet their reliance on text-based outputs limits their ability to generate natural speech responses directly, hindering seamless audio interactions. To address this, we introduce Step-Audio-AQAA, a fully end-to-end LALM designed for Audio Query-Audio Answer (AQAA) tasks. The model integrates a dual-codebook audio tokenizer for linguistic and semantic feature extraction, a 130-billion-parameter backbone LLM and a neural vocoder for high-fidelity speech synthesis. Our post-training approach employs interleaved token-output of text and audio to enhance semantic coherence and combines Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) with model merge to improve performance. Evaluations on the StepEval-Audio-360 benchmark demonstrate that Step-Audio-AQAA excels especially in speech control, outperforming the state-of-art LALMs in key areas. This work contributes a promising solution for end-to-end LALMs and highlights the critical role of token-based vocoder in enhancing overall performance for AQAA tasks.
RepoMaster: Autonomous Exploration and Understanding of GitHub Repositories for Complex Task Solving
May 27, 2025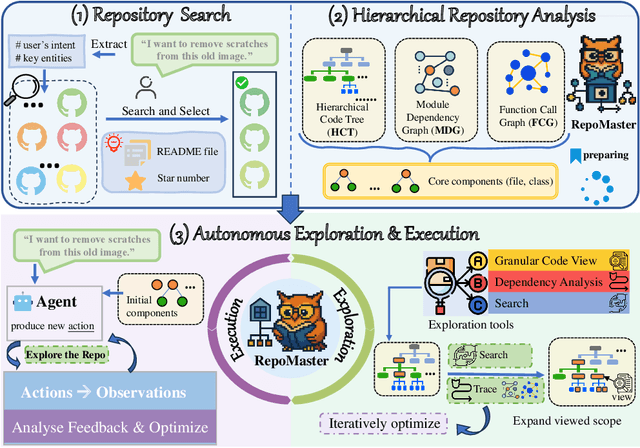
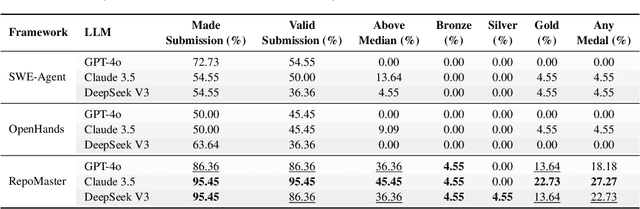
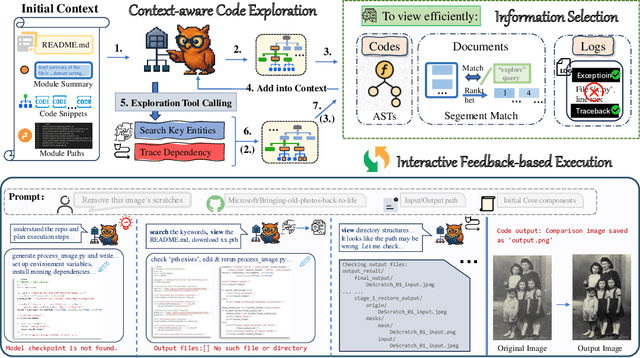
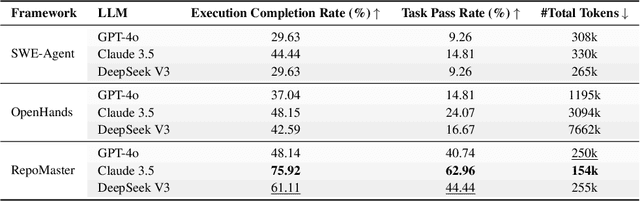
Abstract:The ultimate goal of code agents is to solve complex tasks autonomously. Although large language models (LLMs) have made substantial progress in code generation, real-world tasks typically demand full-fledged code repositories rather than simple scripts. Building such repositories from scratch remains a major challenge. Fortunately, GitHub hosts a vast, evolving collection of open-source repositories, which developers frequently reuse as modular components for complex tasks. Yet, existing frameworks like OpenHands and SWE-Agent still struggle to effectively leverage these valuable resources. Relying solely on README files provides insufficient guidance, and deeper exploration reveals two core obstacles: overwhelming information and tangled dependencies of repositories, both constrained by the limited context windows of current LLMs. To tackle these issues, we propose RepoMaster, an autonomous agent framework designed to explore and reuse GitHub repositories for solving complex tasks. For efficient understanding, RepoMaster constructs function-call graphs, module-dependency graphs, and hierarchical code trees to identify essential components, providing only identified core elements to the LLMs rather than the entire repository. During autonomous execution, it progressively explores related components using our exploration tools and prunes information to optimize context usage. Evaluated on the adjusted MLE-bench, RepoMaster achieves a 110% relative boost in valid submissions over the strongest baseline OpenHands. On our newly released GitTaskBench, RepoMaster lifts the task-pass rate from 24.1% to 62.9% while reducing token usage by 95%. Our code and demonstration materials are publicly available at https://github.com/wanghuacan/RepoMaster.
Unearthing Gems from Stones: Policy Optimization with Negative Sample Augmentation for LLM Reasoning
May 20, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in reasoning language models have witnessed a paradigm shift from short to long CoT pattern. Given the substantial computational cost of rollouts in long CoT models, maximizing the utility of fixed training datasets becomes crucial. Our analysis reveals that negative responses contain valuable components such as self-reflection and error-correction steps, yet primary existing methods either completely discard negative samples (RFT) or apply equal penalization across all tokens (RL), failing to leverage these potential learning signals. In light of this, we propose Behavior Constrained Policy Gradient with Negative Sample Augmentation (BCPG-NSA), a fine-grained offline RL framework that encompasses three stages: 1) sample segmentation, 2) consensus-based step correctness assessment combining LLM and PRM judgers, and 3) policy optimization with NSA designed to effectively mine positive steps within negative samples. Experimental results show that BCPG-NSA outperforms baselines on several challenging math/coding reasoning benchmarks using the same training dataset, achieving improved sample efficiency and demonstrating robustness and scalability when extended to multiple iterations.
DialogueReason: Rule-Based RL Sparks Dialogue Reasoning in LLMs
May 11, 2025Abstract:We propose DialogueReason, a reasoning paradigm that uncovers the lost roles in monologue-style reasoning models, aiming to boost diversity and coherency of the reasoning process. Recent advances in RL-based large reasoning models have led to impressive long CoT capabilities and high performance on math and science benchmarks. However, these reasoning models rely mainly on monologue-style reasoning, which often limits reasoning diversity and coherency, frequently recycling fixed strategies or exhibiting unnecessary shifts in attention. Our work consists of an analysis of monologue reasoning patterns and the development of a dialogue-based reasoning approach. We first introduce the Compound-QA task, which concatenates multiple problems into a single prompt to assess both diversity and coherency of reasoning. Our analysis shows that Compound-QA exposes weaknesses in monologue reasoning, evidenced by both quantitative metrics and qualitative reasoning traces. Building on the analysis, we propose a dialogue-based reasoning, named DialogueReason, structured around agents, environment, and interactions. Using PPO with rule-based rewards, we train open-source LLMs (Qwen-QWQ and Qwen-Base) to adopt dialogue reasoning. We evaluate trained models on MATH, AIME, and GPQA datasets, showing that the dialogue reasoning model outperforms monologue models under more complex compound questions. Additionally, we discuss how dialogue-based reasoning helps enhance interpretability, facilitate more intuitive human interaction, and inspire advances in multi-agent system design.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge