Shan Luo
UniForce: A Unified Latent Force Model for Robot Manipulation with Diverse Tactile Sensors
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Force sensing is essential for dexterous robot manipulation, but scaling force-aware policy learning is hindered by the heterogeneity of tactile sensors. Differences in sensing principles (e.g., optical vs. magnetic), form factors, and materials typically require sensor-specific data collection, calibration, and model training, thereby limiting generalisability. We propose UniForce, a novel unified tactile representation learning framework that learns a shared latent force space across diverse tactile sensors. UniForce reduces cross-sensor domain shift by jointly modeling inverse dynamics (image-to-force) and forward dynamics (force-to-image), constrained by force equilibrium and image reconstruction losses to produce force-grounded representations. To avoid reliance on expensive external force/torque (F/T) sensors, we exploit static equilibrium and collect force-paired data via direct sensor--object--sensor interactions, enabling cross-sensor alignment with contact force. The resulting universal tactile encoder can be plugged into downstream force-aware robot manipulation tasks with zero-shot transfer, without retraining or finetuning. Extensive experiments on heterogeneous tactile sensors including GelSight, TacTip, and uSkin, demonstrate consistent improvements in force estimation over prior methods, and enable effective cross-sensor coordination in Vision-Tactile-Language-Action (VTLA) models for a robotic wiping task. Code and datasets will be released.
UniMorphGrasp: Diffusion Model with Morphology-Awareness for Cross-Embodiment Dexterous Grasp Generation
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Cross-embodiment dexterous grasping aims to generate stable and diverse grasps for robotic hands with heterogeneous kinematic structures. Existing methods are often tailored to specific hand designs and fail to generalize to unseen hand morphologies outside the training distribution. To address these limitations, we propose \textbf{UniMorphGrasp}, a diffusion-based framework that incorporates hand morphological information into the grasp generation process for unified cross-embodiment grasp synthesis. The proposed approach maps grasps from diverse robotic hands into a unified human-like canonical hand pose representation, providing a common space for learning. Grasp generation is then conditioned on structured representations of hand kinematics, encoded as graphs derived from hand configurations, together with object geometry. In addition, a loss function is introduced that exploits the hierarchical organization of hand kinematics to guide joint-level supervision. Extensive experiments demonstrate that UniMorphGrasp achieves state-of-the-art performance on existing dexterous grasp benchmarks and exhibits strong zero-shot generalization to previously unseen hand structures, enabling scalable and practical cross-embodiment grasp deployment.
An Anatomy of Vision-Language-Action Models: From Modules to Milestones and Challenges
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models are driving a revolution in robotics, enabling machines to understand instructions and interact with the physical world. This field is exploding with new models and datasets, making it both exciting and challenging to keep pace with. This survey offers a clear and structured guide to the VLA landscape. We design it to follow the natural learning path of a researcher: we start with the basic Modules of any VLA model, trace the history through key Milestones, and then dive deep into the core Challenges that define recent research frontier. Our main contribution is a detailed breakdown of the five biggest challenges in: (1) Representation, (2) Execution, (3) Generalization, (4) Safety, and (5) Dataset and Evaluation. This structure mirrors the developmental roadmap of a generalist agent: establishing the fundamental perception-action loop, scaling capabilities across diverse embodiments and environments, and finally ensuring trustworthy deployment-all supported by the essential data infrastructure. For each of them, we review existing approaches and highlight future opportunities. We position this paper as both a foundational guide for newcomers and a strategic roadmap for experienced researchers, with the dual aim of accelerating learning and inspiring new ideas in embodied intelligence. A live version of this survey, with continuous updates, is maintained on our \href{https://suyuz1.github.io/VLA-Survey-Anatomy/}{project page}.
SimTac: A Physics-Based Simulator for Vision-Based Tactile Sensing with Biomorphic Structures
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Tactile sensing in biological organisms is deeply intertwined with morphological form, such as human fingers, cat paws, and elephant trunks, which enables rich and adaptive interactions through a variety of geometrically complex structures. In contrast, vision-based tactile sensors in robotics have been limited to simple planar geometries, with biomorphic designs remaining underexplored. To address this gap, we present SimTac, a physics-based simulation framework for the design and validation of biomorphic tactile sensors. SimTac consists of particle-based deformation modeling, light-field rendering for photorealistic tactile image generation, and a neural network for predicting mechanical responses, enabling accurate and efficient simulation across a wide range of geometries and materials. We demonstrate the versatility of SimTac by designing and validating physical sensor prototypes inspired by biological tactile structures and further demonstrate its effectiveness across multiple Sim2Real tactile tasks, including object classification, slip detection, and contact safety assessment. Our framework bridges the gap between bio-inspired design and practical realisation, expanding the design space of tactile sensors and paving the way for tactile sensing systems that integrate morphology and sensing to enable robust interaction in unstructured environments.
ViTacGen: Robotic Pushing with Vision-to-Touch Generation
Oct 15, 2025Abstract:Robotic pushing is a fundamental manipulation task that requires tactile feedback to capture subtle contact forces and dynamics between the end-effector and the object. However, real tactile sensors often face hardware limitations such as high costs and fragility, and deployment challenges involving calibration and variations between different sensors, while vision-only policies struggle with satisfactory performance. Inspired by humans' ability to infer tactile states from vision, we propose ViTacGen, a novel robot manipulation framework designed for visual robotic pushing with vision-to-touch generation in reinforcement learning to eliminate the reliance on high-resolution real tactile sensors, enabling effective zero-shot deployment on visual-only robotic systems. Specifically, ViTacGen consists of an encoder-decoder vision-to-touch generation network that generates contact depth images, a standardized tactile representation, directly from visual image sequence, followed by a reinforcement learning policy that fuses visual-tactile data with contrastive learning based on visual and generated tactile observations. We validate the effectiveness of our approach in both simulation and real world experiments, demonstrating its superior performance and achieving a success rate of up to 86\%.
Embodied Arena: A Comprehensive, Unified, and Evolving Evaluation Platform for Embodied AI
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Embodied AI development significantly lags behind large foundation models due to three critical challenges: (1) lack of systematic understanding of core capabilities needed for Embodied AI, making research lack clear objectives; (2) absence of unified and standardized evaluation systems, rendering cross-benchmark evaluation infeasible; and (3) underdeveloped automated and scalable acquisition methods for embodied data, creating critical bottlenecks for model scaling. To address these obstacles, we present Embodied Arena, a comprehensive, unified, and evolving evaluation platform for Embodied AI. Our platform establishes a systematic embodied capability taxonomy spanning three levels (perception, reasoning, task execution), seven core capabilities, and 25 fine-grained dimensions, enabling unified evaluation with systematic research objectives. We introduce a standardized evaluation system built upon unified infrastructure supporting flexible integration of 22 diverse benchmarks across three domains (2D/3D Embodied Q&A, Navigation, Task Planning) and 30+ advanced models from 20+ worldwide institutes. Additionally, we develop a novel LLM-driven automated generation pipeline ensuring scalable embodied evaluation data with continuous evolution for diversity and comprehensiveness. Embodied Arena publishes three real-time leaderboards (Embodied Q&A, Navigation, Task Planning) with dual perspectives (benchmark view and capability view), providing comprehensive overviews of advanced model capabilities. Especially, we present nine findings summarized from the evaluation results on the leaderboards of Embodied Arena. This helps to establish clear research veins and pinpoint critical research problems, thereby driving forward progress in the field of Embodied AI.
OVGrasp: Open-Vocabulary Grasping Assistance via Multimodal Intent Detection
Sep 04, 2025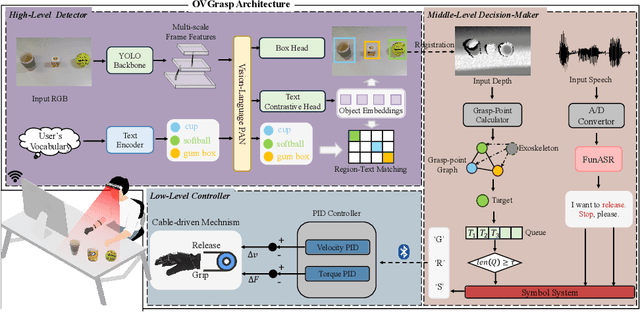
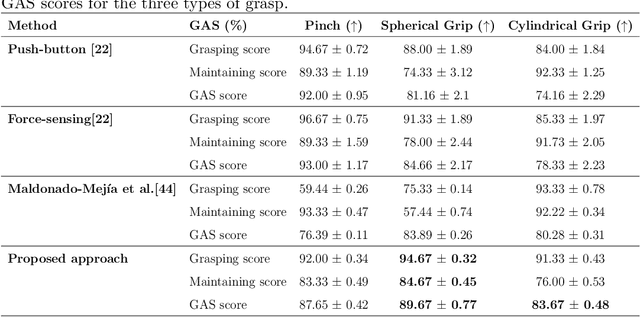
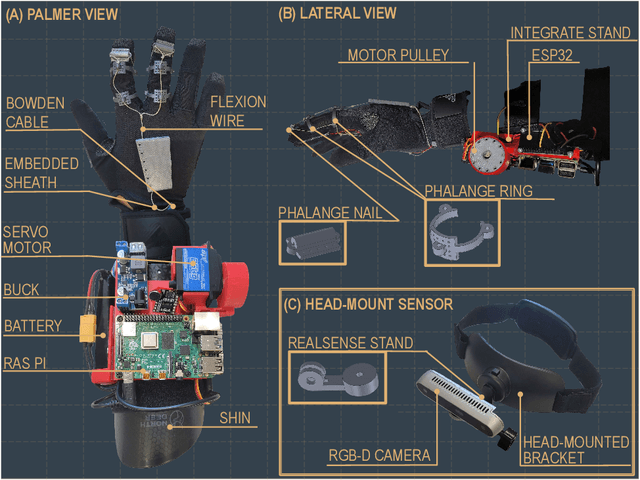
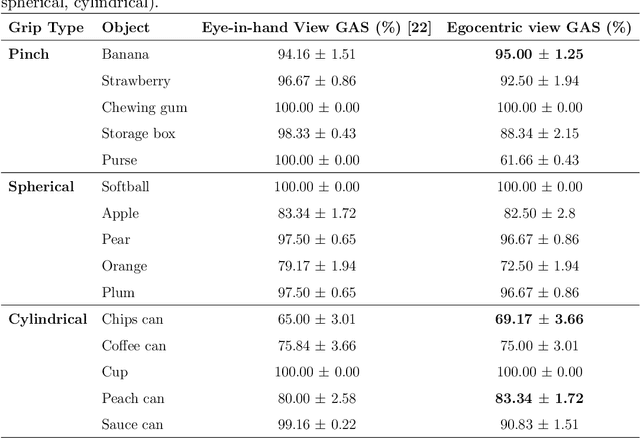
Abstract:Grasping assistance is essential for restoring autonomy in individuals with motor impairments, particularly in unstructured environments where object categories and user intentions are diverse and unpredictable. We present OVGrasp, a hierarchical control framework for soft exoskeleton-based grasp assistance that integrates RGB-D vision, open-vocabulary prompts, and voice commands to enable robust multimodal interaction. To enhance generalization in open environments, OVGrasp incorporates a vision-language foundation model with an open-vocabulary mechanism, allowing zero-shot detection of previously unseen objects without retraining. A multimodal decision-maker further fuses spatial and linguistic cues to infer user intent, such as grasp or release, in multi-object scenarios. We deploy the complete framework on a custom egocentric-view wearable exoskeleton and conduct systematic evaluations on 15 objects across three grasp types. Experimental results with ten participants demonstrate that OVGrasp achieves a grasping ability score (GAS) of 87.00%, outperforming state-of-the-art baselines and achieving improved kinematic alignment with natural hand motion.
ConViTac: Aligning Visual-Tactile Fusion with Contrastive Representations
Jun 25, 2025Abstract:Vision and touch are two fundamental sensory modalities for robots, offering complementary information that enhances perception and manipulation tasks. Previous research has attempted to jointly learn visual-tactile representations to extract more meaningful information. However, these approaches often rely on direct combination, such as feature addition and concatenation, for modality fusion, which tend to result in poor feature integration. In this paper, we propose ConViTac, a visual-tactile representation learning network designed to enhance the alignment of features during fusion using contrastive representations. Our key contribution is a Contrastive Embedding Conditioning (CEC) mechanism that leverages a contrastive encoder pretrained through self-supervised contrastive learning to project visual and tactile inputs into unified latent embeddings. These embeddings are used to couple visual-tactile feature fusion through cross-modal attention, aiming at aligning the unified representations and enhancing performance on downstream tasks. We conduct extensive experiments to demonstrate the superiority of ConViTac in real world over current state-of-the-art methods and the effectiveness of our proposed CEC mechanism, which improves accuracy by up to 12.0% in material classification and grasping prediction tasks.
MultiClear: Multimodal Soft Exoskeleton Glove for Transparent Object Grasping Assistance
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:Grasping is a fundamental skill for interacting with the environment. However, this ability can be difficult for some (e.g. due to disability). Wearable robotic solutions can enhance or restore hand function, and recent advances have leveraged computer vision to improve grasping capabilities. However, grasping transparent objects remains challenging due to their poor visual contrast and ambiguous depth cues. Furthermore, while multimodal control strategies incorporating tactile and auditory feedback have been explored to grasp transparent objects, the integration of vision with these modalities remains underdeveloped. This paper introduces MultiClear, a multimodal framework designed to enhance grasping assistance in a wearable soft exoskeleton glove for transparent objects by fusing RGB data, depth data, and auditory signals. The exoskeleton glove integrates a tendon-driven actuator with an RGB-D camera and a built-in microphone. To achieve precise and adaptive control, a hierarchical control architecture is proposed. For the proposed hierarchical control architecture, a high-level control layer provides contextual awareness, a mid-level control layer processes multimodal sensory inputs, and a low-level control executes PID motor control for fine-tuned grasping adjustments. The challenge of transparent object segmentation was managed by introducing a vision foundation model for zero-shot segmentation. The proposed system achieves a Grasping Ability Score of 70.37%, demonstrating its effectiveness in transparent object manipulation.
Point Cloud-based Grasping for Soft Hand Exoskeleton
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:Grasping is a fundamental skill for interacting with and manipulating objects in the environment. However, this ability can be challenging for individuals with hand impairments. Soft hand exoskeletons designed to assist grasping can enhance or restore essential hand functions, yet controlling these soft exoskeletons to support users effectively remains difficult due to the complexity of understanding the environment. This study presents a vision-based predictive control framework that leverages contextual awareness from depth perception to predict the grasping target and determine the next control state for activation. Unlike data-driven approaches that require extensive labelled datasets and struggle with generalizability, our method is grounded in geometric modelling, enabling robust adaptation across diverse grasping scenarios. The Grasping Ability Score (GAS) was used to evaluate performance, with our system achieving a state-of-the-art GAS of 91% across 15 objects and healthy participants, demonstrating its effectiveness across different object types. The proposed approach maintained reconstruction success for unseen objects, underscoring its enhanced generalizability compared to learning-based models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge