Senbo Wang
Hunyuan-Game: Industrial-grade Intelligent Game Creation Model
May 20, 2025Abstract:Intelligent game creation represents a transformative advancement in game development, utilizing generative artificial intelligence to dynamically generate and enhance game content. Despite notable progress in generative models, the comprehensive synthesis of high-quality game assets, including both images and videos, remains a challenging frontier. To create high-fidelity game content that simultaneously aligns with player preferences and significantly boosts designer efficiency, we present Hunyuan-Game, an innovative project designed to revolutionize intelligent game production. Hunyuan-Game encompasses two primary branches: image generation and video generation. The image generation component is built upon a vast dataset comprising billions of game images, leading to the development of a group of customized image generation models tailored for game scenarios: (1) General Text-to-Image Generation. (2) Game Visual Effects Generation, involving text-to-effect and reference image-based game visual effect generation. (3) Transparent Image Generation for characters, scenes, and game visual effects. (4) Game Character Generation based on sketches, black-and-white images, and white models. The video generation component is built upon a comprehensive dataset of millions of game and anime videos, leading to the development of five core algorithmic models, each targeting critical pain points in game development and having robust adaptation to diverse game video scenarios: (1) Image-to-Video Generation. (2) 360 A/T Pose Avatar Video Synthesis. (3) Dynamic Illustration Generation. (4) Generative Video Super-Resolution. (5) Interactive Game Video Generation. These image and video generation models not only exhibit high-level aesthetic expression but also deeply integrate domain-specific knowledge, establishing a systematic understanding of diverse game and anime art styles.
CDI3D: Cross-guided Dense-view Interpolation for 3D Reconstruction
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:3D object reconstruction from single-view image is a fundamental task in computer vision with wide-ranging applications. Recent advancements in Large Reconstruction Models (LRMs) have shown great promise in leveraging multi-view images generated by 2D diffusion models to extract 3D content. However, challenges remain as 2D diffusion models often struggle to produce dense images with strong multi-view consistency, and LRMs tend to amplify these inconsistencies during the 3D reconstruction process. Addressing these issues is critical for achieving high-quality and efficient 3D reconstruction. In this paper, we present CDI3D, a feed-forward framework designed for efficient, high-quality image-to-3D generation with view interpolation. To tackle the aforementioned challenges, we propose to integrate 2D diffusion-based view interpolation into the LRM pipeline to enhance the quality and consistency of the generated mesh. Specifically, our approach introduces a Dense View Interpolation (DVI) module, which synthesizes interpolated images between main views generated by the 2D diffusion model, effectively densifying the input views with better multi-view consistency. We also design a tilt camera pose trajectory to capture views with different elevations and perspectives. Subsequently, we employ a tri-plane-based mesh reconstruction strategy to extract robust tokens from these interpolated and original views, enabling the generation of high-quality 3D meshes with superior texture and geometry. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms previous state-of-the-art approaches across various benchmarks, producing 3D content with enhanced texture fidelity and geometric accuracy.
Pandora3D: A Comprehensive Framework for High-Quality 3D Shape and Texture Generation
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:This report presents a comprehensive framework for generating high-quality 3D shapes and textures from diverse input prompts, including single images, multi-view images, and text descriptions. The framework consists of 3D shape generation and texture generation. (1). The 3D shape generation pipeline employs a Variational Autoencoder (VAE) to encode implicit 3D geometries into a latent space and a diffusion network to generate latents conditioned on input prompts, with modifications to enhance model capacity. An alternative Artist-Created Mesh (AM) generation approach is also explored, yielding promising results for simpler geometries. (2). Texture generation involves a multi-stage process starting with frontal images generation followed by multi-view images generation, RGB-to-PBR texture conversion, and high-resolution multi-view texture refinement. A consistency scheduler is plugged into every stage, to enforce pixel-wise consistency among multi-view textures during inference, ensuring seamless integration. The pipeline demonstrates effective handling of diverse input formats, leveraging advanced neural architectures and novel methodologies to produce high-quality 3D content. This report details the system architecture, experimental results, and potential future directions to improve and expand the framework. The source code and pretrained weights are released at: https://github.com/Tencent/Tencent-XR-3DGen.
MARS: Mesh AutoRegressive Model for 3D Shape Detailization
Feb 17, 2025

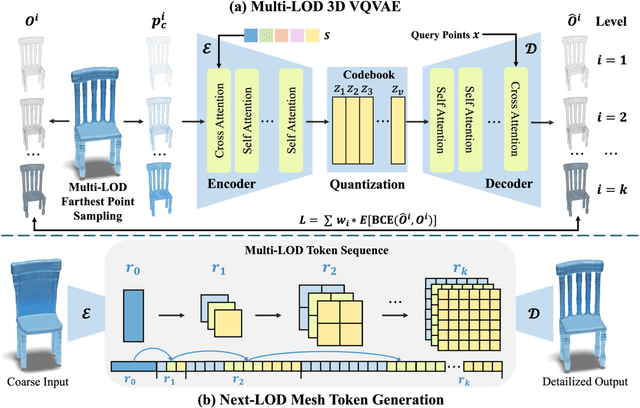

Abstract:State-of-the-art methods for mesh detailization predominantly utilize Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to generate detailed meshes from coarse ones. These methods typically learn a specific style code for each category or similar categories without enforcing geometry supervision across different Levels of Detail (LODs). Consequently, such methods often fail to generalize across a broader range of categories and cannot ensure shape consistency throughout the detailization process. In this paper, we introduce MARS, a novel approach for 3D shape detailization. Our method capitalizes on a novel multi-LOD, multi-category mesh representation to learn shape-consistent mesh representations in latent space across different LODs. We further propose a mesh autoregressive model capable of generating such latent representations through next-LOD token prediction. This approach significantly enhances the realism of the generated shapes. Extensive experiments conducted on the challenging 3D Shape Detailization benchmark demonstrate that our proposed MARS model achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing existing methods in both qualitative and quantitative assessments. Notably, the model's capability to generate fine-grained details while preserving the overall shape integrity is particularly commendable.
BAG: Body-Aligned 3D Wearable Asset Generation
Jan 27, 2025



Abstract:While recent advancements have shown remarkable progress in general 3D shape generation models, the challenge of leveraging these approaches to automatically generate wearable 3D assets remains unexplored. To this end, we present BAG, a Body-aligned Asset Generation method to output 3D wearable asset that can be automatically dressed on given 3D human bodies. This is achived by controlling the 3D generation process using human body shape and pose information. Specifically, we first build a general single-image to consistent multiview image diffusion model, and train it on the large Objaverse dataset to achieve diversity and generalizability. Then we train a Controlnet to guide the multiview generator to produce body-aligned multiview images. The control signal utilizes the multiview 2D projections of the target human body, where pixel values represent the XYZ coordinates of the body surface in a canonical space. The body-conditioned multiview diffusion generates body-aligned multiview images, which are then fed into a native 3D diffusion model to produce the 3D shape of the asset. Finally, by recovering the similarity transformation using multiview silhouette supervision and addressing asset-body penetration with physics simulators, the 3D asset can be accurately fitted onto the target human body. Experimental results demonstrate significant advantages over existing methods in terms of image prompt-following capability, shape diversity, and shape quality. Our project page is available at https://bag-3d.github.io/.
LAM3D: Large Image-Point-Cloud Alignment Model for 3D Reconstruction from Single Image
May 24, 2024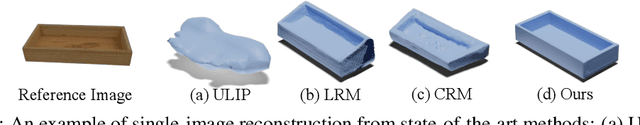
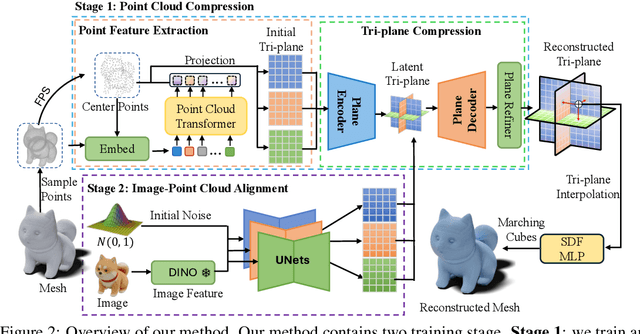
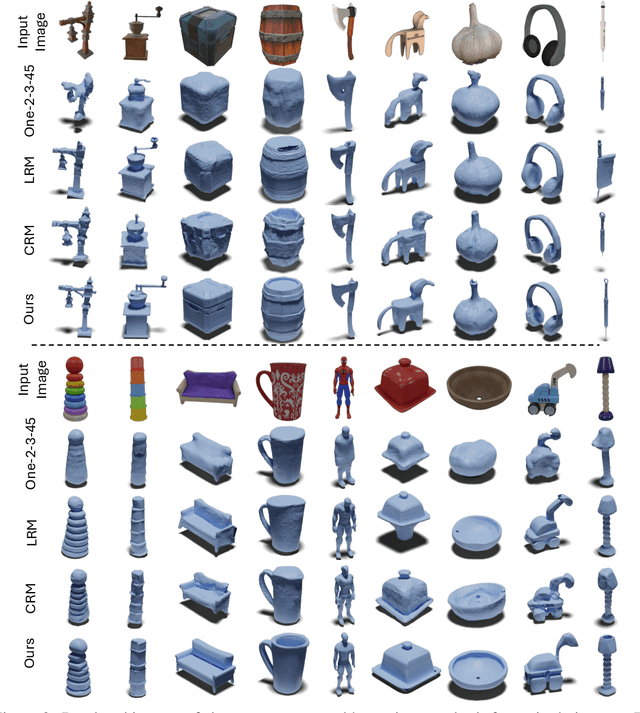
Abstract:Large Reconstruction Models have made significant strides in the realm of automated 3D content generation from single or multiple input images. Despite their success, these models often produce 3D meshes with geometric inaccuracies, stemming from the inherent challenges of deducing 3D shapes solely from image data. In this work, we introduce a novel framework, the Large Image and Point Cloud Alignment Model (LAM3D), which utilizes 3D point cloud data to enhance the fidelity of generated 3D meshes. Our methodology begins with the development of a point-cloud-based network that effectively generates precise and meaningful latent tri-planes, laying the groundwork for accurate 3D mesh reconstruction. Building upon this, our Image-Point-Cloud Feature Alignment technique processes a single input image, aligning to the latent tri-planes to imbue image features with robust 3D information. This process not only enriches the image features but also facilitates the production of high-fidelity 3D meshes without the need for multi-view input, significantly reducing geometric distortions. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art high-fidelity 3D mesh reconstruction from a single image in just 6 seconds, and experiments on various datasets demonstrate its effectiveness.
NeuSDFusion: A Spatial-Aware Generative Model for 3D Shape Completion, Reconstruction, and Generation
Mar 27, 2024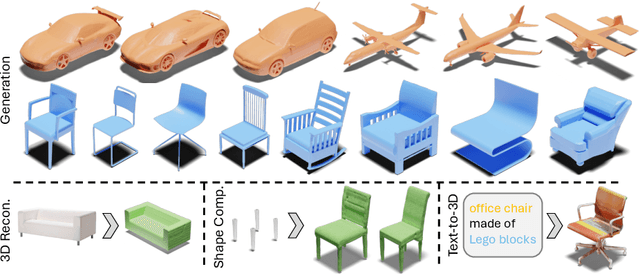
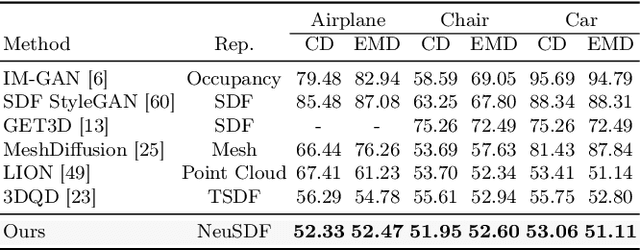
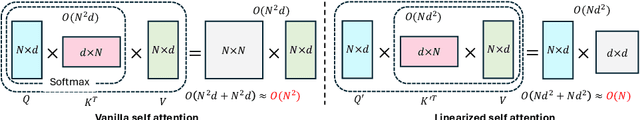
Abstract:3D shape generation aims to produce innovative 3D content adhering to specific conditions and constraints. Existing methods often decompose 3D shapes into a sequence of localized components, treating each element in isolation without considering spatial consistency. As a result, these approaches exhibit limited versatility in 3D data representation and shape generation, hindering their ability to generate highly diverse 3D shapes that comply with the specified constraints. In this paper, we introduce a novel spatial-aware 3D shape generation framework that leverages 2D plane representations for enhanced 3D shape modeling. To ensure spatial coherence and reduce memory usage, we incorporate a hybrid shape representation technique that directly learns a continuous signed distance field representation of the 3D shape using orthogonal 2D planes. Additionally, we meticulously enforce spatial correspondences across distinct planes using a transformer-based autoencoder structure, promoting the preservation of spatial relationships in the generated 3D shapes. This yields an algorithm that consistently outperforms state-of-the-art 3D shape generation methods on various tasks, including unconditional shape generation, multi-modal shape completion, single-view reconstruction, and text-to-shape synthesis.
BlockFusion: Expandable 3D Scene Generation using Latent Tri-plane Extrapolation
Jan 31, 2024



Abstract:We present BlockFusion, a diffusion-based model that generates 3D scenes as unit blocks and seamlessly incorporates new blocks to extend the scene. BlockFusion is trained using datasets of 3D blocks that are randomly cropped from complete 3D scene meshes. Through per-block fitting, all training blocks are converted into the hybrid neural fields: with a tri-plane containing the geometry features, followed by a Multi-layer Perceptron (MLP) for decoding the signed distance values. A variational auto-encoder is employed to compress the tri-planes into the latent tri-plane space, on which the denoising diffusion process is performed. Diffusion applied to the latent representations allows for high-quality and diverse 3D scene generation. To expand a scene during generation, one needs only to append empty blocks to overlap with the current scene and extrapolate existing latent tri-planes to populate new blocks. The extrapolation is done by conditioning the generation process with the feature samples from the overlapping tri-planes during the denoising iterations. Latent tri-plane extrapolation produces semantically and geometrically meaningful transitions that harmoniously blend with the existing scene. A 2D layout conditioning mechanism is used to control the placement and arrangement of scene elements. Experimental results indicate that BlockFusion is capable of generating diverse, geometrically consistent and unbounded large 3D scenes with unprecedented high-quality shapes in both indoor and outdoor scenarios.
${S}^{2}$Net: Accurate Panorama Depth Estimation on Spherical Surface
Jan 14, 2023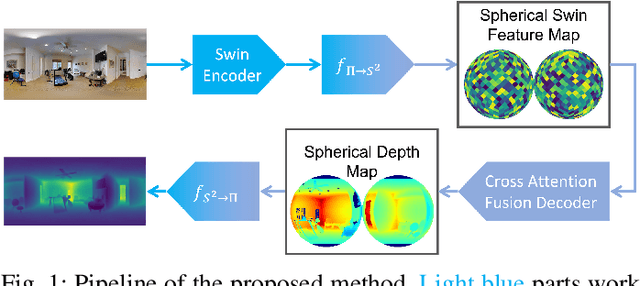
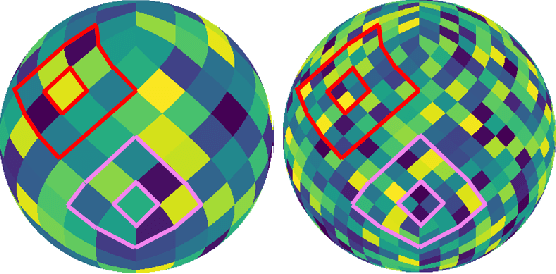
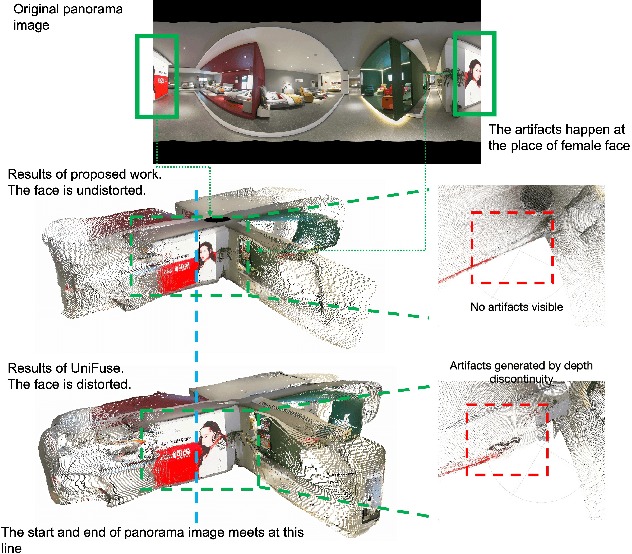
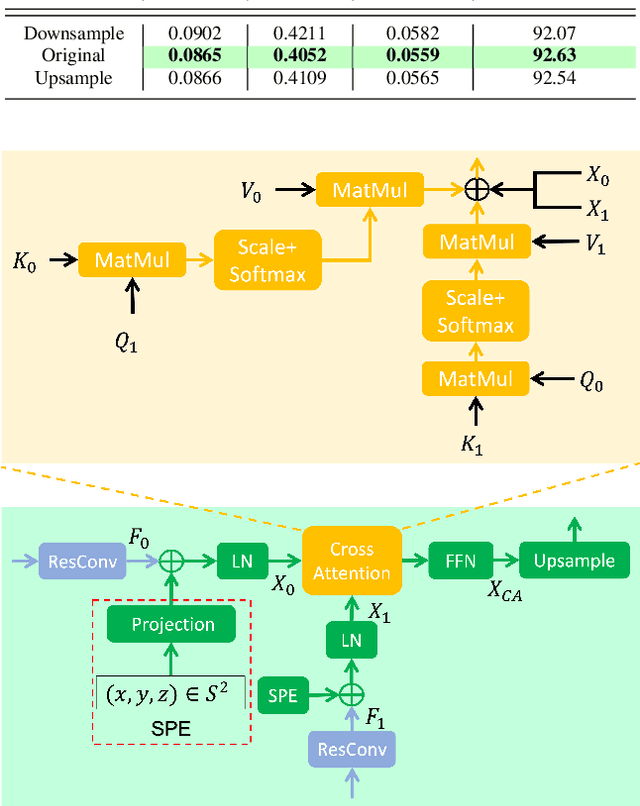
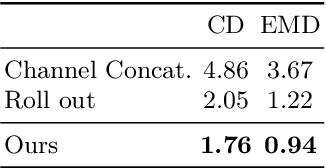
Abstract:Monocular depth estimation is an ambiguous problem, thus global structural cues play an important role in current data-driven single-view depth estimation methods. Panorama images capture the complete spatial information of their surroundings utilizing the equirectangular projection which introduces large distortion. This requires the depth estimation method to be able to handle the distortion and extract global context information from the image. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end deep network for monocular panorama depth estimation on a unit spherical surface. Specifically, we project the feature maps extracted from equirectangular images onto unit spherical surface sampled by uniformly distributed grids, where the decoder network can aggregate the information from the distortion-reduced feature maps. Meanwhile, we propose a global cross-attention-based fusion module to fuse the feature maps from skip connection and enhance the ability to obtain global context. Experiments are conducted on five panorama depth estimation datasets, and the results demonstrate that the proposed method substantially outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods. All related codes will be open-sourced in the upcoming days.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge