Yongqiang Zhao
SimTac: A Physics-Based Simulator for Vision-Based Tactile Sensing with Biomorphic Structures
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Tactile sensing in biological organisms is deeply intertwined with morphological form, such as human fingers, cat paws, and elephant trunks, which enables rich and adaptive interactions through a variety of geometrically complex structures. In contrast, vision-based tactile sensors in robotics have been limited to simple planar geometries, with biomorphic designs remaining underexplored. To address this gap, we present SimTac, a physics-based simulation framework for the design and validation of biomorphic tactile sensors. SimTac consists of particle-based deformation modeling, light-field rendering for photorealistic tactile image generation, and a neural network for predicting mechanical responses, enabling accurate and efficient simulation across a wide range of geometries and materials. We demonstrate the versatility of SimTac by designing and validating physical sensor prototypes inspired by biological tactile structures and further demonstrate its effectiveness across multiple Sim2Real tactile tasks, including object classification, slip detection, and contact safety assessment. Our framework bridges the gap between bio-inspired design and practical realisation, expanding the design space of tactile sensors and paving the way for tactile sensing systems that integrate morphology and sensing to enable robust interaction in unstructured environments.
ViTacGen: Robotic Pushing with Vision-to-Touch Generation
Oct 15, 2025Abstract:Robotic pushing is a fundamental manipulation task that requires tactile feedback to capture subtle contact forces and dynamics between the end-effector and the object. However, real tactile sensors often face hardware limitations such as high costs and fragility, and deployment challenges involving calibration and variations between different sensors, while vision-only policies struggle with satisfactory performance. Inspired by humans' ability to infer tactile states from vision, we propose ViTacGen, a novel robot manipulation framework designed for visual robotic pushing with vision-to-touch generation in reinforcement learning to eliminate the reliance on high-resolution real tactile sensors, enabling effective zero-shot deployment on visual-only robotic systems. Specifically, ViTacGen consists of an encoder-decoder vision-to-touch generation network that generates contact depth images, a standardized tactile representation, directly from visual image sequence, followed by a reinforcement learning policy that fuses visual-tactile data with contrastive learning based on visual and generated tactile observations. We validate the effectiveness of our approach in both simulation and real world experiments, demonstrating its superior performance and achieving a success rate of up to 86\%.
ConViTac: Aligning Visual-Tactile Fusion with Contrastive Representations
Jun 25, 2025Abstract:Vision and touch are two fundamental sensory modalities for robots, offering complementary information that enhances perception and manipulation tasks. Previous research has attempted to jointly learn visual-tactile representations to extract more meaningful information. However, these approaches often rely on direct combination, such as feature addition and concatenation, for modality fusion, which tend to result in poor feature integration. In this paper, we propose ConViTac, a visual-tactile representation learning network designed to enhance the alignment of features during fusion using contrastive representations. Our key contribution is a Contrastive Embedding Conditioning (CEC) mechanism that leverages a contrastive encoder pretrained through self-supervised contrastive learning to project visual and tactile inputs into unified latent embeddings. These embeddings are used to couple visual-tactile feature fusion through cross-modal attention, aiming at aligning the unified representations and enhancing performance on downstream tasks. We conduct extensive experiments to demonstrate the superiority of ConViTac in real world over current state-of-the-art methods and the effectiveness of our proposed CEC mechanism, which improves accuracy by up to 12.0% in material classification and grasping prediction tasks.
Enhancing LLM Generation with Knowledge Hypergraph for Evidence-Based Medicine
Mar 18, 2025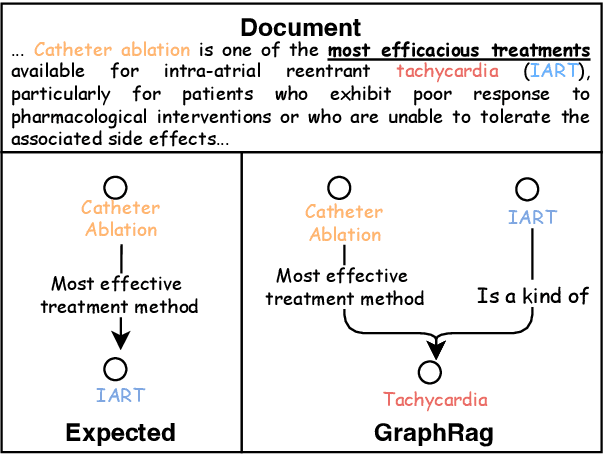
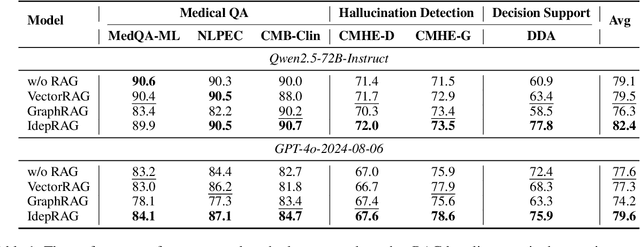
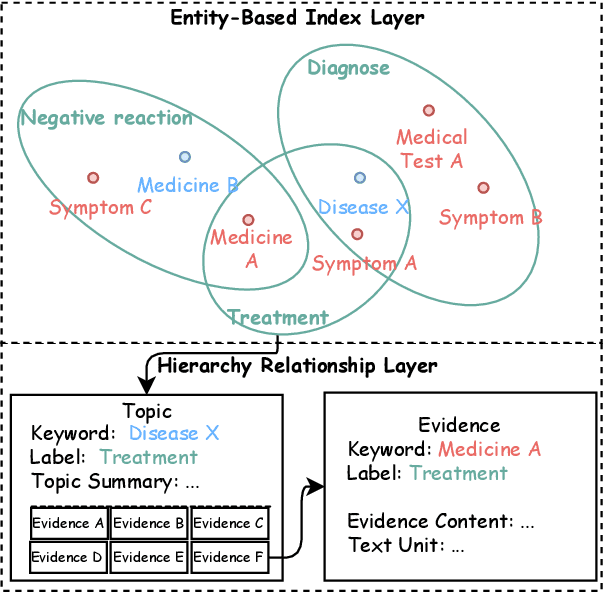
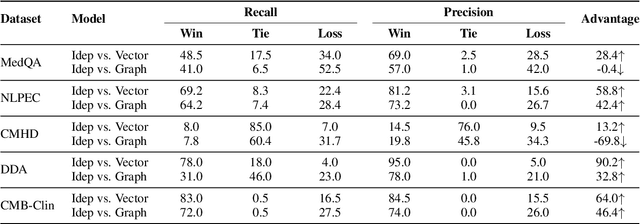
Abstract:Evidence-based medicine (EBM) plays a crucial role in the application of large language models (LLMs) in healthcare, as it provides reliable support for medical decision-making processes. Although it benefits from current retrieval-augmented generation~(RAG) technologies, it still faces two significant challenges: the collection of dispersed evidence and the efficient organization of this evidence to support the complex queries necessary for EBM. To tackle these issues, we propose using LLMs to gather scattered evidence from multiple sources and present a knowledge hypergraph-based evidence management model to integrate these evidence while capturing intricate relationships. Furthermore, to better support complex queries, we have developed an Importance-Driven Evidence Prioritization (IDEP) algorithm that utilizes the LLM to generate multiple evidence features, each with an associated importance score, which are then used to rank the evidence and produce the final retrieval results. Experimental results from six datasets demonstrate that our approach outperforms existing RAG techniques in application domains of interest to EBM, such as medical quizzing, hallucination detection, and decision support. Testsets and the constructed knowledge graph can be accessed at \href{https://drive.google.com/file/d/1WJ9QTokK3MdkjEmwuFQxwH96j_Byawj_/view?usp=drive_link}{https://drive.google.com/rag4ebm}.
General Force Sensation for Tactile Robot
Mar 02, 2025



Abstract:Robotic tactile sensors, including vision-based and taxel-based sensors, enable agile manipulation and safe human-robot interaction through force sensation. However, variations in structural configurations, measured signals, and material properties create domain gaps that limit the transferability of learned force sensation across different tactile sensors. Here, we introduce GenForce, a general framework for achieving transferable force sensation across both homogeneous and heterogeneous tactile sensors in robotic systems. By unifying tactile signals into marker-based binary tactile images, GenForce enables the transfer of existing force labels to arbitrary target sensors using a marker-to-marker translation technique with a few paired data. This process equips uncalibrated tactile sensors with force prediction capabilities through spatiotemporal force prediction models trained on the transferred data. Extensive experimental results validate GenForce's generalizability, accuracy, and robustness across sensors with diverse marker patterns, structural designs, material properties, and sensing principles. The framework significantly reduces the need for costly and labor-intensive labeled data collection, enabling the rapid deployment of multiple tactile sensors on robotic hands requiring force sensing capabilities.
Exploring LLM-based Data Annotation Strategies for Medical Dialogue Preference Alignment
Oct 05, 2024
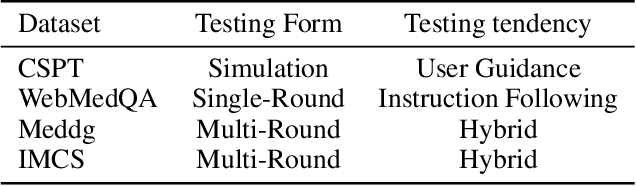

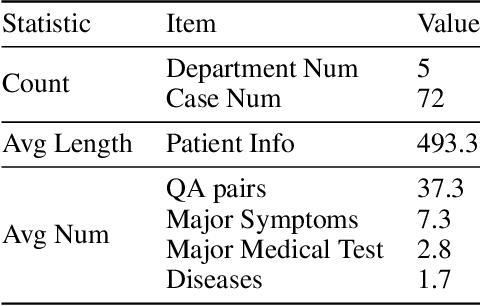
Abstract:This research examines the use of Reinforcement Learning from AI Feedback (RLAIF) techniques to improve healthcare dialogue models, with the aim of tackling the challenges of preference-aligned data annotation while reducing the reliance on medical experts. We argue that the primary challenges in current RLAIF research for healthcare are the limitations of automated evaluation methods and the difficulties in accurately representing physician preferences. To address these challenges, we present a new evaluation framework based on standardized patient examinations. This framework is designed to objectively assess the effectiveness of large language models (LLMs) in guiding users and following instructions, enabling a comprehensive comparison across different models. Furthermore, our investigation of effective ways to express physician preferences using Constitutional AI algorithms highlighted the particular effectiveness of flowcharts. Utilizing this finding, we introduce an innovative agent-based approach for annotating preference data. This approach autonomously creates medical dialogue flows tailored to the patient's condition, demonstrates strong generalization abilities, and reduces the need for expert involvement. Our results show that the agent-based approach outperforms existing RLAIF annotation methods in standardized patient examinations and surpasses current open source medical dialogue LLMs in various test scenarios.
Metasurface-based Snapshot Shortwave-Infrared Hyperspectral Image Reconstruction with Inter and Intra Prior Learning Network
Jul 11, 2024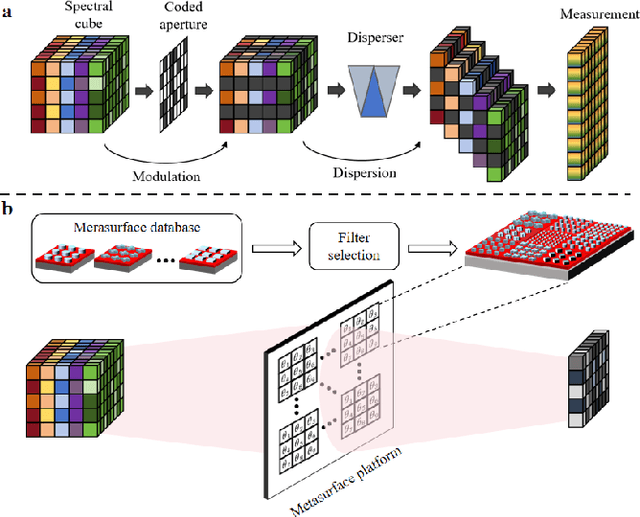
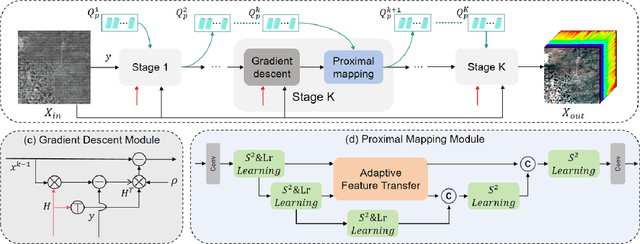
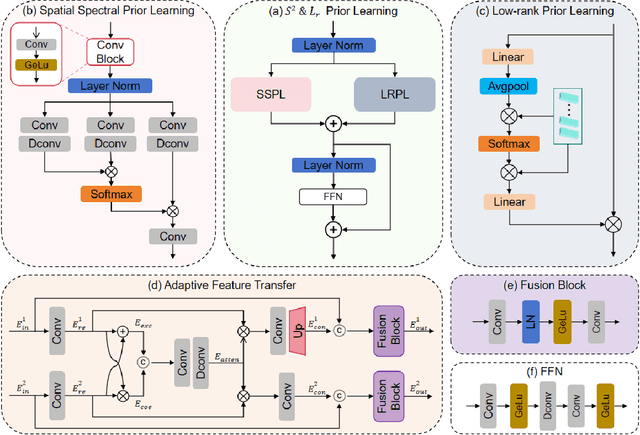
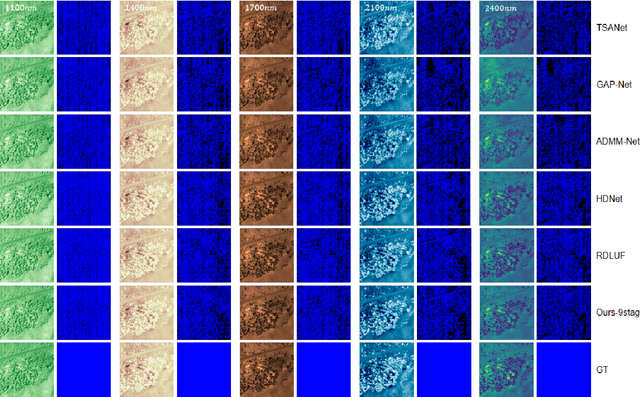
Abstract:Shortwave-infrared(SWIR) spectral information,ranging from 1 {\mu}m to 2.5{\mu}m, breaks the limitations of traditional color cameras in acquiring scene information and has been used in many fields. However, conventional SWIR hyperspectral imaging systems face challenges due to their bulky setups and low acquisition speed. In this work, we introduce a snapshot SWIR hyperspectral imaging system based on a metasurface filter and a corresponding filter selection method to achieve the lowest correlation coefficient among these filters.This systemhas the advantages of small size and snapshot imaging. We propose a novel inter and intra prior learning unfolding framework proposed to achieve high-quality SWIR hyperspectral image reconstruction, which bridges the gap between prior learning and cross-stage information interaction. We also design an adaptive feature transfer mechanism to adaptively the transfer contextual correlation of multi-scale encoder features to prevent detailed information loss in the decoder. Experiment results demonstrate that our method can reconstruct HSI with high speed and superior performance over existing methods.
FOTS: A Fast Optical Tactile Simulator for Sim2Real Learning of Tactile-motor Robot Manipulation Skills
May 01, 2024Abstract:Simulation is a widely used tool in robotics to reduce hardware consumption and gather large-scale data. Despite previous efforts to simulate optical tactile sensors, there remain challenges in efficiently synthesizing images and replicating marker motion under different contact loads. In this work, we propose a fast optical tactile simulator, named FOTS, for simulating optical tactile sensors. We utilize multi-layer perceptron mapping and planar shadow generation to simulate the optical response, while employing marker distribution approximation to simulate the motion of surface markers caused by the elastomer deformation. Experimental results demonstrate that FOTS outperforms other methods in terms of image generation quality and rendering speed, achieving 28.6 fps for optical simulation and 326.1 fps for marker motion simulation on a single CPU without GPU acceleration. In addition, we integrate the FOTS simulation model with physical engines like MuJoCo, and the peg-in-hole task demonstrates the effectiveness of our method in achieving zero-shot Sim2Real learning of tactile-motor robot manipulation skills. Our code is available at https://github.com/Rancho-zhao/FOTS.
Integrating Physician Diagnostic Logic into Large Language Models: Preference Learning from Process Feedback
Jan 11, 2024Abstract:The use of large language models in medical dialogue generation has garnered significant attention, with a focus on improving response quality and fluency. While previous studies have made progress in optimizing model performance for single-round medical Q&A tasks, there is a need to enhance the model's capability for multi-round conversations to avoid logical inconsistencies. To address this, we propose an approach called preference learning from process feedback~(PLPF), which integrates the doctor's diagnostic logic into LLMs. PLPF involves rule modeling, preference data generation, and preference alignment to train the model to adhere to the diagnostic process. Experimental results using Standardized Patient Testing show that PLPF enhances the diagnostic accuracy of the baseline model in medical conversations by 17.6%, outperforming traditional reinforcement learning from human feedback. Additionally, PLPF demonstrates effectiveness in both multi-round and single-round dialogue tasks, showcasing its potential for improving medical dialogue generation.
Enhancing the Spatial Awareness Capability of Multi-Modal Large Language Model
Nov 01, 2023Abstract:The Multi-Modal Large Language Model (MLLM) refers to an extension of the Large Language Model (LLM) equipped with the capability to receive and infer multi-modal data. Spatial awareness stands as one of the crucial abilities of MLLM, encompassing diverse skills related to understanding spatial relationships among objects and between objects and the scene area. Industries such as autonomous driving, smart healthcare, robotics, virtual, and augmented reality heavily demand MLLM's spatial awareness capabilities. However, there exists a noticeable gap between the current spatial awareness capabilities of MLLM and the requirements set by human needs. To address this issue, this paper proposes using more precise spatial position information between objects to guide MLLM in providing more accurate responses to user-related inquiries. Specifically, for a particular multi-modal task, we utilize algorithms for acquiring geometric spatial information and scene graphs to obtain relevant geometric spatial information and scene details of objects involved in the query. Subsequently, based on this information, we direct MLLM to address spatial awareness-related queries posed by the user. Extensive experiments were conducted in benchmarks such as MME, MM-Vet, and other multi-modal large language models. The experimental results thoroughly confirm the efficacy of the proposed method in enhancing the spatial awareness tasks and associated tasks of MLLM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge