Feng Zhang
Rethinking ANN-based Retrieval: Multifaceted Learnable Index for Large-scale Recommendation System
Feb 18, 2026Abstract:Approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) search is widely used in the retrieval stage of large-scale recommendation systems. In this stage, candidate items are indexed using their learned embedding vectors, and ANN search is executed for each user (or item) query to retrieve a set of relevant items. However, ANN-based retrieval has two key limitations. First, item embeddings and their indices are typically learned in separate stages: indexing is often performed offline after embeddings are trained, which can yield suboptimal retrieval quality-especially for newly created items. Second, although ANN offers sublinear query time, it must still be run for every request, incurring substantial computation cost at industry scale. In this paper, we propose MultiFaceted Learnable Index (MFLI), a scalable, real-time retrieval paradigm that learns multifaceted item embeddings and indices within a unified framework and eliminates ANN search at serving time. Specifically, we construct a multifaceted hierarchical codebook via residual quantization of item embeddings and co-train the codebook with the embeddings. We further introduce an efficient multifaceted indexing structure and mechanisms that support real-time updates. At serving time, the learned hierarchical indices are used directly to identify relevant items, avoiding ANN search altogether. Extensive experiments on real-world data with billions of users show that MFLI improves recall on engagement tasks by up to 11.8\%, cold-content delivery by up to 57.29\%, and semantic relevance by 13.5\% compared with prior state-of-the-art methods. We also deploy MFLI in the system and report online experimental results demonstrating improved engagement, less popularity bias, and higher serving efficiency.
KAN-FIF: Spline-Parameterized Lightweight Physics-based Tropical Cyclone Estimation on Meteorological Satellite
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:Tropical cyclones (TC) are among the most destructive natural disasters, causing catastrophic damage to coastal regions through extreme winds, heavy rainfall, and storm surges. Timely monitoring of tropical cyclones is crucial for reducing loss of life and property, yet it is hindered by the computational inefficiency and high parameter counts of existing methods on resource-constrained edge devices. Current physics-guided models suffer from linear feature interactions that fail to capture high-order polynomial relationships between TC attributes, leading to inflated model sizes and hardware incompatibility. To overcome these challenges, this study introduces the Kolmogorov-Arnold Network-based Feature Interaction Framework (KAN-FIF), a lightweight multimodal architecture that integrates MLP and CNN layers with spline-parameterized KAN layers. For Maximum Sustained Wind (MSW) prediction, experiments demonstrate that the KAN-FIF framework achieves a $94.8\%$ reduction in parameters (0.99MB vs 19MB) and $68.7\%$ faster inference per sample (2.3ms vs 7.35ms) compared to baseline model Phy-CoCo, while maintaining superior accuracy with $32.5\%$ lower MAE. The offline deployment experiment of the FY-4 series meteorological satellite processor on the Qingyun-1000 development board achieved a 14.41ms per-sample inference latency with the KAN-FIF framework, demonstrating promising feasibility for operational TC monitoring and extending deployability to edge-device AI applications. The code is released at https://github.com/Jinglin-Zhang/KAN-FIF.
GhostCite: A Large-Scale Analysis of Citation Validity in the Age of Large Language Models
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:Citations provide the basis for trusting scientific claims; when they are invalid or fabricated, this trust collapses. With the advent of Large Language Models (LLMs), this risk has intensified: LLMs are increasingly used for academic writing, yet their tendency to fabricate citations (``ghost citations'') poses a systemic threat to citation validity. To quantify this threat and inform mitigation, we develop CiteVerifier, an open-source framework for large-scale citation verification, and conduct the first comprehensive study of citation validity in the LLM era through three experiments built on it. We benchmark 13 state-of-the-art LLMs on citation generation across 40 research domains, finding that all models hallucinate citations at rates from 14.23\% to 94.93\%, with significant variation across research domains. Moreover, we analyze 2.2 million citations from 56,381 papers published at top-tier AI/ML and Security venues (2020--2025), confirming that 1.07\% of papers contain invalid or fabricated citations (604 papers), with an 80.9\% increase in 2025 alone. Furthermore, we survey 97 researchers and analyze 94 valid responses after removing 3 conflicting samples, revealing a critical ``verification gap'': 41.5\% of researchers copy-paste BibTeX without checking and 44.4\% choose no-action responses when encountering suspicious references; meanwhile, 76.7\% of reviewers do not thoroughly check references and 80.0\% never suspect fake citations. Our findings reveal an accelerating crisis where unreliable AI tools, combined with inadequate human verification by researchers and insufficient peer review scrutiny, enable fabricated citations to contaminate the scientific record. We propose interventions for researchers, venues, and tool developers to protect citation integrity.
MRAD: Zero-Shot Anomaly Detection with Memory-Driven Retrieval
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Zero-shot anomaly detection (ZSAD) often leverages pretrained vision or vision-language models, but many existing methods use prompt learning or complex modeling to fit the data distribution, resulting in high training or inference cost and limited cross-domain stability. To address these limitations, we propose Memory-Retrieval Anomaly Detection method (MRAD), a unified framework that replaces parametric fitting with a direct memory retrieval. The train-free base model, MRAD-TF, freezes the CLIP image encoder and constructs a two-level memory bank (image-level and pixel-level) from auxiliary data, where feature-label pairs are explicitly stored as keys and values. During inference, anomaly scores are obtained directly by similarity retrieval over the memory bank. Based on the MRAD-TF, we further propose two lightweight variants as enhancements: (i) MRAD-FT fine-tunes the retrieval metric with two linear layers to enhance the discriminability between normal and anomaly; (ii) MRAD-CLIP injects the normal and anomalous region priors from the MRAD-FT as dynamic biases into CLIP's learnable text prompts, strengthening generalization to unseen categories. Across 16 industrial and medical datasets, the MRAD framework consistently demonstrates superior performance in anomaly classification and segmentation, under both train-free and training-based settings. Our work shows that fully leveraging the empirical distribution of raw data, rather than relying only on model fitting, can achieve stronger anomaly detection performance. The code will be publicly released at https://github.com/CROVO1026/MRAD.
UserLM-R1: Modeling Human Reasoning in User Language Models with Multi-Reward Reinforcement Learning
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:User simulators serve as the critical interactive environment for agent post-training, and an ideal user simulator generalizes across domains and proactively engages in negotiation by challenging or bargaining. However, current methods exhibit two issues. They rely on static and context-unaware profiles, necessitating extensive manual redesign for new scenarios, thus limiting generalizability. Moreover, they neglect human strategic thinking, leading to vulnerability to agent manipulation. To address these issues, we propose UserLM-R1, a novel user language model with reasoning capability. Specifically, we first construct comprehensive user profiles with both static roles and dynamic scenario-specific goals for adaptation to diverse scenarios. Then, we propose a goal-driven decision-making policy to generate high-quality rationales before producing responses, and further refine the reasoning and improve strategic capabilities with supervised fine-tuning and multi-reward reinforcement learning. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that UserLM-R1 outperforms competitive baselines, particularly on the more challenging adversarial set.
Efficient Paths and Dense Rewards: Probabilistic Flow Reasoning for Large Language Models
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:High-quality chain-of-thought has demonstrated strong potential for unlocking the reasoning capabilities of large language models. However, current paradigms typically treat the reasoning process as an indivisible sequence, lacking an intrinsic mechanism to quantify step-wise information gain. This granularity gap manifests in two limitations: inference inefficiency from redundant exploration without explicit guidance, and optimization difficulty due to sparse outcome supervision or costly external verifiers. In this work, we propose CoT-Flow, a framework that reconceptualizes discrete reasoning steps as a continuous probabilistic flow, quantifying the contribution of each step toward the ground-truth answer. Built on this formulation, CoT-Flow enables two complementary methodologies: flow-guided decoding, which employs a greedy flow-based decoding strategy to extract information-efficient reasoning paths, and flow-based reinforcement learning, which constructs a verifier-free dense reward function. Experiments on challenging benchmarks demonstrate that CoT-Flow achieves a superior balance between inference efficiency and reasoning performance.
SHIELD: Spherical-Projection Hybrid-Frontier Integration for Efficient LiDAR-based Drone Exploration
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces SHIELD, a Spherical-Projection Hybrid-Frontier Integration for Efficient LiDAR-based Drone exploration method. Although laser LiDAR offers the advantage of a wide field of view, its application in UAV exploration still faces several challenges. The observation quality of LiDAR point clouds is generally inferior to that of depth cameras. Traditional frontier methods based on known and unknown regions impose a heavy computational burden, especially when handling the wide field of view of LiDAR. In addition, regions without point cloud are also difficult to classify as free space through raycasting. To address these problems, the SHIELD is proposed. It maintains an observation-quality occupancy map and performs ray-casting on this map to address the issue of inconsistent point-cloud quality during exploration. A hybrid frontier method is used to tackle both the computational burden and the limitations of point-cloud quality exploration. In addition, an outward spherical-projection ray-casting strategy is proposed to jointly ensure flight safety and exploration efficiency in open areas. Simulations and flight experiments prove the effectiveness of SHIELD. This work will be open-sourced to contribute to the research community.
ADHint: Adaptive Hints with Difficulty Priors for Reinforcement Learning
Dec 15, 2025



Abstract:To combine the advantages of Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) and Reinforcement Learning (RL), recent methods have integrated ''hints'' into post-training, which are prefix segments of complete reasoning trajectories, aiming for powerful knowledge expansion and reasoning generalization. However, existing hint-based RL methods typically ignore difficulty when scheduling hint ratios and estimating relative advantages, leading to unstable learning and excessive imitation of off-policy hints. In this work, we propose ADHint, which treats difficulty as a key factor in both hint-ratio schedule and relative-advantage estimation to achieve a better trade-off between exploration and imitation. Specifically, we propose Adaptive Hint with Sample Difficulty Prior, which evaluates each sample's difficulty under the policy model and accordingly schedules an appropriate hint ratio to guide its rollouts. We also introduce Consistency-based Gradient Modulation and Selective Masking for Hint Preservation to modulate token-level gradients within hints, preventing biased and destructive updates. Additionally, we propose Advantage Estimation with Rollout Difficulty Posterior, which leverages the relative difficulty of rollouts with and without hints to estimate their respective advantages, thereby achieving more balanced updates. Extensive experiments across diverse modalities, model scales, and domains demonstrate that ADHint delivers superior reasoning ability and out-of-distribution generalization, consistently surpassing existing methods in both pass@1 and avg@8. Our code and dataset will be made publicly available upon paper acceptance.
Hybrid Attribution Priors for Explainable and Robust Model Training
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Small language models (SLMs) are widely used in tasks that require low latency and lightweight deployment, particularly classification. As interpretability and robustness gain increasing importance, explanation-guided learning has emerged as an effective framework by introducing attribution-based supervision during training; however, deriving general and reliable attribution priors remains a significant challenge. Through an analysis of representative attribution methods in classification settings, we find that although these methods can reliably highlight class-relevant tokens, they often focus on common keywords shared by semantically similar classes. Because such classes are already difficult to distinguish under standard training, these attributions provide insufficient discriminative cues, limiting their ability to improve model differentiation. To overcome this limitation, we propose Class-Aware Attribution Prior (CAP), a novel attribution prior extraction framework that guides language models toward capturing fine-grained class distinctions and producing more salient, discriminative attribution priors. Building on this idea, we further introduce CAP Hybrid, which combines priors from CAP with those from existing attribution techniques to form a more comprehensive and balanced supervisory signal. By aligning a model's self-attribution with these enriched priors, our approach encourages the learning of diverse, decision-relevant features. Extensive experiments in full-data, few-shot, and adversarial scenarios demonstrate that our method consistently enhances both interpretability and robustness.
Make It Long, Keep It Fast: End-to-End 10k-Sequence Modeling at Billion Scale on Douyin
Nov 08, 2025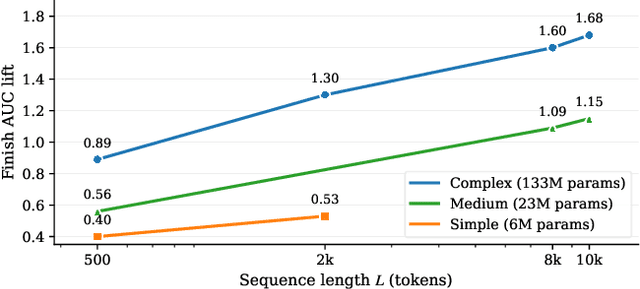
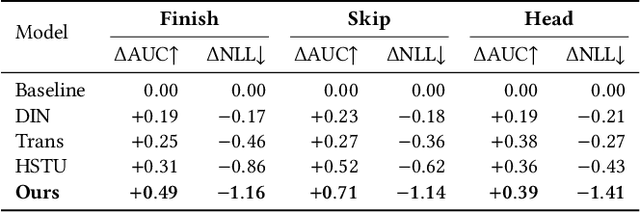
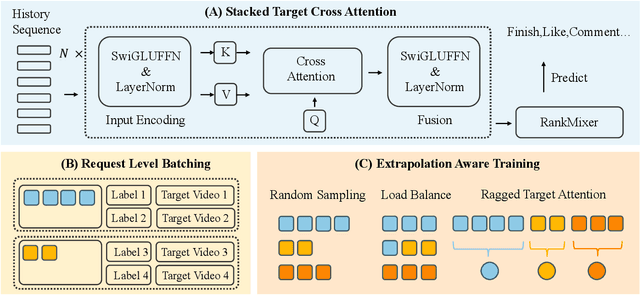

Abstract:Short-video recommenders such as Douyin must exploit extremely long user histories without breaking latency or cost budgets. We present an end-to-end system that scales long-sequence modeling to 10k-length histories in production. First, we introduce Stacked Target-to-History Cross Attention (STCA), which replaces history self-attention with stacked cross-attention from the target to the history, reducing complexity from quadratic to linear in sequence length and enabling efficient end-to-end training. Second, we propose Request Level Batching (RLB), a user-centric batching scheme that aggregates multiple targets for the same user/request to share the user-side encoding, substantially lowering sequence-related storage, communication, and compute without changing the learning objective. Third, we design a length-extrapolative training strategy -- train on shorter windows, infer on much longer ones -- so the model generalizes to 10k histories without additional training cost. Across offline and online experiments, we observe predictable, monotonic gains as we scale history length and model capacity, mirroring the scaling law behavior observed in large language models. Deployed at full traffic on Douyin, our system delivers significant improvements on key engagement metrics while meeting production latency, demonstrating a practical path to scaling end-to-end long-sequence recommendation to the 10k regime.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge