Changxin Gao
DenseGRPO: From Sparse to Dense Reward for Flow Matching Model Alignment
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Recent GRPO-based approaches built on flow matching models have shown remarkable improvements in human preference alignment for text-to-image generation. Nevertheless, they still suffer from the sparse reward problem: the terminal reward of the entire denoising trajectory is applied to all intermediate steps, resulting in a mismatch between the global feedback signals and the exact fine-grained contributions at intermediate denoising steps. To address this issue, we introduce \textbf{DenseGRPO}, a novel framework that aligns human preference with dense rewards, which evaluates the fine-grained contribution of each denoising step. Specifically, our approach includes two key components: (1) we propose to predict the step-wise reward gain as dense reward of each denoising step, which applies a reward model on the intermediate clean images via an ODE-based approach. This manner ensures an alignment between feedback signals and the contributions of individual steps, facilitating effective training; and (2) based on the estimated dense rewards, a mismatch drawback between the uniform exploration setting and the time-varying noise intensity in existing GRPO-based methods is revealed, leading to an inappropriate exploration space. Thus, we propose a reward-aware scheme to calibrate the exploration space by adaptively adjusting a timestep-specific stochasticity injection in the SDE sampler, ensuring a suitable exploration space at all timesteps. Extensive experiments on multiple standard benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed DenseGRPO and highlight the critical role of the valid dense rewards in flow matching model alignment.
Is Nano Banana Pro a Low-Level Vision All-Rounder? A Comprehensive Evaluation on 14 Tasks and 40 Datasets
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:The rapid evolution of text-to-image generation models has revolutionized visual content creation. While commercial products like Nano Banana Pro have garnered significant attention, their potential as generalist solvers for traditional low-level vision challenges remains largely underexplored. In this study, we investigate the critical question: Is Nano Banana Pro a Low-Level Vision All-Rounder? We conducted a comprehensive zero-shot evaluation across 14 distinct low-level tasks spanning 40 diverse datasets. By utilizing simple textual prompts without fine-tuning, we benchmarked Nano Banana Pro against state-of-the-art specialist models. Our extensive analysis reveals a distinct performance dichotomy: while \textbf{Nano Banana Pro demonstrates superior subjective visual quality}, often hallucinating plausible high-frequency details that surpass specialist models, it lags behind in traditional reference-based quantitative metrics. We attribute this discrepancy to the inherent stochasticity of generative models, which struggle to maintain the strict pixel-level consistency required by conventional metrics. This report identifies Nano Banana Pro as a capable zero-shot contender for low-level vision tasks, while highlighting that achieving the high fidelity of domain specialists remains a significant hurdle.
ClothHMR: 3D Mesh Recovery of Humans in Diverse Clothing from Single Image
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:With 3D data rapidly emerging as an important form of multimedia information, 3D human mesh recovery technology has also advanced accordingly. However, current methods mainly focus on handling humans wearing tight clothing and perform poorly when estimating body shapes and poses under diverse clothing, especially loose garments. To this end, we make two key insights: (1) tailoring clothing to fit the human body can mitigate the adverse impact of clothing on 3D human mesh recovery, and (2) utilizing human visual information from large foundational models can enhance the generalization ability of the estimation. Based on these insights, we propose ClothHMR, to accurately recover 3D meshes of humans in diverse clothing. ClothHMR primarily consists of two modules: clothing tailoring (CT) and FHVM-based mesh recovering (MR). The CT module employs body semantic estimation and body edge prediction to tailor the clothing, ensuring it fits the body silhouette. The MR module optimizes the initial parameters of the 3D human mesh by continuously aligning the intermediate representations of the 3D mesh with those inferred from the foundational human visual model (FHVM). ClothHMR can accurately recover 3D meshes of humans wearing diverse clothing, precisely estimating their body shapes and poses. Experimental results demonstrate that ClothHMR significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods across benchmark datasets and in-the-wild images. Additionally, a web application for online fashion and shopping powered by ClothHMR is developed, illustrating that ClothHMR can effectively serve real-world usage scenarios. The code and model for ClothHMR are available at: \url{https://github.com/starVisionTeam/ClothHMR}.
WorldLens: Full-Spectrum Evaluations of Driving World Models in Real World
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Generative world models are reshaping embodied AI, enabling agents to synthesize realistic 4D driving environments that look convincing but often fail physically or behaviorally. Despite rapid progress, the field still lacks a unified way to assess whether generated worlds preserve geometry, obey physics, or support reliable control. We introduce WorldLens, a full-spectrum benchmark evaluating how well a model builds, understands, and behaves within its generated world. It spans five aspects -- Generation, Reconstruction, Action-Following, Downstream Task, and Human Preference -- jointly covering visual realism, geometric consistency, physical plausibility, and functional reliability. Across these dimensions, no existing world model excels universally: those with strong textures often violate physics, while geometry-stable ones lack behavioral fidelity. To align objective metrics with human judgment, we further construct WorldLens-26K, a large-scale dataset of human-annotated videos with numerical scores and textual rationales, and develop WorldLens-Agent, an evaluation model distilled from these annotations to enable scalable, explainable scoring. Together, the benchmark, dataset, and agent form a unified ecosystem for measuring world fidelity -- standardizing how future models are judged not only by how real they look, but by how real they behave.
Learning to Tell Apart: Weakly Supervised Video Anomaly Detection via Disentangled Semantic Alignment
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in weakly-supervised video anomaly detection have achieved remarkable performance by applying the multiple instance learning paradigm based on multimodal foundation models such as CLIP to highlight anomalous instances and classify categories. However, their objectives may tend to detect the most salient response segments, while neglecting to mine diverse normal patterns separated from anomalies, and are prone to category confusion due to similar appearance, leading to unsatisfactory fine-grained classification results. Therefore, we propose a novel Disentangled Semantic Alignment Network (DSANet) to explicitly separate abnormal and normal features from coarse-grained and fine-grained aspects, enhancing the distinguishability. Specifically, at the coarse-grained level, we introduce a self-guided normality modeling branch that reconstructs input video features under the guidance of learned normal prototypes, encouraging the model to exploit normality cues inherent in the video, thereby improving the temporal separation of normal patterns and anomalous events. At the fine-grained level, we present a decoupled contrastive semantic alignment mechanism, which first temporally decomposes each video into event-centric and background-centric components using frame-level anomaly scores and then applies visual-language contrastive learning to enhance class-discriminative representations. Comprehensive experiments on two standard benchmarks, namely XD-Violence and UCF-Crime, demonstrate that DSANet outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods.
VideoLucy: Deep Memory Backtracking for Long Video Understanding
Oct 14, 2025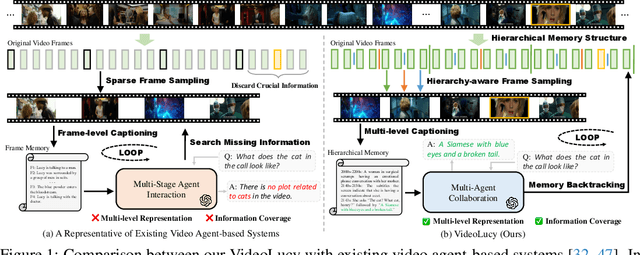
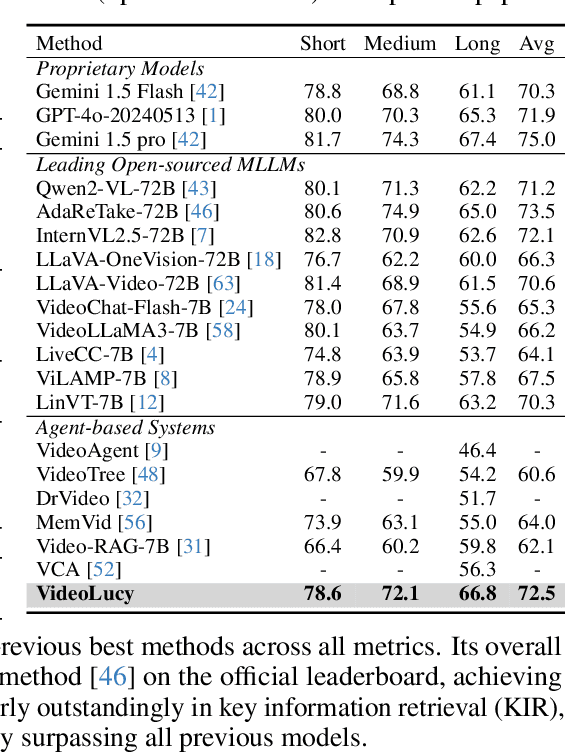
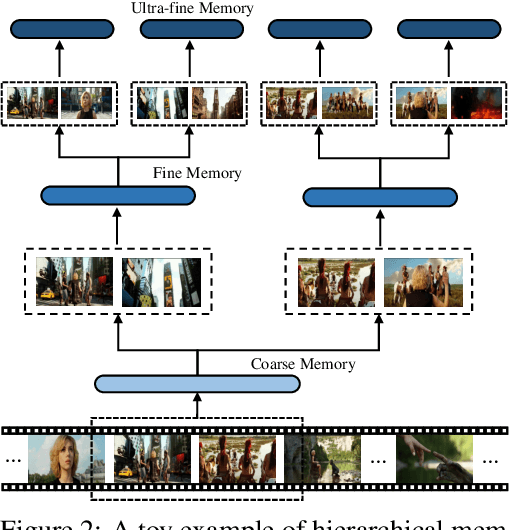

Abstract:Recent studies have shown that agent-based systems leveraging large language models (LLMs) for key information retrieval and integration have emerged as a promising approach for long video understanding. However, these systems face two major challenges. First, they typically perform modeling and reasoning on individual frames, struggling to capture the temporal context of consecutive frames. Second, to reduce the cost of dense frame-level captioning, they adopt sparse frame sampling, which risks discarding crucial information. To overcome these limitations, we propose VideoLucy, a deep memory backtracking framework for long video understanding. Inspired by the human recollection process from coarse to fine, VideoLucy employs a hierarchical memory structure with progressive granularity. This structure explicitly defines the detail level and temporal scope of memory at different hierarchical depths. Through an agent-based iterative backtracking mechanism, VideoLucy systematically mines video-wide, question-relevant deep memories until sufficient information is gathered to provide a confident answer. This design enables effective temporal understanding of consecutive frames while preserving critical details. In addition, we introduce EgoMem, a new benchmark for long video understanding. EgoMem is designed to comprehensively evaluate a model's ability to understand complex events that unfold over time and capture fine-grained details in extremely long videos. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of VideoLucy. Built on open-source models, VideoLucy significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods on multiple long video understanding benchmarks, achieving performance even surpassing the latest proprietary models such as GPT-4o. Our code and dataset will be made publicly at https://videolucy.github.io
Learning Unpaired Image Dehazing with Physics-based Rehazy Generation
Jun 15, 2025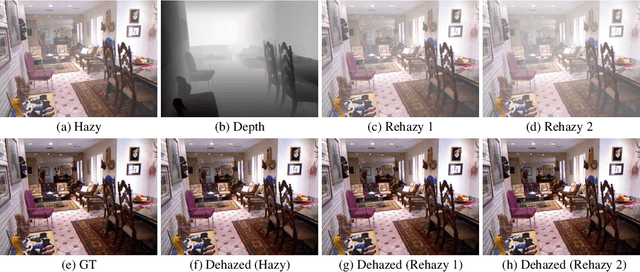
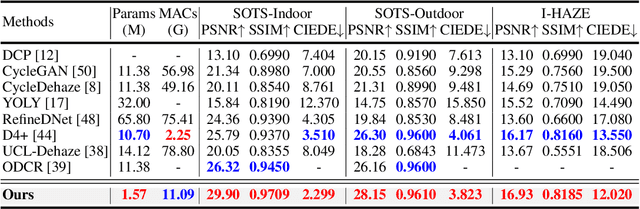
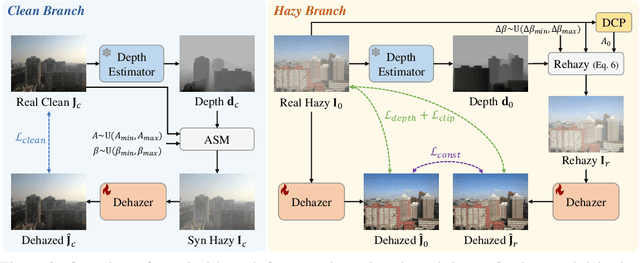
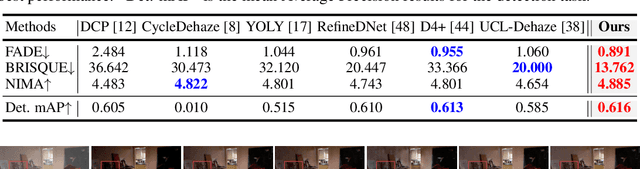
Abstract:Overfitting to synthetic training pairs remains a critical challenge in image dehazing, leading to poor generalization capability to real-world scenarios. To address this issue, existing approaches utilize unpaired realistic data for training, employing CycleGAN or contrastive learning frameworks. Despite their progress, these methods often suffer from training instability, resulting in limited dehazing performance. In this paper, we propose a novel training strategy for unpaired image dehazing, termed Rehazy, to improve both dehazing performance and training stability. This strategy explores the consistency of the underlying clean images across hazy images and utilizes hazy-rehazy pairs for effective learning of real haze characteristics. To favorably construct hazy-rehazy pairs, we develop a physics-based rehazy generation pipeline, which is theoretically validated to reliably produce high-quality rehazy images. Additionally, leveraging the rehazy strategy, we introduce a dual-branch framework for dehazing network training, where a clean branch provides a basic dehazing capability in a synthetic manner, and a hazy branch enhances the generalization ability with hazy-rehazy pairs. Moreover, we design a new dehazing network within these branches to improve the efficiency, which progressively restores clean scenes from coarse to fine. Extensive experiments on four benchmarks demonstrate the superior performance of our approach, exceeding the previous state-of-the-art methods by 3.58 dB on the SOTS-Indoor dataset and by 1.85 dB on the SOTS-Outdoor dataset in PSNR. Our code will be publicly available.
ReID5o: Achieving Omni Multi-modal Person Re-identification in a Single Model
Jun 11, 2025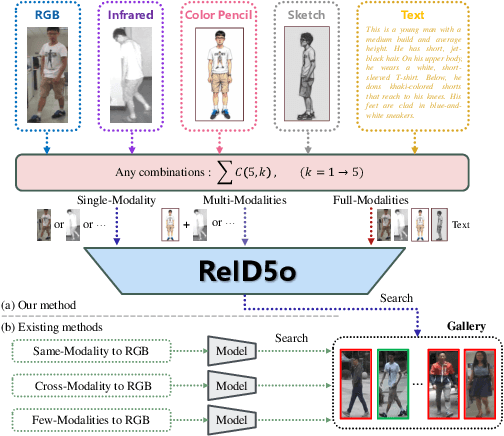
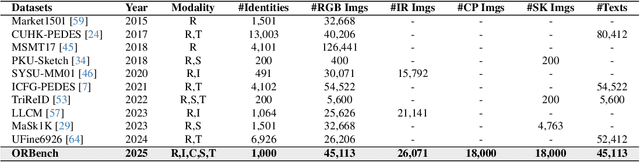
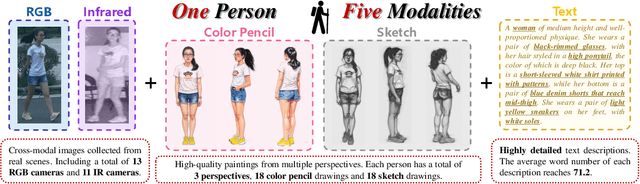
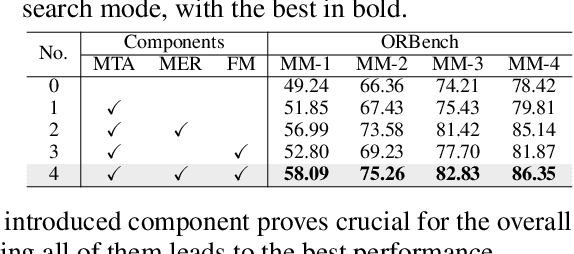
Abstract:In real-word scenarios, person re-identification (ReID) expects to identify a person-of-interest via the descriptive query, regardless of whether the query is a single modality or a combination of multiple modalities. However, existing methods and datasets remain constrained to limited modalities, failing to meet this requirement. Therefore, we investigate a new challenging problem called Omni Multi-modal Person Re-identification (OM-ReID), which aims to achieve effective retrieval with varying multi-modal queries. To address dataset scarcity, we construct ORBench, the first high-quality multi-modal dataset comprising 1,000 unique identities across five modalities: RGB, infrared, color pencil, sketch, and textual description. This dataset also has significant superiority in terms of diversity, such as the painting perspectives and textual information. It could serve as an ideal platform for follow-up investigations in OM-ReID. Moreover, we propose ReID5o, a novel multi-modal learning framework for person ReID. It enables synergistic fusion and cross-modal alignment of arbitrary modality combinations in a single model, with a unified encoding and multi-expert routing mechanism proposed. Extensive experiments verify the advancement and practicality of our ORBench. A wide range of possible models have been evaluated and compared on it, and our proposed ReID5o model gives the best performance. The dataset and code will be made publicly available at https://github.com/Zplusdragon/ReID5o_ORBench.
MP-Mat: A 3D-and-Instance-Aware Human Matting and Editing Framework with Multiplane Representation
Apr 20, 2025

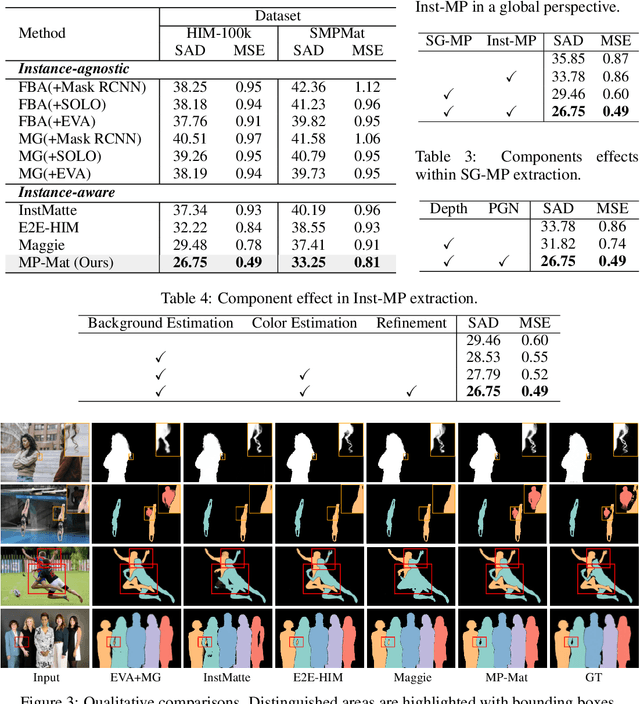

Abstract:Human instance matting aims to estimate an alpha matte for each human instance in an image, which is challenging as it easily fails in complex cases requiring disentangling mingled pixels belonging to multiple instances along hairy and thin boundary structures. In this work, we address this by introducing MP-Mat, a novel 3D-and-instance-aware matting framework with multiplane representation, where the multiplane concept is designed from two different perspectives: scene geometry level and instance level. Specifically, we first build feature-level multiplane representations to split the scene into multiple planes based on depth differences. This approach makes the scene representation 3D-aware, and can serve as an effective clue for splitting instances in different 3D positions, thereby improving interpretability and boundary handling ability especially in occlusion areas. Then, we introduce another multiplane representation that splits the scene in an instance-level perspective, and represents each instance with both matte and color. We also treat background as a special instance, which is often overlooked by existing methods. Such an instance-level representation facilitates both foreground and background content awareness, and is useful for other down-stream tasks like image editing. Once built, the representation can be reused to realize controllable instance-level image editing with high efficiency. Extensive experiments validate the clear advantage of MP-Mat in matting task. We also demonstrate its superiority in image editing tasks, an area under-explored by existing matting-focused methods, where our approach under zero-shot inference even outperforms trained specialized image editing techniques by large margins. Code is open-sourced at https://github.com/JiaoSiyi/MPMat.git}.
Taming Consistency Distillation for Accelerated Human Image Animation
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in human image animation have been propelled by video diffusion models, yet their reliance on numerous iterative denoising steps results in high inference costs and slow speeds. An intuitive solution involves adopting consistency models, which serve as an effective acceleration paradigm through consistency distillation. However, simply employing this strategy in human image animation often leads to quality decline, including visual blurring, motion degradation, and facial distortion, particularly in dynamic regions. In this paper, we propose the DanceLCM approach complemented by several enhancements to improve visual quality and motion continuity at low-step regime: (1) segmented consistency distillation with an auxiliary light-weight head to incorporate supervision from real video latents, mitigating cumulative errors resulting from single full-trajectory generation; (2) a motion-focused loss to centre on motion regions, and explicit injection of facial fidelity features to improve face authenticity. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments demonstrate that DanceLCM achieves results comparable to state-of-the-art video diffusion models with a mere 2-4 inference steps, significantly reducing the inference burden without compromising video quality. The code and models will be made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge